使用Swagger UI的Document和Test API
目录
介绍
配置
可视化
测试
支持属性
支持XML文档
资源/材料/参考资料
介绍
开发人员通常通过浏览器请求或使用POSTMAN, Advanced Rest Client(ARC)等客户端来测试API 。为了公开API的功能,我们还倾向于通过某些需要额外工作的方法公开方法和描述以及相关的数据结构。为了补充这些功能中的一个或两个, Swagger 变得很方便,它通过配置提供API文档和API测试。
Swagger UI是一种可以跨API生命周期使用的工具。Swagger提供易于导航的文档和/或API资源的可视化,并允许从应用程序本身内部与API交互,从而使开发和测试工作以及最终用户体验无缝顺畅。在本文中,我将讨论如何在API中实现swagger并举例说明Swagger UI的一些用例。我将使用.Net Core 2.0 Web API应用程序并使用Visual Studio 2017 IDE。我已经创建了一个带有单个控制器的示例API应用程序,并且有四个方法作为演示的一部分,可供下载。
Swagger提供最强大,最易用的工具,以充分利用OpenAPI规范。 swagger.io
配置
应用程序上的接线Swagger相当小,可以通过四个简单步骤完成,即安装,导入,注册和端点启用。该软件包可以安装在软件包管理器控制台中,也可以通过转到NuGet软件包管理器菜单。
Install-Package Swashbuckle.AspNetCore图1:在Package Manager控制台中安装Swagger
安装完成后,必须将Swagger导入Startup.cs。
using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.Swagger;然后必须在Startup.cs的ConfigureServices方法中注册Swagger成为服务。
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc(_version, new Info { Title = _applicationName, Version = _version });
});最后,应用程序必须在Startup.cs的Configure 方法中为swagger启用JSON和UI端点,以便最终用户可以通过Configure UI与API方法交互。
// Enable Swagger JSON endpoint.
app.UseSwagger();
// Enable swagger-ui (HTML, JS, CSS, etc.)
app.UseSwaggerUI(c =>
{
c.SwaggerEndpoint($"/swagger/{_version}/swagger.json",${_applicationName} {_version}");
});代码段1中显示了Startup.cs文件的完整列表。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.Swagger;
namespace Api
{
public class Startup
{
private string _applicationName;
private string _version;
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_1);
var config = Configuration.GetSection("ApplicationSetting").Get();
_applicationName = config.Name;
_version = config.Version;
// Register the Swagger
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc(_version, new Info { Title = _applicationName, Version = _version });
// Set the comments path for the Swagger JSON and UI.
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
});
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseHsts();
}
// Enable Swagger JSON endpoint.
app.UseSwagger();
// Enable swagger-ui (HTML, JS, CSS, etc.), with the Swagger JSON endpoint.
app.UseSwaggerUI(c =>
{
c.SwaggerEndpoint($"/swagger/{_version}/swagger.json", $"{_applicationName} {_version}");
});
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseMvc();
}
}
} 代码段1:Startup.cs的内容
可视化
完成上述四个步骤后, swagger就准备好了。浏览https://localhost:5001/swagger/v1/swagger.json以获取JSON中的数据(在浏览器或客户端,如POSTMAN,Advanced Rest Client(ARC))。返回的JSON对象提供REST方法的规范(由控制器分隔)和API中使用的对象。一个示例响应是代码段2。
{
"swagger": "2.0",
"info": {
"version": "v1",
"title": "SmartStock API"
},
"paths": {
"/api/Stock": {
"get": {
"tags": [
"Stock"
],
"operationId": "GetStock",
"consumes": [],
"produces": [
"text/plain",
"application/json",
"text/json"
],
"parameters": [],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success",
"schema": {
"uniqueItems": false,
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/Stock"
}
}
}
}
},
"post": {
"tags": [
"Stock"
],
"operationId": "PostStock",
"consumes": [
"application/json-patch+json",
"application/json",
"text/json",
"application/*+json"
],
"produces": [
"text/plain",
"application/json",
"text/json"
],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "stock",
"in": "body",
"required": false,
"schema": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/Stock"
}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success",
"schema": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/Stock"
}
}
}
}
},
"/api/Stock/{symbol}": {
"get": {
"tags": [
"Stock"
],
"operationId": "GetStock",
"consumes": [],
"produces": [
"text/plain",
"application/json",
"text/json"
],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "symbol",
"in": "path",
"required": true,
"type": "string"
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success",
"schema": {
"uniqueItems": false,
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/Stock"
}
}
}
}
}
},
"/api/Stock/{id}": {
"delete": {
"tags": [
"Stock"
],
"operationId": "DeleteStock",
"consumes": [],
"produces": [
"text/plain",
"application/json",
"text/json"
],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "id",
"in": "path",
"required": true,
"type": "string",
"format": "uuid"
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success",
"schema": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
}
}
},
"/api/Values": {
"get": {
"tags": [
"Values"
],
"operationId": "Get",
"consumes": [],
"produces": [
"text/plain",
"application/json",
"text/json"
],
"parameters": [],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success",
"schema": {
"uniqueItems": false,
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
},
"deprecated": true
},
"post": {
"tags": [
"Values"
],
"operationId": "Post",
"consumes": [
"application/json-patch+json",
"application/json",
"text/json",
"application/*+json"
],
"produces": [],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "value",
"in": "body",
"required": false,
"schema": {
"type": "string"
}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success"
}
},
"deprecated": true
}
},
"/api/Values/{id}": {
"get": {
"tags": [
"Values"
],
"operationId": "Get",
"consumes": [],
"produces": [
"text/plain",
"application/json",
"text/json"
],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "id",
"in": "path",
"required": true,
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success",
"schema": {
"type": "string"
}
}
},
"deprecated": true
},
"put": {
"tags": [
"Values"
],
"operationId": "Put",
"consumes": [
"application/json-patch+json",
"application/json",
"text/json",
"application/*+json"
],
"produces": [],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "id",
"in": "path",
"required": true,
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
},
{
"name": "value",
"in": "body",
"required": false,
"schema": {
"type": "string"
}
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success"
}
},
"deprecated": true
},
"delete": {
"tags": [
"Values"
],
"operationId": "Delete",
"consumes": [],
"produces": [],
"parameters": [
{
"name": "id",
"in": "path",
"required": true,
"type": "integer",
"format": "int32"
}
],
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Success"
}
},
"deprecated": true
}
}
},
"definitions": {
"Stock": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"format": "uuid",
"type": "string"
},
"ticker": {
"type": "string"
},
"company": {
"type": "string"
},
"price": {
"format": "double",
"type": "number"
}
}
}
}
}代码段2:JSON响应示例
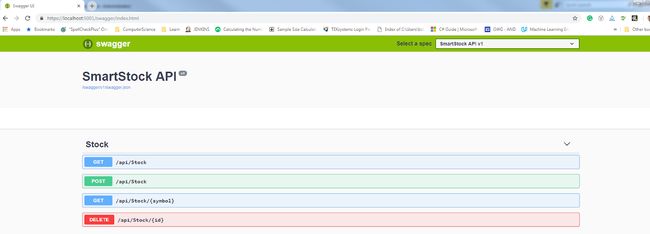
可以通过导航到https://localhost:5001/swagger/index.html来访问Swagger UI ,其中用户可以将JSON响应中可用的相同数据可视化为交互格式。此UI还支持其余方法的实际执行。
图2:在Swagger UI中可视化API
测试
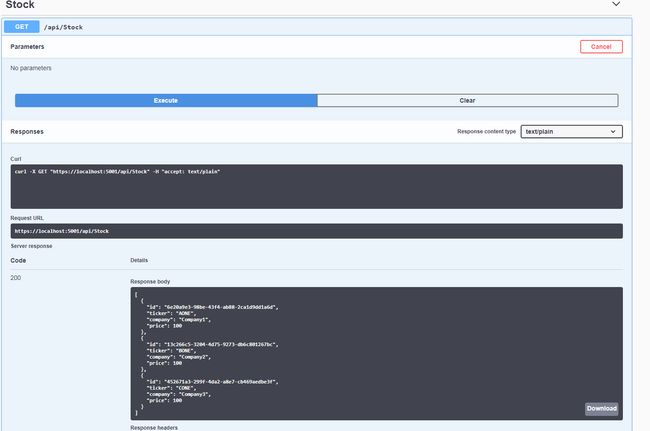
Swagger提供了在没有任何工具的情况下测试API方法的功能。例如,单击 GET(图2中的第一个选项卡)会扩展该方法。通过单击“试一试”然后“执行”,swagger会触发对 /api/stock的'get'方法的调用。请注意,演示应用程序中有一个名为“StockController”的控制器。结果显示在UI中,也可以下载。图3.显示了get方法的结果屏幕。UI中公开的任何方法都可以在UI本身中执行,从而使我们能够直接从API本身测试API。
图3:在Swagger UI中测试API方法
支持属性
默认情况下支持路由属性,Http *属性。图4显示了如何使用HttpGet, HttpPost, HttpDelete修饰的方法反映在Swagger UI中。
图4:反映HTTP属性的Swagger UI
Swagger与.Net中的属性同步。例如,如果使用[Obsolete]属性修饰控制器类,则UI反映控制器“已过时”的事实。图5显示ValuesController标记为“Obsolete”, Swagger UI反映相同且不可点击。当API在不破坏工作代码的情况下逐步取消某些功能时,此功能将变得非常方便。
图5:反映Obsolte属性的Swagger UI
支持XML文档
Swagger支持UI中的文档,其中包含一些配置更改。通过在* .csproj文件中添加以下代码行,将生成XML文档。
....
true
$(NoWarn);1591
使用Startup.cs中的以下代码行,在注册时,UI显示XML文档。
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
...
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
}
);通过更改使用XML路径,Swagger在UI中公开XML文档。
图6:Swagger UI显示文档
Swagger在所有主流浏览器中都受支持,可在本地或Web环境中使用。UI的外观和风格是可定制的。
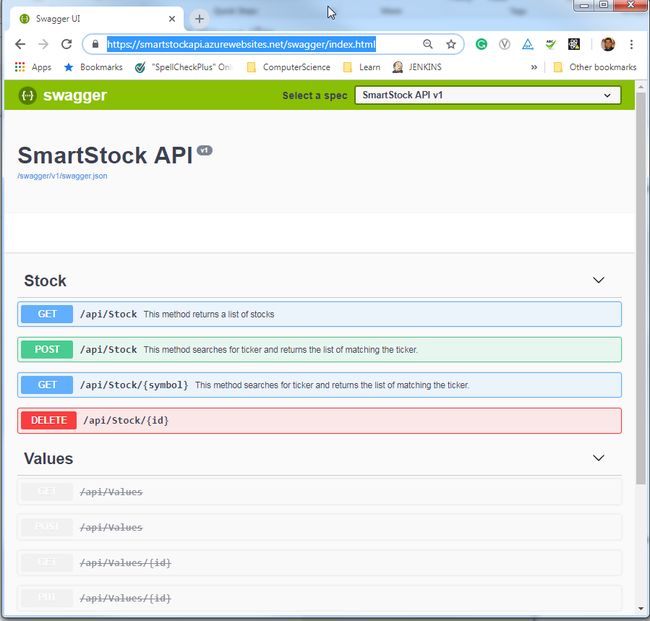
我之前展示了它如何在本地机器上运行。Swagger UI在云上运行良好。部署到Azure的相同应用程序, https://smartstockapi.azurewebsites.net/swagger/index.html 和在我的本地计算机上工作的一样。
图7:云中托管的应用程序中的Swagger UI(Azure)
资源/材料/参考资料
swagger.io
开始使用Swashbuckle和ASP.NET Core
GitHub中的代码
原文地址:https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1271949/Document-and-Test-API-with-Swagger-UI-2