Java对象的比较
目
优先队列的使用
元素的比较
基本元素的比较
对象比较的问题
对象的比较
重写equals方法
基于Comparble接口类的比较
编辑
基于比较器比较
三种方法的比较
集合框架中PriorityQueue的比较方式
使用PriorityQueue创建大小堆,解决TOPK问题
优先队列的使用
PriorityQueue que = new PriorityQueue<>();
que.add(12);
que.add(23);
que.add(8);
que.add(108);
que.add(86);
System.out.println(que.toString()); 注意:默认情况下,PriorityQueue队列是小堆,如果需要大堆需要用户提供比较器
所以此时输出出来的是已经按照小根堆的顺序输出了。
优先级队列在插入元素时有个要求:插入的元素不能是null或者元素之间必须要能够进行比较,为了简单起见,我们只是插入了Integer类型,那优先级队列中能否插入自定义类型对象呢?
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
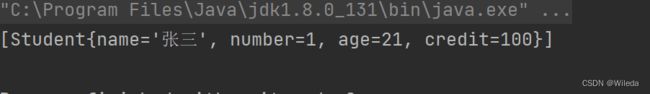
queue.offer(new Student("张三",1,21,100));
System.out.println(queue);
此时只是插入一个对象,并没有报错 ,但是我们继续插入对象
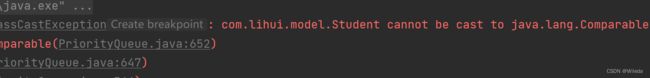
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
queue.offer(new Student("张三",1,21,100));
queue.offer(new Student("李四",2,20,80));
System.out.println(queue); 如图此时出现报错,优先级队列底层使用堆,而向堆中插入元素时,为了满足堆的性质,必须要进行元素的比较,而此时Student是没有办法直接进行比较的,因此抛出异常。
元素的比较
基本元素的比较
public class TestCompare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(a > b);
System.out.println(a < b);
System.out.println(a == b);
char c1 = 'A';
char c2 = 'B';
System.out.println(c1 > c2);
System.out.println(c1 < c2);
System.out.println(c1 == c2);
boolean b1 = true;
boolean b2 = false;
System.out.println(b1 == b2);
System.out.println(b1 != b2);
}
}对象比较的问题
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三",1,21,100);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",2,20,80);
Student s3 = s1;
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
// System.out.println(s1 > s2);//编译报错
System.out.println(s3 == s1);
// System.out.println(s1 < s2);//编译报错
由结果可以看出,对象之间直接比较只能用" == "比较,而不能用">" "<",因为:对于用户实现自定义类型,都默认继承自Object类,而Object类中提供了equal方法,而==默认情况下调用的就是equal方法,但是该方法的比较规则是:没有比较引用变量引用对象的内容,而是直接比较引用变量的地址
那么我们可以怎么样可以比较对象?
对象的比较
重写equals方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj == null || !(obj instanceof Student)){//instanceof 关键字判断是否为Student类
return false;
}
Student student = (Student) obj;
if (this.age != student.getAge()) {
return false;
}
if (!this.name.equals(student.getName())) {
return false;
}
if (this.number != student.getNumber()) {
return false;
}
if (this.credit != student.getCredit()) {
return false;
}
return true;
}覆写基类equal的方式虽然可以比较,但缺陷是:equal只能按照相等进行比较,不能按照大于、小于的方式进行比较。
基于Comparble接口类的比较
重写compareTo方法,大于返回正数,等于返回0,小于返回负数
实现Comparble接口,同时重写compareTo方法,可以指定一个属性进行比较,此时我们对象之间的比较不仅仅用"==",还可以用">" "<"进行比较
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三",1,21,100);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",2,20,80);
Student s3 = s1;
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));
System.out.println(s2.compareTo(s1));
System.out.println(s3.compareTo(s1));
因为我们重写方法时是按照number属性比较的,所以结果如上。Compareble是java.lang中的接口类,可以直接使用。
基于比较器比较
用户自定义比较器类,实现Comparator接口
覆写Comparator中的compare方法
public class StudentCompareWithAge implements Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
}
Student s1 = new Student("张三",1,21,100);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",2,20,80);
Student s3 = s1;
StudentCompareWithAge studentCompareWithAge = new StudentCompareWithAge();
System.out.println(studentCompareWithAge.compare(s1,s2));
System.out.println(studentCompareWithAge.compare(s2,s1));
System.out.println(studentCompareWithAge.compare(s1,s3)); 由于我们重写compare的内容,此时的结果按照年龄的升序来排列我们的对象
三种方法的比较
覆写的方法 说明
Object.equals 因为所有类都是继承自 Object 的,所以直接覆 写即可,不过只能比较相等与否
Comparable.compareTo 需要手动实现接口,侵入性比较强,但一旦实 现,每次用该类都有顺序,属于内部顺序
Comparator.compare 需要实现一个比较器对象,对待比较类的侵入性 弱,但对算法代码实现侵入性
集合框架中PriorityQueue的比较方式
集合框架中的PriorityQueue底层使用堆结构,因此其内部的元素必须要能够比大小,,PriorityQueue采用了:Comparble和Comparator两种方式。
1. Comparble是默认的内部比较方式,如果用户插入自定义类型对象时,该类对象必须要实现Comparble接口,并覆写compareTo方法PriorityQueuequeue1 = new PriorityQueue<>(); queue1.offer(s1); queue1.offer(s2); System.out.println(queue1);
由于Student类重写了compareTo方法,所以不像文章开头例子一样报异常,而是按照升序输出
2. 用户也可以选择使用比较器对象,如果用户插入自定义类型对象时,必须要提供一个比较器类,让该类实现Comparator接口并覆写compare方法。PriorityQueuequeue1 = new PriorityQueue<>(new StudentCompareWithName()); queue1.offer(s1); queue1.offer(s2); System.out.println(queue1); public class StudentCompareWithAge implements Comparator { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); } }
此时我们自定义比较类,基于年龄比较,所以输出结果按照年龄升序输出。
使用PriorityQueue创建大小堆,解决TOPK问题
给定一个数组,其中n个元素,我们找出前k小(或者大)的元素
第一种方法:我们将元素全部放入优先队列,优先队列默认会按照小根堆的方式排列,直接输出即可
public static int[] topK01(int[] array,int k){
int[] result = new int[k];
if(array.length == 0){
return result;
}
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
queue.offer(array[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result[i] = queue.poll();
}
return result;
} 第二种方法:我们创建一个大根堆(如果要输出前k大的,我们创建小根堆),步骤如下:
- 首先创建一个k大小的优先队列
- 如果队列的容量不如k时,直接入队
- 如果队列的容量等于k时,比较堆顶元素与新插入元素大小
- 根据大根小根堆的堆顶元素,选择是否弹出并加入新的元素:
- 如果找前k个最大,用小根堆,入队元素比堆顶元素大,出队堆顶元素并加入新的元素
- 如果找前k个最小,用大根堆,入队元素比堆顶元素小,出队堆顶元素并加入新的元素
public static int[] topK(int[] array,int k){
int[] result = new int[k];
if(array.length == 0){
return result;
}
//重写compartor中的comapre方法,以降序排列
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(i < k){
queue.offer(array[i]);
}else {
if(array[i] < queue.peek()){
queue.poll();
queue.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result[i] = queue.poll();
}
return result;
}