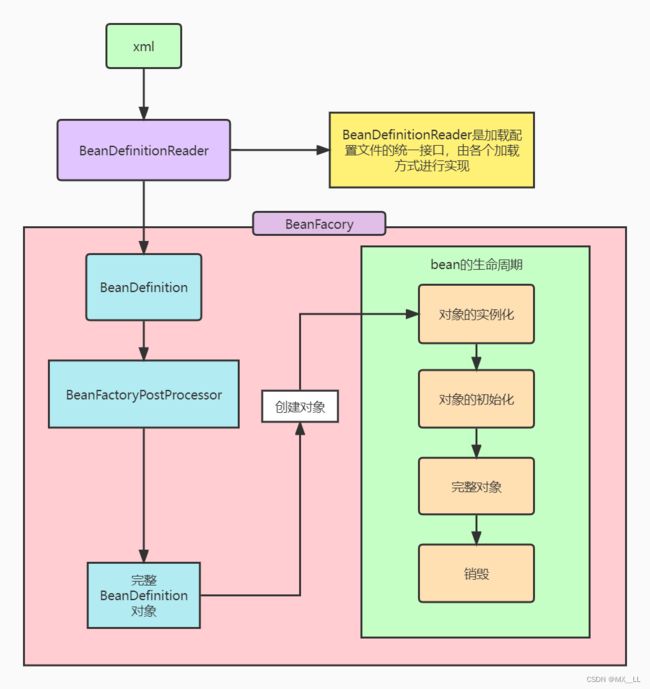
Spring ioc执行流程(粗讲)
#博学谷IT学习技术支持#
java程序猿肯定对spring已经非常熟悉,几乎所有大大小小的项目都会用到spring框架。但是关于基础的spring启动流程有没有去深入的了解过呢。 现在,让我们一起走进spring框架的内部世界。
- Spring-IOC加载流程(1.setConfigLocations方法)
- Spring-IOC refresh() 之prepareRefresh()
本期文章粗略讲解spring ioc的执行流程
关于spring-ioc加载流程,先使用xml配置文件讲一下具体加载流程。
1、我们可以使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类来加载xml配置文件。
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
在构造方法中,会设置配置文件路径,并调用refresh()方法
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
2、接下来看下refresh()方法内部的流程
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//在这个阶段进行xml配置文件的解析,加载beanDefinitions
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
3、BeanDefinitions的创建在obtainFreshBeanFactory()这个方法中,方法内部会执行loadBeanDefinitions方法,然后把加载BeanDefinition的工作交给XmlBeanDefinitionReader类去执行。后面会调用的XmlBeanDefinitionReader.doLoadBeanDefinitions()方法
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
内部包括这两部操作,一步是加载xml文件为Document,然后注册BeanDefinitions,在registerBeanDefinitions内部把BeanDefinitions的加载又交给了BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.registerBeanDefinitions()方法。
BeanDefinitionDocumenReader.registerBeanDefinitions()会根据加载出来的节点,判断是是否为默认节点,从而进行不同的解析操作;最终每个元素节点的解析都会交给BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类去进行;
4、BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类在进行解析时,会根据元素获取对应的namespaceUri,根据namespaceUri去查找NamespaceHandler(如果自定义标签需要进行解析的话,需要在/MATE-INF/spring.handlers里面配置上
namespaceUri=NamespaceHandler的路径,并且自定义一个Handler继承NamespaceHandlerSupport)。
在找到对应的NamespaceHandler后,会执行parse方法,根据元素名称去查找BeanDefinitionParser,BeanDefinition-Parser是对元素的具体解析操作,一个NamespaceHandler可以有多了BeanDefinitionParser(handler中添加init()方法可以添加BeanDefinitionParser);
5、上面完成了beanDefinition的解析,refresh()方法会执行prepareBeanFactory()对BeanFactory进行一些准备工作;
6、接下来调用 postProcessBeanFactory(),该方法在AbstractApplicationContext中为空实现,可对beanFactory或者内部的beanDefinitions进行一些后续操作,如spring-web中的GenericWebApplicationContext中的处理:
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.servletContext != null) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
}
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
}
7、调用invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法,执行BeanFactoryPostProcessors – bean工厂后置处理器;
8、registerBeanPostProcessors 注册BeanPostProcessors后置处理器。把注册操作交给PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate类去执行。首先会根据BeanPostProcessor.class类型在BeanFactory中查找对应beanNames,然后对把获取到的bean后置处理器按顺序添加到BeanFactory中。
9、调用 initMessageSource()方法,主要是对一些国际化的处理。
10、registerListeners() 注册监听器
11、调用 finishBeanFactoryInitialization()方法,开始加载非懒加载的单例bean。在方法内部会调用BeanFactory的preInstantiateSingletons()方法执行具体的bean加载操作;