Hutool的简单使用
1、入门和安装
1.1 简介
Hutool是一个小而全的Java工具类库,通过静态方法封装,降低相关API的学习成本,提高工作效率,使Java拥有函数式语言般的优雅,让Java语言也可以“甜甜的”。
Hutool中的工具方法来自于每个用户的精雕细琢,它涵盖了Java开发底层代码中的方方面面,它既是大型项目开发中解决小问题的利器,也是小型项目中的效率担当;
Hutool是项目中“util”包友好的替代,它节省了开发人员对项目中公用类和公用工具方法的封装时间,使开发专注于业务,同时可以最大限度的避免封装不完善带来的bug。
1.2 由来
Hutool = Hu + tool,是原公司项目底层代码剥离后的开源库,“Hu”是公司名称的表示,tool表示工具。Hutool谐音“糊涂”,一方面简洁易懂,一方面寓意“难得糊涂”。
1.3 包含的组件
一个Java基础工具类,对文件、流、加密解密、转码、正则、线程、XML等JDK方法进行封装,组成各种Util工具类,同时提供以下组件:
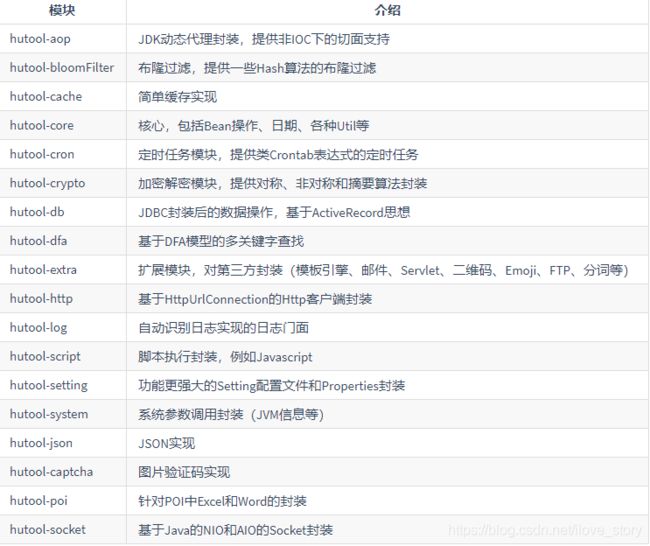
1.4 安装
maven项目导入下列依赖:
cn.hutool
hutool-all
5.4.7
gradle项目导入以下依赖:
compile 'cn.hutool:hutool-all:5.4.7'
2、核心(hutool-core)
2.1 克隆
2.1.1 解决问题
我们知道,JDK中的Cloneable接口只是一个空接口,并没有定义成员,它存在的意义仅仅是指明一个类的实例化对象支持位复制(就是对象克隆),如果不实现这个类,调用对象的clone()方法就会抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常。而且,因为clone()方法在Object对象中,返回值也是Object对象,因此克隆后我们需要自己强转下类型。
2.1.2 深拷贝和浅拷贝
- 浅拷贝指的是只拷贝对象本身(包括基本数据类型变量),而不拷贝引用类型变量指向的对象;
- 深拷贝不仅仅拷贝对象本身,同时也会拷贝引用类型变量所指向的对象。
2.1.3 传统克隆
传统方式的克隆就是实现java.lang.Cloneable接口,并且重写clone方法
public class CloneTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
Student clone = (Student)student.clone();
System.out.println(student.teacher == clone.teacher);//true 浅拷贝
}
public static class Student implements Cloneable{
public String name="zs";
public int age = 23;
public Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
@Override
protected Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new CloneRuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public static class Teacher{}
}
2.1.4 泛型克隆接口
hutool为我们提供了一个Cloneable接口,该接口继承了java.lang.Cloneable接口
public interface Cloneable extends java.lang.Cloneable{
/**
* 克隆当前对象,浅复制
* @return 克隆后的对象
*/
T clone();
}
我们只需要实现这个接口并在重写方法中进行强转,而后调用该类对象的克隆方法就可以得到该类的克隆对象了。
public class CloneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat = new Cat();
Cat clone = cat.clone();
System.out.println(cat.teacher == clone.teacher);//true 浅拷贝
}
private static class Cat implements Cloneable{
public String name = "张三";
public int age = 23;
public Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
@Override
public Cat clone() {
try {
return (Cat) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new CloneRuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
private static class Teacher{}
}
咋一看好像和传统方式没啥太大的区别,也就把强转这一步放入到方法里面去了。但是嘞,还是为我们简化了一点点代码的(对于调用者来说)。
2.1.5 泛型克隆类
可以发现,实现泛型克隆接口依旧要重写clone方法,还是得处理异常,因此,hutool为我们提供了CloneSupport类,它实现了上面的接口:
public class CloneSupport implements Cloneable{
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public T clone() {
try {
return (T) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new CloneRuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public class CloneTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
Student clone = s1.clone();
System.out.println(s1.teacher == clone.teacher);//true 浅拷贝
}
static class Student extends CloneSupport{
public String name = "zs";
public int age = 23;
public Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
}
static class Teacher{}
}
哇塞,继承个类就可以克隆,真香!
2.1.6 深拷贝
要想实现深拷贝的话,我们可以使用ObjectUtil.cloneByStream(obj)
public class CloneTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
Student clone = ObjectUtil.cloneByStream(student);
System.out.println(student.teacher == clone.teacher);//false 深拷贝
}
static class Student implements Serializable{//必须序列化
public String name = "zs";
public int age = 23;
public Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
}
static class Teacher implements Serializable{}//必须序列化
}
2.2 类型转换
2.2.1 解决问题
在Java开发中我们要面对各种各样的类型转换问题,尤其是从命令行获取的用户参数、从HttpRequest获取的Parameter等等,这些参数类型多种多样,我们怎么去转换他们呢?常用的办法是先整成String,然后调用XXX.parseXXX方法,还要承受转换失败的风险,不得不加一层try catch,这个小小的过程混迹在业务代码中会显得非常难看和臃肿。
2.2.2 Convert类
Convert类可以说是一个工具方法类,里面封装了针对Java常见类型的转换,用于简化类型转换。Convert类中大部分方法为toXXX,参数为Object,可以实现将任意可能的类型转换为指定类型。同时支持第二个参数defaultValue用于在转换失败时返回一个默认值。
2.2.3 常见类型转换
//转换为字符串
public static void testToStr(){
int a = 1;
System.out.println(Convert.toStr(a));//1
System.out.println(Convert.toStr(a,"aaa"));//转换失败返回默认值aaa
long[] b = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(Convert.toStr(b));//[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
//转换为指定类型数组
public static void testToXxArray(){
//字符串数组转换为整型数组
String[] a = {"1","2","3","4","5"};
Integer[] intArray = Convert.toIntArray(a);
for (Integer i : intArray) {
System.out.println(i);
}
//整型数组转换为字符串数组
int[] b = {1,2,3,4,5};
String[] strArray = Convert.toStrArray(b);
for (String s : strArray) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//转换为日期对象(太牛逼了)
public static void testToDate(){
//String a = "2017-08-12";
//String a = "2017/08/12";
//String a = "2017-8-12";
String a = "2017-08-12 11:10:56";
Date date = Convert.toDate(a);
System.out.println(date);
}
//转换为集合
public static void testToList(){
String[] a = {"1","2","3","4","5"};
List list = Convert.convert(List.class, a);
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
List list1 = Convert.toList(a);
for (Object o : list1) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
2.3 日期时间
2.3.1 日期时间工具DateUtil
public class DateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//now();
//strToDate();
//testFormat();
//testPart();
//testStartAndEnd();
//testOffset();
testBet();
}
//当前时间
public static void now() {
//当前时间Date对象,格式:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
Date date1 = DateUtil.date();
Date date2 = DateUtil.date(Calendar.getInstance());
Date date3 = DateUtil.date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(date1);//2020-11-03 17:08:09
System.out.println(date2);//2020-11-03 17:08:09
System.out.println(date3);//2020-11-03 17:08:09
//当前时间字符串
String now = DateUtil.now();
System.out.println(now);//2020-11-03 17:08:09
//当前日期字符串
String today = DateUtil.today();
System.out.println(today);//2020-11-03
}
//字符串转日期
public static void strToDate() {
/**
* parse会自动识别一些常见的格式,如:
* yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
* yyyy-MM-dd
* HH:mm:ss
* yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm
* yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS
*/
String dateStr = "2018-11-10";
Date date = DateUtil.parse(dateStr);
System.out.println(date);//2018-11-10 00:00:00
//自定义格式
String dateStr2 = "2019*11*10";
Date date2 = DateUtil.parse(dateStr2, "yyyy*MM*dd");
System.out.println(date2);//2019-11-10 00:00:00
}
//格式化日期输出
public static void testFormat() {
//当前时间
Date date = DateUtil.date();
String f1 = DateUtil.format(date, "yyyy/MM/dd");
System.out.println(f1);//2020/11/03
String f2 = DateUtil.formatDate(date);
System.out.println(f2);//2020-11-03
String f3 = DateUtil.formatDateTime(date);
System.out.println(f3);//2020-11-03 17:22:21
String f4 = DateUtil.formatTime(date);
System.out.println(f4);//17:22:21
}
//获取日期的某个部分
public static void testPart() {
//获取当前时间
Date date = DateUtil.date();
//获取年
int year = DateUtil.year(date);
System.out.println(year);
//获取月
int month = DateUtil.month(date);
System.out.println(month);
//获取日
int day = DateUtil.dayOfMonth(date);
System.out.println(day);
//获取时
int hour = DateUtil.hour(date, true);
System.out.println(hour);
//获取分
int minute = DateUtil.minute(date);
System.out.println(minute);
//获取秒
int second = DateUtil.second(date);
System.out.println(second);
//获取月份枚举
Month month1 = DateUtil.monthEnum(date);
System.out.println(month1);//NOVEMBER
}
//开始和结束时间
public static void testStartAndEnd() {
Date date = DateUtil.date();
//获取今天的开始时间和结束时间
Date beginOfDay = DateUtil.beginOfDay(date);
Date endOfDay = DateUtil.endOfDay(date);
System.out.println(beginOfDay);//2020-11-03 00:00:00
System.out.println(endOfDay);//2020-11-03 23:59:59
//获取本月的开始和结束
Date beginOfMonth = DateUtil.beginOfMonth(date);
Date endOfMonth = DateUtil.endOfMonth(date);
System.out.println(beginOfMonth);//2020-11-01 00:00:00
System.out.println(endOfMonth);//2020-11-30 23:59:59
}
//日期时间偏移
public static void testOffset() {
String dateStr = "2018-11-10 18:25:36";
Date date = DateUtil.parse(dateStr);
Date date1 = DateUtil.offset(date, DateField.DAY_OF_MONTH, 2);//往后两天 2018-11-12 18:25:36
System.out.println(date1);
Date date2 = DateUtil.offsetDay(date, 2);//往后两天 2018-11-12 18:25:36
System.out.println(date2);
Date date3 = DateUtil.offsetHour(date, -3);//往前三个小时 2018-11-10 15:25:36
System.out.println(date3);
Date date4 = DateUtil.tomorrow();//明天
System.out.println(date4);
Date date5 = DateUtil.yesterday();//昨天
System.out.println(date5);
}
//日期时间差
public static void testBet(){
String dateStr1 = "2018-11-23 11:23:45";
Date begin = DateUtil.parse(dateStr1);
System.out.println(begin);
String dateStr2 = "2019-09-11 14:28:45";
Date end = DateUtil.parse(dateStr2);
System.out.println(end);
long betDay = DateUtil.between(begin, end, DateUnit.DAY);//天数差
long betHour = DateUtil.between(begin,end,DateUnit.HOUR);//小时差
System.out.println(betDay);//292
System.out.println(betHour);//7011
}
//格式化时间差
public static void formatBet() {
Date begin = DateUtil.parse("2017-11-10 11:23:56");
Date end = DateUtil.parse("2018-09-12 13:36:56");
long bet = DateUtil.betweenMs(begin, end);//不能使用between方法
System.out.println(DateUtil.formatBetween(bet));//306天2小时13分
}
}
2.4 工具类
2.4.1 StrUtil
public class StrUtilTest {
private static final String s1 = null;
private static final String s2 = "";
private static final String s3 = " ";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//testHasEmpty();
//testHasBlank();
//testRemovePrefix();
//testRemoveSuffix();
//testSub();
testFormat();
}
//hasEmpty():判断字符串是否为null或者为""
public static void testHasEmpty() {
System.out.println(StrUtil.hasEmpty(s1));//true
System.out.println(StrUtil.hasEmpty(s2));//true
System.out.println(StrUtil.hasEmpty(s3));//false
}
//hasBlank():判断字符串是否为null或者为""(不可见字符如空格也会被当作空)
public static void testHasBlank() {
System.out.println(StrUtil.hasBlank(s1));//true
System.out.println(StrUtil.hasBlank(s2));//true
System.out.println(StrUtil.hasBlank(s3));//true
}
//removePrefix():去掉前缀
public static void testRemovePrefix() {
String s1 = " ksaioduhf";
System.out.println(StrUtil.removePrefix(s1," "));//ksaioduhf
}
//removeSuffix():去除后缀
public static void testRemoveSuffix() {
String s1 = "lisi.jpg";
System.out.println(StrUtil.removeSuffix(s1,".jpg"));//lisi
}
//sub():截取
public static void testSub() {
String s1 = "abcdefg";
System.out.println("first:"+StrUtil.sub(s1,0,10));//first:abcdefg 不会发生下标越界了
System.out.println("second:"+StrUtil.sub(s1,2,-3));//second:cd -1表示最后一个字符,所以-3是e
System.out.println("third:"+StrUtil.sub(s1,-3,2));//third:cd 自动修正开始位置和结束位置
}
//format():使用字符串模板代替字符串拼接
public static void testFormat() {
String template = "{}爱{},就像老鼠爱大米";
System.out.println(StrUtil.format(template, "我", "你"));
}
}
2.4.2 ObjectUtil
public class ObjectUtilTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//testEqual();
//testLength();
//testContains();
testIsNull();
}
//equal():判断两个对象是否相等
public static void testEqual() {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.equal(s1, s2));//true
}
//length():获取对象长度
public static void testLength() {
String s1 = "abc";
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
List list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.length(s1));//3
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.length(arr));//5
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.length(list));//5
}
//contains():判断对象中是否包含某元素
public static void testContains() {
String s1 = "abc";
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
List list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.contains(s1,"ab"));//true
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.contains(arr,1));//true
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.contains(list,3));//true
}
//isNull() isNotNull():判断是否为空
public static void testIsNull() {
String s1 = null;
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.isNull(s1));//true
System.out.println(ObjectUtil.isNotNull(s1));//false
}
}
2.4.3 MailUtil
想要使用MailUtil,我们需要引入以下依赖:
# gradle
compile group: 'javax.mail', name: 'mail', version: '1.4.7'
# maven
javax.mail
mail
1.4.7
- 使用配置文件的方式
首先在resources下的config目录创建一个mail.setting(properties文件)
# 发件人
[email protected]
# 密码(授权码)
pass=lxidsstlfcfnchgb
接着就可以发送邮件了
//send方法中,第一个参数表示收件人(可以自己发给自己),第二个参数是邮件主题,第三个参数是邮件内容,第四个参数指明是否是html格式,第五个是可选参数,表示要上传的附件,可上传多个
public class MailUtilTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//发送普通邮件,不带附件(true表示html格式,false代表普通格式)
//MailUtil.send("[email protected]","测试","邮箱工具类的测试",false);
//发送带附件的普通邮件
//MailUtil.send("[email protected]","测试","邮箱工具类的测试",true,new File("E:\\111.txt"));
//发送带附件的html邮件
//MailUtil.send("[email protected]","测试","我是html邮件
",true, FileUtil.file("E:\\222.txt"));
//群发邮件
ArrayList list = CollUtil.newArrayList("[email protected]", "\n" +
"[email protected]");
MailUtil.send(list,"hutool测试","嘿嘿额hi",false, FileUtil.file("E:\\111.txt"));
}
}
- 使用java代码发送邮件
public class MailUtilTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MailAccount mailAccount = new MailAccount();
mailAccount.setFrom("[email protected]");//设置发件人
mailAccount.setPass("lxidsstlfcfnchgb");//密码(授权码)
MailUtil.send(mailAccount,"[email protected]","测试","hutool的测试内容",false, FileUtil.file("E:\\111.txt"));
}
}
2.4.4 QrcodeUtil(二维码工具)
首先引入依赖
# gradle
compile group: 'com.google.zxing', name: 'core', version: '3.3.3'
# maven
com.google.zxing
core
3.3.3
- 生成二维码
//第一个参数是url,第二个参数和第三个参数是宽和高,第三个参数是生成的二维码路径
QrCodeUtil.generate("https://blog.csdn.net/ilove_story/article/details/108027025",300,300, FileUtil.file("E:\\blog.jpg"));
- QrConfig自定义参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
//QrCodeUtil.generate("https://blog.csdn.net/ilove_story/article/details/108027025",300,300, FileUtil.file("E:\\blog.jpg"));
QrConfig config = new QrConfig();
config.setMargin(3);//设置边距
config.setForeColor(Color.CYAN);//设置前景色
config.setBackColor(Color.GRAY);//设置背景色
config.setImg("D:\\下载\\迅雷下载\\图片\\circle03.jpg");//设置logo小图标
QrCodeUtil.generate("https://blog.csdn.net/ilove_story/article/details/108027025",config, FileUtil.file("E:\\blog4.jpg"));
}
2.4.5 CaptchaUtil(验证码工具类)
- 生成线条干扰的验证码(LineCaptcha)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义验证码的长和宽
LineCaptcha lineCaptcha = CaptchaUtil.createLineCaptcha(200, 100);
//将验证码写入文件
lineCaptcha.write(FileUtil.file("E:\\check.jpg"));
//输出code
System.out.println(lineCaptcha.getCode());//zwqno
//校验
if (!lineCaptcha.verify("1234")){
//重新生成验证码
lineCaptcha.createCode();
System.out.println(lineCaptcha.getCode());//3m4l6
//写入
lineCaptcha.write(FileUtil.file("E:\\check.jpg"));
}
}
- 生成圆圈干扰的验证码(CircleCaptcha)
CircleCaptcha circleCaptcha = CaptchaUtil.createCircleCaptcha(200, 100);
circleCaptcha.write(FileUtil.file("E:\\circle.jpg"));
- 生成扭曲干扰验证码(ShearCaptcha)
//四个参数分别为宽、高、字符数、干扰线宽度
ShearCaptcha shearCaptcha = CaptchaUtil.createShearCaptcha(200, 100, 4, 4);
shearCaptcha.write(FileUtil.file("E:\\shear.jpg"));