C++基础编程
一、导言
编写—个C++程序总共分为4个步数
1、创建项目
2、创建文件
3、编写代码
4、运行程序
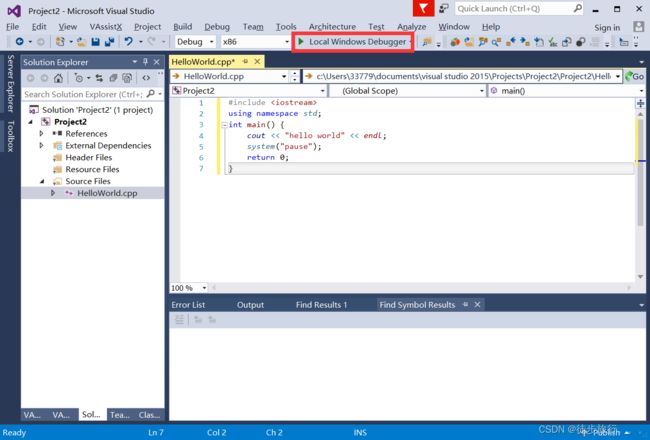
1.1 C++输出hello world
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "hello world" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 1.2注释
作用:在代码中加一些说明和解释,方便自己后其他程序员阅读代码
两种格式:
1、单行注释://描述信息
通常放在一行代码的上方,或者一条语句的末尾,对该行代码说明
2、多行注释:/*描述信息*/
通常放在一段代码的上方,对该段代码做整体说明
提示:编译器在编译代码时,会忽略注释的内容
#include
using namespace std;
//1.单行注释
//2.多行注释
/*
main是一个程序的入口
每个程序都必须有这么一个函数
有且仅有一个
*/
int main() {
//输出hello world
cout << "hello world" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 1.3变量
作用:给一段指定的内存空间起名,方便操作这段内存
语法:数据类型 变量名=初始值;
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//变量创建的语法:数据类型 变量名=初始值
int a = 10;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 1.4常量
作用:用于记录程序中不可更改的数据
C++定义常量的两种方式:
1、#define宏常量:#define 常量名 常量值
通常在文件上方定义,表示一个常量
2、const修饰的变量:const 数据类型 常量名=常量值
通常在变量定义前加关键字const,修饰该变量为常量,不可修改
#include
using namespace std;
//常量定义1:#define 常量名 常量值
#define Day 7
int main() {
//Day=10;发生错误,常量一旦修改就会报错
cout <<"一周总共有" << Day <<"天" << endl;
//常量定义2:const 数据类型 常量名 = 常量值
const int month = 12;
//month=24;发生错误,常量一旦修改就会报错
cout << "一年有"< 1.5关键字
作用:关键字时C++中预先保留的单词(标识符)
在定义变量或者常量时,不要用关键字
C++关键字如下:
asm、do、if、return、typedef、auto、double、inline、short、typeid、dynamic_cast、signed、typename、break、else、long、sizeof、union、case、enum、mutable、static、unsigned、catch、explicit、namespace、static_cast、using、char、export、new、struct、virtual、class、extern、operator、switch、void、const、false、private、template、volatile、const_cast、float、protected、this、wchar_t、continue、for、public、throw、while、default、friend、register、true、delete、goto、reinterpret_cast、try
提示:在给变量或者常量起名称时,不要用C++的关键字,否则会产生歧义。
#include
using namespace std;
/*
asm、auto、bool、break、case、catch、char、class、const、const_cast、continue、default、delete、do、double、dynamic_cast、else、enum、explicit、export、extern、false、float、for、friend、goto、if、inline、int、long、mutable、namespace、new、operator、private、protected、public、register、reinterpret_cast、return、short、signed、sizeof、static、static_cast、struct、switch、template、this、throw、true、try、typedef、typeid、typename、union、unsigned、using、virtual、void、volatile、wchar_t、while
*/
int main() {
//不要用关键字给变量或者常量起名称
//int int = 10 ; 错误,第二个int是关键字,不可以作为变量的名称
system("pause");
return 0;
} 1.6标识符命名规则
作用:C++规定给标识符(变量、常量)命名时,有一套自己的规则
1、标识符不能时关键字
2、标识符只能由字母、数字、下划线组成
3、第一个字符必须为字母或下划线
4、标识符中字母区分大小写
建议:给标识符命名时,争取做到见名知意的效果,方便自己和他人阅读
#include
using namespace std;
/*
标识符命名规则
作用:C++规定给标识符(变量、常量)命名时,有一套自己的规则
·标识符不能是关键字
·标识符只能由字母、数字、下划线组或
·第一个字符必须为字母或下划线
·标识符中字母区分大小写
建议:给标识符命名时,争取做到见名知意的效果,方便自己和他人的阅读
*/
int main() {
//int int = 10 ; 标识符不可以是关键字
//标识符是由字母、数字、下划线构成
int abc = 10;
int abc123 = 10;
int _abc12 = 10;
//int 123abc = 10 ; 标识符第一个字符只能是字母或下划线
int aaa = 100;
cout << aaa << endl;
//cout< 二、数据类型
2.1整型
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//整型(2个字节)
//短整型(-32768——32767)
short num1 = 10;
//超过范围,变成最大或最小
//整型(4个字节)
int num2 = 100;
//长整型(Windows为4个字节,Linux为8个字节)
long num3 = 100;
//长长整型(8个字节)
long long num4 = 100;
cout << "num1=" << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2=" << num2 << endl;
cout << "num3=" << num3 << endl;
cout << "num4=" << num4 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 2.2sizeof关键字
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//可以利用sizeof求出数据类型占用内存大小
//语法:sizeof(数据类型/变量)
cout << "short占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(short) << endl;
short num1 = 10;
cout << "short占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num1) << endl;
cout << "int占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(int) << endl;
int num2 = 10;
cout << "int占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num2) << endl;
cout << "long占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(long) << endl;
long num3 = 10;
cout << "long占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num3) << endl;
cout << "long long占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(long long) << endl;
long long num4 = 10;
cout << "long long占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num4) << endl;
//整型大小的比较
//short 2.3实型(浮点型)
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//float单精度
//double双精度
//默认情况下:输出一个小数,最多显示6位有效数字
//单精度:float 变量名 = 变量值f
float f1 = 3.14f;
cout << "f1=" << f1 << endl;
//双精度:double 变量名 =变量值
double d1 = 3.14;
cout << "d1=" << d1 << endl;
//统计float和double占用内存空间
//float占4个字节
cout << "float占用内存空间:" << sizeof(float) << endl;
//double占8个字节
cout << "double占用内存空间:" << sizeof(double) << endl;
//科学计数法
float f2 = 3e2;//3*10^2
cout << "f2=" << f2 << endl;
float f3 = 3e-2;//3*0.1^2
cout << "f3=" << f3 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 2.4字符型
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//字符型语法:char ch='a';
//变量值必须用单引号括起来
//变量值只能是一个字符
//字符型占用1个字节
//字符型变量并不是把字符本身放到内存中存储,而是将对应的ASCII编码放入到存储单元
char ch = 'a';
cout << ch << endl;
cout <<"char字符型变量占用的内存空间:" << sizeof(char) << endl;
cout << "char字符型变量占用的内存空间:" << sizeof(ch) << endl;
//char ch2="b";创建字符型变量时不能用双引号
//char ch3='ab';创建字符型变量时只能有一个字符
//字符型变量对应的ASCII编码
//a->97,A->65
cout << "ch对应的ASCII码:" << int(ch) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 2.5转义字符
#include
using namespace std;
/*
转义字符:
\n:换行
\t:水平制表,可以整齐的输出数据
\\:代表一个反斜线字符"\"
*/
int main() {
cout << "hello world\n" ;
cout << "\\" << endl;
//一个\t占用8个位置
cout << "aaa\thello world" << endl;
cout << "a\thello world" << endl;
cout << "aaaaa\thello world" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 2.6字符串型
#include
using namespace std;
#include //用C++风格的字符串时,要包含这个头文件
int main() {
//C风格的字符串
//char 字符串名[]="字符串值"
char str[] = "hello world";
cout << str << endl;
//C++风格的字符串
//string 字符串名="字符串值"
//包含一个头文件:#include
string str2 = "hello world";
cout << str2 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 2.7布尔类型bool
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//创建bool类型:bool 变量名 = true / false
bool flag = true;//true代表真:1
cout << flag << endl;
flag = false;//false代表假:0
cout << flag << endl;
//bool类型占用1个字节
cout << "bool类型占用的内存空间:" << sizeof(bool) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 2.8数据的输入
#include
using namespace std;
#include
int main() {
//数据输入:cin>>变量名;
//整型
int a = 0;
cout << "请给整型变量a赋值:" << endl;
cin >> a;
cout << "整型变量a=" << a << endl;
//浮点型
float f = 3.14f;
cout << "请给浮点型变量f赋值:" << endl;
cin >> f;
cout << "浮点型变量f=" << f << endl;
//字符型
char ch = 'a';
cout << "请给字符型变量ch赋值:" << endl;
cin >> ch;
cout << "字符型变量ch=" << ch << endl;
//字符串型
string str = "hello";
cout << "请给字符串型变量str赋值:" << endl;
cin >> str;
cout << "字符串型变量str=" << str << endl;
//布尔型
bool flag=false;
cout << "请给布尔型变量flag赋值:" << endl;
cin >> flag;//输入数字(0为假,非0都为真)
cout << "布尔型变量flag=" << flag << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 三、运算符
3.1算术运算符——加减乘除
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//+:正号,-:负号,+:加,-:减,*:乘,/:除
//加减乘除
int a1 = 10;
int b1 = 3;
cout << a1 + b1 << endl;
cout << a1 - b1 << endl;
cout << a1 * b1 << endl;
//两个整数相除,结果依然是整数,向下取整
cout << a1 / b1 << endl;
int a2 = 10;
int b2 = 20;
cout << a2 / b2 << endl;
int a3 = 10;
int b3 = 0;
//两个数相除,除数不可以为0
//cout << a3 / b3 << endl; 报错,除数不可以为0
//两个小数可以相除,结果是小数
double d1 = 0.5;
double d2 = 0.22;
cout << d1 / d2 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 3.2算术运算符——取模(取余)
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//%:取模(取余)
int a1 = 10;
int b1 = 3;
cout << a1 % b1 << endl;
int a2 = 10;
int b2 = 20;
cout << a2 % b2 << endl;
int a3 = 10;
int b3 = 0;
//两个数取模是基于除法运算的,所以不能进行取模运算
//cout << a3 % 0 << endl;
//两个小数之间不能做取模运算
double d1 = 3.14;
double d2 = 1.1;
//cout << d1 % d2 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 3.3算术运算符——前置后置递增递减
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//前置递增
int a = 10;
++a;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
//后置递增
int b = 10;
b++;
cout << "b=" << b << endl;
//前置和后置的区别
//前置递增:先让变量+1,然后进行表达式运算
int a2 = 10;
int b2 = ++a2 * 10;
cout << "a2=" << a2 << endl;
cout << "b2=" << b2 << endl;
//后置递增:先进行表达式运算,然后让变量+1
int a3 = 10;
int b3 = a3++ * 10;
cout << "a3=" << a3 << endl;
cout << "b3=" << b3 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 3.4赋值运算符
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//赋值运算符
//=
int a = 10;
a = 100;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
//+=
a = 10;
a += 2;//a=a+2;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
//-=
a = 10;
a -= 2;//a = a - 2;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
//*=
a = 10;
a *= 2;//a=a*2;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
// /=
a = 10;
a /= 2;//a = a / 2;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
//%=
a = 10;
a %= 2;//a = a % 2;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 3.5比较运算符
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//比较运算符
//==
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << (a == b) << endl;
// !=
cout << (a != b) << endl;
//>
cout << (a > b) << endl;
//<
cout << (a < b) << endl;
//>=
cout << (a >= b) << endl;
//<=
cout << (a <= b) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 3.6逻辑运算符——非
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//!:非
int a = 10;
//在C++中,只要不是0,其他都为真
cout << !a << endl;
cout << !!a << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.7逻辑运算符——与
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//与&&:同真为真,其余为假
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
cout << (a && b) << endl;
a = 0;
b = 10;
cout << (a && b) << endl;
a = 0;
b = 0;
cout << (a && b) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 3.8逻辑运算符——或
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//或||:同假为假,其余为真
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
cout << (a || b) << endl;
a = 0;
b = 10;
cout << (a || b) << endl;
a = 0;
b = 0;
cout << (a || b) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
四、程序流程结构
4.1选择结构——单行if语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//单行格式if语句:if(条件){条件满足执行的语句}
//用户输入分数,如果分数大于600,视为考上一本大学,在屏幕上输出
//注意:if条件后面不要加分号
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;
if (score >= 600) {
cout << "恭喜你考上一本大学" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 4.2选择结构——多行if 语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//if-else
//用户输入分数,如果分数大于600,视为考上一本大学,在屏幕上输出
//如果没考上一本大学,打印未考上一本大学
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;
if (score >= 600) {
cout << "恭喜你考上一本大学" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "未考上一本大学" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 4.3选择结构——多条件的if语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//多条件的if语句:if(条件1){条件1满足执行的语句 }else if(条件2){条件2满足执行的语句}... else{都不满足执行的语句}
//输入一个考试分数,如果大于600分,视为考上一本大学,在屏幕输出
//大于500,视为考上二本大学,屏幕输出
//大于400,视为考上三本大学,屏幕输出
//小于等于400分,视为未考上本科,屏幕上输出
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;
if (score >= 600) {
cout << "恭喜你考上一本大学" << endl;
}else if (score >= 500) {
cout << "恭喜你考上二本大学" << endl;
}else if (score >= 400) {
cout << "恭喜你考上三本大学" << endl;
}else{
cout << "未考上大学" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 4.4选择结构——嵌套if语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//多条件的if语句:if(条件1){条件1满足执行的语句 }else if(条件2){条件2满足执行的语句}... else{都不满足执行的语句}
//输入一个考试分数,如果大于600分,视为考上一本大学,在屏幕输出
//大于500,视为考上二本大学,屏幕输出
//大于400,视为考上三本大学,屏幕输出
//小于等于400分,视为未考上本科,屏幕上输出
//在一本分数中,如果大于700分,考入北大,大于650分,考入清华,大于600考入人大。
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;
if (score >= 600) {
cout << "恭喜你考上一本大学" << endl;
if (score >= 700) {
cout << "恭喜你考上北大" << endl;
}
else if (score >= 650) {
cout << "恭喜你考上清华" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "恭喜你考上人大" << endl;
}
}
else if (score >= 500) {
cout << "恭喜你考上二本大学" << endl;
}
else if (score >= 400) {
cout << "恭喜你考上三本大学" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "未考上大学" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 4.5选择结构案例——三只小猪称体重
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、创建三只小猪的体重变量
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int num3 = 0;
//2、让用户输入三只小猪的重量
cout << "请输入小猪A的体重" << endl;
cin >> num1;
cout << "请输入小猪B的体重" << endl;
cin >> num2;
cout << "请输入小猪C的体重" << endl;
cin >> num3;
cout << "小猪A的体重为:" << num1 << endl;
cout << "小猪B的体重为:" << num2 << endl;
cout << "小猪C的体重为:" << num3 << endl;
// 3、判断哪只最重
if (num1 > num2) {
if (num1 > num3) {
cout << "小猪A最重" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "小猪C最重" << endl;
}
}
else {
if (num2 > num3) {
cout << "小猪B最重" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "小猪C最重" << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 4.6选择结构——三目运算符
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//三目运算符
//表达式1?表达式2:表达式3
//如果表达式1的值为真,执行表达式2,并返回表达式2的结果;
//如果表达式1的值为假,执行表达式3,并返回表达式3的结果。
//创建三个变量a b c
//将a和b做比较,将变量大的值赋值给变量c
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 0;
c = (a > b) ? a : b;
cout << "c=" << c << endl;
//在C++中三目运算符返回的是变量,可以继续赋值
(a > b ? a : b) = 100;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
cout << "b=" << b << endl;
(a < b ? a : b) = 100;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
cout << "b=" << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 4.7选择结构——switch语句
#include
using namespace std;
/*
switch(表达式){
case结果1:执行语句; break;
case结果2:执行语句; break;
...
default:执行语句; break ;
}
*/
int main() {
//给电影进行打分
//10~9经典
//8~7非常好
//6~5一般
//5以下烂片
int score = 0;
cout << "请给电影打分:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您打的分数是:" << score << endl;
switch (score) {
case 10:
case 9:
cout << "您认为是经典电影" << endl;
break;
case 8:
case 7:
cout << "您认为电影非常好" << endl;
break;
case 6:
case 5:
cout << "您认为电影一般" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "您认为电影是烂片" << endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 五、程序流程结构2
5.1循环结构——while循环语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//while循环
//在屏幕中打印0~9
int num = 0;
//注意:要避免死循环
while (num < 10) {
cout << num << endl;
num++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 5.2循环结构案例——猜数字
#include
using namespace std;
//time系统时间头文件包含
#include
int main() {
//添加随机数种子,作用利用当前系统时间生成随机数,防止每次随机数都一样
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int num = rand() % 100 + 1;//rand()%100生成0~99之间的随机数
int val = 0;
while (1) {
cin >> val;
if (val > num) {
cout << "猜测过大" << endl;
}
else if (val < num) {
cout << "猜测过小" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "猜测成功" << endl;
break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 5.3循环结构——do...while语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// do. ..while语句
//在屏幕中输出0到9这10个数字
int num = 0;
do {
cout << num << endl;
num++;
} while (num < 10);
//do...while和while循环区别在于do...while会先执行一次循环语句
system("pause");
return 0;
} 5.4循环结构案例——水仙花数
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num = 100;
int a = 0;//百位
int b = 0;//十位
int c = 0;//个位
while (num < 1000) {
a = num / 100;
b = (num / 10) % 10;
c = num % 10;
if (a * a * a + b * b * b + c * c * c == num) {
cout << num << endl;
}
num++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 5.5循环结构——for循环语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 5.6循环结构案例——敲桌子
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//练习案例:敲桌子
//案例描述:从1开始数到数字100, 如果数字个位含有7,或者数字十位含有7,或者该数字是7的倍数,我们打印敲桌子,其余数字直接打印输出。
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if (i % 7 == 0 || i / 10 == 7 || i % 10 == 7) {
cout << "敲桌子" << endl;
}
else {
cout << i << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 5.7循环结构——嵌套循环
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
cout << "* ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 5.8嵌套循环案例——乘法表
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
cout << i << "*" << j <<"="<< i * j << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 六、跳转语句
6.1跳转语句——break语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// break出现在switch语句中
cout << "请选择副本难度" << endl;
cout << "1、普通" << endl;
cout << "2、中等" << endl;
cout << "3、困难" <> select;
switch (select) {
case 1:
cout << "您选择的是普通难度" << endl;
break;//退出switch语句
case 2:
cout << "您选择的是中等难度" << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "您选择的是困难难度" << endl;
break;
default:
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 6.2跳转语句——break语句2
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//break出现在循环语句中
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//如果i等于5,退出循环,不再打印
if (i == 5){
break;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 6.3跳转语句——break语句3
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//break出现在嵌套循环语句中
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
if (j == 5) {
break;//退出内凄循环
}
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 6.4跳转语句——continue语句
作用:在循环语句中,跳过本次循环中余下尚未执行的语句,继续执行下一次循环
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// continue语句
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
//如果是奇数输出,偶数不输出
if (i % 2 == 0) {
continue;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} #include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// continue语句
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
//如果是奇数输出,偶数不输出
if (i % 2 == 0) {
//continue;
break;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 6.5跳转语句——goto语句
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//goto语句
cout << "1、xxxx" << endl;
cout << "2、xxxx" << endl;
goto FLAG;
cout << "3、xxxx" << endl;
cout << "4、Xxxx" << endl;
FLAG:
cout << "5、xxxx" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 七、数组
数组:就是一个集合,里面存放了相同类型的数据元素
特点1:数组中的每个数据元素都是相同的数据类型
特点2:数组时由连续的内存位置组成的
以为数组定义的三种方式:
1、数据类型 数组名[数组长度]
2、数据类型 数组名[数组长度]={值1, 值2, ....};
3、数据类型 数组名[]={值1, 值2, ....};
7.1一维数组的定义
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 0;
arr[1] = 1;
arr[2] = 2;
arr[3] = 3;
arr[4] = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
int arr2[5] = { 0,1,2 };
//如果在初始化数据时候,没有全部填写完,会用0来填补剩余数据
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << arr2[i] << endl;
}
int arr3[] = { 10,20,30,4,0,5,2,1 };
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
cout << arr3[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 7.2一维数组——数组名
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//数组名用途
// 1、可以通过数组名统计整个数组占用内存大小
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
cout << "整个数组占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(arr) << endl;
cout << "每个元素占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "数组中元素个数为:" << sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
//2、可以通过数组名查看数组首地址
cout << "数组首地址为:" << (int)arr << endl;
cout << "数组中第一个元素地址为:" << (int)&arr[0] << endl;
cout << "数组中第二个元素地址为:" << (int)&arr[1] << endl;
//数组名是常量,不可以进行赋值操作
//arr = 100;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 7.3一维数组案例——五只小猪称体重
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、创建5只小猪体重的数组
int arr[5] = { 300,350,200,400,250 };
//2、从数组中找到最大值
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
//3、打印最大值
cout <<"最重的小猪体重为:"<< max << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 7.4一维数组案例——数组元素逆置
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//实现数组元素逆置
//1、创建数组
int arr[5] = { 1,3,2,5,4 };
cout << "数组逆置前:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
//2、实现逆置
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < 5 / 2; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[4 - i];
arr[4 - i] = temp;
}
//3、打印逆置后的数组
cout << "数组逆置后:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 7.5一维数组——冒泡排序
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//利用冒泡排序实现升序序列
int arr[9] = { 4,2,8,0,5,7,1,3,9 };
cout << "排序前:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 9 - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9 - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 7.6二维数组的定义
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 二维数组定义方式
//1. 数据类型 数组名[行数][列数];
//2.数据类型 数组名[行数][列数]= { {数据1,数据2},{数据3,数据4 }};
//3.数据类型 数组名[行数][列数]={数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4};
//4.数据类型 数组名[][列数]={ 数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4};
//1. 数据类型 数组名[行数][列数];
int arr1[2][3];
arr1[0][0] = 0;
arr1[0][1] = 1;
arr1[0][2] = 2;
arr1[1][0] = 3;
arr1[1][1] = 4;
arr1[1][2] = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cout << arr1[i][j] << endl;
}
}
//2.数据类型 数组名[行数][列数]= { {数据1,数据2},{数据3,数据4 }};
int arr2[2][3] = {
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cout << arr2[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//3.数据类型 数组名[行数][列数]={数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4};
int arr3[2][3] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5 };
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cout << arr3[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//4.数据类型 数组名[][列数]={ 数据1,数据2,数据3,数据4};
int arr4[][3] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cout << arr4[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
7.7二维数组——数组名
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//二维数组名称用途
//1、可以查看占用内存空间大小
int arr[2][3] ={
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6}
};
cout << "二维数组占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(arr) << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一行占用内存为:"<< sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一个元素占用内存为: " << sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组行数为:" << sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;
cout << "二维数组列数为:" << sizeof(arr[0]) / sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;
//2、可以查看二维数组的首地址
cout << "二维数组首地址为:" << (int)arr << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一行首地址为:" << (int)arr[0] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第二行首地址为:" << (int)arr[1] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第一个元素首地址:"<< (int)&arr[0][0] << endl;
cout << "二维数组第工个元素首地址:"<< (int)&arr[0][0] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 7.8二维数组案例——考试成绩统计
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//二维数组案例-考试成绩统计
//1、创建二维数组
int scores[3][3] = { {100,100,100},{90,50,100},{60,70,80} };
string names[3] = { "张三","李四","王五" };
//2、统计每个人的总和分数
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
sum += scores[i][j];
cout << scores[i][j] << "\t";
}
cout < 八、函数
8.1函数的定义
#include
using namespace std;
//函数的定义
//语法:
//返回值类型 函数名(参数列表){ 函数体语句 return表达式}
//加法函数,实现两个整型相加,并且将相加的结果进行返回
int add(int numl, int num2) {
int sum = numl + num2;
return sum;
}
int main() {
system("pause");
return 0;
} 8.2函数的调用
#include
using namespace std;
//定义加法函数
//函数定义的时候,num1和num2并没有真是数据,他只是一个形式上的参数,简称形参
int add(int num1, int num2) {
int sum = num1 + num2;
return sum;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
//函数调用语法:函数名称(参数)
//a和b称为实际参数,简称实参
//当调用函数时候,实参的值会传递给形参
int c = add(a, b);
cout << c << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 8.3函数——值传递
#include
using namespace std;
//值传递
//定义函数,实现两个数字进行交换函数
//如果函数不需要返回值,声明的时候可以写void
void swap(int num1, int num2) {
cout << "交换前:"<< endl;
cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;
int temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;
// return; 返回值不需要的时候,可以不写return
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
//当我们做值传递的时候,函数的形参发生改变,并不会影响实参
swap(a, b);
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 8.4函数——常见样式
#include
using namespace std;
//函数常见样式
//1、无参无返
void test01() {
cout << "this is test01 " << endl;
}
//2、有参无返
void test02(int a) {
cout << "this is test02 a = " << a << endl;
}
//3、无参有返
int test03() {
cout << "this is test03 " << endl;
return 1000;
}
//4、有参有返
int test04(int a) {
cout << "this is test04 a = " << a << endl;
return a;
}
int main() {
//无参无返函数调用
test01();
//有参无返函数调用
int a = 10;
test02(a);
//无参有返函数调用
int b = test03();
cout << b << endl;
//有参有返函数调用
int c = test04(100);
cout << c << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 8.5函数的声明
#include
using namespace std;
//函数的声明
//比较函数,实现两个整型数字进行比较,返回较大的值
//提前告诉编译器函数的存在,可以利用函数的声明
//函数的声明
//声明可以写多次,但是定义只能有一次
int max(int a, int b);
int max(int a, int b);
int max(int a, int b);
int main() {
int max(int a, int b);
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << max(a, b) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//定义
int max(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
} 8.6函数的分文件编写
函数分文件编写一般有4个步骤
1、创建后缀名为.h的头文件
2、创建后缀名为.cpp的源文件
3、在头文件中写函数的声明
4、在源文件中写函数的定义
头文件swap.h
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
//函数的声明
void swap(int a, int b); 源文件swap.cpp
#include "swap.h"
void swap(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}#include
using namespace std;
#include "swap.h"
//函数的分文件编写
//实现两个数字进行交换的函数
//函数的声明
void swap(int a,int b);
/*
//函数的定义
void swap(int a, int b){
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}
*/
//1.创建后缀名为.h的头文件
//2.创建后缀名为.cpp的源文件
//3.在头文件中写函数的声明
//4.在源文件中写函数的定义
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swap(a, b);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 九、指针
9.1指针的定义和使用
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、定义指针
int a = 10;
//指针定义的语法:数据类型 *指针变量名;
int * p;
//让指针记录变量a的地址
p= &a;
cout << "a的地址为:" << &a << endl;
cout << "指针p为:" << p << endl;
//2、使用指针
//可以通过解引用的方式来找到指针指向的内存
//指针前加*代表解引用,找到指针指向的内存中的数据
*p= 1000;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "*p = " << * p << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 9.2指针所占内存空间
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//指针所占内存空间
int a = 10;
//int *p;
//p = &a;
int *p = &a;
//在32位操作系统下,指针是占4个字节空间大小,不管是什么数据类型
//在64位操作系统下,指针是占8个字节空间大小,不管是什么数据类型
cout << "sizeof(int *) = " << sizeof(int *) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(float *) = " << sizeof(float *) << endl;
cout<<"sizeof(double *) = " < 9.3空指针
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//空指针
//1、空指针用于给指针变量进行初始化
int * p = NULL;
//2、空指针是不可以进行访问的
//0~255之间的内存编号是系统占用的,因此不可以访问
//*p = 100;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 9.4野指针
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//野指针
//在程序中,尽量避免出现野指针
int* p =(int *) 0x1100;
//cout << *p << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 9.5const修饰指针
const修饰指针有三种情况:
1、const修饰指针——常量指针
2、const修饰常量——指针常量
3、const既修饰指针,又修饰常量
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、const修饰指针常量指针
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
const int * p = &a;
//指针指向的值不可以改,指针的指向可以改
//*p=20;错误
p = &b;//正确
//2、const修饰常量
int* const p2 = &a;
*p2 = 100;//正确的
//p2 = &b;//错误的,指针的指向不可以改
// 3、const修饰指针和常量
const int * const p3 = &a;
//指针的指向和指针指向的值都不可以改
//*p3 = 100;//错误
//p3 = &b; //错误
system("pause");
return 0;
} 9.6指针和数组
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
//指针和数组
//利用指针访问数组中的元素
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
cout << "第一个元素为:" << arr[0] << endl;
int* p = arr;//arr就是数组的首地址
cout << "利用指针访问第一个元素:" << *p << endl;
p++;//让指针向后偏移4个字节
cout << "利用指针访问第二个元素:" << *p << endl;
cout << "利用指针遍历数组"<< endl;
int * p2 = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << *p2 << endl;
p2++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 9.7指针和函数
#include
using namespace std;
//实现两个数字进行交换
void swap01(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "swap01 a=" << a << endl;
cout << "swap01 b=" << b << endl;
}
//实现两个数字进行交换
void swap02(int *p1, int *p2) {
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
cout << "swap02 *p1=" << *p1 << endl;
cout << "swap02 *p2=" << *p2 << endl;
}
int main() {
//指针和函数
//1、值传递
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swap01(a, b);
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
cout << "b=" << b << endl;
//2、地址传递
swap02(&a, &b);
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
cout << "b=" << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 9.8指针数组函数案例——冒泡排序
#include
using namespace std;
//冒泡排序函数
void bubbleSort(int* arr, int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
//1、先创建数组
int arr[10] = { 4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5 };
//数组长度
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//2、创建函数,实现冒泡排序
bubbleSort(arr, len);
//3、打印排序后的数组
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 十、结构体
10.1结构体的定义和使用
#include
using namespace std;
#include
//1、创建学生数据类型:学生包括(姓名,年龄,分数)
//自定义数据类型,一些类型集合组成的一个类型
//语法:struct 类型名称{成员列表};
struct Student {
//成员列表
//姓名
string name;
//年龄
int age;
//分数
int score;
}s3;//顺便创建绪构体变量
//2、通过学生类型创建具体学生
//2.1 struct Student s1
//2.2 struct Student s2 = {i ... }
//2.3在定义结构体时顺便创建结构体变量
int main() {
//2.1 struct Student s1
//struct Student s1;
//struct关键字可以省略
Student s1;
//给s1属性赋值, 通过.访问结构体变量中的属性
s1.name = "张三";
s1.age = 18;
s1.score = 100;
cout << "姓名:" << s1.name << ",年龄:" << s1.age << ",成绩:" << s1.score << endl;
//2.2 struct Student s2 = {i ... }
struct Student s2={ "李四",19,80};
cout << "姓名:" << s2.name << ",年龄:" << s2.age << ",成绩:" << s2.score << endl;
//2.3在定义结构体时顺便创建结构体变量
s3.name = "王五";
s3.age = 20;
s3.score = 90;
cout << "姓名:" << s3.name << ",年龄:" << s3.age << ",成绩:" << s3.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 10.2结构体数组
#include
using namespace std;
#include
//结构体数组
struct Student {
//姓名
string name;
//年龄
int age;
//分数
int score;
};
int main() {
//2、创建结构体数组
struct Student stuArr[3] = {
{"张三",18,100},
{"李四",19,90},
{"王五",20,80}
};
//3、给结构体数组中的元索赋值
stuArr[2].name = "赵六";
stuArr[2].age = 30;
stuArr[2].score = 60;
//4、遍历结构体数组
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << "姓名:" << stuArr[i].name << ",年龄:" << stuArr[i].age << ",分数:" << stuArr[i].score << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 10.3结构体指针
#include
using namespace std;
//结构体指针
//定义学生的结构体
struct Student {
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
int score;//分数
};
int main() {
//1、创建学生结构体变量
struct Student s = { "张三",18,100 };
//2、通过指针指向结构体变量
struct Student* p = &s;
//3、通过指针访问结构体变量中的数据
///通过结构体指针访问结构体中的属性,需要利用’->'
cout<< "姓名:" << p->name << ",年龄:" << p->age << ",分数:" << p->score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 10.4结构体嵌套结构体
#include
using namespace std;
#include
//定义学生的结构体
struct student {
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
int score;//分数
};
//定义老师结构体
struct teacher {
int id;//教师编号
string name;//教师姓名
int age;//教师年龄
struct student stu;//辅导的学生
};
int main() {
//结构体嵌套结构体
//创建老师
teacher t;
t.id = 10000;
t.name = "老王";
t.age = 50;
t.stu.name = "小王";
t.stu.age = 18;
t.stu.score = 90;
cout << "老师的编号:" << t.id << ",老师的姓名:" << t.name << ",老师的年龄:" << t.age << ",老师辅导的学生的姓名:" << t.stu.name << ",老师辅导的学生的年龄:" << t.stu.age << ",老师辅导的学生的成绩:" << t.stu.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 10.5结构体做函数参数
#include
using namespace std;
#include
//定义学生的结构体
struct student {
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
int score;//分数
};
//打印学生信息函数
//1、值传递
void printStudent1(struct student s){
s.age = 100;
cout << "子函数1中打印 姓名:" << s.name << ",年龄:" << s.age << ",分数: " << s.score << endl;
}
//2、地址传递
void printStudent2(struct student* s) {
s->age = 90;
cout << "子函数2中打印 姓名:" << s->name << ",年龄:" << s->age << ",分数: " << s->score << endl;
}
int main() {
//结构体做函数参数
//将学生传入到一个参数中,打印学生身上的所有信息
//创建结构体变量
struct student s;
s.name ="张三";
s.age = 20;
s.score = 85;
cout << "main函数中打印 姓名:" << s.name << ",年龄:" << s.age << ",分数: " << s.score << endl;
printStudent1(s);
cout << "main函数中打印 姓名:" << s.name << ",年龄:" << s.age << ",分数: " << s.score << endl;
printStudent2(&s);
cout << "main函数中打印 姓名:" << s.name << ",年龄:" << s.age << ",分数: " << s.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 10.6结构体中const使用场景
#include
using namespace std;
#include
//定义学生的结构体
struct student {
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
int score;//分数
};
void printStudents(const student *s) {
//没有const,可以修改,main函数中的数据也会改变
//s->age = 150;//加入const之后,不能修改,一旦修改就会报错
cout << "函数中 姓名:" << s->name << ",年龄:" << s->age << ",成绩:" << s->score << endl;
}
int main() {
//创建结构体变量
struct student s = { "张三",18,100 };
cout << "main 姓名:" << s.name << ",年龄:" << s.age << ",成绩:" << s.score << endl;
//通过函数打印结构体变量信息
printStudents(&s);
cout << "main 姓名:" << s.name << ",年龄:" << s.age << ",成绩:" << s.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} 10.7结构体案例1
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include
//学生的结构体
struct student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
//老师的结构体定义
struct Teacher{
//姓名
string tName;
//学生数组
struct student sArray[5];
};
//给老师和学生赋值的函数
void allocateSpace(struct Teacher tArray[],int len) {
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
//给老师开始赋值
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tArray[i].tName = "Teacher_";
tArray[i].tName += nameSeed[i];
//通过循环给每名老师所带的学生赋值
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
tArray[i].sArray[j].name = "student_";
tArray[i].sArray[j].name += nameSeed[j];
int random = rand() % 61+40;
tArray[i].sArray[j].score = random;
}
}
}
//打印所有信息
void printInfo(struct Teacher tArray[],int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << "老师姓名:" << tArray[i].tName << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cout <<"\t学生姓名:"<< tArray[i].sArray[j].name << ",学生成绩" << tArray[i].sArray[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
//随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//创建3名老师的数组
struct Teacher tArray[3];
//通过函数给3名老师的信息赋值,并给老师带的学生信息赋值
int len = sizeof(tArray) / sizeof(tArray[0]);
allocateSpace(tArray, len);
//打印所有老师及所带的学生信息
printInfo(tArray, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 10.8结构体案例2
#include
using namespace std;
#include
//1、设计英雄结构体
struct Hero {
string name;
int age;
string sex;
};
void bubbleSort(struct Hero heroArray[], int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) {
if (heroArray[j].age > heroArray[j + 1].age) {
struct Hero temp = heroArray[j];
heroArray[j] = heroArray[j + 1];
heroArray[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main8() {
//2、创建数组存放5名英雄
struct Hero heroArray[5] = {
{"刘备",23,"男"},
{"关羽",22,"男"},
{"张飞",20,"男"},
{"赵云",21,"男"},
{"貂蝉",19,"女"}
};
int len = sizeof(heroArray) / sizeof(heroArray[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << "姓名:" << heroArray[i].name << ",年龄:" << heroArray[i].age << ",性别:" << heroArray[i].sex << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//3、对数组进行排序,按照年龄进行升序排序
bubbleSort(heroArray, len);
//4、将排序后的结果打印输出
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << "姓名:" << heroArray[i].name << ",年龄:" << heroArray[i].age << ",性别:" << heroArray[i].sex << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 十一、通讯录管理系统
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#define MAX 1000
//菜单界面
void showMenu() {
cout << "*****************************" << endl;
cout << "***** 1、添加联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 2、显示联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 3、删除联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 4、查找联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 5、修改联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 6、清空联系人 *****" << endl;
cout << "***** 0、退出通讯录 *****" << endl;
cout << "*****************************" << endl;
}
struct Person {
string m_name;
int m_sex;
int m_age;
string m_phone;
string m_address;
};
struct Addressbooks {
struct Person personArray[MAX];
int m_size;
};
void addPerson(struct Addressbooks* abs) {
if (abs->m_size == MAX) {
cout << "通讯录已满,无法添加!" << endl;
return;
}
else {
cout << "请输入姓名:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[abs->m_size].m_name;
cout << "请输入性别:" << endl;
cout << "1——男" << endl;
cout << "2——女" << endl;
int sex = 0;
while (true) {
cin >> sex;
if (sex == 1 || sex == 2) {
abs->personArray[abs->m_size].m_sex=sex;
break;
}
else {
cout << "输入错误,请重新输入:" << endl;
}
}
cout << "请输入年龄:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[abs->m_size].m_age;
cout << "请输入电话号:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[abs->m_size].m_phone;
cout << "请输入地址:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[abs->m_size].m_address;
abs->m_size++;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void showPerson(Addressbooks* abs) {
if (abs->m_size == 0) {
cout << "当前记录为空" << endl;
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < abs->m_size; i++) {
cout << "姓名:" << abs->personArray[i].m_name << endl;
cout << "性别:" << ((abs->personArray[i].m_sex==1)?"男":"女") << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << abs->personArray[i].m_age << endl;
cout << "电话:" << abs->personArray[i].m_phone << endl;
cout << "住址:" << abs->personArray[i].m_address << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
int isExist(Addressbooks* abs, string name) {
for (int i = 0; i < abs->m_size; i++) {
if (abs->personArray[i].m_name == name) {
return i;
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
}
void deletePerson(Addressbooks* abs) {
cout << "请输入联系人的姓名:" << endl;
string name;
cin >> name;
int ret = isExist(abs, name);
if ( ret == -1) {
cout << "联系人不存在" << endl;
}
else {
for (int i = ret; i < abs->m_size - 1; i++) {
abs->personArray[i] = abs->personArray[i + 1];
}
abs->m_size - 1;
cout << "删除成功" << endl;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void findPerson(Addressbooks* abs) {
cout << "请输入您要查找的联系人:" << endl;
string name;
cin >> name;
int ret = isExist(abs, name);
if (ret == -1) {
cout << "联系人不存在" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "姓名:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_name << endl;
cout << "性别:" << ((abs->personArray[ret].m_sex == 1) ? "男" : "女") << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_age << endl;
cout << "电话:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_phone << endl;
cout << "住址:" << abs->personArray[ret].m_address << endl;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void modifyPerson(Addressbooks* abs) {
cout << "请输入您要修改的联系人:" << endl;
string name;
cin >> name;
int ret = isExist(abs, name);
if (ret == -1) {
cout << "查无此人" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "请输入姓名:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[ret].m_name;
cout << "请输入性别:" << endl;
cout << "1——男" << endl;
cout << "2——女" << endl;
int sex = 0;
while (true) {
cin >> sex;
if (sex == 1 || sex == 2) {
abs->personArray[ret].m_sex = sex;
break;
}
else {
cout << "输入错误,请重新输入:" << endl;
}
}
cout << "请输入年龄:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[ret].m_age;
cout << "请输入电话号:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[ret].m_phone;
cout << "请输入地址:" << endl;
cin >> abs->personArray[ret].m_address;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void clearPerson(Addressbooks* abs) {
if (abs->m_size == 0) {
cout << "当前联系人为空" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "是否确定删除所有联系人(1:确定)" << endl;
int flag = 0;
cin >> flag;
if (flag == 1) {
abs->m_size = 0;
cout << "所有联系人已清空" << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
int main() {
Addressbooks abs;
abs.m_size = 0;
int select = 0;
while (true) {
showMenu();
cin >> select;
switch (select) {
case 1:
addPerson(&abs);
break;
case 2:
showPerson(&abs);
break;
case 3:
deletePerson(&abs);
break;
case 4:
modifyPerson(&abs);
break;
case 5:
findPerson(&abs);
break;
case 6:
clearPerson(&abs);
break;
case 0:
cout << "欢迎下次使用" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}