vue中全局状态存储 pinia和vuex对比 pinia比vuex更香 Pinia数据持久化及数据加密
前言
毕竟尤大佬都推荐使用pinia,支持vue2和vue3!
如果熟悉vuex,花个把小时把pinia看一下,就不想用vuex了
- 支持选项式api和组合式api写法
- pinia没有mutations,只有:state、getters、actions
- pinia分模块不需要modules
- pinia 没有命名空间模块。
- pinia 无需动态添加(底层通过 getCurrentInstance 获取当前 vue 实例进行关联)。
- pinia 是平面结构(利于解构),没有嵌套,可以任意交叉组合。

先介绍两个官网:
pinia官网
保持pinia的数据持久化用pinia-plugin-persistedstate (推荐使用这个,其他的也可以,如:pinia-plugin-persist可能会遇到bug)
pinia-plugin-persistedstate 官网
如果需要对本地存储加密的话使用 secure-ls 插件:原理是重构localStorage 和 sessionStorage 的setItem和getItem方法,同理vuex里面也可以使用
secure-ls 网址
安装
npm install pinia pinia-plugin-persistedstate
创建store
在根目录下创建store文件夹,新建index.ts文件
import { createPinia } from 'pinia';
import createPersistedState from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'; //引入pinia数据持久化插件
const pinia = createPinia();
pinia.use(createPersistedState);
export default pinia;
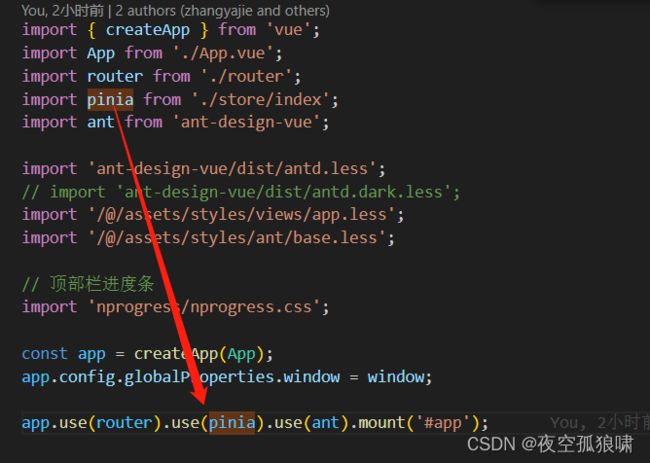
挂载
Pinia数据持久化及数据加密
这里使用的pinia数据的持久化,和本地加密存储
pinia中不在用modules分模块,简单理解一个ts文件一个模块吧,注意每个模块尽量统一风格,导出变量use开头
下面是个示例:
store文件夹中的 counter.ts 这里用到了,数据持久化和数据加密
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; // 定义一个pinia的一个模块
//这里是练习pinia用的
import type { StorageLike } from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate';
import SecureLS from 'secure-ls';
// encryptionSecret:自定义密钥
const ls = new SecureLS({
isCompression: false,
encryptionSecret: '38c31684-d00d-30dc-82e0-fad9eec46d1d',
});
const st: StorageLike = {
setItem(key: string, value: string) {
ls.set(key, value);
},
getItem(key: string): string | null {
return ls.get(key);
},
};
//'第一个参数是id标识,pinia的名字','第二个参数是个对象'
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => {
return {
count: 10,
msg: '菠萝头的使用',
price: 100,
};
},
actions: {
add() {
this.count += 1;
},
del() {
this.count -= 1;
},
promiseIncrement() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.count++;
resolve(this.count);
}, 1000);
});
},
priceAdd(a: any, b: any) {
console.log(a, b);
this.price++;
},
},
getters: {
getCount(state) {
//在使用时,把方法名当属性用就行
return state.count * state.price;
},
},
// persist: true, 默认存储在 localStorage上面的
persist: {
storage: st, // 上面申明的类型
// storage: localStorage,
// key: 'counter',
},
});
moduleIdentifiers.ts文件,无加密
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
let moduleIdentifiers: Array<String> = [];
export const useModuleIdentifiers = defineStore('moduleIdentifiers', {
state: () => {
return {
moduleIdentifiers,
};
},
actions: {
setModuleIdentifiers(aside: Array<String>) {
this.moduleIdentifiers = aside;
},
},
getters: {},
persist: true,
// persist: {
// storage: localStorage,
// },
});
页面中使用
<template>
<a-layout class="layout">
<Header />
<a-layout-content class="main-container">
<a-button @click="back">返回上一页</a-button>
<div class="title">
<h1>pinia</h1>
<div class="button-box">
<a-button type="primary" @click="test">去练习vuex</a-button>
<a-button type="primary" @click="changePina(1)">add同步</a-button>
<a-button type="primary" @click="changePina(2)">promise异步</a-button>
<a-button type="primary" @click="changePina(3)">test</a-button>
<a-button type="primary" @click="changePina(5)">$patch</a-button>
<a-button type="primary" @click="changePina(6)">getters</a-button>
<a-button type="primary" @click="changePina(4)">reset</a-button>
</div>
</div>
<div class="card">
<a-button>stata.count: {{ count }}</a-button>
<a-button>stata.msg: {{ msg }}</a-button>
<a-button>stata.price: {{ price }}</a-button>
</div>
</a-layout-content>
</a-layout>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { reactive, computed } from 'vue';
import { useRouter } from 'vue-router';
import Header from '/@/components/Header/index.vue';
import { useCounterStore } from '/@/store/counter';
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia';
let pinia = useCounterStore();
//使用storeToRefs解构保持响应性,当然也可以直接结构,根据具体情况而定
let { count, price, msg, getCount } = storeToRefs(pinia);
// const count = computed(() => pinia.count)
const changePina = (type: number) => {
if (type == 1) {
pinia.add();
} else if (type == 2) {
pinia.promiseIncrement();
} else if (type == 3) {
pinia.priceAdd(1, 2);
} else if (type == 4) {
pinia.$reset();
} else if (type == 5) {
pinia.$patch((state) => {
state.count += 2;
state.price += 2;
state.msg = '$patch批量修改';
});
} else if (type == 6) {
console.log(pinia.getCount);
//如果想使用解构,一定要用 storeRoRefs
console.log(getCount);
}
};
const router = useRouter();
const test = () => {
router.push('/ncov/test');
};
const back = () => {
router.push('/ncov/task');
};
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.layout {
min-width: 1400px;
min-height: 100vh;
}
.main-container {
flex-direction: row;
min-height: calc(100vh - 76px);
padding: 19px 70px;
background-color: @bg-color;
}
.title {
font-weight: 600;
font-size: 24px;
margin: 30px 0;
.flex-type(space-between);
:deep(.ant-btn) {
margin-left: 10px;
}
}
.card {
background-color: @white-color;
padding: 30px;
:deep(.ant-btn) {
margin-left: 10px;
}
}
.select-box {
margin-bottom: 40px;
.flex-type(flex-start);
:deep(.ant-select) {
width: 120px;
margin-right: 40px;
}
}
:deep(.ant-cascader-menu-item:hover) {
background: @bg-color;
}
:deep(.ant-input:focus, .ant-input:hover, .ant-cascader-input:hover) {
border-color: rgba(122, 132, 198, 1);
}
</style>
详情解析
上面的代码已经包含了 State、Getters、Actions(同步/异步)、$reset、$patch、
State:存数据
Getters:计算属性
Actions:更改state的值
$reset:重置state到最初状态
$patch:批量修改state的值
其他还有替换所有state的值等,参考官网