树莓派+MediaPipe+PCA9685+自制摄像机云台实现人脸跟踪移动
目录
- 前言
- 一、准备材料
- 二、代码部分
-
- 前言
- 1.引入库
- 2.客户端(即PC端)
- 3.服务端(即树莓派端)
- 演示
前言
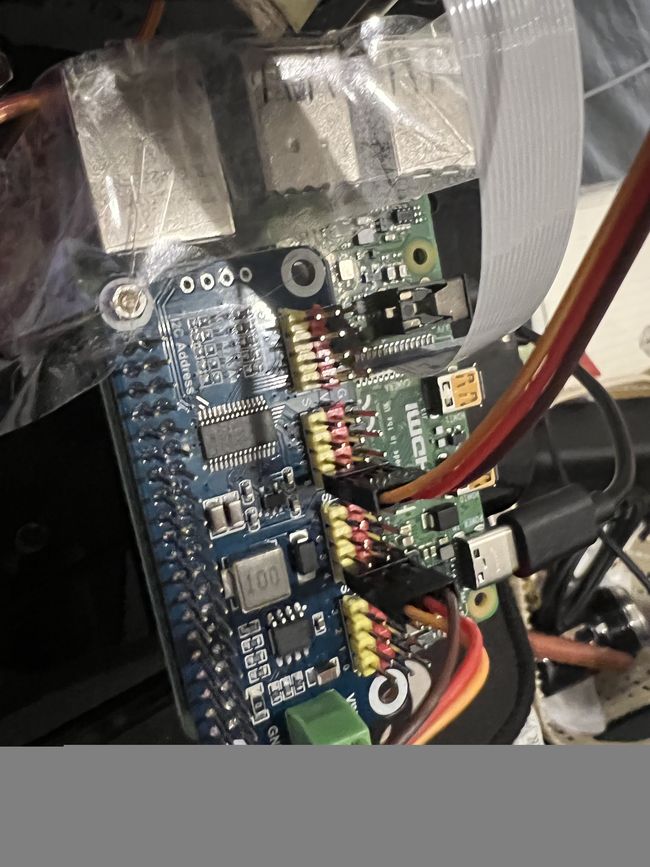
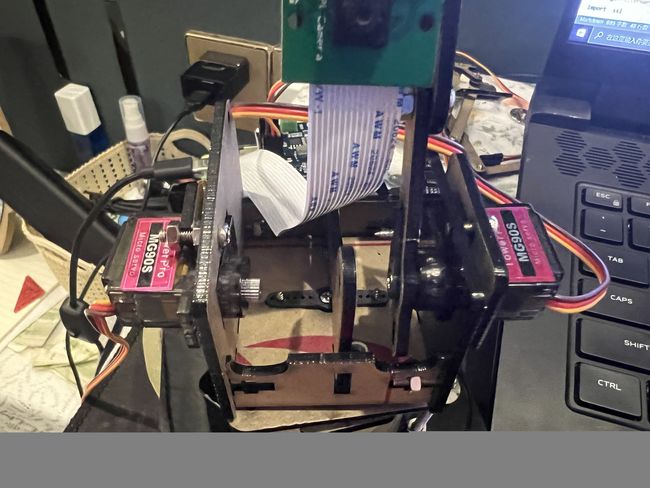
博主闲得无聊,利用某宝几十块钱的机械臂自制了一个摄像头云台,使用了两个MG90S舵机和一块PCA9685驱动的16路舵机扩展板,再通过谷歌的MediaPipe库实现摄像机跟随人脸移动的功能,代码十分简单,快来给你的树莓派添加一个新玩法吧~
一、准备材料
①树莓派(这个肯定需要有的)
②摄像头

③PCA9685驱动的16路舵机扩展板(关于这部分的教程可以百度或谷歌一下,建议先调试成功后再开始这个项目,不然容易把舵机烧坏)
⑤制作云台的工具(我是用某宝买的四自由度亚克力机械臂拆出来做的)
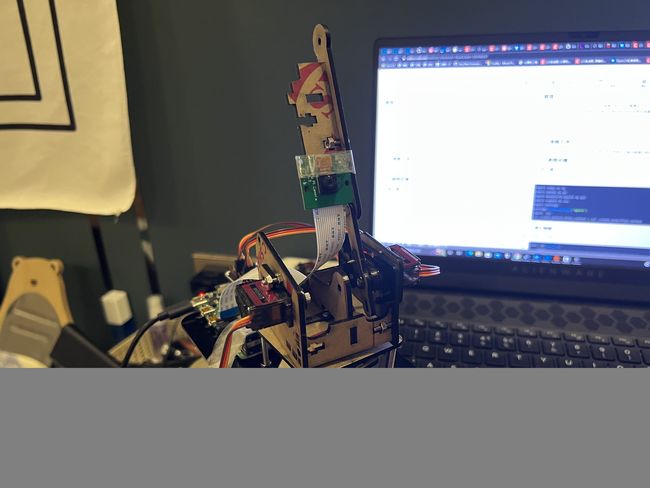
二、代码部分
前言
代码经过测试,Mediapipe项目部署在树莓派上的视频帧率只有十几帧左右,如果真的想流畅运行,就需要借助MJPG-streamer工具传输树莓派上的摄像头视频到PC端,然后在PC端进行脸部识别,这样可以实现几乎0延迟传输并控制云台移动,且PC端运算能力强,可以做更多处理。
具体实现步骤可以进这篇某乎上看看
树莓派利用MJPG-streamer传输摄像头视频
1.引入库
Mediapipe
sudo pip3 install mediapipe-rpi3
如果是4版本则使用用命令:
sudo pip3 install mediapipe-rpi4
导入控制舵机的PCA驱动(这部分工作可以网上搜一下“树莓派PCA控制舵机”)
sudo pip install adafruit-pca9685
2.客户端(即PC端)
client.py 用于定义客户端
import socket
class connect_Raspberry():
def __init__(self,host,port):
print("客户端开启")
# 套接字接口
self.mySocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 设置ip和端口
try:
self.mySocket.connect((host, port)) #连接到服务器
print("连接到服务器")
except: #连接不成功,运行最初的ip
print('连接RASP不成功')
def send(self, words):
# 发送消息
msg = words
# 编码发送
self.mySocket.send(msg.encode("utf-8"))
# print("成功发送消息")
def close(self):
self.mySocket.close()
print("与树莓派丽连接中断\n")
exit()
main.py 用于接收树莓派视频以及人脸识别,并发送识别位置到树莓派
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
import numpy as np
import client
#检测脸部
mp_face_detection = mp.solutions.face_detection
mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
#通信传输
myRaspConnection = client.connect_Raspberry('你的树莓派ip', 8888)
if __name__ == "__main__":
capture = cv2.VideoCapture("http://你的树莓派ip:8080/?action=stream")
ref, frame = capture.read()
fps = 0.0
while(True):
ref, frame = capture.read()
h,w,_ = np.shape(frame)
if not ref:
break
image = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#脸部检测
with mp_face_detection.FaceDetection(model_selection=0, min_detection_confidence=0.8) as face_detection:
results = face_detection.process(image)
if results.detections:
for detection in results.detections:
box=detection.location_data.relative_bounding_box
#cx,cy,cw,ch=box
cx=box.xmin
cy=box.ymin
cw=box.width
ch=box.height
cv2.rectangle(image, (int(cx*w) , int(cy*h)), (int((cx+cw)*w) , int((cy+ch)*h)),(0, 255, 0), 2)
#控制云台
msg = str(int(cx*w)) + " " + str(int(cy*h)) + " " + str(int((cx+cw)*w)) + " " + str(int((cy+ch)*h))
myRaspConnection.send(msg)
frame = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# cv2.rectangle(frame, (int(cx*w) , int(cy*h)), (int((cx+cw)*w) , int((cy+ch)*h)),(0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("video",frame)
c= cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xff
if c==27:
capture.release()
break
print("Video Detection Done!")
capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3.服务端(即树莓派端)
sever.py 用于定义服务端
import socket
print("服务开启")
mySocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host = "你的树莓派ip"
port = 8888 #自己定义的端口号
mySocket.bind((host, port))
mySocket.listen(10)
main.py 用于接收pc端的人脸位置信息,并控制云台移动
import time
import sever
import Adafruit_PCA9685
def set_servo_angle(channel, angle):#输入角度转换成12^精度的数值
date=int(4096*((angle*11)+500)/20000)#进行四舍五入运算 date=int(4096*((angle*11)+500)/(20000)+0.5)
pwm.set_pwm(channel, 0, date)
pwm = Adafruit_PCA9685.PCA9685()
pwm.set_pwm_freq(50)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("等待连接")
client,address = sever.mySocket.accept()
print("新连接")
print("IP is %s" % address[0])
print("port is %d\n" % address[1])
beangle = 100 #每个人的初始角度不同,建议先自己测试好角度
beangle0 = 60
#舵机插的通道口
channel1 = 4 #上下
channel2 = 8 #左右
#变化幅度(这个越大,舵机动的幅度就越大)
angleFreq = 1
#超出屏幕范围(这个调大后,脸部离视频边界检测更灵敏)
changeFreq = 20
#初始化角度
set_servo_angle(channel1,beangle)
set_servo_angle(channel2,beangle0)
while True:
msg = client.recv(1024)
msg = msg.decode("utf-8")
if msg != "":
mess = msg.split(' ')
x0 = int(mess[0])#左上角x
y0 = int(mess[1])#左上角y
x1 = int(mess[2])#右下角x
y1 = int(mess[3])#右下角y
#超出屏幕外
if x0 < changeFreq:
beangle += angleFreq
if beangle >= 180:
beangle = 180
set_servo_angle(channel1,beangle)
if y0 < changeFreq:
beangle0 += angleFreq
if beangle0 >= 180:
beangle0 = 180
set_servo_angle(channel2,beangle0)
if x1 > 640 - changeFreq: #窗口宽为640
beangle -= angleFreq
if beangle <= 30:
beangle = 30
set_servo_angle(channel1,beangle)
if y1 > 480 - changeFreq: #窗口高为480
beangle0 -= angleFreq
if beangle0 <= 30:
beangle0 = 30
set_servo_angle(channel2,beangle0)


