Leetcode周赛 | 2023-7-30--我真是个废物
2023-7-30--我真是个废物
- 题1
-
- 体会
- 我的代码
- 题2
-
- 体会
- 我的代码
- 题3
-
- 体会
- 我的代码
题1
体会
根本没想到用双指针。原因是,没想到还要用一个字典去维护子数组中各个数字的出现频次,以及出现频次不小于1 (也就是大于0) 的数字个数。
class Solution:
def countCompleteSubarrays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
# 查看目标需要有多少个不同的数字
m = len(set(nums))
n = len(nums)
l, r = 0, 0
# 分别记录出现的频次和出现频次大于 0 的数的个数
cnt = Counter()
different_values = 0
ans = 0
while l < n:
while r < n and different_values < m:
cnt[nums[r]] += 1
# 频次变为 1 时,出现频次大于 0 的数的个数增加 1
if cnt[nums[r]] == 1: different_values += 1
r += 1
if different_values < m: break
# [l, r-1], ..., [l, n-1] 总共有 n - r + 1 个区间
ans += n - r + 1
cnt[nums[l]] -= 1
# 频次变为 0 时,出现频次大于 0 的数的个数减少 1
if cnt[nums[l]] == 0: different_values -= 1
l += 1
return ans
上面的代码中,根本没用到 Counter() , 就是当一个字典来用的。换成字典是一样的。
class Solution:
def countCompleteSubarrays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
# 查看目标需要有多少个不同的数字
m = len(set(nums))
n = len(nums)
l, r = 0, 0
# 分别记录出现的频次和出现频次大于 0 的数的个数
cnt = {}
different_values = 0
ans = 0
while l < n:
while r < n and different_values < m:
cnt[nums[r]] = cnt.get(nums[r],0)+1
# 频次变为 1 时,出现频次大于 0 的数的个数增加 1
if cnt[nums[r]] == 1: different_values += 1
r += 1
if different_values < m: break
# [l, r-1], ..., [l, n-1] 总共有 n - r + 1 个区间
ans += n - r + 1
cnt[nums[l]] -= 1
# 频次变为 0 时,出现频次大于 0 的数的个数减少 1
if cnt[nums[l]] == 0: different_values -= 1
l += 1
return ans
我的代码
题2
体会
class Solution:
def minimumString(self, a: str, b: str, c: str) -> str:
length, res = inf, ''
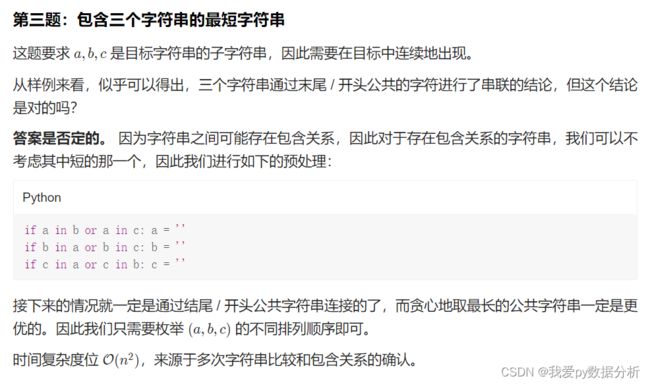
if a in b or a in c: a = ''
if b in a or b in c: b = ''
if c in a or c in b: c = ''
for x, y, z in permutations((a, b, c)):
tmp = ''
for i in range(min(len(x), len(y)), 0, -1):
if x[-i:] == y[:i]: tmp = x + y[i:]; break
else: tmp = x + y
for i in range(min(len(tmp), len(z)), 0, -1):
if tmp[-i:] == z[:i]: tmp = tmp + z[i:]; break
else: tmp = tmp + z
if len(tmp) < length or (len(tmp) == length and tmp < res):
length = len(tmp)
res = tmp
return res
太恐怖了,这个编程技巧, if else 还能这样用的 ?
本题只有三个字符串,一共可能的组合也没几种,那就全部遍历!一定要区分,是处理固定个数目标的题,还是处理N个目标的题,固定个数的可以全部遍历。
我的代码
题3
体会
mod = 10 ** 9 + 7
class Solution:
def countSteppingNumbers(self, low: str, high: str) -> int:
low = str(int(low) - 1)
@cache
def getRes(idx, start, bind, lastVal):
if idx == len(x): return 1 if start else 0
# 如果数字还没开始,那么可以到下一个位再开始
res = 0 if start else getRes(idx+1, False, False, 0)
# 可能转移成的数字:如果数字还未开始
for i in ([lastVal-1, lastVal+1] if start else range(1, 10)):
# 判断数字是否合法:有无本身超出数字集 / 大于了给定的 x 的情况
if i < 0 or i > 9: continue
if bind and i > x[idx]: break
# 看上界是否还有限制作用
note = bind and i == x[idx]
res += getRes(idx+1, True, note, i)
return res % mod
x = [int(x) for x in high]
ans = getRes(0, False, True, 0)
getRes.cache_clear()
# 注意这里要清空下 cache,否则同个状态对于两个 x 判断结果不同会造成答案错误
x = [int(x) for x in low]
ans -= getRes(0, False, True, 0)
getRes.cache_clear()
return ans % mod # 减了之后可能变成负数,记得取模