Springboot源码学习-启动流程
程序入口
1、spring boot应用入口,启动类中调用SpringApplication.run方法,方法参数中可以传入启动类,也可以传入其他配置类。
示例所传入的配置类为启动类,也就是主类。
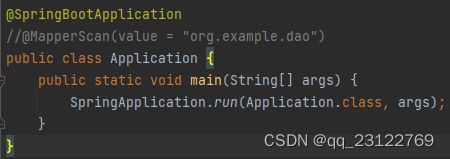
2、跟踪run方法,该方法返回的是一个ConfigurableApplicationContext对象,并且其内部创建了一个SpringApplication对象,然后调用了它的run方法。
ConfigurableApplicationContext:可配置的应用程序上下文,是一个接口,此处返回的是它的一个实现类对象。
可以将返回的这个context理解成Spring的IOC容器,我们可以通过其getBean方法获取到Bean。
IOC:控制反转,将对象的创建、管理和销毁等工作(即控制权)交给Spring容器,而不是开发者;开发者使用时只需要从容器中获取即可。
Bean:可以简单理解为交由Spring容器创建、组装和管理的Java对象。

3、看看SpringApplication的构造方法主要做了什么,注释版代码如下:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//通过判断classpath中是否能加载到指定的类,来推断当前web应用类型,最终返回为WebApplicationType.SERVLET。
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//读取classpath下所有META-INF目录下的spring.factories文件,实例化其中配置的BootstrapRegistryInitializer对象。
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
//同上,读取spring.factories文件,实例化其中配置的ApplicationContextInitializer对象。
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//同上,读取spring.factories文件,实例化其中配置的ApplicationListener对象。
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//通过堆栈信息中main方法的调用信息,推断应用主类,比如示例工程的启动类Application。
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
具体分析:
1)deduceFromClasspath方法,通过判断classpath中是否能加载到指定的类,来推断当前web应用类型。
2)三个getSpringFactoriesInstances(xxx.class)方法,均扫描classpath下所有META-INF目录下的spring.factories文件(这些文件中包含了当前库需要告知spring的属性信息),然后实例化相关的对象。包括:
- BootstrapRegistryInitializer,引导注册表初始化器,此处结果为空,暂不关注;
- ApplicationContextInitializer,应用上下文,也就是Spring容器初始化器(不同的初始化器中封装了各自对Spring容器的初始化操作);
- ApplicationListener,应用程序监听器。
通过debug可以看到此次加载到的是下图中两个spring.factories文件中的ApplicationContextInitializer配置:

4、SpringApplication对象实例化后,进入其run方法,核心操作包括:创建容器、准备容器、刷新容器。

接下来重点分析这三个关于Spring容器的方法。
创建容器
调用createApplicationContext方法,创建一个ConfigurableApplicationContext接口实现类的对象作为Spring容器。
SpringApplication类中有一个接口类型的成员变量:applicationContextFactory
private ApplicationContextFactory applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT;
ApplicationContextFactory是一个函数式接口,applicationContextFactory是该接口的默认实现(lambda表达式形式),createApplicationContext方法中,就是调用了applicationContextFactory的create方法,执行了这个默认的实现,返回了一个AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类型的实例,这个类是ConfigurableApplicationContext接口的实现类,也是我们容器的实际类型。
ApplicationContextFactory接口部分代码如下:

准备容器
prepareContext方法源码如下:
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//使用之前设置的所有ApplicationContextInitializer,对容器进行初始化
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
//获取该容器的beanFactory,并注册引导专用的单例bean
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
//默认关闭循环引用,即循环依赖
((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
//加载来源,这里拿到的是示例代码主类"org.example.Application"
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//装载bean到容器中
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
其中有两个比较关键的地方:
1、ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
这里开始出现一个ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口类型的变量,它可以通过context.getBeanFactory()方法获取到。
追踪源码,发现context中确实有一个该类型的成员变量,叫beanFactory,它是在context实例化过程中,由context父类的构造函数进行实例化的,实际类型为DefaultListableBeanFactory。源码如下:

2、load方法,装载bean到容器中。
1)该方法内部,首先调用createBeanDefinitionLoader方法,创建了一个BeanDefinitionLoader。该方法需要一个BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的入参。这里通过getBeanDefinitionRegistry方法强转context后传入参数。创建完loader后,又继续调用其load方法。
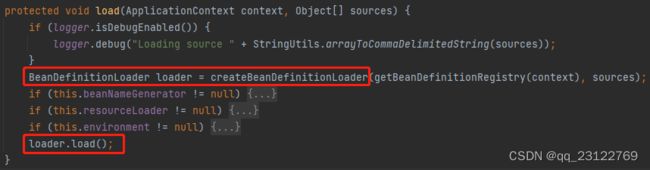
BeanDefinitionRegistry:bean定义信息注册表接口,提供BeanDefinition注册相关的操作。
BeanDefinition:描述bean信息的最小接口。
context所属的AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类,以及其成员beanFactory所属的DefaultListableBeanFactory类,均实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口。
2)继续跟进load方法,直到进入AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader类的doRegisterBean方法。
这里主要进行了以下操作:
- 根据提供的配置类(这里是启动类,即主类),创建一个带有标准注解元数据(StandardAnnotationMetadata)的bean definition,这里是一个AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition类的对象;
- 生成与bean definition对应的beanName;
- 处理@Lazy、@Primary、@DependsOn等通用注解,设置bean definition对应属性值;其中用到了AnnotationsScanner类的相关方法扫描注解;
- 调用BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition方法,注册bean definition。
private <T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> beanClass, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, @Nullable Supplier<T> supplier,
@Nullable BeanDefinitionCustomizer[] customizers) {
//创建一个带有标准注解元数据(StandardAnnotationMetadata)的bean definition
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(beanClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(supplier);
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
//生成beanName
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
//处理@Lazy、@Primary、@DependsOn等通用注解,设置bean definition相关属性值
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
//...
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
//注册bean definition
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
3)进入BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition方法,最终调用的是registry.registerBeanDefinition,也就是DefaultListableBeanFactory类中的registerBeanDefinition方法。
注册bean definition的核心操作,就是在DefaultListableBeanFactory类的成员变量beanDefinitionMap和beanDefinitionNames中添加bean definition信息。

这里可以看到,除了刚注册的"application"这个bean definition,有5个bean definition已经存在了,它们是在application context的构造方法中创建reader的过程中注册的:

BeanDefinition的大致结构如下:

到这里,准备容器工作完成。主要就是从容器中获取beanFactory,并为主类构建一个beanDefinition,生成beanName,然后调用beanFactory的registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition),完成主类BeanDefinition的注册(将beanName、beanDefinition放入beanFactory中相关的集合里)。
刷新容器
跟踪refreshContext(context)方法,直到进入到AbstractApplicationContext类的refresh()方法中,部分源码如下:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//准备好要刷新的上下文,设置它的启动日期和活动标志,以及执行所有属性源的初始化。
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//获得新鲜的bean factory,这里是通知子类刷新内部的bean factory。
//实际子类中实现的刷新操作是设置了bean factory的serializationId为配置类(即主类)的beanName。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//配置bean factory的标准上下文特征,比如类加载器 class loader,以及一些后置处理器 post processor。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
//允许context对bean factory 做一些处理。
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor,包括配置类解析,注册、修改bean definition等。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//实例化BeanPostProcessor对象,添加到bean factory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
//启动web server,默认tomcat
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//实例化剩余的非懒初始化的单例bean,完成bean factory的初始化
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
//...
}
finally {
//...
}
}
}
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
配置bean factory的标准上下文特征,比如类加载器 class loader,以及一些后置处理器 post processor。
BeanPostProcessor:bean后置处理器接口。允许在bean初始化之前或之后对bean进行自定义修改,也就是postProcess操作。
通过debug可以看到配置结果:

invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor,包括配置类解析,注册、修改bean definition等。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor:bean factory后置处理器接口,允许对bean definition进行自定义修改。
1)进入PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法。
通过debug可以看到,容器中已经存在两个BeanFactoryPostProcessor:
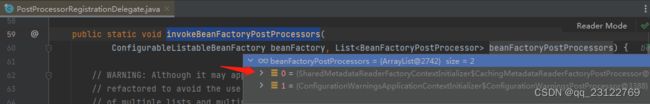
这两个BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在容器准备阶段,执行applyInitializers(context),应用各种初始化器的时候被添加进去的。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法总体来说,就是先调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 注册 bean definition,其中最重要的是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor对配置类的解析(以启动类为入口);然后调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor,对 bean definition做相关的处理。部分源码如下:
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//先处理一波现有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子接口)
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//获取bean factory中 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 类型的bean definition;
//这里最终找到的是 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 配置类后处理器。
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//优先处理实现了PriorityOrdered接口的post processor
//获取ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实例
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//核心:调用ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,处理配置bean。
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
//再次获取bean factory中 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 类型的bean definition,这次处理实现Ordered接口的。
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
//最后循环处理完剩下的,以及可能再创建的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
//对处理过的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,调用其postProcessBeanFactory方法。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
//按照优先级处理剩下的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor:继承BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,允许在BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的方法回调之前,使用此接口来添加新的bean definition。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor处理配置类的过程
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
//遍历bean factory中的bean definition
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
//检查是否是配置类,这里只有主类符合要求(@SpringBootApplication注解内包含@Configuration注解)
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
//构建配置类解析器
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
StartupStep processConfig = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.config-classes.parse");
//解析候选的BeanDefinitionHolder(BeanDefinitionHolder保存了beanDefinition和beanName)
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
processConfig.tag("classCount", () -> String.valueOf(configClasses.size())).end();
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate方法源码如下:
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate(
BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) {
String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName();
if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return false;
}
AnnotationMetadata metadata;
if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition &&
className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) {
// Can reuse the pre-parsed metadata from the given BeanDefinition...
//拿到注解元数据
metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata();
}
else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) {
// Check already loaded Class if present...
// since we possibly can't even load the class file for this Class.
Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass();
if (BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
EventListenerFactory.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass)) {
return false;
}
metadata = AnnotationMetadata.introspect(beanClass);
}
else {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className);
metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " +
className, ex);
}
return false;
}
}
//通过注解元数据获取@Configuration注解的属性,其中使用了AnnotationsScanner.scan方法进行注解扫描。
Map<String, Object> config = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(Configuration.class.getName());
if (config != null && !Boolean.FALSE.equals(config.get("proxyBeanMethods"))) {
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL);
}
else if (config != null || isConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) {
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE);
}
else {
return false;
}
// It's a full or lite configuration candidate... Let's determine the order value, if any.
Integer order = getOrder(metadata);
if (order != null) {
beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order);
}
return true;
}
沿着parser.parse(candidates)方法往下走,直到processConfigurationClass:
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate<String> filter) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
if (existingClass != null) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
if (existingClass.isImported()) {
existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
}
// Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.
return;
}
else {
// Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.
// Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.
this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
}
}
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);
do {
//处理配置类
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
//处理完之后添加到配置类集合中
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
doProcessConfigurationClass方法中包含处理配置类的核心逻辑:
@Nullable
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
//如果配置类注解元数据中包含@Component注解,则优先递归处理它的内部类。此处同样使用了AnnotationsScanner.scan方法进行注解扫描。
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
//处理@PropertySource注解,加载属性配置
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
//扫描并拿到@ComponentScan注解的属性。
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
/*
解析@ComponentScan注解属性,扫描目标package下的.class文件,拿到其注解元数据,然后根据排除和包含的规则(比如排除主类,
包含@Component注解等)筛选出候选组件类,创建对应的BeanDefinition,将组装成的BeanDefinitionHolder放入返回集合,最后在
bean工厂中注册BeanDefinition。
*/
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
//检查扫描到的组件类是否有进一步的配置注解,如果有则进行递归解析
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
//处理@Import注解
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
//检索@Bean注解的方法,添加到ConfigurationClass对象中。
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
getImports(sourceClass),递归查找。
private void collectImports(SourceClass sourceClass, Set<SourceClass> imports, Set<SourceClass> visited)
throws IOException {
if (visited.add(sourceClass)) {
//以主类为例,拿到注解信息后遍历,首层只有一个@SpringBootApplication
for (SourceClass annotation : sourceClass.getAnnotations()) {
//获取注解类名
String annName = annotation.getMetadata().getClassName();
//判断是否是Import,不是则继续往下一层找
if (!annName.equals(Import.class.getName())) {
//递归入口
collectImports(annotation, imports, visited);
}
}
//扫描当前sourceClass的@Import注解,拿到value属性,再把属性值组装成sourceClass,放进imports集合
imports.addAll(sourceClass.getAnnotationAttributes(Import.class.getName(), "value"));
}
}
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
private void processImports(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass,
Collection<SourceClass> importCandidates, Predicate<String> exclusionFilter,
boolean checkForCircularImports) {
if (importCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (checkForCircularImports && isChainedImportOnStack(configClass)) {
this.problemReporter.error(new CircularImportProblem(configClass, this.importStack));
}
else {
this.importStack.push(configClass);
try {
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
/*
如果实现ImportSelector接口,实例化这个selector,调用getExclusionFilter拿到它的exclusionFilter(排除过滤器,lambda
表达式形式),然后跟传进来的默认exclusionFilter组成or的关系,有一个成立即成立。这个排除规则在调用类似asSourceClass方
法对配置类进行包装时生效。
*/
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportSelector selector = ParserStrategyUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class,
this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
Predicate<String> selectorFilter = selector.getExclusionFilter();
if (selectorFilter != null) {
exclusionFilter = exclusionFilter.or(selectorFilter);
}
//如果实现DeferredImportSelector接口,则把这个selector先存起来,推迟处理
if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector);
}
else {
String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames, exclusionFilter);
processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, exclusionFilter, false);
}
}
//判断是否实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,如果是的话,实例化这个registrar对象,绑定到当前配置类,后续会用它来注册bean definition
else if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// delegate to it to register additional bean definitions
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar registrar =
ParserStrategyUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class,
this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
configClass.addImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(registrar, currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
}
//既不是ImportSelector,也不是ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,按配置类处理。
else {
// Candidate class not an ImportSelector or ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// process it as an @Configuration class
this.importStack.registerImport(
currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName());
processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass), exclusionFilter);
}
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" +
configClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex);
}
finally {
this.importStack.pop();
}
}
}
当processConfigurationClass方法结束,也就是主配置类处理完毕,回到parser.parse方法中,我们自己编写的配置类已经都解析到了,但是我们依赖的第三方自动配置类还没有处理。这时用到刚才保存起来的 ImportSelector,导入自动配置类。
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
public void process() {
List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors;
this.deferredImportSelectors = null;
try {
if (deferredImports != null) {
DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler();
deferredImports.sort(DEFERRED_IMPORT_COMPARATOR);
deferredImports.forEach(handler::register);
handler.processGroupImports();
}
}
finally {
this.deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
handler.processGroupImports();
public void processGroupImports() {
for (DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping : this.groupings.values()) {
Predicate<String> exclusionFilter = grouping.getCandidateFilter();
//此时这个AutoConfigurationImportSelector内部的AutoConfigurationGroup对象里的条目是空的,需要通过getImports()来获取。
grouping.getImports().forEach(entry -> {
ConfigurationClass configurationClass = this.configurationClasses.get(entry.getMetadata());
try {
//处理每个条目记录的ImportClass,也就是引入的自动配置类,可能会再进入processConfigurationClass方法进行解析。
processImports(configurationClass, asSourceClass(configurationClass, exclusionFilter),
Collections.singleton(asSourceClass(entry.getImportClassName(), exclusionFilter)),
exclusionFilter, false);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" +
configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex);
}
});
}
}
grouping.getImports()
public Iterable<Group.Entry> getImports() {
for (DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport : this.deferredImports) {
this.group.process(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getImportSelector());
}
return this.group.selectImports();
}
this.group.process(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getImportSelector());
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) {
Assert.state(deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector,
() -> String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s",
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(),
deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName()));
//获取自动配置类条目
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector) deferredImportSelector)
.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry);
for (String importClassName : autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()) {
this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata);
}
}
((AutoConfigurationImportSelector) deferredImportSelector).getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata)
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
//读取META-INF/spring.factories文件(这里读了缓存)中EnableAutoConfiguration属性值,这里拿到135个配置类
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
/*
getConfigurationClassFilter()读取spring.factories中的AutoConfigurationImportFilter属性值,拿到了3个过滤器:
OnWebApplicationCondition,对应@ConditionalOnWebApplication注解;
OnClassCondition,对应@ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnMissingClass注解;
OnBeanCondition,对应@ConditionalOnBean、@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate、@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解。
然后对刚才的135个配置类进行过滤。
调用filter方法,通过过滤器筛选出最终符合要求的自动配置类。比如OnClassCondition过滤器,就是用来判断某个类是否存在;他会检查配置类是否有@ConditionalOnClass(value=XXX)这种注解;如果它有这个注解,但是它所依赖的XXX类不存在,那么这个配置类就会被过滤掉。
这里最终过滤之后剩下了32个自动配置类。
*/
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
getImports方法获取到的Entry结构如下图:

随着引入的自动配置类逐个解析完毕,parser.parse方法结束,配置类解析完毕。接下来需要利用这些配置类进行bean definition的注册,
也就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions方法中的这一行:this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
具体逻辑在下面这个方法中:
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) {
if (trackedConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass)) {
String beanName = configClass.getBeanName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
this.registry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
this.importRegistry.removeImportingClass(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
return;
}
//如果是被引入的,直接注册bean definition
if (configClass.isImported()) {
registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass);
}
//如果有@Bean方法,对方法进行解析(包括方法注解、方法名等),利用这些信息注册bean definition
for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) {
loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod);
}
//通过导入的资源文件注册bean definition
loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources());
/*
通过注册器注册bean definition,比如之前启动类@AutoConfigurationPackage注解中包含的
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)注解,引入的就是一个ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
*/
loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars());
}
顺带看下刚才引入的AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar:
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
/*
PackageImports构造方法中,解析当前配置类(这里是启动类)的@AutoConfigurationPackage注解属性,设置packageNames,如果没有值就用当前配置类所在的包名。
register方法注册一个名为"org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationPackages"的 bean definition,用来保存这些自动配置包路径名。
*/
register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImports(metadata));
}
}
到这里,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的处理基本就结束了,后续还会处理一些其他的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 和 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
这一步主要是从bean factory 中找到类型为BeanPostProcessor 的bean definition,然后进行实例化和初始化,得到BeanPostProcessor对象,添加到bean factory中。
onRefresh();
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
//启动web服务(默认tomcat)
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
初始化剩余的单例bean,完成bean factory的初始化。详情转到Spring boot启动流程-bean的实例化和初始化
doGetBean
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object beanInstance;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
//getSingleton,先尝试从缓存中获取已经实例化的单例bean,这里也允许为正在创建中的bean提供一个早期访问的引用(解决循环依赖)。
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
//如果bean没有获取到,则在这里判断是否满足:父工厂存在且当前工厂中没有对应的bean definition;
//如果满足,则在父工厂中查找;
//如果不满足,则先确保当前bean所依赖的bean已经初始化,然后再创建当前bean实例。
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
StartupStep beanCreation = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.beans.instantiate")
.tag("beanName", name);
try {
if (requiredType != null) {
beanCreation.tag("beanType", requiredType::toString);
}
//RootBeanDefinition,本质上是Spring BeanFactory运行时的统一bean definition视图
//获取merged bean definition,所谓的merged,是检查当前bean definition是否为子bean definition,如果是的话需要与父bean definition进行合并。
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
//确保当前bean所依赖的bean已经初始化完毕
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.(创建bean实例)
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new ScopeNotActiveException(beanName, scopeName, ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
beanCreation.tag("exception", ex.getClass().toString());
beanCreation.tag("message", String.valueOf(ex.getMessage()));
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
finally {
beanCreation.end();
}
}
return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);
}
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
getSingleton重载方法 -> createBean
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
//实例化之前,给BeanPostProcessors一个机会来返回一个目标bean实例的代理,需要实现InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口。
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
createBean -> doCreateBean:
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//实例化bean
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
//调用BeanPostProcessor,解析@Autowire,@Resource等注解?
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references(提前缓存单例以解决循环引用问题)
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
//获取对bean进行早期访问的引用,添加到bean factory的singletonFactories变量中。
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.(初始化bean)
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
doCreateBean -> createBeanInstance
createBeanInstance -> instantiateBean:
populateBean:
instantiateBean
instantiate
instantiateClass
populateBean
initializeBean
adaptBeanInstance