.NET知识梳理——4.特性Attribute
1. 特性
1.1 特性Attribute
特性就是一个类,继承自Attribute抽象类(该类无抽象方法、避免实例化),约定俗成用Attribute类结尾,标记时可省略掉Attribute。
用[]修饰,标记到字段,实际上就是调用构造函数,可以指定属性、字段。
AttributeTargets,枚举表示可修饰的对象(类、方法、属性等)
特性对程序运行和编译器有影响([Obsolete]影响编译)。
1.2 声明和使用Attribute,AttributeUsage
4.2.1 声明Attribute
public class CustomAttribute:Attribute//继承自Attribute
{
private int _Id = 0;
private string _Name = null;
public string Remark;//字段
public string Description { get; set; }//属性
public CustomAttribute()//构造函数重载
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.GetType().Name}无参构造函数");
}
public CustomAttribute(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.GetType().Name}.{name} string构造函数");
}
public CustomAttribute(int age)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.GetType().Name}.{age} age构造函数");
}
public void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name is :{this._Name},age is {this._Id},Remark is {this.Remark},Descripiton is {Description}");
}
}
}
4.2.2 使用Attribute
[Custom]//根据4.2.3的设置AttributeUsage设置,可以设置不同的元素、同一元素可以设置多个属性
public class People
{
public void Say()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello everybody");
}
[Custom]
[Custom(116)]
public string Study(string name)
{
return $"{name} like study";
}
}
4.2.3 AttributeUsage
指定另一个属性类的用法。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.All,AllowMultiple =true, Inherited =true)]
4.2.3.1 AttributeTargets:
获取一组标识所指示的特性可以应用于哪些程序元素//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于程序集。
Assembly = 1,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于模块中。
Module = 2,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于类。
Class = 4,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于结构;即,类型值。
Struct = 8,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于枚举。
Enum = 16,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于构造函数。
Constructor = 32,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于方法。
Method = 64,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于属性。
Property = 128,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于字段。
Field = 256,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于事件。
Event = 512,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于接口。
Interface = 1024,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于参数。
Parameter = 2048,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于委托。
Delegate = 4096,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于返回的值。
ReturnValue = 8192,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于泛型参数。
GenericParameter = 16384,
//
// 摘要:
// 特性可以应用于任何应用程序元素。
All = 32767
4.2.3.2 AllowMultiple
获取或设置一个布尔值,该值指示是否可以为一个程序元素指定多个实例所指示的特性
4.2.3.3 Inherited
该值确定指示的属性是否由派生类和重写成员继承,默认值为 true
1.3 运行中获取Attribute:额外信息 额外操作
4.3.1 自定义的Attribute
public class CustomAttribute:Attribute
{
private int _Id = 0;
private string _Name = null;
public string Remark;
public string Description { get; set; }
public CustomAttribute()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.GetType().Name}无参构造函数");
}
public CustomAttribute(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.GetType().Name}.{name} string构造函数");
}
public CustomAttribute(int age)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.GetType().Name}.{age} age构造函数");
}
public void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name is :{this._Name},age is {this._Id},Remark is {this.Remark},Descripiton is {Description}");
}
}
4.3.2 定义触发
public class InvokeCenter
{
public static void ManagerPeople
where T : People
{
Console.WriteLine($"Name is {t.Name},Age is {t.Age}");
t.Say();
t.Study("Olive");
Type type = t.GetType();
if(type.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute),true))
{
object[] attributeArr = type.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
foreach(CustomAttribute attr in attributeArr)
{
attr.Show();
}
foreach(var prop in type.GetProperties())
{
if(prop.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute),true))
{
object[] propAttributeArr = prop.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
foreach(CustomAttribute custom in propAttributeArr)
{
custom.Show();
}
}
}
foreach (var method in type.GetMethods())
{
if (method.IsDefined(typeof(CustomAttribute), true))
{
object[] propAttributeArr = method.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(CustomAttribute), true);
foreach (CustomAttribute custom in propAttributeArr)
{
custom.Show();
}
}
}
}
}
4.3.3 标记、触发
4.3.3.1标记
[Custom]
public class People
{
[Custom(30)]
public int Age { get; set; }
[Custom("墨遥")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Custom("墨遥",Description ="你好啊", Remark ="周末")]
public void Say()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello everybody");
}
[Custom]
[Custom(116)]
public string Study(string name)
{
return $"{name} like study";
}
}
4.3.3.2 触发
InvokeCenter.ManagerPeople
1.4 Remark封装、Attribute验证
1.4.1 特性封装提供额外信息Remark封装
1.4.1.1 定义RemarkAttribute
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field)]//该特性只能作用于字段上
public class RemarkAttribute:Attribute
{
public string Remark { get; private set; }
public RemarkAttribute(string remark)
{
this.Remark = remark;
}
}
1.4.1.2 定义枚举、标记特性
public enum UserState
{
[Remark("正常")]
Normal=0,
[Remark("已冻结")]
Frozen =1,
[Remark("已删除")]
Deleted =2
}
1.4.1.3 为枚举添加扩展方法
///
/// 为Enum类型新增扩展方法,获取添加在字段上的特性的Remark信息
///
public static class AttributeExtend
{
public static string GetRemark(this Enum value)
{
Type type = value.GetType();
var field = type.GetField(value.ToString());
if (field.IsDefined(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true))
{
RemarkAttribute attribute = (RemarkAttribute)field.GetCustomAttribute(typeof(RemarkAttribute), true);
return attribute.Remark;
}
else
return value.ToString();
}
}
1.4.1.4 调用
UserState userState = UserState.Deleted;
userState.GetRemark();
1.4.2 特性封装提供额外行为Validate验证
1.4.2.1 定义抽象的ValidateAttribute
///
/// 校验抽象类
///
public abstract class AbstractValidateAttribute:Attribute
{
///
/// 抽象校验方法,子类需要实现该方法
///
///
/// 校验失败的提示,来自于Descripiton
///
public abstract bool Validate(object obj,out string errorInfo);
///
/// 用来表述校验规则
///
public string Description { get; set; }
}
1.4.2.2 实现抽象的ValidateAttribute
1.4.2.2.1 LongAttribute(数据范围)
///
/// 数据范围校验特性
///
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class LongAttribute:AbstractValidateAttribute
{
private long _min = 0;
private long _max = 0;
public LongAttribute(long min,long max)
{
_min = min;
_max = max;
}
public override bool Validate(object obj, out string error)
{
error = Description;
return obj != null
&& long.TryParse(obj.ToString(), out long v)
&& v >= this._min
&& v <= this._max;
}
}
}
1.4.2.2.2 RequiredAttribute(必填)
///
/// 必填校验特性
///
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class RequiredAttribute:AbstractValidateAttribute
{
public override bool Validate(object obj,out string error)
{
error = Description;
return obj != null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(obj.ToString());
}
}
1.4.2.2.3 StringLengthAttribute(字符串长度)
///
/// 字符串长度校验特性
///
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property)]
public class StringLengthAttribute:AbstractValidateAttribute
{
private int _min = 0;
private int _max = 0;
public StringLengthAttribute(int min, int max)
{
_min = min;
_max = max;
}
public override bool Validate(object obj, out string error)
{
error = Description;
return obj != null
&& obj.ToString().Length >= this._min
&& obj.ToString().Length <= this._max;
}
}
1.4.2.3 为类扩展校验方法
需要传入一个out类型的string参数,作为校验信息的汇总
public static class AttributeExtend
{
public static bool Validate
{
Type type = t.GetType();
errorInfo = "";
bool result = true;
foreach (var prop in type.GetProperties())
{
if (prop.IsDefined(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true))
{
object oValue = prop.GetValue(t);
foreach (AbstractValidateAttribute attribute in prop.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AbstractValidateAttribute), true))
{
string error = "";
if (!attribute.Validate(oValue, out error))
{
errorInfo += error + "\r\n";
result=false;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
1.4.2.4 标记特性
[Custom("Olive",Description ="中国人", Remark ="Very Good")]
public class Chinese
{
[Required(Description ="ID为必填项")]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required(Description = "Name为必填项")]
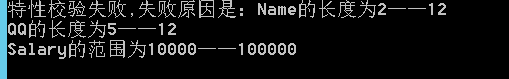
[StringLength(2,12,Description = "Name的长度为2——12")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required(Description = "Age为必填项")]
public int Age { get; set; }
[Required(Description = "QQ为必填项")]
[StringLength(5, 12,Description = "QQ的长度为5——12")]
public string QQ { get; set; }
[Long(10000,100000, Description = "Salary的范围为10000——100000")]
public int Salary { get; set; }
}
1.4.2.5 调用
Chinese chinese = new Chinese() { Id = 1, Name = "墨", Age = 30, QQ = "318950585318950585", Salary = 250000 };
var error = "";
if (chinese.Validate(out error))
{
Console.WriteLine("特性校验成功");
}
else
Console.WriteLine($"特性校验失败,失败原因是:{error}");
结果如下: