golang利用gco获取windows系统cpu信息
golang利用gco获取windows系统cpu信息
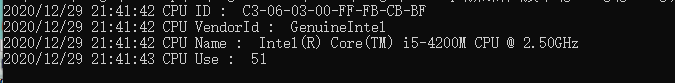
- 效果图
- 原理:
- 细节注意
- 代码
-
- 关注ManGe分享更多知识
效果图
原理:
- 调用汇编 cpuid指令
- 调用 windows.h 的 GetSystemTimes
细节注意
- malloc开辟的空间要在使用结束后用free回收,具体写法如下代码
代码
// 代码出处我的开源项目: https://github.com/mangenotwork/servers-online-manage
// 获取windows系统cpu信息与使用率实例
package main
/*
#include
#include
#include
struct cpuid_result {
DWORD eax;
DWORD ebx;
DWORD ecx;
DWORD edx;
};
// 执行汇编cpuid
static inline struct cpuid_result cpuid(unsigned int op)
{
struct cpuid_result result;
__asm volatile(
"mov %%ebx, %%edi;"
"cpuid;"
"mov %%ebx, %%esi;"
"mov %%edi, %%ebx;"
: "=a" (result.eax),
"=S" (result.ebx),
"=c" (result.ecx),
"=d" (result.edx)
: "0" (op)
: "edi");
return result;
}
static inline unsigned int cpuid_eax(unsigned int op)
{
//unsigned int eax, ebx, ecx, edx;
struct cpuid_result regs;
regs = cpuid(op);
return regs.eax;
}
void get_cpu_vendor(char* cpu_vendor, unsigned int* cpuid_level)
{
unsigned int cpuid_op = 0x00000000;
char vendor_name[16] = {'\0'};
struct cpuid_result result;
unsigned int level = 0;
vendor_name[0] = '\0';
//eax为0表示读取vendor id,一共12字节,依次在ebx、edx、ecx。
result = cpuid(cpuid_op);
level = result.eax;
vendor_name[0] = (result.ebx >> 0) & 0xff;
vendor_name[1] = (result.ebx >> 8) & 0xff;
vendor_name[2] = (result.ebx >> 16) & 0xff;
vendor_name[3] = (result.ebx >> 24) & 0xff;
vendor_name[4] = (result.edx >> 0) & 0xff;
vendor_name[5] = (result.edx >> 8) & 0xff;
vendor_name[6] = (result.edx >> 16) & 0xff;
vendor_name[7] = (result.edx >> 24) & 0xff;
vendor_name[8] = (result.ecx >> 0) & 0xff;
vendor_name[9] = (result.ecx >> 8) & 0xff;
vendor_name[10] = (result.ecx >> 16) & 0xff;
vendor_name[11] = (result.ecx >> 24) & 0xff;
vendor_name[12] = '\0';
strcpy(cpu_vendor, vendor_name);
*cpuid_level = level;
}
void get_cpu_id(char* cpu_id, unsigned int* cpu_sign)
{
unsigned int cpuid_op = 0x00000001;
struct cpuid_result result;
unsigned int sign = 0, id = 0;
unsigned int tmp = 0;
result = cpuid(cpuid_op);
sign = result.eax;
id = result.edx;
sprintf(cpu_id, "%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X", (sign >> 0) & 0xff, (sign >> 8) & 0xff, (sign >> 16) & 0xff, (sign >> 24) & 0xff,
(id >> 0) & 0xff, (id >> 8) & 0xff, (id >> 16) & 0xff, (id >> 24) & 0xff);
*cpu_sign = sign;
}
struct cpuinfo_x86 {
//CPU family
DWORD x86;
//CPU vendor
DWORD x86_vendor;
//CPU model
DWORD x86_model;
//CPU stepping
DWORD x86_step;
};
// 参考IA32开发手册第2卷第3章。CPUID exa==0x01的图3-6
static inline void get_fms(struct cpuinfo_x86 *c, DWORD tfms)
{
c->x86 = (tfms >> 8) & 0xf;
c->x86_model = (tfms >> 4) & 0xf;
c->x86_step = tfms & 0xf;
if (c->x86 == 0xf)
c->x86 += (tfms >> 20) & 0xff;
if (c->x86 >= 0x6)
c->x86_model += ((tfms >> 16) & 0xF) << 4;
}
// 参考IA32开发手册第2卷第3章。CPUID exa==0x01的图3-6
void get_cpu_fms(unsigned int* family, unsigned int* model, unsigned int* stepping)
{
unsigned int cpuid_op = 0x00000001;
struct cpuinfo_x86 c;
unsigned int ver = 0;
ver = cpuid_eax(cpuid_op);
get_fms(&c, ver);
*family = c.x86;
*model = c.x86_model;
*stepping = c.x86_step;
}
void get_cpu_name(char* processor_name)
{
unsigned int cpuid_op = 0x80000002;
struct cpuid_result regs;
char temp_processor_name[49];
char* processor_name_start;
unsigned int *name_as_ints = (unsigned int *)temp_processor_name;
unsigned int i;
//用cpuid指令,eax传入0x80000002/0x80000003/0x80000004,
//共3个,每个4个寄存器,每个寄存器4字节,故一共48字节。
//参考IA32开发手册第2卷第3章。
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
regs = cpuid(cpuid_op + i);
name_as_ints[i * 4 + 0] = regs.eax;
name_as_ints[i * 4 + 1] = regs.ebx;
name_as_ints[i * 4 + 2] = regs.ecx;
name_as_ints[i * 4 + 3] = regs.edx;
}
temp_processor_name[49] = '\0'; // 最后的字节为0,结束
processor_name_start = temp_processor_name;
while (*processor_name_start == ' ')
processor_name_start++;
memset(processor_name, 0, 49);
strcpy(processor_name, processor_name_start);
}
void get_address_bits(unsigned int* linear, unsigned int* physical)
{
unsigned int cpuid_op = 0x80000008;
unsigned int tmp = 0;
tmp = cpuid_eax(cpuid_op);
*linear = (tmp >> 8) & 0xff;
*physical = (tmp >> 0) & 0xff;
}
char* WindowsGetCpuVendorId(){
char* vendor_id;
vendor_id = (char *)malloc(49);
char buffer[49] = { '\0' };
unsigned int num = 0;
memset((void *)buffer, '\0', sizeof(buffer));
get_cpu_vendor(buffer,&num);
strcpy(vendor_id, buffer);
return vendor_id;
}
char* WindowsGetCpuId(){
char* id;
id = (char *)malloc(49);
char buffer[49] = { '\0' };
unsigned int num = 0;
memset((void *)buffer, '\0', sizeof(buffer));
get_cpu_id(buffer,&num);
strcpy(id, buffer);
return id;
}
char* WindowsGetCpuName(){
char* name;
name = (char *)malloc(100);
get_cpu_name(name);
return name;
}
double FileTimeToDouble(FILETIME* pFiletime)
{
return (double)((*pFiletime).dwHighDateTime * 4.294967296E9) + (double)(*pFiletime).dwLowDateTime;
}
double m_fOldCPUIdleTime;
double m_fOldCPUKernelTime;
double m_fOldCPUUserTime;
BOOL Initialize()
{
FILETIME ftIdle, ftKernel, ftUser;
BOOL flag = FALSE;
if (flag = GetSystemTimes(&ftIdle, &ftKernel, &ftUser))
{
m_fOldCPUIdleTime = FileTimeToDouble(&ftIdle);
m_fOldCPUKernelTime = FileTimeToDouble(&ftKernel);
m_fOldCPUUserTime = FileTimeToDouble(&ftUser);
}
return flag;
}
//获取cpu使用
int GetCPUUseRate()
{
int nCPUUseRate = -1;
FILETIME ftIdle, ftKernel, ftUser;
if (GetSystemTimes(&ftIdle, &ftKernel, &ftUser))
{
double fCPUIdleTime = FileTimeToDouble(&ftIdle);
double fCPUKernelTime = FileTimeToDouble(&ftKernel);
double fCPUUserTime = FileTimeToDouble(&ftUser);
nCPUUseRate= (int)(100.0 - (fCPUIdleTime - m_fOldCPUIdleTime) / (fCPUKernelTime - m_fOldCPUKernelTime + fCPUUserTime - m_fOldCPUUserTime)*100.0);
m_fOldCPUIdleTime = fCPUIdleTime;
m_fOldCPUKernelTime = fCPUKernelTime;
m_fOldCPUUserTime = fCPUUserTime;
}
return nCPUUseRate;
}
//获取cpu使用
int cpu()
{
if (!Initialize())
{
getch();
return -1;
}
else
{
Sleep(1000);
return GetCPUUseRate();
}
return -1;
}
*/
import "C"
import (
"log"
"unsafe"
)
//获取cpu的VendorId
func GetCpuVendorId() string {
//定义一个字符串指针接收C 函数返回值
var out *C.char = C.WindowsGetCpuVendorId()
//释放这个指针 前提是使用了malloc
defer C.free(unsafe.Pointer(out))
return C.GoString(out)
}
//获取cpu的 CpuId
func GetCpuId() string {
var out *C.char = C.WindowsGetCpuId()
defer C.free(unsafe.Pointer(out))
return C.GoString(out)
}
//获取cup的 CpuName
func GetCpuName() string {
var out *C.char = C.WindowsGetCpuName()
defer C.free(unsafe.Pointer(out))
return C.GoString(out)
}
//获取cpu使用率
func GetCPUUse() int {
return int(C.cpu())
}
func main() {
log.Println("CPU ID : ", GetCpuId())
log.Println("CPU VendorId : ", GetCpuVendorId())
log.Println("CPU Name : ", GetCpuName())
log.Println("CPU Use : ", GetCPUUse())
}
关注ManGe分享更多知识
https://github.com/mangenotwork