【C++】异常的使用和细节
传统C语言错误异常的方式
C语言一般使用
assert来处理错误,assert确实很不错,可以把错误的行数都提示出来,但是,assert有一个致命的缺点,就是触发assert之后就会终止程序,还有一点就是在release环境下,assert是不起作用的。
C++异常处理方式
异常是一种处理错误的方式,当触发了异常的判定条件,就会自动捕获异常信息,但是程序不会终止,会继续运行,就不会导致一个用户触发了异常导致所有用户掉线的情况了。
- throw:程序出现问题的时候,通过throw去抛出异常的。
- catch:异常可以通过catch捕获到,throw就是把信息传递给catch了。
- try:在try代码块中可以放你想捕获异常的模块,try后面一般会跟很多个catch来捕获异常。
try
{
// 保护的标识代码
}catch( ExceptionName e1 )
{
// catch 块
}catch( ExceptionName e2 )
{
// catch 块
}catch( ExceptionName eN )
{
// catch 块
}
ExceptionName:异常类名字
异常的使用
异常的抛出和匹配原则
- 异常是通过抛出对象而引发的,匹配就是根据对象类型来匹配。
- 触发了异常的代码,会从throw开始找最近的catch,然后被捕获。
- 抛出异常之后,其实是一个即将被销毁的变量,需要生成一份拷贝对象,因为抛出的异常对象是一个临时的对象,出了作用域会被销毁的,被捕获的也是这个拷贝对象。
- catch(…)可以捕获任意类型的异常,但是没有错误信息。
- 抛出的异常类型可以是派生类的对象,然后用基类捕获。
#include异常的重新抛出
有可能单个的catch不能完全处理一个异常,在进行一些校正处理以后,希望再交给更外层的调用 链函数来处理,catch则可以通过重新抛出将异常传递给更上层的函数进行处理。
#include对于上述程序,如果触发了异常,
arr的空间不会正确释放,因此会导致内存泄漏,可以如下修改,在**Func()**当中进行二次捕获异常。
#include这样就不会有空指针问题了。
异常安全问题
- 最好不要再构造函数里面抛异常,可能导致初始化不完全。
- 最好不要在析构函数内抛异常,可能导致资源清理不完全。
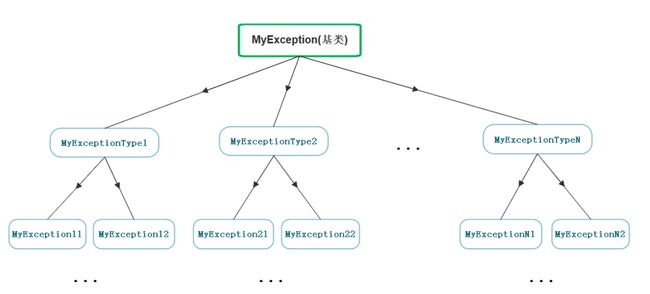
自定义异常体系
实际使用中很多公司都会自定义自己的异常体系进行规范的异常管理,因为一个项目中如果大家 随意抛异常,那么外层的调用者基本就没办法玩了,所以实际中都会定义一套继承的规范体系。 这样大家抛出的都是继承的派生类对象,捕获一个基类就可以了
#include如果是网络错误,我们可以写成重试3次发送再抛出异常。
void SeedMsg(const string& s)
{
// 要求出现网络错误重试三次
srand(time(0));
if (rand() % 3 == 0)
{
throw HttpServerException("网络错误", 500, "get");
}
else if (rand() % 4 == 0)
{
throw HttpServerException("权限不足", 101, "post");
}
cout << "发送成功:" << s << endl;
}
void HttpServer()
{
// 要求出现网络错误,重试3次
string str = "今晚一起看电影怎么样?";
//cin >> str;
int n = 3;
while (n--)
{
try
{
SeedMsg(str);
// 没有发生异常
break;
}
catch (const Exception& e)
{
// 网络错误 且 重试3次内
if (e.getid() == 500 && n > 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
throw e; // 重新抛出
}
}
}
}