LeetCode 热题100道(中等题整理)
1. 两数相加

示例:
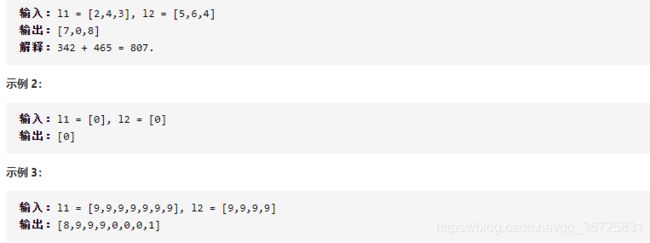
分析:
老实人本来准备把两个链表转成整型相加再转回链表,被[1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1]教做人了,unsigned long都顶不住…
注意链表是实际数字的逆序,所以可以直接遍历相加,注意进位就行。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
int carry = 0;
ListNode *sumList = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *sumNode = sumList;
while (l1 != nullptr || l2 != nullptr){
int x = l1 != nullptr ? l1->val : 0;
int y = l2 != nullptr ? l2->val : 0;
int sum = x + y + carry;
if(sum >= 10){
carry = 1;
sum = sum - 10;
}else{
carry = 0;
}
sumNode->next = new ListNode(sum);
l1 = l1 != nullptr ? l1->next : nullptr;
l2 = l2 != nullptr ? l2->next : nullptr;
sumNode = sumNode->next;
}
if(carry != 0){
sumNode->next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return sumList->next;
}
};
执行用时:24 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了93.87%的用户
内存消耗:69.4 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了62.48%的用户
2. 无重复字符的最长子串
示例:

分析:
滑动窗口,判断重复字符,可以用unorderd_set,也可以遍历查找。
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int start = 0, end = 0;
int len = s.size();
int max_count = 0, temp_count = 0;
char temp_char;
while(end < len){
temp_char = s[end];
for(int i = start; i < end; i++){
//出现重复字符,开始位置移到重复的下一位
if(temp_char == s[i]){
start = i + 1;
break;
}
}
end++;
temp_count = end -start;
max_count = max(max_count , temp_count);
}
return max_count;
}
};
执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了97.69%的用户
内存消耗:6.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了91.11%的用户
用哈希,std::unordered_set
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
// 哈希集合,记录每个字符是否出现过
unordered_set<char> occ;
int n = s.size();
// 右指针,初始值为 -1,相当于我们在字符串的左边界的左侧,还没有开始移动
int rk = -1, ans = 0;
// 枚举左指针的位置,初始值隐性地表示为 -1
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i != 0) {
// 左指针向右移动一格,移除一个字符
occ.erase(s[i - 1]);
}
while (rk + 1 < n && !occ.count(s[rk + 1])) {
// 不断地移动右指针
occ.insert(s[rk + 1]);
++rk;
}
// 第 i 到 rk 个字符是一个极长的无重复字符子串
ans = max(ans, rk - i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
};
3. 最长回文子串
回文的意思是正着念和倒着念一样,如:上海自来水来自海上
法一:翻转字符串求公共串,结果超时了…
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
if(s.length()==1) return s;//大小为1的字符串必为回文串
string rev=s;//rev存放s反转结果
string res;//存放结果
std::reverse(rev.begin(),rev.end());
if(rev==s) return s;
int len=0;//存放回文子串的长度
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)//查找s与rev的最长公共子串
{
string temp;//存放待验证子串
for(int j=i;j<s.length();j++)
{
temp=temp+s[j];
if(len>=temp.length())
continue;
else if(rev.find(temp)!=-1)//在rev中找到temp
{
string q=temp;//q用来验证temp是否是回文子串
std::reverse(q.begin(),q.end());
if(q==temp)
{
len=temp.length();
res=temp;
}
}
else break;
}
temp="";
}
return res;
}
};
法二 : 中心扩展法,(传参用引用效率高)
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int len=s.size();
if(len==0||len==1)
return s;
int start=0;//记录回文子串起始位置
int end=0;//记录回文子串终止位置
int mlen=0;//记录最大回文子串的长度
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int len1=expendaroundcenter(s,i,i);//一个元素为中心
int len2=expendaroundcenter(s,i,i+1);//两个元素为中心
mlen=max(max(len1,len2),mlen);
if(mlen>end-start+1)
{
start=i-(mlen-1)/2;
end=i+mlen/2;
}
}
return s.substr(start,mlen);
//该函数的意思是获取从start开始长度为mlen长度的字符串
}
private:
int expendaroundcenter(string &s,int left,int right)
//计算以left和right为中心的回文串长度
{
int L=left;
int R=right;
while(L>=0 && R<s.length() && s[R]==s[L])
{
L--;
R++;
}
return R-L-1;
}
};
法三 : 动态规划
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int len=s.size();
if(len==0||len==1)
return s;
int start=0;//回文串起始位置
int max=1;//回文串最大长度
vector<vector<int>> dp(len,vector<int>(len));//定义二维动态数组
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)//初始化状态
{
dp[i][i]=1;
if(i<len-1&&s[i]==s[i+1])
{
dp[i][i+1]=1;
max=2;
start=i;
}
}
for(int l=3;l<=len;l++)//l表示检索的子串长度,等于3表示先检索长度为3的子串
{
for(int i=0;i+l-1<len;i++)
{
int j=l+i-1;//终止字符位置
if(s[i]==s[j]&&dp[i+1][j-1]==1)//状态转移
{
dp[i][j]=1;
start=i;
max=l;
}
}
}
return s.substr(start,max);//获取最长回文子串
}
};
4. 盛最多水的容器

分析:
双指针法:
水量 = 两个指针指向的数字中较小值∗指针之间的距离
理解:双指针代表的是 可以作为容器边界的所有位置的范围。在一开始,双指针指向数组的左右边界,表示 数组中所有的位置都可以作为容器的边界,因为我们还没有进行过任何尝试。在这之后,我们每次将 对应的数字较小的那个指针 往 另一个指针 的方向移动一个位置,就表示我们认为 这个指针不可能再作为容器的边界了。
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int left = 0, right = height.size() - 1;
int max_area = 0, temp_area = 0;
while(left < right){
temp_area = (right - left) * min(height[left], height[right]);
max_area = max(max_area, temp_area);
if(height[left] < height[right]){
left++;
}else{
right--;
}
}
return max_area;
}
};
5. 三数之和
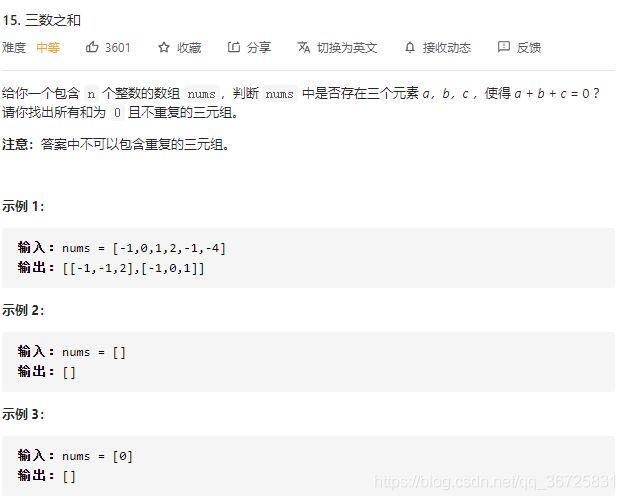
分析:
方法:首先确定一个数,然后利用双指针去找另外的两个数,注意一些去重的判断。
四数之和方法类似,固定两个数。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(len < 3)
return res;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
//固定第一个数为nums[i]
for(int i = 0; i <len ; i++){
// 第一个数大于 0,后面都是递增正数,不可能相加为零了
if(nums[i] > 0){
return res;
}
// 第一个数相同,pass
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){
continue;
}
//双指针法
int left = i + 1, right = len -1;
while(left < right){
if(nums[left] + nums[right] + nums[i] > 0){
right--;
}
else if(nums[left] + nums[right] + nums[i] < 0){
left++;
}
else{
res.push_back(vector<int>{nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]});
left++;
right--;
//第一个数固定后,第二个数和第三个数去重
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left-1]){
left++;
}
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right+1]){
right--;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};

