C:语言相关tips
一、数组和链表的联系
数组和链表都是线性表数据结构。
二、数组和链表的区别
1.数组可以随机以及顺序存取,而链表只能顺序存取。
2.数组静态分配内存,链表动态分配内存。
3.数组是一种线性表数据结构,有一组连续的内存空间,链表是通过指针将一组零散的内存块串联起来使用的数据结构,不需要一块连续的内存空间。
———————————————————————————————————————————
- C语言中,数组和下标可以互换,这是由数组下标的指针定义决定的,由于存在加法交换律,只要一个是指针,另一个是整型就行,而无关顺序,a[3]等价于3[a],等价于*(a+3),等价于*(3+a)。
- 求数组元素的个数:j = sizeof(a) / sizeof a[0];
- 修改指针指向的地址
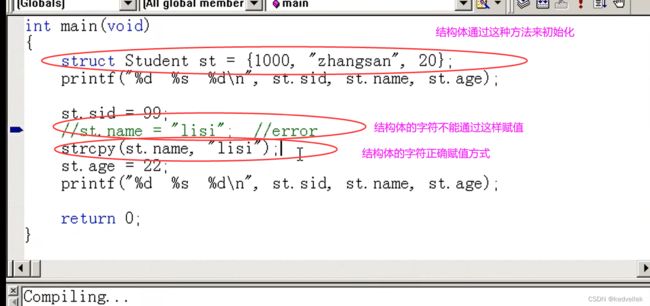
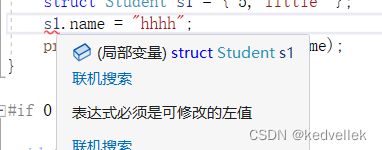
- 结构体
struct Student s1;
struct Student * p = &s1;
p→xx == (*p).xx (*p).xx==s1.xx 所以p→xx==s1.xx
- 静态变量和动态变量:使用malloc()分配的变量属于动态的(程序运行时可申请不同大小内存或销毁),反之属于静态(程序运行时已经固定分配好了程序运行完后才会销毁)。
 第一个字节的地址当做是整型的地址。所谓的整型地址代表第一个字节的地址是代表四个字节的地址。
第一个字节的地址当做是整型的地址。所谓的整型地址代表第一个字节的地址是代表四个字节的地址。
[] ==*()
→==(*).
三、变量命名规则
四、sscanf的用法
读取解析一行GPS原始数据
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* set_opt(fd,115200,8,'N',1) 串口参数的设置*/
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop)
{
struct termios newtio,oldtio;
if ( tcgetattr( fd,&oldtio) != 0) {
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return -1;
}
bzero( &newtio, sizeof( newtio ) );
newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
newtio.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG); /*Input*/
newtio.c_oflag &= ~OPOST; /*Output*/
switch( nBits )
{
case 7:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
}
switch( nEvent )
{
case 'O':
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD;
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
break;
case 'E':
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
break;
case 'N':
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
break;
}
switch( nSpeed )
{
case 2400:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400);
break;
case 4800:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800);
break;
case 9600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
case 115200:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200);
break;
default:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
}
if( nStop == 1 )
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
else if ( nStop == 2 )
newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; /* 读数据时的最小字节数: 没读到这些数据我就不返回! */
newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0; /* 等待第1个数据的时间:
* 比如VMIN设为10表示至少读到10个数据才返回,
* 但是没有数据总不能一直等吧? 可以设置VTIME(单位是10秒)
* 假设VTIME=1,表示:
* 10秒内一个数据都没有的话就返回
* 如果10秒内至少读到了1个字节,那就继续等待,完全读到VMIN个数据再返回
*/
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH);
if((tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio))!=0) //设置行规程
{
perror("com set error");
return -1;
}
//printf("set done!\n");
return 0;
}
int open_port(char *com)
{
int fd;
//fd = open(com, O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY);
fd = open(com, O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY); //O_RDWR可读可写 O_NOCTTY不要把单做控制台
if (-1 == fd){
return(-1);
}
if(fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0)<0) /* 设置串口为阻塞状态 1.fcntl ( fd, FSETFL,FNDELAY);
读数据时不等待,没有数据就返回0
2.fcntl(FD,F_SETFL,O);
读数据时,没有数据阻塞
*/
{
printf("fcntl failed!\n");
return -1;
}
return fd;
}
/* 读一行GPS原始数据*/
/* eg. $GPGGA,082559.00,4005.22599,N,11632.58234,E,1,04,3.08,14.6,M,-5.6,M,,*76" */
/* 回车换行*/
int read_gps_raw_data(int fd, char *buf)
{
int i = 0;
int iRet;
char c;
int start = 0;
while (1)
{
iRet = read(fd, &c, 1); //读一个数据保存的c
if (iRet == 1)
{
if (c == '$') //判断第一个字符是否为数据起始符$
start = 1;
if (start)
{
buf[i++] = c;
}
if (c == '\n' || c == '\r')
return 0;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
}
/*解析数据*/
/* eg. $GPGGA,082559.00,4005.22599,N,11632.58234,E,1,04,3.08,14.6,M,-5.6,M,,*76" */
int parse_gps_raw_data(char *buf, char *time, char *lat, char *ns, char *lng, char *ew)
{
char tmp[10];
if (buf[0] != '$')
return -1;
else if (strncmp(buf+3, "GGA", 3) != 0) //字串相比较
return -1;
else if (strstr(buf, ",,,,,")) //strstr 查找数据中是否有,,,,,这样连续的字符串
{
printf("Place the GPS to open area\n");
return -1;
}
else {
//printf("raw data: %s\n", buf);
sscanf(buf, "%[^,],%[^,],%[^,],%[^,],%[^,],%[^,]", tmp, time, lat, ns, lng, ew);
//将原始数据的buf中的字符串存到指定的buf中(从字符串读取格式化输入)
//[^,]scanf的高级用法,^表示剔除不包含,[^,]表示遇到,就停止
return 0;
}
}
/*
* ./serial_send_recv
argv[1] 传入的是设备节点
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int iRet;
char c;
char buf[1000];
char time[100];
char Lat[100];
char ns[100];
char Lng[100];
char ew[100];
float fLat, fLng;
/* 1. open */
/* 2. setup
* 115200,8N1
* RAW mode
* return data immediately
*/
/* 3. write and read */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: \n");
printf("%s \n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open_port(argv[1]);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
iRet = set_opt(fd, 9600, 8, 'N', 1);
if (iRet)
{
printf("set port err!\n");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
/* eg. $GPGGA,082559.00,4005.22599,N,11632.58234,E,1,04,3.08,14.6,M,-5.6,M,,*76"*/
/* read line */
iRet = read_gps_raw_data(fd, buf);
/* parse line */
if (iRet == 0)
{
iRet = parse_gps_raw_data(buf, time, Lat, ns, Lng, ew);
}
/* printf */
if (iRet == 0)
{
printf("Time : %s\n", time);
printf("ns : %s\n", ns);
printf("ew : %s\n", ew);
printf("Lat : %s\n", Lat);
printf("Lng : %s\n", Lng);
/* 纬度格式: ddmm.mmmm */
sscanf(Lat+2, "%f", &fLat);
fLat = fLat / 60; //分化成度
fLat += (Lat[0] - '0')*10 + (Lat[1] - '0'); //字符减去字符‘0’就等于数值
/* 经度格式: dddmm.mmmm */
sscanf(Lng+3, "%f", &fLng);
fLng = fLng / 60;
fLng += (Lng[0] - '0')*100 + (Lng[1] - '0')*10 + (Lng[2] - '0');
printf("Lng,Lat: %.06f,%.06f\n", fLng, fLat);
//%.06f 小数点后保存6位
}
}
return 0;
}
C 库函数 – sscanf() | 菜鸟教程
五.define 标记符
深入理解#define预处理,预处理器运算符# ## #@_梦起丶的博客-CSDN博客_预处理器运算符
宏定义中的特殊参数(#、##、...和__VA_ARGS__) - 百度文库
六.数组链表通讯录实习增删查改
参考文章: C语言实现动态通讯录(附带文件保存)_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
qsort 的搜索結果
七.优秀博文
7.1文件读写
c语言的文件操作详解_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
strerror函数详解 看这一篇就够了-C语言(函数讲解、 使用用法举例、作用)_嘎嘎烤鸭的博客-CSDN博客
指针从入门到熟练掌握_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
自定义类型-结构体详解_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客_自定义结构体
C语言预处理指令-单片机必备技能_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客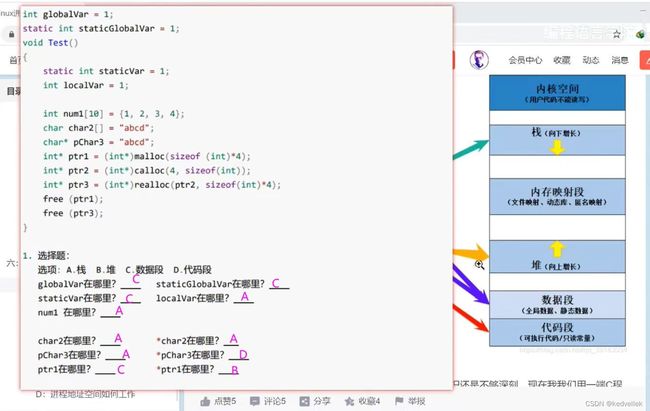
<C/C++内存管理>——《C++初阶》_新晓·故知(考研停更)的博客-CSDN博客
https://blog.csdn.net/DlMmU/article/details/79799191
static,const,volatile,extern,register关键字深入解析_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
C语言和C++不同,为什么const不能在C语言中定义数组大小原因_Mr番茄蛋的博客-CSDN博客_const的数不能放数组
声明和定义的区别_黎先生你好的博客-CSDN博客_声明和定义的区别
lv_obj_add_state(sw, chk ? LV_STATE_CHECKED : 0); // 添加事件
7.2 switch 选择不仅对应数字也可以用字符,但存在有问题。
深入理解时间和空间复杂度_时间复杂度和空间复杂度的概念_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
动态内存分配及动态顺序表的实现_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
malloc的返回值一定要做检查
使用realloc重新分配空间时一定要先拿一个临时指针来接收返回值,不能直接用原来空间的指针来接收,若realloc 分配空间失败会返回一个NULL直接用原来空间的指针来接收会导致原来的空间直接找不到啦。
如何规避野指针
1.指针初始化
2.小心指针越界
3.指针指向空间释放即使置NULL
4.避免返回局部变量的地址
5.指针使用之前检查有效性
C语言深度解剖之数据到底在内存中如何存储_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
整型提升、算术转化、变量内容的存入和取出
C语言链表超详解_链表c语言_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
C语言操作符详解_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
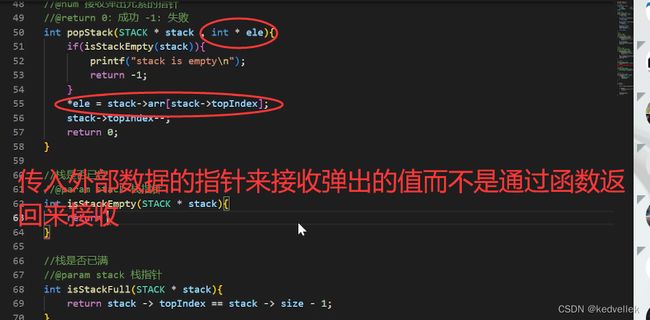
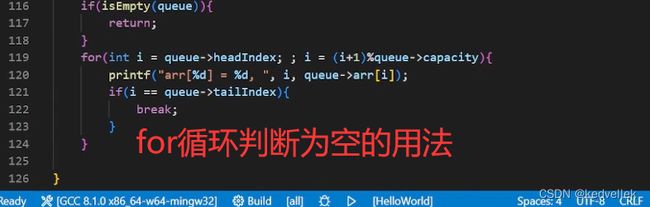
C语言栈和队列的实现_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
C语言实现栈_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
C语言指针进阶_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
qsort函数和qsort函数的模拟实现_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
qsort()函数和bsearch()函数_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
(70条消息) C语言指针面试题-1_*--*++cpp+3_HZCVinter的博客-CSDN博客
字符串与内存操作函数详解与模拟实现_源字符串和目的字符串_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
08_strtok字符串切割函数_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
函数栈帧的形成与释放_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
牛客网刷题-合并两个有序数组_牛客网有序序列合并_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客 标准库 - inttypes.h - 《阮一峰《C 语言教程》》 - 书栈网 · BookStack
标准库 - inttypes.h - 《阮一峰《C 语言教程》》 - 书栈网 · BookStack
UNUSED参数,这个宏,很秀 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)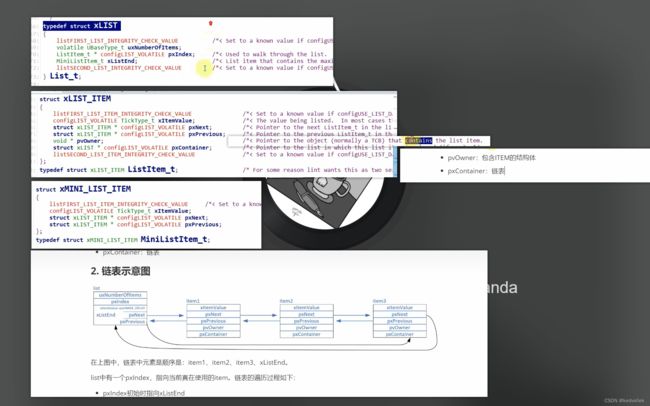
牛客网刷题-环形链表_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客牛客网刷题-合并两个排序的链表_数据结构两个链表合并排序_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param element int整型
* @return 无
*
* C语言声明定义全局变量请加上static,防止重复定义
*/
#include
#include
typedef int QDataType ;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode * next;
QDataType data;
} QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode * head;
QNode * tail;
} Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue * pq)
{
if(pq == NULL){
return ;
}
pq->head = pq->tail =NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue * pq)
{
if(pq == NULL){
return;
}
QNode * cur = pq->head;
while (cur) {
QNode * next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail =NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue * pq , QDataType data)
{
if (pq == NULL) {
return;
}
QNode * NewNode = (QNode *)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(NewNode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
NewNode->data = data;
NewNode->next = NULL;
if(pq -> tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = NewNode;
}
else {
pq->tail->next = NewNode;
pq ->tail = NewNode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue * pq)
{
if (pq == NULL) {
return;
}
if(pq->head->next == NULL){
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else {
QNode * next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue * pq)
{
if (pq == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue * pq)
{
if (pq == NULL)
{
exit (-1);
}
return pq->tail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue * pq)
{
if (pq == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
int count = 0;
QNode * cur = pq->head;
while (cur) {
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue *pq)
{
return pq->head == NULL;
}
Queue q1,q2;
void push(int element) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&q1))
{
QueuePush(&q1, element);
}
else {
QueuePush(&q2,element);
}
}
int pop() {
/*判断出非空队列与空队列*/
Queue * EmptyQueue = &q1;
Queue * NonEmptyQueue = &q2;
if (!QueueEmpty(&q1)) {
NonEmptyQueue = &q1;
EmptyQueue = &q2;
}
//倒腾数据:非空队列往空队列里面倒腾数据(最后一个元素不动)
while (QueueSize(NonEmptyQueue)>1)
{
QueuePush(EmptyQueue,QueueFront(NonEmptyQueue));
QueuePop(NonEmptyQueue);
}
//出栈最后一个元素
int top = QueueFront(NonEmptyQueue);
QueuePop(NonEmptyQueue);
return top;
}
int top() {
if(!QueueEmpty(&q1)){
return QueueBack(&q1);
}
else {
return QueueBack(&q2);
}
}
bool empty() {
return QueueEmpty(&q1)&&QueueEmpty(&q2);
} (87条消息) 牛客网-《刷C语言百题》第一期_牛客网c语言题库_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客牛客网-《刷C语言百题》第三期_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客牛客网-《刷C语言百题》第四期_牛客网c语言题库_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客牛客网-《刷C语言百题》第五期_@rivencode的个人主页_rivencode的博客-CSDN博客
单链表的删除指定元素_单链表删除指定元素_ForYanC的博客-CSDN博客
删除单链表指定元素_在一个带头结点的单链表中,删除指定位置location的元素 ,若给定的位置不合法则提_decouples的博客-CSDN博客
移除链表中指定元素-三种实现方法
八.函数为参数,可不用与用
//读取卡号,做数据回填,成功读取到卡号就退出 ,另一个是回调功能函数
uint8_t readCard(uint8_t *readUid,void(*funCallBack)(void))
{
uint8_t Temp[5];
if (PCD_Request(0x52, Temp) == 0)
{
if (PCD_Anticoll(readUid) == 0)
{
if(funCallBack!=NULL)
funCallBack();
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
这个函数就是卡号读取,第一个参数readUid是你要存放读取卡号的地址,第二个参数是一个函数传参,可以理解为回调函数,也就是,你想在读取到卡号之后做什么事情,都可以写在这个函数里,这是一个函数地址,如果你只需要读到卡号后回填数据,其他什么都不做,第二个参数填NULL即可,返回值为,读到卡号返回0,失败返回1。
eg:至于函数,比如说刷卡成功,蜂鸣器响一下,可以写在函数里,然后传过去。