【python】利用BeautifulSoup提取html中的标签、数据
对于不熟悉HTML和正则表达式的人,可以用第三方模块包BeautifulSoup来提取HTML或XML中的数据。
实例化BeautifulSoup对象:
使用解析器分析指定的网页源代码,得到源代码的结构模型
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests as re
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'}
rsp=re.get(url='https://ww.baidu.com',headers=headers)
#打开百度网页
soup=BeautifulSoup(rsp.text,'lxml')
#获取源代码,并实例化BeautifulSoup对象
print(soup)
定位标签
通过标签名进行定位
源代码中可能会有多个同名标签,通过标签名定位只能返回第一个标签:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests as re
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'}
rsp=re.get(url='https://ww.baidu.com',headers=headers)
#打开百度网页
soup=BeautifulSoup(rsp.text,'lxml')
#获取源代码,并实例化BeautifulSoup对象
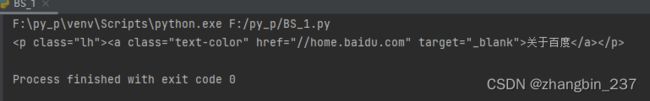
print(soup.p)
#通过标签名定位第一个标签
通过标签属性定位
标签的属性有class、id,平时使用主要使用class属性(因为class是python的关键词,所以使用时需要加下划线)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests as re
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'}
rsp=re.get(url='https://ww.baidu.com',headers=headers)
#打开百度网页
soup=BeautifulSoup(rsp.text,'lxml')
#获取源代码,并实例化BeautifulSoup对象
print(soup.find(class_='s-center-box'))
#通过标签名定位第一个属性为"s-center-box"的标签
print(soup.find_all(class_='s-center-box'))
#通过标签名定位所有属性为"s-center-box"的标签,并以数组的形式返回
此外,还可以通过标签名+属性的方式定位
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests as re
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'}
rsp=re.get(url='https://ww.baidu.com',headers=headers)
#打开百度网页
soup=BeautifulSoup(rsp.text,'lxml')
#获取源代码,并实例化BeautifulSoup对象
print(soup.find('div',class_='s-center-box'))
#通过标签名定位第一个属性为"s-center-box"的div标签
print(soup.find_all('div',class_='s-center-box'))
#通过标签名定位所有属性为"s-center-box"的div标签,并以数组的形式返回
通过选择器进行定位
使用select()函数可以返回所有符合条件的标签,常用的有id选择器、class选择器、标签选择器、层级选择器
id选择器、class选择器、标签选择器的用法:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests as re
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'}
rsp=re.get(url='https://ww.baidu.com',headers=headers)
#打开百度网页
soup=BeautifulSoup(rsp.text,'lxml')
#获取源代码,并实例化BeautifulSoup对象
print(soup.select('#s_wrap')) #id选择器,要加#符号,然后加id
print(soup.select('.bdpfmenu')) #class选择器,要加.符号,然后加class属性
print(soup.select('li')) #标签选择器,直接写标签的类型
层级选择器可以先定位外层标签,再定位内存标签,一层层向内定位就可以找到需要的标签
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests as re
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'}
rsp=re.get(url='https://ww.baidu.com',headers=headers)
#打开百度网页
soup=BeautifulSoup(rsp.text,'lxml')
#获取源代码,并实例化BeautifulSoup对象
print(soup.select('div>li')) #div标签下的li标签,其中div和li之间没有其他层级
print(soup.select('div>li>#s_wrap')) #div标签下li标签中id为s_wrap的标签
print(soup.select('div li')) #div标签下的li标签,其中div和li可以有任意层级
上述为距离,baidu页面中没有实际的标签
从标签中提取文本和属性
string属性可以返回标签下的“直系”文本,该标签下其他标签的文本不提取
而text属性时指定标签下的所有文本
字典取值的方式可以取出属性值
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests as re
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.1; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'}
rsp=re.get(url='https://ww.baidu.com',headers=headers)
#打开百度网页
soup=BeautifulSoup(rsp.text,'lxml')
#获取源代码,并实例化BeautifulSoup对象
print(soup.select('.title-content-title')[0].string) #class属性为title-content-title的标签直系文本
print(soup.select('.title-content-title')[0].text) #class属性为title-content-title的标签下所有文本
print(soup.find(class_='s-center-box')['class']) #指定标签的属性