MyBatis使用方法
简介
MyBatis是⼀款优秀的持久层框架, 它⽀持⾃定义 SQL、存储过程以及⾼级映射. MyBatis去除了⼏乎所有的JDBC代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的⼯作.MyBatis可以通过简单的XML或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接⼝和Java POJO为数据库中的记录。
简单来说 MyBatis 是更简单完成程序和数据库交互的⼯具,也就是更简单的操作和读取数据库⼯具。
使用
前置操作
添加MyBatis依赖
MyBatis Framework和MySQL Driver都要添加, MyBatis只是个桥梁, 内部还是靠JDBC
配置连接
application.yml文件里配置
# 数据库连接配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mycnblog?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
配置 MyBatis 中的 XML 路径
application.yml文件里配置
MyBatis 的 XML 中保存是查询数据库的具体操作 SQL
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/**Mapper.xml
搭好格式
①在resource文件夹下新建mapper文件夹存放XxxMapper.xml文件
②源代码目录下新建mapper文件夹存放接口定义
③指定MyBatis映射器XML文件的位置配置
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/**Mapper.xml
④可以新建model文件夹存放对象的定义
举例(selectAll)
定义接口
定义对象属性
配置xml文件
在resource下的mapper里定义xml文件, 名字最好和接口名字一样
sql传参数
使用@Param注解加参数
查
①queryById(@Param("uid") Integer id)select * from userinfo where id = #{uid}
将id参数映射到sql语句里的uid参数
②queryById(@Param("uid") Integer id)select * from userinfo where id = #{param1}
param1代表第一个参数,和①的效果一样
③当只有一个参数的时候,可以不加@Param注解. 不过sql里面的#{..}要写参数名, 可以随便写
增
为了防止参数列表过长, 使用传对象的方法
首先接口的参数是对象: Integer insert(User user)
配置sql语句,把要传的参数写上insert into userinfo (username,password,photo) values (#{username},#{password},#{photo})
使用Setter方法设置参数给对象, 在传对象
如果给传入的对象加@Param注解,那么sql语句就不能直接写属性名, 要写#{对象.属性}:
接口定义: Integer insert2(@Param("userinfo") User user);
SQL语句: insert into userinfo (username, password, photo) values (#{userinfo.username},#{userinfo.password},#{userinfo.photo})
改
接口定义:void update(User user);
sql语句update userinfo set username = #{username},password=#{password} where id = #{id}
测试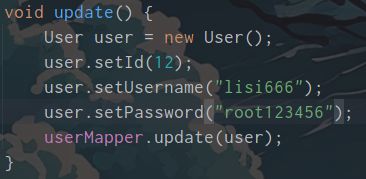
删
Integer delete(Integer id);
sql语句: delete from userinfo where id=#{id}
测试: 
多表查询
补充
sql里#{}和${}区别
问题:
根据名称来查询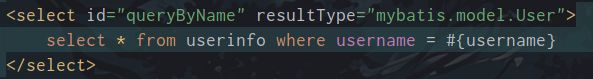
如果是#正常查询, 则错误 , 因为把查询的 " a d m i n " 当成了列 < b r / > − − − − 如果手动操作数据库 , 输入 : < b r / > − − − − ‘ s e l e c t ∗ f r o m u s e r i n f o w h e r e u s e r n a m e = " a d m i n " ‘ 则会正常查出来 < b r / > − − − − 要是 : < b r / > − − − − ‘ s e l e c t ∗ f r o m u s e r i n f o w h e r e u s e r n a m e = a d m i n ‘ 则会报错 : 没找到 a d m i n 列 < b r / > 所以说 则错误, 因为把查询的"admin"当成了列
----如果手动操作数据库,输入:
----`select * from userinfo where username = "admin"`则会正常查出来
----要是:
----`select * from userinfo where username = admin`则会报错:没找到admin列
所以说 则错误,因为把查询的"admin"当成了列<br/>−−−−如果手动操作数据库,输入:<br/>−−−−‘select∗fromuserinfowhereusername="admin"‘则会正常查出来<br/>−−−−要是:<br/>−−−−‘select∗fromuserinfowhereusername=admin‘则会报错:没找到admin列<br/>所以说传递的参数直接放进了sql语句中,没有自己加引号,可以自己加上引号select * from userinfo where username = '${username}'
原因:
- #{} : 是预编译处理, 相当于占位符
- ${} : 是字符直接替换, 字符的内容直接被当做sql语句, 会导致不安全的现象, 也就是sql注入
如果参数从"admin"变成"' or 1='1",那么sql就会变成select * from userinfo where username = '' or 1='1', 就变成了username=空或者1=‘1’, 那么结果就查出来了
使用情况 < b r / > ① o r d e r b y ( 只能用 使用情况
①order by(只能用 使用情况<br/>①orderby(只能用)Listselect * from userinfo order by id #{order}
执行会出错
所以排序的时候, 只能使用KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '#' at position 89: …l注入
②like(#̲ + concat()),程序正确运行,但存在sql注入问题. 需要使用mysql内置函数like concat(‘%’,‘m’,‘%’)(用于将多个字符串拼接在一起),就可以:select * from userinfo where username like concat(‘%’,#{name},‘%’)`正确查询
xml更多属性
insert into userinfo (username, password, photo) values (#{userinfo.username},#{userinfo.password},#{userinfo.photo})
这段代码是针对数据库插入操作的语句:useGeneratedKeys="true":这是一个属性, 当设置为"true"时, 表示数据库会生成并返回自动生成的主键值. keyProperty="id":这是另一个属性, 它指定了用于存储自动生成的主键值的Java对象属性名. 在这里, 它的意思是, 数据库生成的主键值将被设置到Java对象的"id"属性中。
重命名
当java代码里的参数名和数据库的字段名不一致的时候,可以重命名,例如对于userinfo表:
定义一个resultMap并写好id, 将User里面的属性对应到字段名
然后使用的时候,加上resultMap="BaseMap"就可以了
(要是字段没写全的话,没写的字段会按默认规则映射, 不过最好写全)
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="mybatis.model.User">
<id property="id" column="id">id>
<result property="name" column="username">result>
<result property="pwd" column="password">result>
<result property="createTime" column="createtime">result>
<result property="updateTime" column="updatetime">result>
resultMap>
<select id="queryAllByMap" resultMap="BaseMap">
select * from userinfo
select>
如果出现错误的话,可尝试修改配置JDBC的url参数
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://地址:端口/数据库名?useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&characterEncoding=utf8
可能遇到的错误表明应用程序无法获取到JDBC连接,并且出现了Public Key Retrieval is not allowed的异常。这种情况通常是由于数据库连接字符串配置问题引起的。在MySQL数据库中,可能需要设置allowPublicKeyRetrieval参数来允许公钥检索。这个参数用于决定是否在连接过程中从服务器获取公钥。
测试
测试接口
在接口定义处生成->测试, 勾选需要测试的方法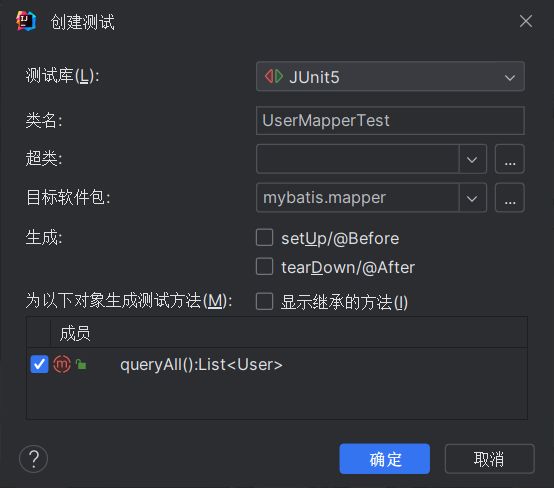
给测试文件加上相应的注解, 并写好测试方法
可以看到打印的日志内容是正确的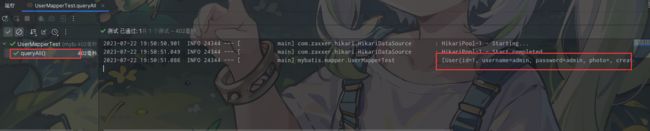
打印sql日志
mybatis:
configuration: # 配置打印 MyBatis 执行的 SQL
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
运行的时候就能看到具体的执行过程(以queryByName为例), 可以看到参数具体变成了什么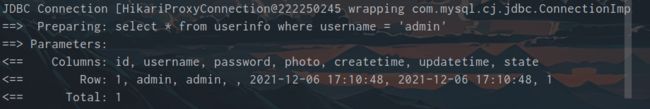
具体业务举例
查询所有用户
UserController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/selectAll")
public List<User> selectAllUser(){
return userService.selectAllUser();
}
}
UserService
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public List<User> selectAllUser() {
return userMapper.queryAll();
}
}
访问http://localhost:8080/user/selectAll,得到
[
{
"id": 1,
"username": "admin",
"password": "admin",
"photo": "",
"createTime": "2021-12-06T09:10:48.000+00:00",
"updateTime": "2021-12-06T09:10:48.000+00:00"
},
{
"id": 2,
"username": "lisi",
"password": "123456",
"photo": "4556a",
"createTime": "2023-07-25T03:46:06.000+00:00",
"updateTime": "2023-07-25T03:46:06.000+00:00"
},
{
"id": 13,
"username": "lisi",
"password": "123456",
"photo": "4556a",
"createTime": "2023-07-25T05:14:14.000+00:00",
"updateTime": "2023-07-25T05:14:14.000+00:00"
}
]
多表查询
一对一的表映射
写法1(不推荐)
**用User对象接受对应的属性**
ArticleInfo: 
xml: **(尽量不要出现from * 的情况)**
使用association连接另一个表, 并引入其resultMap(路径+result的id)
写法2(常用)
**将User对象里面的属性拆解出来**
ArticleInfo: 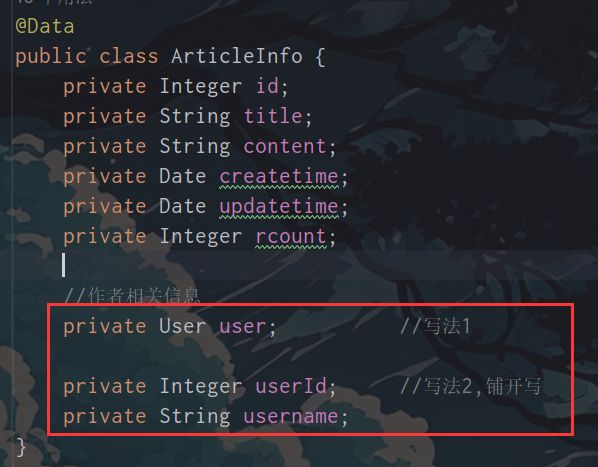
xml: **(尽量不要出现from * 的情况)**
动态SQL
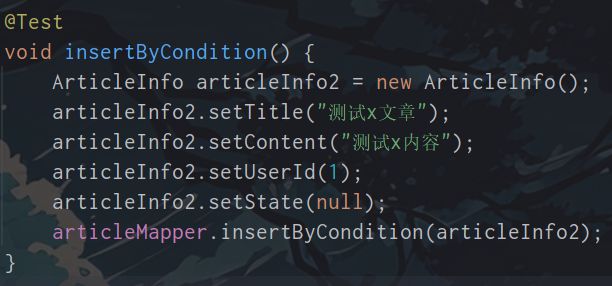
**默认值!=null**
有时候, 例如填写表单的时候,有些是必填,有些非必填. 如果直接这样提交的话, 字段会被赋值为null, 但有时有的字段有默认值,不写的话应该是默认值而不是null,所以要根据填写了哪些字段动态sql(另外还有条件判断等情况)
例如:
对于插入内容是null,结果也是null,但他默认值是1,而不是null


标签
缺点
当每个属性都加, 那么如果第一个和最后一个为空, 那么sql语句必然因逗号而语法错误
标签
<insert id="insertByCondition">
insert into articleinfo
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" prefixOverrides="," suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="title!=null">
title,
if>
<if test="content!=null">
content,
if>
<if test="userId!=null">
uid,
if>
<if test="state!=null">
state
if>
trim>
values
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" prefixOverrides="," suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="title!=null">
#{title},
if>
<if test="content!=null">
#{content},
if>
<if test="userId!=null">
#{userId},
if>
<if test="state!=null">
#{state}
if>
trim>
insert>
标签
一般情况: (加上1=1防止and破坏sql格式)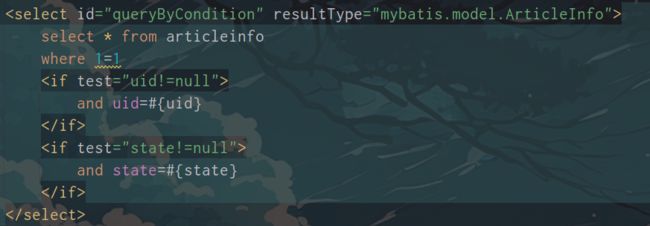
使用:
①生成where关键字
②去除多余的and
③如果没有where条件,就不生成where关键字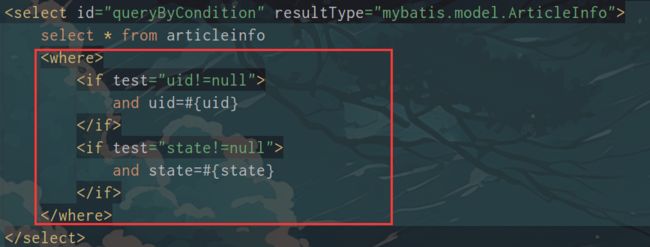
举例: 

标签
①生成set关键字
②去除最后的逗号
(虽然也可以用标签,但这样更简单
举例: 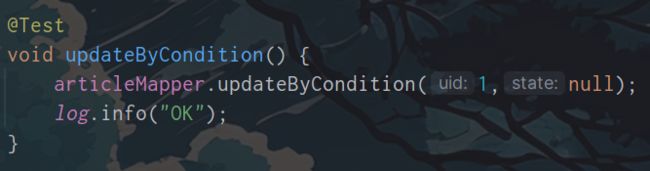

标签
批量操作
示例: 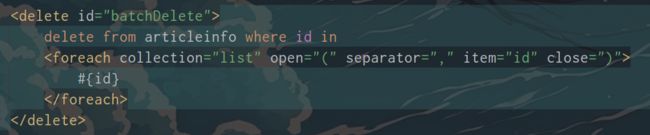
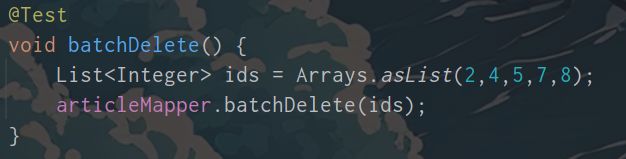

补充:
collection也可以是参数的名称. 测试方法的参数列表加上@Param("ids")然后写collection="ids"也可以
注解实现sql
**只适合写简单的, 复杂的很难写**
接口实现上加上注解
然后不需要写xml就可以直接使用
其他
“XML标签具有空体”
在MyBatis中,如果你使用了像、等标签,而这些标签没有子元素(称为空体),可能会导致警告提示"XML标签具有空体"。虽然这个警告不会影响代码的执行,但是为了代码的可读性和规范性,我们可以消除这个警告。
<resultMap id="BaseMap2" type="mybatis.model.ArticleInfo">
<id property="id" column="id">id>
<result property="title" column="title">result>
<result property="content" column="content">result>
<result property="createtime" column="createtime">result>
<result property="updatetime" column="updatetime">result>
<result property="rcount" column="rcount">result>
<result property="userId" column="userid">result>
resultMap>
消除"XML标签具有空体"警告的方法是在空标签上添加一个闭合斜杠/,表示它是一个自闭合标签,而不是一个空标签。这样做可以告诉解析器这是一个完整的标签,不需要进一步的子元素。
<resultMap id="BaseMap2" type="mybatis.model.ArticleInfo">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="title" column="title" />
<result property="content" column="content" />
<result property="createtime" column="createtime" />
<result property="updatetime" column="updatetime" />
<result property="rcount" column="rcount" />
<result property="userId" column="userid" />
resultMap>