(电力开发)DLT645-2007协议基本结构解析
目录
- 一 基本介绍
-
- 1.1 字节格式
- 1.2 帧格式
-
- 1.2.1 帧起始符 68H
- 1.2.2 地址域 A0~A5
- 1.2.3 控制码 C
- 1.2.4 数据域长度 L
- 1.2.5 数据域(DATA)
-
- 1.2.5.1 数据标识
- 1.2.5.2 数据项与数据块
- 1.2.6 校验码 (CS)
- 1.2.7 结束符 16H
- 1.2.8 前导字节
- 1.2.9 传输次序
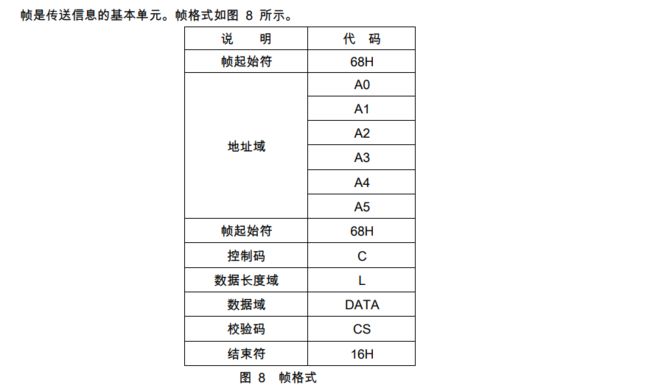
本协议为主-从结构的半双工通信方式。手持单元或其它数据终端为主站,多功能电能表为从站。每个 多功能电能表均有各自的地址编码。通信链路的建立与解除均由主站发出的信息帧来控制。每帧由帧起始符、从站地址域、控制码、数据长度、数据域、帧信息纵向校验码及帧结束符7个域组成。每部分由若干 字节组成。
一 基本介绍
1.1 字节格式
每字节含8位二进制码,传输时加上一个起始位(0)、一个偶校验位和一个停止位(1), 共11位,D0 是字节的最低有效位,D7 是字节的最高有效位,先传低位,后传高位。 (小端序)
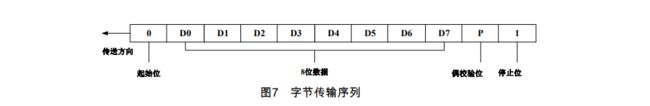
EG:当一个字节值为10101010(二进制)需要进行串行传输时,按照描述的方式添加起始位、偶校验位和停止位。下面是这个字节的传输过程:
原始字节值:10101010
添加起始位、偶校验位和停止位后的传输序列:01010101011
解释:
- 起始位:0(固定为0,表示传输开始)
- 数据位:10101010(原始字节值)
- 偶校验位:1(由于原始字节中有4个1,所以偶校验位设置为1,以保持数据位中1的总数为偶数)
- 停止位:1(固定为1,表示传输结束)
因此,该字节的传输序列为01010101011。在串行传输中,这个序列会按照从最低有效位到最高有效位的顺序进行传输。
这里解释一下小端序与大端序吧?
在计算机中,字节的存储和传输方式可以使用大端序(Big-Endian)或小端序(Little-Endian)。大端序是指高位字节存储在低地址,低位字节存储在高地址;小端序则相反,低位字节存储在低地址,高位字节存储在高地址。
1.2 帧格式
1.2.1 帧起始符 68H
标识一帧信息的开始,其值为 68H=01101000B
1.2.2 地址域 A0~A5
- 地址域由 6 个字节构成,每字节 2 位 BCD 码。地址长度可达12位十进制数,每块表具有唯一的 通信地址,且与物理层信道无关.当使用的地址码长度不足 6 字节时,高位用“0”补足 (简单来说,每块电表都应该有他唯一的地址标识长度一般12位,不足前面补0)
- 当通信地址为 999999999999H为广播地址,只针对特殊命令有效,如广播校时和广播冻结等。广播命令不要求从站应答。
- 地址域支持缩位寻址,即从若干低位起,剩余高位补 AAH 作为通配符进行读表操作,从站应答帧的 地址域返回实际通信地址。
- 地址域传输时低字节在前,高字节在后。
那如何理解BCD码?
BCD码(Binary Coded Decimal)是一种用二进制编码表示十进制数字的编码方式。它将每个十进制数字编码为一个4位的二进制数。
- 十进制数字:十进制数字由0到9的数字组成。
- 二进制编码:BCD码使用4位的二进制数来表示每个十进制数字。每个BCD码的有效位数为4位,取值范围从0000到1001。
- 位权:BCD码的每个位都有一个位权,从最低位到最高位分别是1、2、4和8。这些位权对应于十进制数字中的个位、十位、百位和千位。
- BCD码转换:将一个十进制数字转换为BCD码,需要将该数字的每一位分别转换为对应的4位BCD码。
例如,将十进制数字37转换为BCD码:
- 十进制数字3的BCD码是0011。
- 十进制数字7的BCD码是0111。
因此,十进制数字37的BCD码表示为0011 0111。
EG:
29 25 07 07 21 20本身是由6个字节组成,并且每个字节使用2位BCD码进行编码。
每个字节使用2位BCD码,因此可以表示的十进制数字范围是 00 到 99。
字节1:29 (0010 1001)
字节2:25 (0010 0101)
字节3:07 (0000 0111)
字节4:07 (0000 0111)
字节5:21 (0010 0001)
字节6:20 (0010 0000)
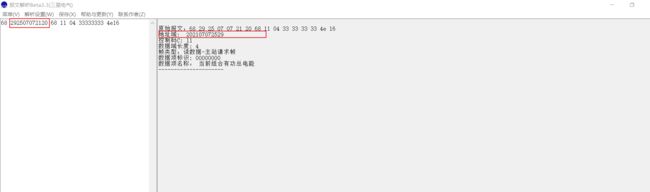
在DLT645协议中规定,表号字段,数据字段都是逆序的,也就是与实际表号循序相反,我们反过来看就可以得到表地址:202107072529
那如何用代码来写呢?
/**
* @description:
* @author: shu
* @createDate: 2023/5/17 21:09
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Address {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 模拟数据帧
String data = "6872003209172068910833333433B93433336D16";
// 68H 帧起始符
String start = data.substring(0, 2);
// 6个字节的地址域
String address = data.substring(2, 14);
// 利用BCD码转换
String addressBCD = addressToString(stringToBytes(address));
System.out.println("表地址:" + addressBCD);
short[] shorts = addressTo645(addressBCD);
String string = bytesToString(shorts);
System.out.println("数据帧:" + string);
}
/**
* 将6个字节的地址域,每字节2位 BCD码,转换为12位10进制数
*/
public static String addressToString(byte[] arrAddr) {
return String.format("%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x", arrAddr[5], arrAddr[4], arrAddr[3], arrAddr[2], arrAddr[1], arrAddr[0]);
}
public static short[] addressTo645(String decimalStr) {
int length = decimalStr.length();
int paddingLength = 12 - length;
int startIndex = 0;
if (paddingLength > 0) {
int paddedValue = Integer.parseInt(decimalStr) << (paddingLength * 4);
decimalStr = String.format("%012x", paddedValue);
} else {
startIndex = length - 12;
decimalStr = decimalStr.substring(startIndex);
}
short[] addrArray = new short[6];
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
addrArray[5-i] = Short.parseShort(decimalStr.substring(startIndex + i * 2, startIndex + i * 2 + 2), 16);
}
return addrArray;
}
/**
* 将String类型转换成byte数组
*/
public static byte[] stringToBytes(String str) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[str.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
String subStr = str.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2);
bytes[i] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(subStr, 16);
}
return bytes;
}
/**
* 将byte数组转换成String类型
*/
public static String bytesToString(short[] bytes) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("");
if (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0) {
return null;
}
for (short b : bytes) {
int v = b & 0xFF;
String hv = Integer.toHexString(v);
if (hv.length() < 2) {
stringBuilder.append(0);
}
stringBuilder.append(hv);
}
return stringBuilder.toString().toUpperCase();
}
}
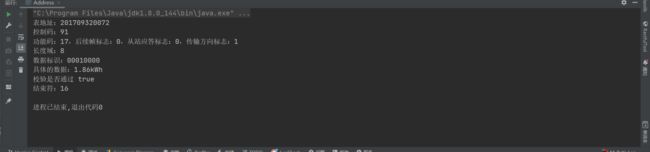
1.2.3 控制码 C
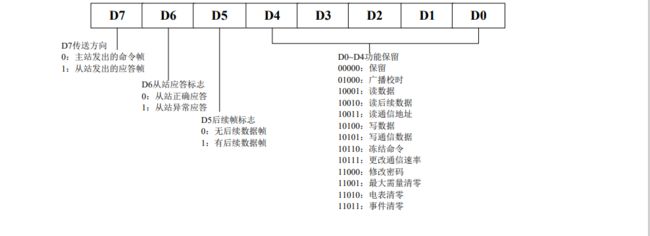
EG: 68 72 00 32 09 17 20 68 91 08 33 33 34 33 B9 34 33 33 6D 16
控制域:91 转换成二进制:10010001
我们对比上面的协议可以发现,
D0-D4:10001 ,代表读取数据
D5, 0 无后续字节
D6, 从站正常应答
D7,主站发出的命令帧
/**
* 解析控制码
*/
public static void parseControl(byte[] control) {
// D0-D4:功能码
String function = String.format("%d", control[0]&0x1F);
// D5:后续帧标志
String next = String.format("%d", control[0]>>5&0x01);
// D6:从站应答标志
String response = String.format("%d", control[0]>>6&0x01);
// D7:传输方向标志
String direction = String.format("%d", control[0]>>7&0x01);
// 一起解析
System.out.println("功能码:" + function + ",后续帧标志:" + next + ",从站应答标志:" + response + ",传输方向标志:" + direction);
}
/**
* 构造控制码
* @param function 功能码
* @param next 后续帧标志 0:结束帧 1:有后续帧
* @param response 从站应答标志 0:应答正常 1:应答异常
* @param direction 传输方向标志 0:主站发出的帧 1:从站发出的帧
* @return
*/
public static byte[] buildControl(String function, String next, String response, String direction) {
byte[] control = new byte[1];
control[0] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(function) | Integer.parseInt(next) << 5 | Integer.parseInt(response) << 6 | Integer.parseInt(direction) << 7);
return control;
}
1.2.4 数据域长度 L
L 为数据域的字节数。读数据时 L≤200,写数据时 L≤50,L=0 表示无数据域。
EG: 08 代表数据域长度: 8代表后面有8个字节的数据域,这里需要注意上面读与写的数据量限制
/**
* 解析数据域长度
*/
public static int parseLength(byte[] length) {
return length[0] & 0xFF;
}
/**
* 构造数据域长度
*/
public static byte[] buildLength(int length) {
byte[] len = new byte[1];
len[0] = (byte) length;
return len;
}
1.2.5 数据域(DATA)
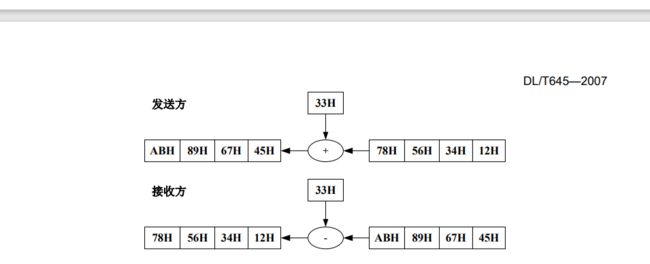
数据域包括数据标识、密码、操作者代码、数据、帧序号等,其结构随控制码的功能而改变。传输 时发送方按字节进行加 33H 处理,接收方按字节进行减 33H 处理。
EG: 33 33 34 33 B9 34 33 33
1.2.5.1 数据标识
数据标识用四个字节区分不同数据项目,四字节分别用DI3、DI2、DI1和DI0代表。每字节采用十六进制 编码。数据类型分为七类:电能量、最大需量及发生时间、变量、事件记录、参变量、冻结量、负荷记录。 (四个字节)
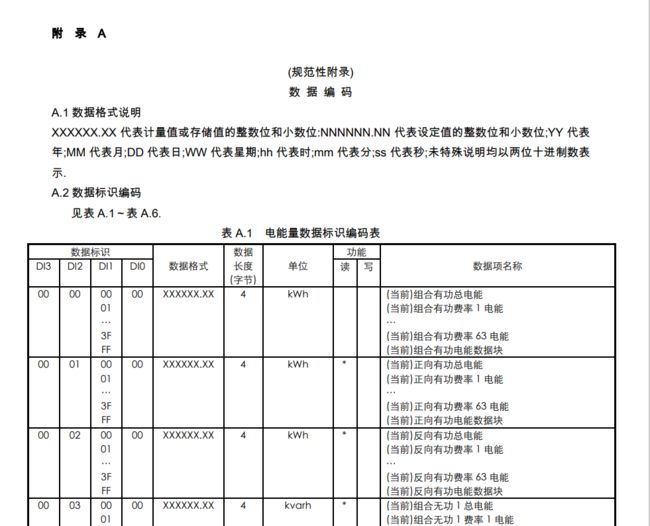
EG: 33 34 33 33 按照规则解析减去33 00 01 00 00 所以说数据标识代表当前正向有功电能总
/**
* 解析4个字节的数据标识
*/
public static String parseDataIdentifier(byte[] dataIdentifier) {
// 每个字节-33H处理
for (int i = 0; i < dataIdentifier.length; i++) {
dataIdentifier[i] = (byte) (dataIdentifier[i] - 0x33);
}
return String.format("%02x%02x%02x%02x", dataIdentifier[3], dataIdentifier[2], dataIdentifier[1], dataIdentifier[0]);
}
/**
* 构造4个字节的数据标识
*/
public static byte[] buildDataIdentifier(String dataIdentifier) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[dataIdentifier.length() / 2];
System.out.println("dataIdentifier:" + bytes.length);
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
String subStr = dataIdentifier.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2);
bytes[3-i] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(subStr, 16) + 0x33);
}
return bytes;
}
具体的数据项需要参考协议
1.2.5.2 数据项与数据块
- 除特殊说明的数据项以ASCⅡ码表示外,其他数据项均采用压缩 BCD 码表示。
- 数据标识符DI2 、DI1 、DI0中任意一字节取值为 FFH 时(其中 DI3 不存在 FFH 的情况),代表该 字节定义的所有数据项与其它三字节组成的数据块。
- a) 标识码 DI3DI2DI1DI0=00010000H(数据项)表示当前正向有功总电能。 b) 标识码 DI3DI2DI1DI0=000100FFH(数据块)表示正向有功总电能数据块,包含当前、上1结算日~ 上12结算日正向有功总电能数据。 c) 标识码 DI3DI2DI1DI0=0001FF00H (数据块)表示当前正向有功电能量数据块,包含总、费率1、 费率2….的当前正向有功电能量数据。
/**
* 解析返回的具体数据
*/
public static String parseData(byte[] data) {
// 每个字节-33H处理
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
data[i] = (byte) (data[i] - 0x33);
}
StringBuilder dataStr = new StringBuilder();
// BCD码转换成10进制
for (byte b : data) {
dataStr.insert(0, String.format("%02x", b));
}
return Double.parseDouble(dataStr.toString()) * 0.01 + "kWh";
}
/**
* 构造返回的具体数据
*/
public static byte[] buildData(String data) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[data.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
String subStr = data.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2);
bytes[bytes.length - 1 - i] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(subStr, 16) + 0x33);
}
return bytes;
}
1.2.6 校验码 (CS)
从第一个帧起始符开始到校验码之前的所有各字节的模 256 的和,即各字节二进制算术和,不计 超过 256 的溢出值。
public static byte calculateChecksum(byte[] data) {
int count = 0;
int len = data.length - 2;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
count += data[i];
}
return (byte)(count & 0xFF);
}
1.2.7 结束符 16H
标识一帧信息的结束,其值为 16H=00010110B。
1.2.8 前导字节
在主站发送帧信息之前,建议先发送 4 个字节 FEH,以唤醒接收方
1.2.9 传输次序
所有数据项均先传送低位字节,后传送高位字节。数据传输的举例:电能量值为 123456.78kWh,
大部分具体的规则介绍完了,但是要用很多具体项需要自己去看与写参考协议
/**
* @description:
* @author: shu
* @createDate: 2023/5/17 21:09
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Address {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 模拟数据帧
String data = "6872003209172068910833333433B93433336D16";
// 68H 帧起始符
String start = data.substring(0, 2);
// 6个字节的地址域
String address = data.substring(2, 14);
// 利用BCD码转换
String addressBCD = addressToString(stringToBytes(address));
System.out.println("表地址:" + addressBCD);
// 1个字节的控制码
String control = data.substring(16, 18);
System.out.println("控制码:" + control);
parseControl(stringToBytes(control));
// 1个字节的长度域
String length = data.substring(18, 20);
System.out.println("长度域:" + parseLength(stringToBytes(length)));
// 4个字节的数据标识
String dataIdentifier = data.substring(20, 28);
String dataIdentifier1 = parseDataIdentifier(stringToBytes(dataIdentifier));
System.out.println("数据标识:" + dataIdentifier1);
// 4个字节的数据单元标识
String dataUnitIdentifier = data.substring(28, 36);
String parseData = parseData(stringToBytes(dataUnitIdentifier));
System.out.println("具体的数据:" + parseData);
// 校验和
String checkSum = data.substring(36, 38);
byte[] stringToBytes = stringToBytes(checkSum);
// 16H 结束c
boolean b = stringToBytes[0] == calculateChecksum(stringToBytes(data));
System.out.println("校验是否通过 "+b);
// 16H 结束c
String end = data.substring(38);
System.out.println("结束符:" + end);
}
/**
* 将6个字节的地址域,每字节2位 BCD码,转换为12位10进制数
*/
public static String addressToString(byte[] arrAddr) {
return String.format("%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x", arrAddr[5], arrAddr[4], arrAddr[3], arrAddr[2], arrAddr[1], arrAddr[0]);
}
public static short[] addressTo645(String decimalStr) {
int length = decimalStr.length();
int paddingLength = 12 - length;
int startIndex = 0;
if (paddingLength > 0) {
int paddedValue = Integer.parseInt(decimalStr) << (paddingLength * 4);
decimalStr = String.format("%012x", paddedValue);
} else {
startIndex = length - 12;
decimalStr = decimalStr.substring(startIndex);
}
short[] addrArray = new short[6];
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
addrArray[5 - i] = Short.parseShort(decimalStr.substring(startIndex + i * 2, startIndex + i * 2 + 2), 16);
}
return addrArray;
}
/**
* 将String类型转换成byte数组
*/
public static byte[] stringToBytes(String str) {
if (str == null || str.equals("")) {
return null;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[str.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
String subStr = str.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2);
bytes[i] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(subStr, 16);
}
return bytes;
}
/**
* 将byte数组转换成String类型
*/
public static String bytesToString(short[] bytes) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("");
if (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0) {
return null;
}
for (short b : bytes) {
int v = b & 0xFF;
String hv = Integer.toHexString(v);
if (hv.length() < 2) {
stringBuilder.append(0);
}
stringBuilder.append(hv);
}
return stringBuilder.toString().toUpperCase();
}
/**
* 将byte数组转换成String类型
*/
public static String bytesToString1(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("");
if (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0) {
return null;
}
for (short b : bytes) {
int v = b & 0xFF;
String hv = Integer.toHexString(v);
if (hv.length() < 2) {
stringBuilder.append(0);
}
stringBuilder.append(hv);
}
return stringBuilder.toString().toUpperCase();
}
/**
* 解析控制码
*/
public static void parseControl(byte[] control) {
// D0-D4:功能码
String function = String.format("%d", control[0] & 0x1F);
// D5:后续帧标志
String next = String.format("%d", control[0] >> 5 & 0x01);
// D6:从站应答标志
String response = String.format("%d", control[0] >> 6 & 0x01);
// D7:传输方向标志
String direction = String.format("%d", control[0] >> 7 & 0x01);
// 一起解析
System.out.println("功能码:" + function + ",后续帧标志:" + next + ",从站应答标志:" + response + ",传输方向标志:" + direction);
}
/**
* 构造控制码
*
* @param function 功能码
* @param next 后续帧标志 0:结束帧 1:有后续帧
* @param response 从站应答标志 0:应答正常 1:应答异常
* @param direction 传输方向标志 0:主站发出的帧 1:从站发出的帧
* @return
*/
public static byte[] buildControl(String function, String next, String response, String direction) {
byte[] control = new byte[1];
control[0] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(function) | Integer.parseInt(next) << 5 | Integer.parseInt(response) << 6 | Integer.parseInt(direction) << 7);
return control;
}
/**
* 解析数据域长度
*/
public static int parseLength(byte[] length) {
return length[0] & 0xFF;
}
/**
* 构造数据域长度
*/
public static byte[] buildLength(int length) {
byte[] len = new byte[1];
len[0] = (byte) length;
return len;
}
/**
* 解析4个字节的数据标识
*/
public static String parseDataIdentifier(byte[] dataIdentifier) {
// 每个字节-33H处理
for (int i = 0; i < dataIdentifier.length; i++) {
dataIdentifier[i] = (byte) (dataIdentifier[i] - 0x33);
}
return String.format("%02x%02x%02x%02x", dataIdentifier[3], dataIdentifier[2], dataIdentifier[1], dataIdentifier[0]);
}
/**
* 构造4个字节的数据标识
*/
public static byte[] buildDataIdentifier(String dataIdentifier) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[dataIdentifier.length() / 2];
System.out.println("dataIdentifier:" + bytes.length);
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
String subStr = dataIdentifier.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2);
bytes[3 - i] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(subStr, 16) + 0x33);
}
return bytes;
}
/**
* 解析返回的具体数据
*/
public static String parseData(byte[] data) {
// 每个字节-33H处理
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
data[i] = (byte) (data[i] - 0x33);
}
StringBuilder dataStr = new StringBuilder();
// BCD码转换成10进制
for (byte b : data) {
dataStr.insert(0, String.format("%02x", b));
}
return Double.parseDouble(dataStr.toString()) * 0.01 + "kWh";
}
/**
* 构造返回的具体数据
*/
public static byte[] buildData(String data) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[data.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
String subStr = data.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2);
bytes[bytes.length - 1 - i] = (byte) (Integer.parseInt(subStr, 16) + 0x33);
}
return bytes;
}
public static byte calculateChecksum(byte[] data) {
int count = 0;
int len = data.length - 2;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
count += data[i];
}
byte b = (byte) (count & 0xFF);
return b;
}
}