QT中使用ffmpeg的api进行视频的播放
在了解ffmpeg使用api进行视频的播放之前,我们首先了解一下视频的播放流程。
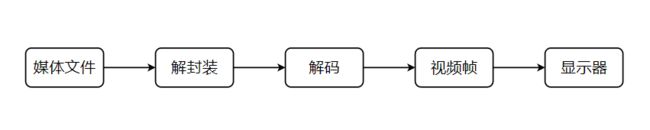
一、视频的播放流程
首先是我们最常见的视频文件,在播放流程中首先是要打开视频文件,将视频文件中的数据进行解封装,之后再将解封装之后的视频进行解码。解码之后的视频便是视频帧的数据,之后将视频帧数据一帧一帧的显示在显示器上。
在使用api进行视频播放的时候也是通过这个流程。接下来我们看具体的实现。
二、ffmpeg中的数据结构体
在了解使用api之前,还需要先了解一下ffmpeg中的相关结构体,在了解了这些结构体之后,可以更容易的理解代码。
AVFormatContext:此结构体存储音视频封装格式中包含的信息,并且这个结构体是贯穿整个播放流程的。在这个结构体中主要包含AVInputFormat,AVOutputFormat、AVStream等。
struct AVInputFormat *iformat; // 输入数据的封装格式
AVIOContext *pb; // 输入数据的缓存
unsigned int nb_streams; // 音视频流的个数
AVStream **streams; // 音视频流
char filename[1024]; // 文件名
int64_t duration; // 时长(单位:微秒us,转换为秒需要除以1000000)
int bit_rate; // 比特率(单位bps,转换为kbps需要除以1000)
AVDictionary *metadata; // 元数据
**AVCodecContext:**是一个描述编解码器上下文的结构体,包含了众多编解码器需要的参数信息。
enum AVMediaType codec_type; // 编解码器的类型(视频,音频...)
struct AVCodec *codec; // 采用的解码器AVCodec(H.264,MPEG2...)
int bit_rate; // 平均比特率
uint8_t *extradata; int extradata_size; // 针对特定编码器包含的附加信息(例如对于H.264解码器来说,存储SPS,PPS等)
AVRational time_base; // 根据该参数,可以把PTS转化为实际的时间(单位为秒s)
int width, height; // 如果是视频的话,代表宽和高
int refs; // 运动估计参考帧的个数(H.264的话会有多帧,MPEG2这类的一般就没有了)
int sample_rate; // 采样率(音频)
int channels; // 声道数(音频)
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt; // 采样格式
int profile; // 型(H.264里面就有,其他编码标准应该也有)
int level; // 级(和profile差不太多)
AVCodec:是存储编码器信息的结构体。
const char *name; // 编解码器的名字的简称
const char *long_name; // 编解码器名字的全称
enum AVMediaType type; // 指明了类型,是视频,音频,还是字幕
enum AVCodecID id; // ID,不重复
const AVRational *supported_framerates; // 支持的帧率(仅视频)
const enum AVPixelFormat *pix_fmts; // 支持的像素格式(仅视频),如RGB24、YUV420P等。
const int *supported_samplerates; // 支持的采样率(仅音频)
const enum AVSampleFormat *sample_fmts; // 支持的采样格式(仅音频)
const uint64_t *channel_layouts; // 支持的声道数(仅音频)
int priv_data_size; // 私有数据的大小
AVFrame:该结构描述解码的(原始的)音频或视频数据。AVFrame必须使用av_frame_alloc()进行分配。请注意,这只是分配AVFrame本身,必须管理数据的缓冲区通过其他方式。AVFrame必须使用av_frame_free()释放。
AVPacket:是存储压缩编码数据相关信息的结构体。
uint8_t *data; // 压缩编码的数据。
/* 例如对于H.264来说。1个AVPacket的data通常对应一个NAL。
注意:在这里只是对应,而不是一模一样。他们之间有微小的差别:使用FFMPEG类库分离出多媒体文件中的H.264码流。因此在使用FFMPEG进行音视频处理的时候,常常可以将得到的AVPacket的data数据直接写成文件,从而得到音视频的码流文件。*/
int size; // data的大小
int64_t pts; // 显示时间戳
int64_t dts; // 解码时间戳
int stream_index; // 标识该AVPacket所属的视频/音频流。
三、ffmpeg函数介绍
void avdevice_register_all(void);
初始化libavdevice并且注册所有的输入和输出设备。
AVFormatContext *avformat_alloc_context(void);
分配AVFormatContext。此函术分配的AVFormatContext结构体需要avformat_free_context()来释放上下文以及框架在其中分配的所有内容。
返回值:
分配的AVFormatContext结构体。
int avformat_open_input (AVFormatContext **ps, const char *url, ff_const59 AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options);
功能:打开输入流并读取标题,并将视频信息写入到AVFormatContext中。
打开输入流并读取标题。编解码器如果未打开。流必须使用avformat_close_input()关闭。
参数:
ps:指向用户提供的AVFormatContext(由avformat_alloc_context分配)的指针。可能是指向NULL的指针,在这种情况下,AVFormatContext由该函数分配并写入ps。请注意,用户提供的AVFormatContext将在失败时释放。
url:要打开的流的URL。
fmt:如果非NULL,此参数将强制使用特定的输入格式。否则将自动检测格式。
options:一个充满AVFormatContext和解复用器私有选项的字典。返回时,此参数将被销毁,并替换为包含未找到的选项的dict。可能为NULL。
返回值:
成功时为0,失败时为负AVERROR。
into avformat_find_stream_info (AVFormatContext *ic, AVDictionary **options);
功能:读取媒体文件的数据包以获取流信息。
参数:
ic:媒体文件上下文
options:如果非NULL,则ic.nb_streams指向字典的指针长数组,其中第i个成员包含与第i个流对应的编解码器的选项。返回时,每个字典都将填充未找到的选项。
返回值:如果返回值大于等于0则说明成功,返回其他我失败。
AVCodec* avcodec_find_decoder (enum AVCodecID id);
功能:根据提供的AVCodecID寻找一个已经注册的解码器;
参数:所请求解码器的AVCodecID;
返回值:如果找到返回一个AVCodec,失败则返回nullptr;
int avcodec_open2 (AVCodecContext *avctx, const AVCodec *codec, AVDictionary **options);
功能:初始化AVCodecContext以使用给定的AVCodec。在使用此函数之前,必须使用avcodec_alloc_text3()分配上下文。
参数:
avctx:要初始化的上下文;
codec:要为其打开此上下文的编解码器。如果之前已将非NULL编解码器传递给avcodec_alloc_text3()或此上下文,则此参数必须为NULL或等于之前传递的编解码器;
options:一个充满AVCodecContext和编解码器专用选项的字典。返回时,此对象将填充未找到的选项。可以为nullptr;
返回值:成功时为零,错误时为负值;
av_frame_alloc:分配AVFrame并将其字段设置为默认值。主要该函数只分配AVFrame的空间,它的data字段的指定的buffer需要其它函数分配。返回为一个AVFream对象。
int av_read_frame (AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
功能:返回流的下一帧。此函数返回文件中存储的内容,并且不验证解码器是否有有效的帧。它会将存储在文件中的内容拆分为多个帧,并为每个调用返回一个帧。它不会省略有效帧之间的无效数据,从而给解码器提供解码所可能的最大信息。
成功后,返回的数据包被引用计数(pkt->buf被设置),并且无限期有效。当不再需要数据包时,必须使用av_packet_unref()释放该数据包。对于视频,数据包只包含一帧。
参数:
s:媒体上下文结构体;
pkt:返回的数据包
返回值:0(如果正常),<0(如果出现错误或文件结束)。出现错误时,pkt将为空(好像它来自av_packet_alloc())。
int avcodec_send_packet (AVCodecContext *avctx, const AVPacket *avpkt);
功能:将原始数据包数据作为输入提供给解码器。
参数:
avctx:编解码器上下文
avpkt:输入的AVPacket。通常,这将是一个单独的视频帧,或几个完整的音频帧。数据包的所有权仍然属于调用者,解码器不会写入数据包。解码器可以创建对分组数据的引用(或者如果分组没有被引用计数则复制它);
返回值:成功时为0。
否则为负错误代码:AVERROR(EAGAIN):在当前状态下不接受输入-用户必须使用avcodec_receive_frame() 读取输出(一旦读取了所有输出,则应重新发送数据包,并且使用EAGAIN调用不会失败)。
AVERROR_EOF:解码器已被刷新,无法向其发送新的数据包(如果发送了1个以上的刷新数据包,也会返回) AVERROR(EINVAL):编解码器未打开,它是编码器,或需要刷新
AVERROR(ENOMEM):无法将数据包添加到内部队列,或类似的其他错误:合法解码错误
int avcodec_receive_frame (AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame);
功能:返回解码器的解码输出数据。
参数:
avctx:编解码器上下文
frame:这将被设置为由解码器分配的参考计数的视频或音频帧(取决于解码器类型)。请注意,在执行其他操作之前,函数将始终调用av_frame_unref(frame)。这是输出。
返回值:0:成功,返回了一个帧AVERROR(EAGAIN):在这种状态下输出不可用-用户必须尝试发送新的输入 AVERROR_EOF:解码器已完全刷新,将不再有输出帧AVERROR(EINVAL):编解码器未打开,或者是编码器AVERROR_input_CHANGED:当前解码的帧相对于第一个解码的帧更改了参数。设置标志AV_CODEC_flag_DROCHANGED时适用。其他负值:合法解码错误
struct SwsContext* sws_getContext (int srcW, int srcH, enum AVPixelFormat srcFormat, int dstW, int dstH, enum AVPixelFormat dstFormat, int flags, SwsFilter *srcFilter, SwsFilter *dstFilter, const double *param);
功能:分配并返回SwsContext;
参数:
srcW 源图像的宽度;
srcH 源图像的高度;
srcFormat 源图像格式;
dstW 目标图像的宽度;
dstH 目标图像的高度;
dstFormat 目标图像格式;
flags 指定用于重新缩放的算法和选项;
srcFilter 可以是nullptr;
dstFilter 可以是nullptr;
param 用于调整所用缩放器的额外参数对于SWS_BICUBIC param[0]和[1]调整基函数的形状,param[0]调整f(1)和param[1]f´(1)对于SWS_GAUSS param[0]调整指数,因此截止频率对于SWS_LANZOS param[0]调整窗口函数的宽度;
返回值:指向已分配上下文的指针,或者出现错误时为NULL;
int av_image_get_buffer_size(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height, int align);
功能:返回存储具有给定参数的图像所需的数据量的大小(以字节为单位)。
参数:
pix_fmt 图像的像素格式;
width 以像素为单位的图像宽度;
height 以像素为单位的图像高度;
align 假定的行大小对齐;
返回值:返回以字节为单位的缓冲区大小,失败时为负错误代码;
void *av_malloc(size_t size) av_malloc_attrib av_alloc_size(1);
功能:分配一个对齐方式适合所有内存访问的内存块(包括CPU上可用的矢量)。
参数:size 要分配的内存块的大小(以字节为单位);
int av_image_fill_arrays(uint8_t *dst_data[4], int dst_linesize[4],
const uint8_t *src,
enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height, int align);
功能:根据指定的图像参数和提供的数组设置数据指针和行大小。
参数:
st_data 要填写的数据指针;
dst_linesize 对要填充的dst_data中的图像进行行化;
src 缓冲区,它将包含或包含实际的图像数据,可以为NULL;
pix_fmt 图像的像素格式;
width 以像素为单位的图像宽度;
height 以像素为单位的图像高度;
align src中用于行大小对齐的值;
返回值:返回src所需的字节大小,为负错误代码
int sws_scale(struct SwsContext *c, const uint8_t *const srcSlice[],
const int srcStride[], int srcSliceY, int srcSliceH,
uint8_t *const dst[], const int dstStride[]);
功能:在srcSlice中缩放图像切片,并将生成的缩放切片放在dst中的图像中。切片是图像中连续行的序列。
参数:
c 以前使用创建的缩放上下文sws_getContext()
srcSlice 包含指向源切片
srcStride 数组,该数组包含源图像
srcSliceY 切片在源图像中的位置过程,即数字(从零)在切片的第一行的图像中
rcSliceH 源切片的高度,即数字切片中的行数
dst 包含指向目的地图像
dst 遍历包含目的地图像
返回值:输出切片的高度
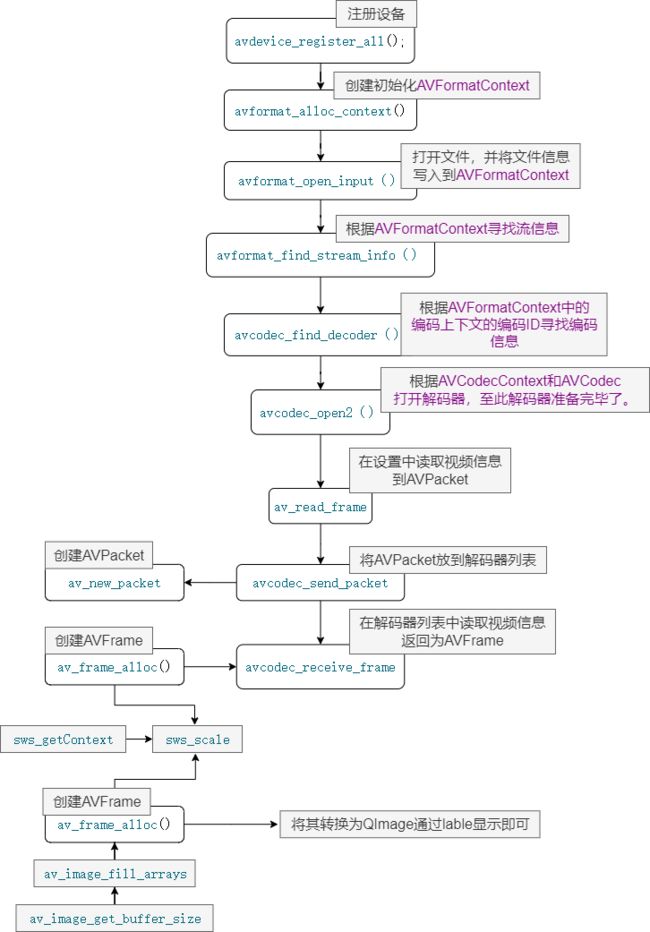
四、ffmpeg api播放视频的函数调用流程
五、代码
打开文件代码
#ifndef FFMPEGAPIOPENDEVICE_H
#define FFMPEGAPIOPENDEVICE_H
#include
#include
#include
extern "C"{
#include "libavutil/avassert.h"
#include "libavutil/channel_layout.h"
#include "libavutil/opt.h"
#include "libavutil/imgutils.h"
#include "libavformat/avformat.h"
#include "libswscale/swscale.h"
#include "libswresample/swresample.h"
#include "libavdevice/avdevice.h"
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
}
class ffmpegApiOpenDevice : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit ffmpegApiOpenDevice(QObject *parent = nullptr);
~ffmpegApiOpenDevice();
void initFfmpeg(QString filePath = "");
private:
int openVideoDevice(AVFormatContext *pIFormatCtx,QString filePath);
void openStream(AVFormatContext *pIFormatCtx,int videoindex);
private:
AVFormatContext *m_pIfmtCtx = nullptr; //AVFormatContext是一个贯穿ffmpeg整个流程的结构体,其中包含了其他的几个结构体
int m_videoStreamindex = -1; //流index
AVCodecContext *m_pICodecCtx = nullptr; //编码上下文结构体
AVCodec *m_pICodec = nullptr; //编码
AVFrame *m_pIFrame = nullptr; //AVFrame结构体一般用于存储原始数据(即非压缩数据,例如对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM)
AVPacket *m_pIPacket = nullptr; //AVPacket是FFmpeg中很重要的一个数据结构,
bool isOpenFile = false;
signals:
void sendFrameSignal(AVCodecContext *pICodecCtx,AVFrame *pIFrame);
public slots:
void displayVideo();
};
#endif // FFMPEGAPIOPENDEVICE_H
#include "ffmpegapiopendevice.h"
#include "video/ffmpegapisavevideo.h"
ffmpegApiOpenDevice::ffmpegApiOpenDevice(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{
avdevice_register_all();
}
ffmpegApiOpenDevice::~ffmpegApiOpenDevice()
{
avcodec_close(m_pICodecCtx);
av_frame_free(&m_pIFrame);
av_packet_free(&m_pIPacket);
avformat_close_input(&m_pIfmtCtx);
}
void ffmpegApiOpenDevice::initFfmpeg(QString filePath)
{
//创建一个AVFormatContext结构体,它是一个贯穿ffmpeg整个流程的结构体,其中包含了其他的几个结构体
m_pIfmtCtx = avformat_alloc_context();
//打开设备
m_videoStreamindex = openVideoDevice(m_pIfmtCtx,filePath);
//打开流
openStream(m_pIfmtCtx,m_videoStreamindex);
//至此,流的通路已经打通
//创建AVPacket
int y_size = m_pICodecCtx->width * m_pICodecCtx->height;
m_pIPacket = static_cast(av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket))); //分配一个packet
av_new_packet(m_pIPacket, y_size); //分配packet的数据
}
void ffmpegApiOpenDevice::displayVideo()
{
while(1){
if(m_pIPacket == nullptr){
continue;
}
//获取像素帧到frame中
m_pIFrame = av_frame_alloc();
//将读取的帧数据存储到m_pIPacket中
if (av_read_frame(m_pIfmtCtx, m_pIPacket) < 0) //从设备中读取数据写入到AVPacket
{
break; //这里认为视频读取完了
}
if (m_pIPacket->stream_index == m_videoStreamindex) { //判断流是不是我们需要的流
int ret;
ret = avcodec_send_packet(m_pICodecCtx, m_pIPacket);
av_packet_unref(m_pIPacket);
if(ret!=0){
return;
}
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(m_pICodecCtx, m_pIFrame);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)
continue;
if(ret!=0){
qDebug()<<"avcodec_receive_frame failed !";
return;
}
emit sendFrameSignal(m_pICodecCtx,m_pIFrame);
}
if(isOpenFile){//这里是为播放视频做的延时,延时31ms差不多就是25帧
QThread::msleep(25);
}
}
}
int ffmpegApiOpenDevice::openVideoDevice(AVFormatContext *pIFormatCtx,QString filePath)
{
//使用libavdevice读取数据,和直接打开视频文件比较类似,使用libavdevice的时候,唯一的不同在于需要首先查找用于输入的设备
AVInputFormat *ifmt;
int videoindex = -1;//码流的索引
//2、根据输入格式的短名称查找AVInputFormat。
ifmt = av_find_input_format("vfwcap");
//3、根据上一个函数获取到的输入格式,打开摄像机设备。并将摄像机的相关信息写入到pIFormatCtx中。
int ret = 0;
if(filePath.isEmpty()){
isOpenFile = false;
ret = avformat_open_input(&pIFormatCtx,"0",ifmt,nullptr);
}else{
isOpenFile = true;
ret = avformat_open_input(&pIFormatCtx,filePath.toUtf8(),nullptr,nullptr);
}
if(ret != 0){
qDebug() << "Couldn't open input stream.\n";
return -1;
}
//4、根据avformat_open_input打开设备的信息寻找pIFormatCtx中是否有数据流。
if(avformat_find_stream_info(pIFormatCtx,nullptr) < 0)
{
qDebug() << "Couldn't find stream information.\n";
return -1;
}else{
qDebug() << "Success find stream information!\n";
}
//5、在pIFormatCtx中循环查找数据包包含的流信息,直到找到视频类型的流,便将流ID记录 videoindex中
for(int i = 0; i < static_cast(pIFormatCtx->nb_streams); i++)
{
if(static_cast(pIFormatCtx->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type) == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)
{
videoindex=i;
break;
}
}
if(videoindex==-1)
{
qDebug() << "Couldn't find a video stream.\n";
}else{
qDebug() << "Success find a video stream!\n";
}
return videoindex;
}
void ffmpegApiOpenDevice::openStream(AVFormatContext *pIFormatCtx,int videoindex)
{
//获取流中的编码上下文
m_pICodecCtx = pIFormatCtx->streams[videoindex]->codec;
//根据六种的编码上下文获取编码器ID
m_pICodec = avcodec_find_decoder(m_pICodecCtx->codec_id);
// AVCodec *codec = avcodec_find_encoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);//软编码
// AVCodec * codec = avcodec_find_encoder_by_name("nvenc_h264");//硬编码
if(m_pICodec == nullptr)
{
qDebug() << ("Codec not found.\n");
}else{
qDebug() << "Codec found Successfuly!\n";
}
//8、打开解码器
if(avcodec_open2(m_pICodecCtx, m_pICodec,nullptr)<0)
{
qDebug() << ("Could not open codec.\n");
}else{
qDebug() << "Success open codec!\n";
}
}
显示代码
#ifndef FFMPEGAPIDISPLAY_H
#define FFMPEGAPIDISPLAY_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
extern "C"{
#include "libavutil/avassert.h"
#include "libavutil/channel_layout.h"
#include "libavutil/opt.h"
#include "libavutil/imgutils.h"
#include "libavformat/avformat.h"
#include "libswscale/swscale.h"
#include "libswresample/swresample.h"
#include "libavdevice/avdevice.h"
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
}
#define MaxFrameNum 10
class ffmpegApiDisplay : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit ffmpegApiDisplay(QObject *parent = nullptr);
void initDisplay(AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx);
void insertFrame(AVFrame *frame);
void stopDisplay();
private:
SwsContext* img_convert_ctx;
AVFrame* m_pIFrameRGB = nullptr;
uint8_t *pIBuffer; //开辟存储像素点的存储地址
AVCodecContext *m_pCodecCtx;
QVector m_frameVector;
QImage m_image;
bool state = false;
bool photograph = false;
signals:
void sendImageSignal(QImage img);
public slots:
void display();
};
#endif // FFMPEGAPIDISPLAY_H
#include "ffmpegapidisplay.h"
ffmpegApiDisplay::ffmpegApiDisplay(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{
}
void ffmpegApiDisplay::initDisplay(AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx)
{
m_pCodecCtx = pCodecCtx;
img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(m_pCodecCtx->width, m_pCodecCtx->height,
m_pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, m_pCodecCtx->width, m_pCodecCtx->height,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGB32, SWS_BICUBIC, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr);
int pixSize = av_image_get_buffer_size(AV_PIX_FMT_RGB32, m_pCodecCtx->width, m_pCodecCtx->height,16);
//创建保存空间,底层使用malloc进行内存空间的开辟。
pIBuffer = static_cast(av_malloc(static_cast(pixSize)));
//创建图像转换之后的帧
m_pIFrameRGB = av_frame_alloc();
av_image_fill_arrays(m_pIFrameRGB->data,
m_pIFrameRGB->linesize,
pIBuffer,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGB32,
m_pCodecCtx->width,
m_pCodecCtx->height,
16);
state = true;
}
void ffmpegApiDisplay::insertFrame(AVFrame *frame)
{
if(m_frameVector.length()>MaxFrameNum){
m_frameVector.pop_front();
}
m_frameVector.append(frame);
}
void ffmpegApiDisplay::stopDisplay()
{
state = false;
}
void ffmpegApiDisplay::display()
{
while(state){
if(m_frameVector.isEmpty()){
continue;
}
AVFrame *pIFrame = m_frameVector.front();
int length = m_frameVector.length();
m_frameVector.pop_front();
if(pIFrame == nullptr){
continue;
}
static int i=0;
i++;
qDebug()<<"ffmpegApiDisplay::display() 输出frame :"<(pIFrame->data),
pIFrame->linesize, 0, m_pCodecCtx->height, m_pIFrameRGB->data,
m_pIFrameRGB->linesize);
QImage tmpImg(static_cast(pIBuffer),m_pCodecCtx->width,m_pCodecCtx->height,QImage::Format_RGB32);
QImage image = tmpImg.copy();//把图像复制一份 传递给界面显示
if(photograph){//此部分和拍照功能相关
m_image = tmpImg.copy();
photograph = false;
}
emit sendImageSignal(image); //发送信号
}
sws_freeContext(img_convert_ctx);
av_frame_free(&m_pIFrameRGB);
}
完整代码路径:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_43812868/88157743?spm=1001.2014.3001.5503