Qt 动态库和静态库的创建与使用
前言
c/c++开发中都会用到动态库和静态库。首先动态库和静态库的区别是什么呢?
简单来讲,静态库,如果某个程序需要调用了一个静态库中的方法,在该程序编译时候会将该静态库一起编译进去,即会直接整合到目标程序中,编译成功的可执行文件可独立运行。静态库的扩展名一般为“.a”或“.lib”,windows 则是.dll
而动态库,某个程序在编译的时候,在程序里只有一个“指向”的位置而已,也就是说当可执行文件需要使用到函数库的机制时,程序才会去读取函数库来使用,也就是说可执行文件无法单独运行。
静态库与动态库优缺点大概如下
1、静态库
优点:
①静态库被打包到应用程序中加载速度快
②发布程序无需提供静态库,移植方便
缺点:
①相同的库文件数据可能在内存中被加载多份,消耗系统资源,浪费内存
②库文件更新需要重新编译项目文件,生成新的可执行程序,浪费时间。
2、动态库
优点:
①可实现不同进程间的资源共享
②动态库升级简单,只需要替换库文件,无需重新编译应用程序
③可以控制何时加载动态库,不调用库函数动态库不会被加载
缺点:
①加载速度比静态库慢
②发布程序需要提供依赖的动态库
动态库
动态库的创建
1、新建项目,选择Library->c++Library,选择Shared Library 即共享库(动态库), Qt module那里跟实际需要选择模块;
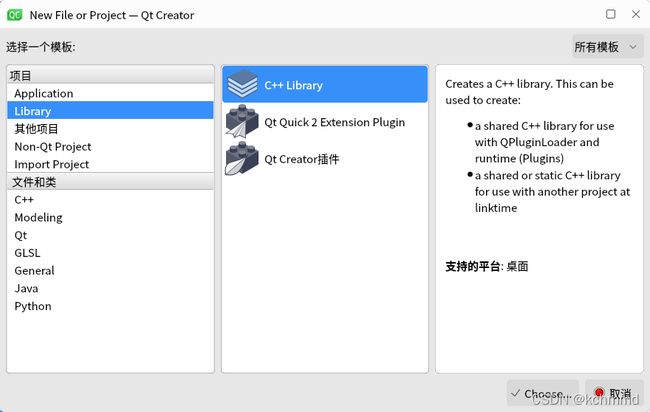
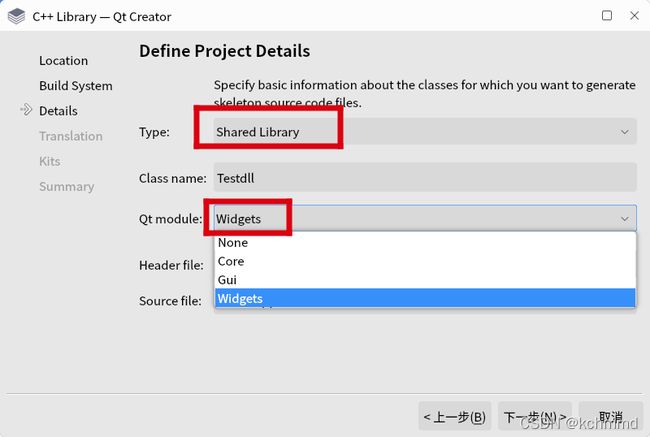
2、新建完成后会生成如下几个文件,testdll_global.h文件中是宏定义,可将此文件宏定义内容复制到testdll.h文件中,就不需要testdll_global.h文件了

#ifndef TESTDLL_GLOBAL_H
#define TESTDLL_GLOBAL_H
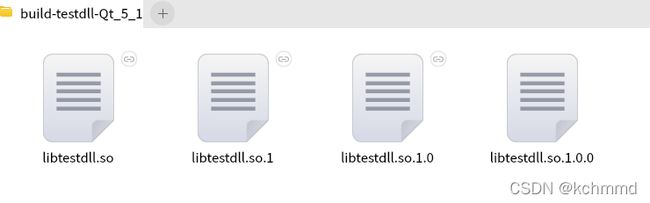
#include 如果在QtCreator工具上编译的话,如果编译运行会提示如下窗口,因为是生成动态库,不能直接运行,但在build构建目录下已经生成libtestdll.so.1.0.0及它的连接文件,这就算创建成功了

动态库使用
动态库使用有隐式调用和显式调用。
动态库隐式调用
1、新建一个项目后,点击右键选择添加库->外部库->选择库的路径,点击先一步,然后完成。
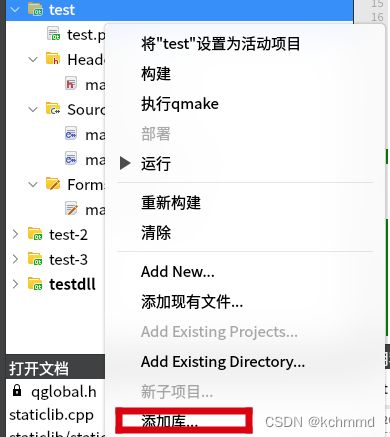
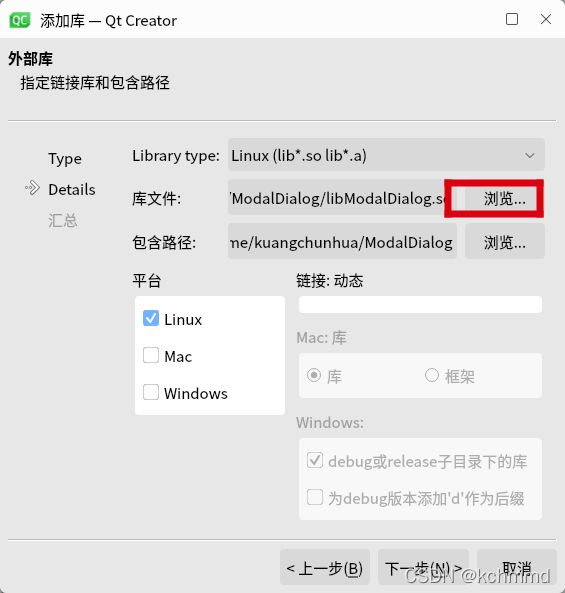
2、在.pro文件中会生成库链接地址配置
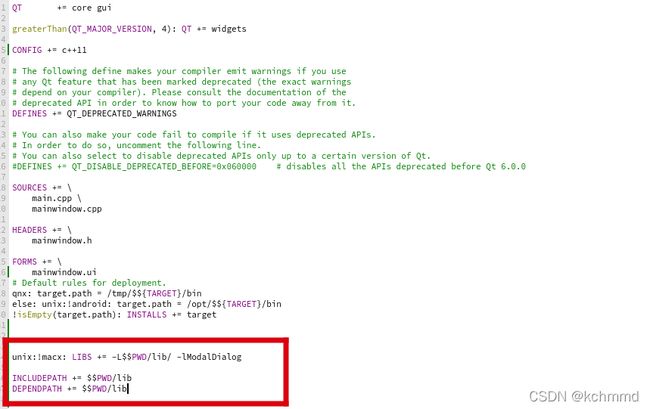
3、此时在需要调用的地方,加上头文件"testdll.h",就可以使用库中的方法了。
动态库显式调用
显示调用不需要修改.pro文件,也不需要加头文件,主要是通过 QLibrary 方法
1、头文件#include
2、QLibrary mylib(“/xxx/xxx/testldd.so”); 即里面参数为库地址
3、然后 if(mylib.load()) 通过load()函数去加载动态库 (加载后,库将保留在内存中,直到应用程序终止。我们可以尝试使用 unload( ) 来卸载库)
4、 声明函数指针,通过resolve得到库中函数地址
typedef void (*Fun)();
Fun method = (Fun)mylib.resolve(“method-name”);
if(!method) //判断是否获取成功
5、最后再调用即可
动态库制作示例代码
按照上面新建动态库项目就可以得到.pro文件
testso.pro文件
QT -= gui
TEMPLATE = lib
DEFINES += TESTSO_LIBRARY
CONFIG += c++11
# The following define makes your compiler emit warnings if you use
# any Qt feature that has been marked deprecated (the exact warnings
# depend on your compiler). Please consult the documentation of the
# deprecated API in order to know how to port your code away from it.
DEFINES += QT_DEPRECATED_WARNINGS
# You can also make your code fail to compile if it uses deprecated APIs.
# In order to do so, uncomment the following line.
# You can also select to disable deprecated APIs only up to a certain version of Qt.
#DEFINES += QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE=0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.0.0
SOURCES += \
testso.cpp
HEADERS += \
testso.h
# Default rules for deployment.
unix {
target.path = /usr/lib
}
win32:{
//动态库生成路径配置
CONFIG(release, debug|release):{
DESTDIR = $$PWD/../lib/win/x86/release
}
else:CONFIG(debug, debug|release):{
DESTDIR = $$PWD/../lib/win/x86/debug
}
}
!isEmpty(target.path): INSTALLS += target
testso.h文件
#ifndef TESTSO_H
#define TESTSO_H
#include testso.cpp文件
#include "testso.h"
QString getString()
{
return QString("hello I`m dll!");
}
在终端 执行 qmake -> make 可在当前目录下生成.so库文件,windows则是.dll
动态库隐式使用示例代码
新建Application项目后,右键添加库路径后,会在pro文件中加入
test.pro文件
QT += core gui
greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets
CONFIG += c++11
# The following define makes your compiler emit warnings if you use
# any Qt feature that has been marked deprecated (the exact warnings
# depend on your compiler). Please consult the documentation of the
# deprecated API in order to know how to port your code away from it.
DEFINES += QT_DEPRECATED_WARNINGS
# You can also make your code fail to compile if it uses deprecated APIs.
# In order to do so, uncomment the following line.
# You can also select to disable deprecated APIs only up to a certain version of Qt.
#DEFINES += QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE=0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.0.0
SOURCES += \
main.cpp \
mainwindow.cpp
HEADERS += \
mainwindow.h
FORMS += \
mainwindow.ui
# Default rules for deployment.
qnx: target.path = /tmp/$${TARGET}/bin
else: unix:!android: target.path = /opt/$${TARGET}/bin
!isEmpty(target.path): INSTALLS += target
//下面这三行就是 右键添加库地址后生成的
unix:!macx: LIBS += -L$$PWD/../testso/ -ltestso
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD/../testso
DEPENDPATH += $$PWD/../testso
maindialog.h就是生成默认的未修改,选择Qwidget也可以的
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include maindialog.cpp 这里就是使用的地方,加上头文件,调用里面的getString
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include "testso.h"
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent)
: QMainWindow(parent)
, ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
qDebug()<<getString();
}
MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
delete ui;
}
动态库显式使用示例代码
新建Application项目后,不用添加库和头文件,只需调用QLibrary相关方法即可
这里只有mainwindow.cpp不同,
mainwindow.cpp文件
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include 静态库制作
静态制作与动态库差不同,只是在新建lib库时选择 statically :Linked Library 静态库。在编译后,会生成.a的文件
静态库使用
静态库使用,首先也是在项目中右键添加库路径,不同的是需要把静态库的头文件即.h文件复制并导入到使用程序项目中再使用。