(k8s日志收集)kubernetes守护进程方式部署filebeat收集k8s集群容器日志elasticsearch+kibana+filebeat
文章目录
- 前言
- 部署filebeat
- 登录kibana查看日志
- 总结
前言
上篇文章讲了使用ECK部署Kubernetes使用ECK部署Elasticsearch8.0和Kibana集群(k8s)
这篇文章见如何使用filebeat收集k8s容器pod日志
部署filebeat
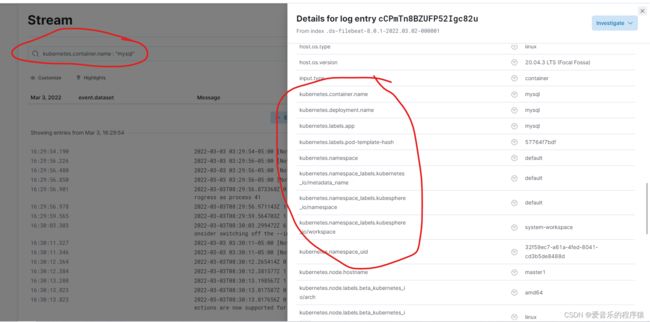
首先先要明白k8s容器日志默认存储路径是/var/log/containers/
部署方式有三种
一是可以通过直接linux系统部署方式,收集/var/log/containers/目录下k8s容器日志,每个节点都有这个目录
二是docker容器运行filebeat,并挂载/var/log/containers数据卷,这样也能收集日志
三是在k8s上使用守护进程的方式保证每个节点都运行一个filebeat实列,并且挂在数据卷/var/log/containers,类型是hostpath
这里我们采用第三种方式,也比较方便统一管理
根据官方文档https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/current/running-on-kubernetes.html
官方已经为我们提供了响应的yml文件,只需要在其基础上修改即可
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: filebeat-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
data:
filebeat.yml: |-
filebeat.inputs:
- type: container
paths:
- /var/log/containers/*.log
processors:
- add_kubernetes_metadata:
host: ${NODE_NAME}
matchers:
- logs_path:
logs_path: "/var/log/containers/"
# To enable hints based autodiscover, remove `filebeat.inputs` configuration and uncomment this:
#filebeat.autodiscover:
# providers:
# - type: kubernetes
# node: ${NODE_NAME}
# hints.enabled: true
# hints.default_config:
# type: container
# paths:
# - /var/log/containers/*${data.kubernetes.container.id}.log
processors:
- add_cloud_metadata:
- add_host_metadata:
cloud.id: ${ELASTIC_CLOUD_ID}
cloud.auth: ${ELASTIC_CLOUD_AUTH}
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ['${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:elasticsearch}:${ELASTICSEARCH_PORT:9200}']
username: ${ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME}
password: ${ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD}
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: filebeat
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
serviceAccountName: filebeat
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
hostNetwork: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
containers:
- name: filebeat
image: docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:8.0.1
args: [
"-c", "/etc/filebeat.yml",
"-e",
]
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_HOST
value: elasticsearch
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_PORT
value: "9200"
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME
value: elastic
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD
value: changeme
- name: ELASTIC_CLOUD_ID
value:
- name: ELASTIC_CLOUD_AUTH
value:
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
# If using Red Hat OpenShift uncomment this:
#privileged: true
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/filebeat.yml
readOnly: true
subPath: filebeat.yml
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/filebeat/data
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
defaultMode: 0640
name: filebeat-config
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
# data folder stores a registry of read status for all files, so we don't send everything again on a Filebeat pod restart
- name: data
hostPath:
# When filebeat runs as non-root user, this directory needs to be writable by group (g+w).
path: /var/lib/filebeat-data
type: DirectoryOrCreate
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: filebeat
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources:
- namespaces
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources:
- replicasets
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat
# should be the namespace where filebeat is running
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups:
- coordination.k8s.io
resources:
- leases
verbs: ["get", "create", "update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- configmaps
resourceNames:
- kubeadm-config
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
---
需要改动的地方大概有这几处

可以使用kubernetes模板
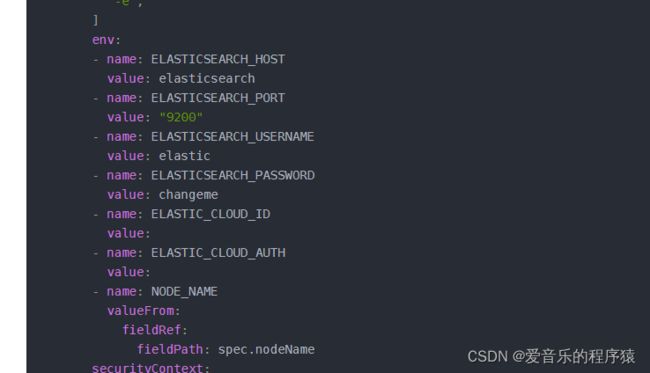
elasticsearch连接相应的配置
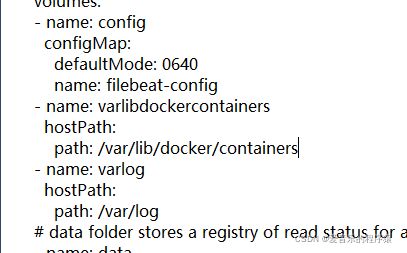
hostpath路径加上/var/log/containers/,进行修改
下面放上我大致修改后的
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: filebeat-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
data:
filebeat.yml: |-
# To enable hints based autodiscover, remove `filebeat.inputs` configuration and uncomment this:
filebeat.autodiscover:
providers:
- type: kubernetes
node: ${NODE_NAME}
hints.enabled: true
hints.default_config:
type: container
paths:
- /var/log/containers/*${data.kubernetes.container.id}.log
processors:
- add_cloud_metadata:
- add_host_metadata:
cloud.id: ${ELASTIC_CLOUD_ID}
cloud.auth: ${ELASTIC_CLOUD_AUTH}
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ['${ELASTICSEARCH_HOST:elasticsearch}:${ELASTICSEARCH_PORT:9200}']
username: ${ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME}
password: ${ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD}
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: filebeat
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
serviceAccountName: filebeat
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
hostNetwork: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
containers:
- name: filebeat
image: docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:8.0.1
args: [
"-c", "/etc/filebeat.yml",
"-e",
]
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_HOST
value: quickstart-es-http.default.svc.cluster.local
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_PORT
value: "9200"
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME
value: elastic
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD
value: password
- name: ELASTIC_CLOUD_ID
value:
- name: ELASTIC_CLOUD_AUTH
value:
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
# If using Red Hat OpenShift uncomment this:
#privileged: true
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/filebeat.yml
readOnly: true
subPath: filebeat.yml
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/filebeat/data
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/log/containers
readOnly: true
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
defaultMode: 0640
name: filebeat-config
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/log/containers
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
# data folder stores a registry of read status for all files, so we don't send everything again on a Filebeat pod restart
- name: data
hostPath:
# When filebeat runs as non-root user, this directory needs to be writable by group (g+w).
path: /var/lib/filebeat-data
type: DirectoryOrCreate
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: filebeat
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources:
- namespaces
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources:
- replicasets
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat
# should be the namespace where filebeat is running
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups:
- coordination.k8s.io
resources:
- leases
verbs: ["get", "create", "update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- configmaps
resourceNames:
- kubeadm-config
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
---
里面具体的配置路径按自己环境修改
保存文件名为filebeat-kubernetes.yaml
执行
kubectl apply -f filebeat-kubernetes.yaml
等待所有pod就绪
登录kibana查看日志
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容