C++基础知识 (命名空间、输入输出、函数的缺省参数、函数重载)
⭐️ 第一个 c++ 代码
例1:
#include #include标准输入输出std是c++标准库的命名空间,将标准库的定义实现都放到这个命名空间中using namespace std展开std里的内容coutc代表的是console控制台的意思,out有输出的意思<<流运算符 流插入endl等价于'\n'
⭐️ 命名空间
在 c++ 中,变量、函数和类的名称存在于全局作用域中,可能会导致冲突。比如:在 #include 中存在一个 rand 函数,当你再定义一个全局的 rand 变量这时编译器就会报错。而使用命名空间将变量、类型、函数放在一个域中以放命名冲突,使用 namespace 关键字来创建命名空间。
命名空间的定义和访问
语法: namespace name {}
例2:
// 定义命名空间
namespace mySpace {
char name[10] = "sunwukong";
int age = 18;
char gender = 'male';
int add(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
struct Node {
int val;
struct Node* next;
};
}
// 命名空间的访问
int main() {
struct mySpace::Node node;
node.val = 10;
cout << mySpace::age << endl;
cout << mySpace::add(10, 20) << endl;
return 0;
}
ps: 若是变量或者函数直接使用命名空间的 name::来访问即可。但是如果是结构类型 mySpace::struct Node 这样的写法是 error 的。要在 struct 后面写命名空间 struct mySpace::Node。
命名空间可以嵌套
namespace N1 {
int a;
int b;
namespace N2 {
int c;
int d;
}
}
ps: 还有一种情况,若在许多文件中存在多个相同的命名空间,编译器最后会合成为同一个命名空间。
例3:
#include ps: 以上代码会有局部优先的问题,所以最终 num 访问结果是 1,但是也可以访问到全局的 num 使用 :: 默认代表访问全局域 ,例如:cout << ::num << endl;。:: 前面加上命名空间的名称代表访问命名空间的某个对象。
命名空间的使用
name::a加命名空间名称及作用域限定符using name::a使用using将命名空间中某个成员引入using namespace name使用using namespace引入命名空间
⭐️ c++ 输入输出
例4:
#include cin、coutc代表console有控制台的意思in有内的意思out有外的意思,cin标准输入对象(键盘)、cout标准输出对象(控制台),必须包含stdcout和cin是全局的的流对象,它们都包含在<<是留插入运算符、>>是流提取运算符c++的输入输出可以自动识别类型
⭐️ 函数的缺省参数
缺省参数是声明或者定义函数时为函数的参数指定一个默认值。在调用函数时,如果没有指定实参则采用默认值(缺省参数),否则使用指定实参。
例5:
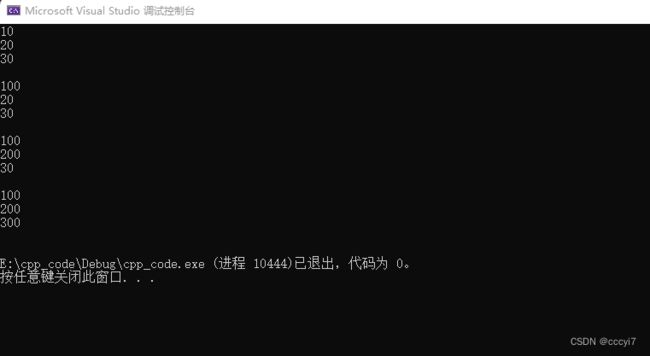
#include - 全缺省参数
#include - 半缺省参数
void Func(int a , int b = 20, int c = 30) {
cout << a << endl;
cout << b << endl;
cout << c << endl << endl;
}
ps: 半缺省参数必须从右向左依次来给出,不可以隔着给。缺省参数不能在函数声明和定义中同时出现(一般在声明中出现)。
⭐️ 函数重载
c++ 允许在同一个作用域中声明功能类似的同名函数,这些同名函数的形参类型(参数个数、类型、顺序)不同, 常用来处理功能类似但数据类型不同的问题。
// 类型不同
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
// 顺序不同
void f(int a, char b) {
cout << "void f(int a, char b)" << endl;
}
void f(char a , int b) {
cout << "void f(char b , int a)" << endl;
}
// 个数不同
void f() {
cout << "void f()" << endl;
}
void f(int a) {
cout << "void f(int a)" << endl;
}