CCNP路由实验之七 动态路由之BGP
CCNP路由实验之七 动态路由之BGP
动态路由协议能够自己主动的发现远程网络,仅仅要网络拓扑结构发生了变化,路由器就会相互交换路由信息,不仅能够自己主动获知新添加的网络,还能够在当前网络连接失败时找出备用路径。依据是否在一个自治域内部使用,动态路由协议分为内部网关协议(IGP)和外部网关协议(EGP)。这里的自治域指一个具有统一管理机构、统一路由策略的网络。自治域内部採用的路由选择协议称为内部网关协议,经常使用的有RIP、EIGRP、OSPF、IS-IS;外部网关协议主要用于多个自治域之间的路由选择,经常使用的是BGP和BGP-4。在一个路由器中,可同一时候配置静态路由和一种或多种动态路由。它们各自维护的路由表都提供给转发程序,但这些路由表的表项间可能会发生冲突。这样的冲突可通过配置各路由表的优先级来解决。通常静态路由具有默认的最高优先级,当其它路由表表项与它矛盾时,均按静态路由转发。
简单介绍
BGP用来连接Internet上独立系统的路由选择协议。它是Internetproject任务组制定的一个加强的、完好的、可伸缩的协议。BGP4支持CIDR寻址方案,该方案添加了Internet上的可用IP地址数量。BGP是为代替最初的外部网关协议EGP设计的,也被觉得是一个路径矢量协议。 BGP 是唯一一个用来处理像因特网大小的网络的协议,也是唯一能够妥善处理好不相关路由域间的多路连接的协议。BGP系统的主要功能是和其它的 BGP 系统交换网络可达信息。网络可达信息包括列出的自治系统(AS)的信息。这些信息有效地构造了 AS 互联的拓朴图并由此清除了路由环路,同一时候在 AS 级别上可实施策略决策。尽管BGP协议是为自治系统间的路由选择而设计,但它也能够用于自治系统内部,是一类双重路由选择协议。两个能够在自治系统之间进行通信的BGP相邻结点必须存在于同一个物理链路上。位于同一个自治系统内的BGP路由器能够互相通信,以确保它们对整个自治系统的全部信息都同样,并且通过信息交换后,它们将决定自治系统内哪个BGP路由器作为连接点来负责接收来自自治系统外部的信息。有些自治系统仅仅作为一个传输数据的通道,这些自治系统既不是数据的发起端,也不是数据的接收端。BGP协议必须与存在于这些自治系统内部的路由协议打交道,以使数据能正确通过它们。BGP协议的路由刷新消息由“网络号:自治系统路径”对所组成,每一个自治系统路径都是一系列自治系统的名字字符串,它记录了通向终于目标所经过的网络。BGP与RIP和OSPF的不同之处在于BGP使用TCP作为其传输层协议。两个执行BGP的系统之间建立一条TCP(port179)连接,即是单播的路由协议,它们交换整个BGP路由表。从这个时候開始,在路由表发生变化时,再发送更新信号。BGP是一个距离向量协议,可是与(通告到目的地址跳数的)RIP不同的是,BGP列举了到每一个目的地址的路由(自治系统到达目的地址的序列号)。这样就排除了一些距离向量协议的问题。採用16bit数字表示自治系统标识。尽管BGP协议保持通向特定目标的全部路径的路由选择表,但在路由选择刷新消息中仅仅说明最佳路径。BGP协议的路由度量方法能够是一个随意单位的数,它指明某一个特定路径可供參考的程度,这些度量方法通常都是由网络管理人员通过配置文件来设置。可參考的程度能够基于不论什么数字准则,比如终于系统计数(计数越小时路径越佳)、数据链路的类型。
BGP 的两种邻居——IBGP和EBGP,BGP的邻居关系(或称通信对端/对等实体)是通过人工配置实现的,对等实体之间通过TCP(port179)会话交互数据。BGP路由器会周期地发送19字节的保持存活keep-alive消息来维护连接(默认周期为30秒)。在路由协议中,仅仅有BGP使用TCP作为传输层协议。同一个自治系统(AS)中的两个或多个对等实体之间执行的BGP 被称为 IBGP(Internal/Interior BGP)。归属不同的AS的对等实体之间执行的BGP称为EBGP(External/Exterior BGP)。在AS边界上与其它AS交换信息的路由器被称作边界路由器(border/edge router)。在互联网操作系统(Cisco IOS)中,IBGP通告的路由的距离为200,优先级比EBGP和不论什么内部网关协议(IGP)通告的路由都低。其它的路由器实现中,优先级顺序也是EBGP高于IGP,而IGP又高于IBGP。在建立邻居关系的时候,我们都採用Loopback地址来建立,但要保证Loopback地址可达,採用Loopback地址建立的邻居不会应为链路的down而断。
IBGP路由通告:BGP Speaker 从IBGP获得的路由不会通告给它的IBGP邻居(在一定的程度上能避免AS内的环路),就会造成不是与该路由器建立邻居不能学到路由,解决方式:①採用全连接②採用RR反射器③採用联盟的方式。
EBGP路由通告:BGP Speaker 从EBGP获得的路由会向全部的BGP对等体通告(包括IBGP和EBGP)
我们知道,在自治系统内部使用IGP路由协议;而在不同自治系统之间使用BGP路由协议,EBGP用于在不同自治系统之间,IBGP也是应用于自治系统内部,此时就要理解他们之间的关系:
IGP的能力限制,IGP处理路由的条目有限,而眼下internet上核心路由器的路由表已经超过10万条。假如没有IBGP,那么这些路由仅仅能採取重分发的方式直接导入到IGP中,这样做的缺点非常明显:第一,IGP协议的作者并没有打算让IGP来处理如此大量的路由,IGP本身也无法处理这样大的路由数量;第二,假设非要让IGP来处理,那么依据IGP的处理原则,假如这10万路由中不论什么一条路由发生变化,那么执行IGP的路由器就不得不又一次计算路由这样的计算量对于绝大多数路由器来说是无法负担的
路由环路的问题。BGP是靠路由属性来防止路由环路的,比如AS_PATH属性,假如说没有IBGP协议,那么当全部BGP路由重分发到IGP中后,路由属性必定丢失,这就破坏了BGP的路由环路防止机制,产生了路由环路的隐患。
IBGP之间是TCP连接,也就意味着IBGP邻居採用的是逻辑连接的方式,两个IBGP连接不一定存在实际的物理链路。所以须要有IGP来提供路由,以完毕BGP路由的递归查找。 BGP协议本身实际上并不发现路由,BGP将路由发现的工作全部移交给了IGP协议,它本身着重于路由的控制。因此,假设没有IGP,那么BGP也就毫无用处了。
EBGP与IBGP的差别:
路由环路的避免措施不一样,IBGP强制规定ibgp speaker不同意把从一个ibgp邻居学习到的前缀传递给其它ibgp邻居,因此IBGP要求逻辑全连接。EBGP没有这样的要求,EBGP对路由环路的避免是通过AS_PATH属性来实现的。
使用的BGP属性不同,比如IBGP能够传递LOCAL_PREF(本地优先属性),而EBGP不行。
IBGP有同步的要求,而EBGP没有同步的要求
IBGP不须要IBGP邻居之间有物理连接,仅仅须要逻辑连接就可以,而EBGP下普通情况下都要求EBGP邻居之间存在物理连接。
BGP属性:
路由器发送关于目标网络的BGP更新消息,更新的度量值被称为路径属性。属性能够是公认的或可选的、强制的或自由决定的、传递的或非传递的。属性也能够是部分的。并不是组织的和有组合的都是合法的,路径属性分为4类:公认必遵、公认自决、可选过渡、可选非过渡。当中公认必遵、公认自决为
公认属性;可选过渡、可选非过渡为非公认属性被称为可选的,可选属性能够是传递的或非传递的,可选属性不要求全部的BGP实现都支持。对于不支持的可选传递属性,路由器将其原封不动的传递给其它BGP路由器,在这样的情况下,属性被标记为部分的。对于可选非传递属性,路由器必须将其删除,而不将其传递给其它BGP路由器。
(1)公认必遵(Well-Known Mandatory)是公认全部BGP实现都必须识别的属性,这些属性被传递给BGP邻居。公认强制属性必须出如今路由描写叙述中,公认自由决定属性能够不出如今路由描写叙述中,例如以下:
ORIGIN(起源):这个属性说明了源路由是如何放到BGP表中的。有三个可能的源IGP,EGP,以及INCOMPLETE.路由器在多个路由选择的处理中使用这个信息。路由器选择具有最低ORIGIN类型的路径。
AS_PATH(AS路径):指出包括在UPDATE报文中的路由信息所经过的自治系统的序列。
Next_HOP(下一跳)声明路由器所获得的BGP路由的下一跳,对EBGP会话来说,下一跳就是通告该路由的邻居路由器的源地址。
(2)公认自决(Well-Known Discretionary)
LOCAL_PREF(本地优先级):本地优先级属性是用于告诉自治系统内的路由器在有多条路径的时候,如何离开自治系统。本地优先级越高,路由优先级越高。
ATOMIC_AGGREGATE(原子聚合):原子聚合属性指出已被丢失了的信息。
(3)可选过渡(Optional Transitive)
AGGREGATOR(聚合者):此属性标明了实施路由聚合的BGP路由器ID和聚合路由的路由器的AS号。
COMMUNITY(团体):此属性指共享一个公共属性的一组路由器。
(4)可选非过渡(Optional Nontransitive)
MED(多出口区分):该属性通知AS以外的路由器採用哪一条路径到达AS,它也被觉得是路由的外部度量,低MED值表示高的优先级。
ORIGINATOR_ID(起源ID):路由反射器会附加到这个属性上,它携带本AS路由器的路由器ID,用以防止环路。
CLUSTER_LIST(簇列表):此属性显示了採用的反射路径。
BGP术语
BGP两个版本号:BGP4因特网上所用的主要区域间路由选择协议的第4版,它支持CIDR并使用路由集合机制减小路由表的大小;BGP4+使BGP4能够支持多种网络层协议,如IPv6和IPX等
BGP邻居就是BGP对等体(peer),BGP邻居关系就是对等体关系。每一个邻居都要手动指定。在大规模网络中十分麻烦
BGP Peer Group它相当于是一个容器,这个容器拥有着BGP參数和策略,仅仅要将BGP邻居放入这个容器中,那么该邻居就可以获得容器的全部參数和策略,从而大大简化为每一个邻居反复配置同样參数和策略。Peer Group唯一的限制就是,同一个Peer Group中的全部邻居,必须全部为iBGP邻居,或者全部为eBGP邻居,也就是说不能将iBGP邻居和eBGP邻居同一时候混杂在同一个Peer Group中,可是假设全部都为eBGP邻居,这些邻居能够是随意AS的,而不必全部邻居都是同一个AS的。在使用Peer Group配置邻居后,能够对Peer Group配置參数和策略,也能够对Peer Group中的单个邻居配置參数和策略。Peer Group配置降低工作量的同一时候,也能保证邻居策略的多样化。
BGP团体:能够简化路由策略的管理,使多个AS中的一组BGP路由器共享同样的策略。团体是一个路由属性,在BGP对等体之间传播,它并不受到AS范围的限制。
路由反射器:为保证IBGP对等体之间的连通性,须要在IBGP对等体之间建立全连接关系。假设在一个AS内部有n台路由器,那么应该建立的IBGP连接数就为n(n-1)/2。当IBGP对等体数目非常多时,对网络资源和CPU资源的消耗都非常大。利用路由反射能够解决这一问题。在一个AS内,当中一台路由器作为路由反射器RR(Route Reflector),其它路由器作为客户机(Client)与路由反射器之间建立IBGP连接。路由反射器在客户机之间传递(反射)路由信息,而客户机之间不须要建立BGP连接。既不是反射器也不是客户机的BGP路由器被称为非客户机(Non-Client)。非客户机与路由反射器之间,以及全部的非客户机之间仍然必须建立全连接关系。路由反射器和它的客户机组成了一个集群(Cluster)。某些情况下,为了添加网络的可靠性和防止单点故障,能够在一个集群中配置一个以上的路由反射器。这时,位于同样集群中的每一个路由反射器都要配置同样的Cluster_ID,以避免路由循环。
联盟:处理AS内部的IBGP网络连接激增的还有一种方法,它将一个自治系统划分为若干个子自治系统,每一个子自治系统内部的IBGP对等体建立全连接关系,子自治系统之间建立联盟内部EBGP连接关系。在不属于联盟的BGP发言者看来,属于同一个联盟的多个子自治系统是一个总体,外界不须要了解内部的子自治系统情况,联盟ID就是标识联盟这一总体的自治系统号。联盟的缺陷是:从非联盟方案向联盟方案转变时,要求路由器又一次进行配置,逻辑拓扑也要改变。
BGP三种路由类型
AS间路由发生在不同AS的两个或多个BGP路由器之间,这些系统的对等路由器使用BGP来维护一致的网络拓扑视图,AS间通信的BGP邻居必须处于同样的物理网络。因特网就是使用这样的路由的实例,由于它由多个AS(或称管理域)构成,很多域为构成因特网的研究机构、公司和实体。BGP经经常使用于为因特网内提供最佳路径而做路由选择。
AS内部路由发生在同一AS内的两个或多个BGP路由器间,同一AS内的对等路由器用BGP来维护一致的系统拓扑视图。BGP也用于决定哪个路由器作为外部AS的连接点。再次重申,因特网提供了AS间路由的实例。一个组织,如大学,能够利用BGP在其自己的管理域(或称AS)内提供最佳路由。BGP协议既能够提供AS间也能够提供AS内部路由。
贯穿(pass-through)AS路由发生在通过不执行BGP的AS交换数据的两个或多个BGP对等路由器间。在贯穿AS环境中,BGP通信既不源自AS内,目的也不在该AS内的节点,BGP必须与AS内使用的路由协议交互以成功地通过该AS传输BGP通信
八、BGP路由更新:与其它路由协议一样,BGP维护路由表、发送路由更新信息且基于路由metric决定路由。BGP系统的主要功能是交换其它BGP系统的网络可达信息,包括AS路径的列表信息,此信息可用于建立AS系统连接图,以消除路由环,及执行AS策略确定。
每一个BGP路由器维护到特定网络的全部可用路径构成的路由表,可是它并不清除路由表,它维持从对等路由器收到的路由信息直到收到增值(incremental)更新。
BGP设备在初始数据交换和增值更新后交换路由信息。当路由器第一次连接到网络时,BGP路由器交换它们的整个BGP路由表,相似的,当路由表改变时,路由器发送路由表中改变的部分。BGP路由器并不周期性发送路由更新,且BGP路由更新仅仅包括到某网络的最佳路径。
BGP用单一的路由metric决定到给定网络的最佳路径。这一metric含有指定链路优先级的随意单元值,BGP的metric通常由网管赋给每条链路。赋给一条链路的值能够基于随意数目的尺度,包括途经的AS数目、稳定性、速率、延迟或代价等。
九、BGP消息类型
初始消息在对等路由器间打开一个BGP通信会话,是建立传输协议后发送的第一个消息,初始消息由对等设备发送的keep-alive消息确认,且必须得到确认后才干够交换更新、通知和keep-alive消息。
更新消息用于提供到其它BGP系统的路由更新,使路由器能够建立网络拓扑的一致视图。更新用TCP发送以保证传输的可靠性。 更新消息能够从路由表中清除一条或多条失效路由,同一时候公布若干路由。
通知消息在检查到有错误时发送。通知消息用于关闭一条活动的会话,并通知其它路由器为何关闭该会话。
keep-alive消息通知对等BGP路由器该设备仍然alive。keep-alive消息公布足够频繁以防止会话过期
十、BGP数据包分组
标记 - 含有认证值。
长度 - 指示消息的总长度,以字节计。
类型 - 标识消息类型为下列类型之中的一个: 初始 、更新 、通知 、keep-alive 、数据(为可选域,含有上层信息)
初始消息格式:BGP初始消息由BGP信头和附加域构成,在信头的类型域中标识为BGP初始消息的BGP分组包括下列各域,这些域为两个BGP路由器建立对等关系提供了交换方案:
版本号 - 提供BGP版本号号,使接收者能够确认它是否与发送者执行同一版本号协议。自治系统 - 提供发送者的AS号。
保持时间(Hold-time)- 在发送者被觉得失效前最长的不接收消息的秒数。
BGP标识 - 提供发送者的标识(IP地址),在启动时决定,对全部本地接口和全部对等BGP路由器而言都是同样的。
可选參数长度 - 标识可选參数域的长度(假设存在的话)。
可选參数 - 包括一组可选參数。眼下仅仅定义了一个可选參数类型:认证信息。认证信息含有下列两个域:
认证码:标识使用的认证类型。
认证数据:包括由认证机制使用的数据。
C)更新消息格式:BGP更新消息由BGP信头和附加域构成,收到更新消息分组后,路由器就能够从其路由表中添加或删除指定的表项以保证路由的准确性。更新消息包括下列域:
失效路由长度 - 标识失效路由域的总长度或该域不存在。
失效路由 - 包括一组失效路由的IP地址前缀。
总路径属性长度 - 标识路径属性域的总长度或该域不存在。
路径属性 - 描写叙述公布路径的属性,可能的值例如以下:
源:必选属性,定义路径信息的来源。
AS路径:必选属性,由一系列AS路径段组成。
下一跳:必选属性,定义了在网络层可达信息域中列出的应用作到目的地下一跳的边
缘路由器的IP地址。
多重出口区分:可选属性,用于在到相邻AS的多个出口间进行区分。
本地优先权:可选属性,用以指定公布路由的优先权等级。
原子聚合:可选属性,用于公布路由选择信息。
聚合:可选属性,包括聚合路由信息。
网络层可达信息 - 包括一组公布路由的IP地址前缀。
D)通知消息格式:通知消息分组用于给对等路由器通知某种错误情况。
错误码 - 标识发生的错误类型。以下为定义的错误类型:
消息头错:指出消息头出了问题,如不可接受的消息长度、标记值或消息类型。
初始消息错:指出初始消息出了问题,如不支持的版本号号,不可接受的AS号或IP地址或
不支持的认证码。
更新消息错:指更新消息出了问题,如属性列表残缺、属性列表错误或无效的下一跳属性。
保持时间过期:指出保持时间已过期,这之后BGP节点就被觉得已失效。
有限状态机错:指示期望之外的事件。
终止:发生严重错误时依据BGP设备的请求关闭BGP连接。
错误子码 - 提供关于报告的错误的更详细的信息。
错误数据 - 包括基于错误码和错误子码域的数据,用于检測通知消息发送的原因。
十一、BGP邻居协商建立会话的5种状态:
Idle:查找路由表,该过程BGP对它的资源进行初始化,复位一个连接重试计时器, 发起一条TCP 连接,并開始倾听远程对等体所发起的连接。
Connect:找到路由表后进行TCP三次握手,TCP 连接成功,则转到OpenSent状态,TCP连接失败,则转到active 状态,将尝试再次连接。
Open Sent:握上手后发送Open message消息,等待其对等体发送打开消息,假设出错,则发送一条出错消息并退回空暇状态,假设无错,则開始发送Keepalive 并复位keepalive 计时器。
Open Confirm:收到对方发来的Open消息,假设收到keepalive 消息,BGP 就进入established状态,邻居关系协商完毕;假设系统收到一条更新或keepalive 消息,它将又一次启动保持计时器;假设收到Notification消息,BGP 就退回到空暇状态。
Established:会话建立,邻居关系协商过程终于状态;这时BGP将開始与它的对等体交换路由更新数据包。
BGP协议的特点
BGP是一种AS(自治区域)外部路由协议,主要负责本自治区域和外部的自治区域间的路由可达信息的交换。因此,它所关心的拓扑结构是AS(自治区域)的拓扑结构,BGP通过UPDATE消息中路由的AS属性来构造AS的拓扑结构图,进一步通过此结构图来选择路由。
与OSPF,RIP等IGP协议相比,BGP的拓扑图要更抽象和粗略一些。由于IGP协议构造的是AS内部的路由器的拓扑结构图。IGP把路由器抽象成若干端点,把路由器之间的链路抽象成边,依据链路的状态等參数和一定的度量标准,每条边配以一定的权值,生成拓扑图。依据此拓扑图选择代价(两点间经过的边的权值和)最小的路由。这里有一个假设,即路由器(端点)转发数据包是没有的代价的。而在BGP中,拓扑图的端点是一个AS区域,边是AS之间的链路。此时,数据包经过一个端点(AS自治区域)时的代价就不能假设为0了,此代价要由IGP来负责计算。这体现了EGP和IGP是分层的关系。即IGP负责在AS内部选择花费最小的路由,EGP负责选择AS间花费最小的路由。BGP作为EGP的一种,选择路由时考虑的是AS间的链路花费,AS区域内的花费(由BGP路由器配置)等因素。
如上所述,内部网关协议IGP需引入AS自治区域内部网络拓扑图其它各点的路由,同一时候向其它端点发送本端点(路由器)所知的路由,如直接路由、静态路由等。作为外部网关协议,BGP发送和引入路由的单位是整个AS自治区域,即BGP要发送本地路由器所在的AS内部的全部路由,引入其它AS自治区域的全部路由(假设不使用路由策略控制发送和引入)。其路由数量显然要远远大于IGP发送和引入的路由数量。因此,相似于IGP那样定时对外广播路由信息是不可取的。BGP採用发送路由增量(Incremental)的方法,完毕全部路由信息的通告和维护:初始化时发送全部的路由给BGP对端(BGP Peer),同一时候在本地保存了已经发送给BGP对端的路由信息。当本地的BGP收到了一条新路由时(如通过IGP注入了新路由或加入了新的静态路由),与保存的已发送信息进行比較,如未发送过,则发送,如已发送过则与已经发送的路由进行比較,如新路由花费更小,则发送此新路由,同一时候更新已发送信息,反之则不发送。当本地BGP发现一条路由失效时(如相应port失效),如此路由已发送过,则向BGP对端发送一个退出路由消息。
BGP遇到的挑战和限制
(1)I-BGP的Full-Mesh问题: BGP路由协议分为I-BGP和E-BGP两个部分。I-BGP用于自治域内的路由器之间,E-BGP用于自治域间的路由器之间。假设一个AS内部存在非bgp路由器,那么就出现了BGP和IGP的边界,须要在边界路由器将BGP路由公布到igp中,才干保证AS所通告到外部的BGP路由在AS内部是连通的.实际上是要求BGP路由和igp路由的同步。假设将BGP路由公布到igp中,由于BGP路由主要是来自AS外部的路由(来自internet),那么结果是igp路由器要维护数以万计的外部路由,对路由器的CPU和memeory以及AS内部的链路带宽的占用将带来巨大的开销. 因此AS内部全部路由器应尽可能执行fullmesh iBGP,就能够关闭全部路由器的同步而不影响路由的通告和连通性.。可是此时还有一个问题来了,当AS内部路由器数量非常多时,须要建立N*(N-1)/2个ibgp会话,带来过度的系统开销,扩展性不好,眼下这个问题解决的方法有两种:联盟和路由反射。 另外为避免在AS内部的循环路由,BGP不会向内部BGP PEER通告它从其它内部BGP PEER中获得的路由,此时利用路由反射能够解决这一问题。在一个AS内,当中一台路由器作为路由反射器RR(Route Reflector),其它路由器作为客户机(Client)与路由反射器之间建立IBGP连接。路由反射器在客户机之间传递(反射)路由信息,而客户机之间不须要建立BGP连接。
(2)更改路由策略时路由振荡的问题 : BGP属于增量更新的路由协议,当有新的路由要公布时,路由器会向邻居发送Update信息,而假设要删除某条路由时,就会发送Withdraw信息。BGP路由的Flap的定义是:当一条路由在被收回(Withdraw)后,又被广播(Update)出来,视为一次Flap。由于不论什么一条路由的收回和更新都会导致一台路由器整个路由表又一次计算,因此当Flap的情况比較多时,对路由器设备的负载将产生巨大的压力。依据笔者在实际工作中的经验,普通情况下,一台高端路由器在计算BGP路由的时候,CPU的负载基本上在80%~90%左右,有时甚至达到100%,占用了差点儿全部的CPU资源。尽管眼下大部分的高端路由器都将路由计算的模块与转发模块分布在不同的硬件上,来降低主CPU忙导致的路由器性能下降的问题,可是路由表的频繁变化和更新,对整个设备的执行还是有一定的影响的,并且这样的计算会随着路由的收回或广播,继续向自治域内部扩展,使内部的路由器产生同样的问题。眼下解决的办法:Damping
(3)其它因素影响路由器的性能: 如路由的数目、BGP路由表的大小和路由计算的方式等 另外,网络越大,路由条目越多,配置和管理的工作也就越复杂,这就须要在网络设计的时候尽量简化配置,降低管理人员的工作强度,避免人为原因造成故障。解决的方法有: peer group 、路由聚合
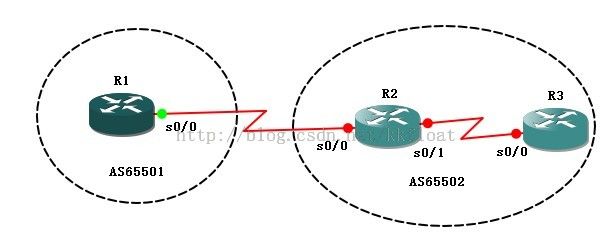
实验一:BGP基本配置
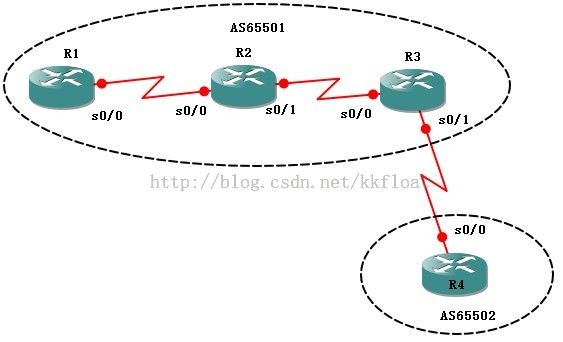
R1配置:
R1#conf t
R1(config)#int s0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip router isis //将接口宣告到ISIS路由进程
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router isis //开启ISIS内部路由协议
R1(config-router)#net49.0001.1111.1111.1111.00
R1(config-router)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 65501 //开启bgp进程,自治号位65501
R1(config-router)#no synchronization //关闭同步
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0 mask255.255.255.0 //宣告网络到BGP进程
R1(config-router)#neighbor192.168.12.2 remote-as 65501 //手动配置R2为邻居
R1(config-router)#neighbor192.168.23.2 remote-as 65501 //手动配置R3为邻居
R2配置:
R2#conft
R2(config)#ints0/0
R2(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#iprouter isis
R2(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R2(config-if)#nosh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#ints0/1
R2(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R2(config-if)#iprouter isis
R2(config-if)#nosh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#routerisis
R2(config-router)#net49.0001.2222.2222.2222.00
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#routerbgp 65501
R2(config-router)#nosynchronization
R2(config-router)#net192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#net192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#neighbor192.168.12.1 remote-as 65501
R2(config-router)#neighbor192.168.23.2 remote-as 65501
R3配置:
R3#conft
R3(config)#ints0/0
R3(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#iprouter isis
R3(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R3(config-if)#nosh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#ints0/1
R3(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.34.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#iprouter isis
R3(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R3(config-if)#nosh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#routerisis
R3(config-router)#net49.0001.3333.3333.3333.00
R3(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#routerbgp 65501
R3(config-router)#nosyn
R3(config-router)#net192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#net192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei192.168.12.1 remote-as 65501
R3(config-router)#nei192.168.23.1 remote-as 65501
R3(config-router)#nei192.168.34.2 remote-as 65502
R4配置:
R4#conft
R4(config)#ints0/0
R4(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.34.2 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R4(config-if)#nosh
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#intlo 0
R4(config-if)#ipadd 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#routerbgp 65502
R4(config-router)#nosyn
R4(config-router)#net4.4.4.4 mask 255.255.255.255
R4(config-router)#net192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R4(config-router)#nei192.168.34.1 remote-as 65501
R4(config-router)#exit
完毕以上配置后,全网互通就能够互通了,此时我们查看下R1和R4的路由表,发现有一条带B标记的路由到达对方。同一时候查看BGP邻居
R1#ship rou
Codes:C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O -OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 -OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPFexternal type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 -IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidatedefault, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded staticroute
Gatewayof last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected,Serial0/0
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.4 [200/0] via192.168.34.2, 00:20:09
iL1 192.168.23.0/24 [115/20] via 192.168.12.2, Serial0/0
iL1 192.168.34.0/24 [115/30] via 192.168.12.2, Serial0/0
R1#ship bgp summary
BGProuter identifier 192.168.12.1, local AS number 65501
BGPtable version is 9, main routing table version 9
4network entries using 468 bytes of memory
6path entries using 312 bytes of memory
4/3BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 496 bytes of memory
1BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory
0BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGPusing 1300 total bytes of memory
BGPactivity 4/0 prefixes, 6/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
192.168.12.2 465501 61 60 9 0 0 00:55:01 2
192.168.23.2 465501 48 46 9 0 0 00:41:44 3
分析:
在自治区域65501内各路由器通过ISIS路由协议,建立到达彼此的路由条目。然后各路由器开启BGP协议,BGP协议依据路由表与其它路由器建立iBGP对等体关系(邻居),彼此交互路由信息。接着R3与物理链接的R4上的自治区域65502的BGP协议建立EBGP关系,彼此交换路由信息。
实验二、使用环回口建立IBGP邻居关系
事实上IBGP和EBGP都能够用环回口或者物理接口建立邻居,可是通常EBGP用物理接口建立邻居,由于EBGP之间牵扯到多跳的问题,且EBGP邻居之间没有不论什么IGP协议的支持,所以环回口是不可达的,尽管能够在临界路由器上配置一条默认路由来可达,可是还要配置nei x.x.x.x 的多跳,由于EBGP默认仅仅传一跳。
对于IBGP之间,由于有IGP的协议支持,所以环回口都是可达的,最重要的就是环回口的稳定性大大优于物理接口。 并且使用环回接口能够充分利用邻居间的多条链路实现冗余
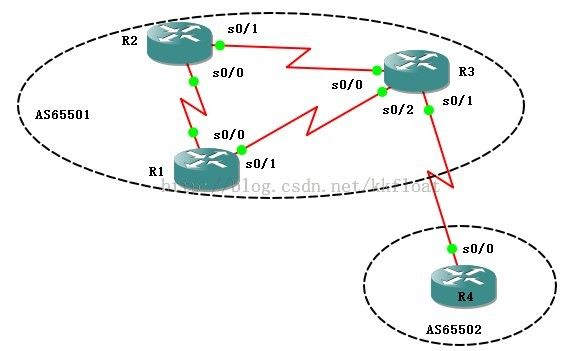
R1配置:
R1#conf t
R1(config)#int s0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip router isis //将接口宣告到ISIS路由进程
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int s0/1
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.13.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip router isis
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config)#int lo0
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1255.255.255.255
R1(config-if)#ip router isis
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router isis //开启ISIS内部路由协议
R1(config-router)#net49.0001.1111.1111.1111.00
R1(config-router)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 65501 //开启bgp进程,自治号位65501
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 //设置BGP路由ID
R1(config-router)#no synchronization //关闭同步
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.12.0 mask255.255.255.0 //宣告网络到BGP进程
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0////宣告网络到BGP进程
R1(config-router)#nei2.2.2.2 remote-as 65501 //指定与R2环回口建立邻居
R1(config-router)#nei2.2.2.2 update-source loopback 0//指定本端更新port为环回口
R1(config-router)#nei2.2.2.2 next-hop-self //要求下一跳更新源
R1(config-router)#nei3.3.3.3 remote-as 65501//指定与R3环回口建立邻居
R1(config-router)#nei3.3.3.3 update-source loopback 0//指定本端更新port为环回口
R1(config-router)#NEI3.3.3.3 next-hop-self //要求下一跳更新源
R2配置:
R2#conft
R2(config)#ints0/0
R2(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#iprouter isis
R2(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R2(config-if)#nosh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#ints0/1
R2(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R2(config-if)#iprouter isis
R2(config-if)#nosh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#intlo0
R2(config-if)#ipadd 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
R2(config-if)#iprouter isis
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#routerisis
R2(config-router)#net49.0001.2222.2222.2222.00
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#routerbgp 65501
R2(config-router)#bgprouter-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#nosynchronization
R2(config-router)#net192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#net192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#nei1.1.1.1 remote-as 65501
R2(config-router)#nei1.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
R2(config-router)#nei1.1.1.1 next-hop-self
R2(config-router)#nei3.3.3.3 remote-as 65501
R2(config-router)#nei3.3.3.3 update-source loopback 0
R2(config-router)#nei3.3.3.3 next-hop-self
R3配置:
R3#conft
R3(config)#ints0/0
R3(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#iprouter isis
R3(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R3(config-if)#nosh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#ints0/1
R3(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.34.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#iprouter isis
R3(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R3(config-if)#nosh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#intlo0
R3(config-if)#ipadd 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
R3(config-if)#iprouter isis
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#routerisis
R3(config-router)#net49.0001.3333.3333.3333.00
R3(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#routerbgp 65501
R3(config-router)#bgprouter-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-router)#nosyn
R3(config-router)#net192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#net192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#net192.168.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei1.1.1.1 remote-as 65501
R3(config-router)#nei1.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
R3(config-router)#nei1.1.1.1 next-hop-self
R3(config-router)#nei2.2.2.2 remote-as 65501
R3(config-router)#nei2.2.2.2 update-source loopback 0
R3(config-router)#nei2.2.2.2 next-hop-self
R3(config-router)#nei192.168.34.2 remote-as 65502
R4配置:
R4#conft
R4(config)#ints0/0
R4(config-if)#ipadd 192.168.34.2 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#clockrate 64000
R4(config-if)#nosh
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#intlo 0
R4(config-if)#ipadd 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#routerbgp 65502
R4(config-router)#nosyn
R4(config-router)#net4.4.4.4 mask 255.255.255.255
R4(config-router)#net192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R4(config-router)#nei192.168.34.1 remote-as 65501
R4(config-router)#exit
此时全网已经互通,并且查看R1的BGP邻居:
R1#ship bgp summary
BGProuter identifier 1.1.1.1, local AS number 65501
BGPtable version is 31, main routing table version 31
5network entries using 585 bytes of memory
8path entries using 416 bytes of memory
4/3BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 496 bytes of memory
1BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory
0BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGPusing 1521 total bytes of memory
BGPactivity 15/10 prefixes, 22/14 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
2.2.2.2 4 65501 201 197 31 0 0 03:12:37 2
3.3.3.3 4 65501 207 207 31 0 0 03:20:41 4
实验三、去掉私有AS
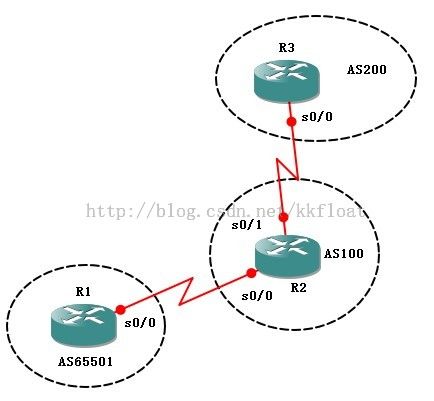
R1配置:
R1#conf t
R1(config)#int lo0
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int s0/0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 65501
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2 remote-as 100
R2配置:
R2#conf t
R2(config)#int s0/0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int s0/1
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1 remote-as 65501
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.2 remote-as 200
R3配置:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#int s0/0
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 200
R3(config-router)#bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.1 remote-as 100
完毕配置后,此时全网互通正常,我们来看看R3的BGP路由表,
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 100 65501 i
*> 192.168.12.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 100 i
* 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 100 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
此时会发现AS65501这个私有自治号(AS大于65500的都是私有).注意在公网上是不能有私有AS号的 ,此时我们使用neighbor x.x.x.x remove-private-as 命令能够强制BGP丢弃私有AS编号,通常这个命令配置在外部的BGP邻居上,当向外公布的更新路由中含有私有AS编号的时候,这个私有的AS编号将被过滤,然后再次查看R3的BGP路由表
R2#conf t
R2(config)#router bgp 100
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.2remove-private-as
R2(config-router)#do clear ip bgp * soft out
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 6, local router ID is3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 100 i
*> 192.168.12.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 1 00 i
* 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 100 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
当配置这条命令的时候须要注意以下的几个注意事项.
这条命令仅仅能使用在EBGP的邻居上
假设更新路由中仅仅含有私有的AS编号那么BGP会过滤掉这些私有编号
假设在AS_PATH路径中既包括私有的又包括公有的AS编号那么BGP将不会对私有的AS编号进行过滤
假设在AS_PATH中包括有EBGP邻居的AS编号那么BGP也不会将私有的AS编号进行过滤
假设AS_PATH 包括联盟那么仅仅有当私有AS编号出如今联盟后面的时候BGP才会将私有的AS编号清除
实验四、BGP的Weight属性 (Cisco私有)
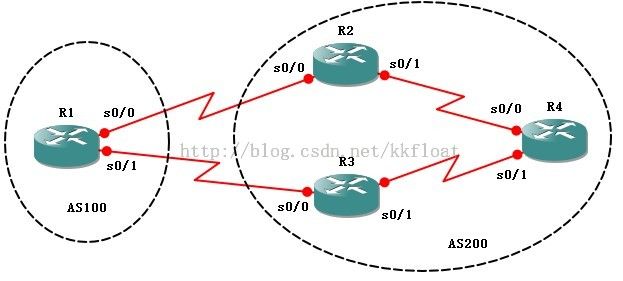
R1配置:
R1#conf t
R1(config)#int lo0
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int s0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int s0/1
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#net 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 192.168.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2 remote-as 200
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.2 remote-as 200
R2配置:
R2#conf
R2(config)#int s0/0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int s0/1
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.24.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1 remote-as 100
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.2 remote-as 200
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.2 remote-as 200
R3配置:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#int s0/0
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int s0/1
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.34.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 200
R3(config-router)#bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.1 remote-as 100
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.2 remote-as 200
R4配置:
R4#conf t
R4(config)#int s0/0
R4(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R4(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no sh
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#int s0/1
R4(config-if)#ip add 192.168.34.2 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R4(config-if)#no sh
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 200
R4(config-router)#bgp router-id 4.4.4.4
R4(config-router)#net 192.168.24.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R4(config-router)#net 192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.1 remote-as 200
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.1 remote-as 200
查看R4的BGP路由表,我们发现R4到1.1.1.1的网络走的是R2.
R4#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i -internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i1.1.1.0/24 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i
* i 192.168.13.1 0 100 0 100 i
*>i192.168.12.0 192.168.24.1 0 100 0 i
* i 192.168.13.1 0 100 0 100 i
* i192.168.13.0 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i
*>i 192.168.34.1 0 100 0 i
* i192.168.24.0 192.168.24.1 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i192.168.34.0 192.168.34.1 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
此时通过调整Weight来改变选路,使R4到1.1.1.1网络走R3,然后查看R4
R4#conf t
R4(config)#router bgp 200
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.1 weight 100 //设置此邻居传过来的bgp路由的权重设置成100.
R4(config-router)#do clear ip bgp * in //不中断邻居关系,更新bgp路由
R4(config-router)#do sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 12, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i -internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i1.1.1.0/24 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i
*>i 192.168.13.1 0 100 100 100 i
* i192.168.12.0 192.168.24.1 0 100 0 i
*>i 192.168.13.1 0 100 100 100 i
* i192.168.13.0 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i
*>i 192.168.34.1 0 100 100 i
* i192.168.24.0 192.168.24.1 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i192.168.34.0 192.168.34.1 0 100 100 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
依据调整weight值,R4如今到1.1.1.0网络走了R3,可是这个调整同一时候影响了其它路由条目,这不是我们希望的。可见neighbor x.x.x.x weight xxx配置方法尽管最简单,可是它并不能精确地针对某条路由实现weight值的改变,实际上当将某个邻居的weight设置好以后,那么这个邻居通告过来的全部路由都会被本地路由器加上同样的weigh权重,那么应该如何合理的设置Weight值呢?以下进一步调整
R4#conf t
R4(config)#access-list 1 permit 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 //创建訪问控制列表
R4(config)#route-map weight_100 permit 1 //创建策略
R4(config-route-map)#match ip add 1 将訪问控制列表应用到策略中
R4(config-route-map)#set weight 100 //对符合条件的条目设置weight为100
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#route-map weight_100 permit 2//创建空的策略,同意其它不变
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 200
R4(config-router)#no nei 192.168.34.1 weight 100 //清除之前的设置
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.1 route-map weight_100 in//将策略应用到进方向
R4(config-router)#do clear ip bgp * soft in //不中断邻居关系,更新bgp路由
R4#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i -internal,
r RIB-failure, SStale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i1.1.1.0/24 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i
*>i 192.168.13.1 0 100 100 100 i
*>i192.168.12.0 192.168.24.1 0 100 0 i
* i 192.168.13.1 0 100 0 100 i
* i192.168.13.0 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i
*>i 192.168.34.1 0 100 0 i
* i192.168.24.0 192.168.24.1 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i192.168.34.0 192.168.34.1 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
此时达到我们的理想了,总结:
(1) Weight仅仅具有本地意义他不能被路由器传递仅仅在本路由其上有效.
(2) Weight:是思科的私有属性
(3)在cisco中,weight属性的优先级是最高的.在其它厂商中,从Local_pref属性開始。
(3)weight属性默认会设置为32768.其它路由的权重默觉得0.
(4)假设有多条前往同一个目的路由器,那么将会选择权重高地路由优先。
(5)weight是一个入站策略仅仅能用in的方向,用out方向是无效的,由于这个属性不会传递到邻居去的。
实验五、BGP的next-hop-self属性
R1配置:
R1#conf t
R1(config)#int lo 0
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int s0/0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 65501
R1(config-router)#net 1.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255
R1(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2 remote-as 65502
R2配置:
R2#conf t
R2(config)#int s0/0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int s0/1
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 65502
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1 remote-as 65501
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.2 remote-as 65502
R3配置:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#int s0/0
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 65502
R3(config-router)#bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.1 remote-as 65502
R3(config-router)#net 3.3.3.3 mask 255.255.255.255
此时我们查看R3的路由表,会发现根本没有学习到R1的路由。查看R3的BGP路由你会发现存在两条R1的路由,指向的下一跳是192.168.12.0网段,可是却是无效的路由由于,R3并没有192.168.12.0的路由。原因是对于IBGP,起源AS内部的路由的NEXT-HOP就是通告该路径的邻居的ip(假设有设定更新源,则为更新源地址)。而对于EBGP从外部AS注入进来的路由的NEXT-HOP通常会不变地带入IBGP中,也始终指向的是下一个AS(即本AS对端的EBGP邻居接口IP)。
R3#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRPexternal, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1,E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-ISsummary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * -candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodicdownloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
3.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
C 3.3.3.3 isdirectly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.23.0/24 isdirectly connected, Serial0/0
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router IDis 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i1.1.1.1/32 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 65501 i
*> 3.3.3.3/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 65501 i
*> 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
要想解决问题有三种方法:
R2上在BGP进程中使用Network命令宣告自己的直连网络
R2与R3之间执行某种IGP路由协议,并在IGP中宣告自己的网络
R2中使用BGPnext-hop-self,强迫路由器通告自己是发送BGP更新的下一跳,同样假设R1内部的自治区域还有其它路由,那么R1也要做配置。即:
R2#conf t
R2(config)#routerbgp 65502
R2(config-router)#nei192.168.23.2 next-hop-self
总结:
1、BGP协议路由更新有个前提条件:下一条路由可达,假设不可达,则不会把接受到的路由装入路由表并更新给其余的peer。而通常情况下,下一条路由可达须要依赖IGP,非常少网络会把bgp import到IGP的。
2、依据要求1,EBGP传送路由给peer时缺省会把next-hop设定为自己。
3、IBGP传送路由给peer时缺省不会改变next-hop,为了满足1,AS边界路由器(EBGP/IBGP)在传送路由给IBGP peer时通常须要设置next-hop-self,否则IBGP peer会因路由的下一跳不可达而拒绝IBGP Peer路由。BGP一般仅仅在解析路由的下一跳,为了防止下跳不可达的问题,就用策略了。EBGP给ibgp的时候,一般就要用这个了。但在MPLS中,有时候却不用这个也是能够的。用直连接口建立外部邻居,并把与外部邻居的直连的port执行与as一样的igp,为passive模式.能够解决。
实验六、BGP 的MED属性和local Pref
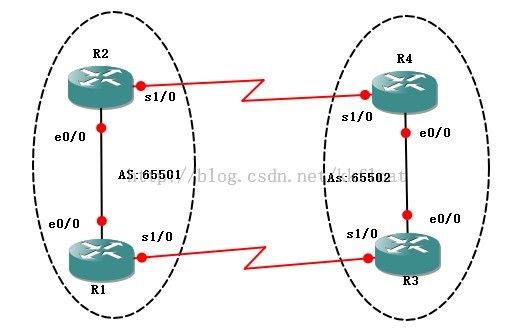
R1的配置:
R1#conf t
R1(config)#int e0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int s1/0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int lo 0
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 65501
R1(config-router)#bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 192.168.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 1.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2 remote-as 65501
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.2 remote-as 65502
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2 next-hop-self
R2配置:
R2#conf t
R2(config)#int e0/0
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int s1/0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.1255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int lo0
R2(config-if)#ip add 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 65501
R2(config-router)#bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.24.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#net 2.2.2.2 mask 255.255.255.255
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1 remote-as 65501
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.2 remote-as 65502
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1 next-hop-self
R3配置:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#int s1/0
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int e0/0
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.34.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int lo0
R3(config-if)#ip add 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 65502
R3(config-router)#bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-router)#net 3.3.3.3 mask 255.255.255.255
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.1 remote-as 65501
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.2 remote-as 65502
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.2 next-hop-self
R4配置:
R4#CONF T
R4(config)#int e0/0
R4(config-if)#ip add 192.168.34.2 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no sh
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#int s1/0
R4(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R4(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no sh
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#int lo0
R4(config-if)#ip add 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
R4(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 65502
R4(config-router)#bgp router-id 4.4.4.4
R4(config-router)#net 192.168.24.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R4(config-router)#net 192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R4(config-router)#net 4.4.4.4 mask 255.255.255.255
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.1 remote-as 65501
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.1 remote-as 65502
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.1 next-hop-self
完毕以上配置后应该全网互通。此时我们查看R1的路由表
R1#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRPexternal, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2- OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-ISsummary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * -candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodicdownloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directlyconnected, Ethernet0/0
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
C 1.1.1.1 is directlyconnected, Loopback0
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directlyconnected, Serial1/0
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
B 2.2.2.2 [200/0] via192.168.12.2, 00:05:53
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
B 3.3.3.3 [20/0] via192.168.13.2, 00:02:40
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
B 4.4.4.4 [20/0] via192.168.13.2, 00:03:10
B 192.168.24.0/24 [200/0] via192.168.12.2, 00:05:54
B 192.168.34.0/24 [20/0] via192.168.13.2, 00:03:11
R2#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRPexternal, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2- OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-ISsummary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * -candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodicdownloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directlyconnected, Ethernet0/0
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
B 1.1.1.1 [200/0] via192.168.12.1, 00:06:57
B 192.168.13.0/24 [200/0] via192.168.12.1, 00:06:57
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
C 2.2.2.2 is directlyconnected, Loopback0
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
B 3.3.3.3 [20/0] via192.168.24.2, 00:03:54
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1subnets
B 4.4.4.4 [20/0] via192.168.24.2, 00:35:09
C 192.168.24.0/24 is directlyconnected, Serial1/0
B 192.168.34.0/24 [20/0] via192.168.24.2, 00:35:10
依据路由表发现R1到达3.3.3.3和4.4.4.4网络都是从R3走;R2到达3.3.3.3和4.4.4.4网络都是从R4走。可是我们希望实现分流策略,即R1和R2到达4.4.4.4走R4,同一时候R1与R2到达R3的网络3.3.3.3时走R3出去。此时我们能够使用BGP的MED属性实现要求:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#access-list 1 permit 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 //在R3上标示出要施加策略的网络
R3(config)#route-map no4 permit 10 //创建一条同意的route-map策略
R3(config-route-map)#match ip addrees 1 //将策略应用到匹配的网络
R3(config-route-map)#set metric 1 //设置策略改变网络的metric參数
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#route-map no4 permit 11 //创建一条空route-map策略,同意其它全部不变
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 65502
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.1 route-map no4 out //将route-map策略传输给邻居
R3(config-router)#end
R3#clear ip bgp * soft out //不中断BGP邻居关系,向本路由器的全部BGP邻居又一次发送一次BGP路由信息
R4#conf t
R4(config)#access-list 1 permit 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
R4(config)#route-map no3 permit 10
R4(config-route-map)#match ip address 1
R4(config-route-map)#set metric 1
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#route-map no3 permit 11
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 65502
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.1 route-map no3 out
R3(config-router)#end
R4#clear ip bgp * soft out
再次查看R1和R2的路由表,此时已经达到我们的目的。
R1#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B- BGP
D - EIGRP,EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPFNSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF externaltype 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS,su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-ISinter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P -periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
1.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.1 isdirectly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
2.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 2.2.2.2[200/0] via 192.168.12.2, 00:23:35
3.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 3.3.3.3[20/0] via 192.168.13.2, 00:07:24
4.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.4[200/0] via 192.168.12.2, 00:03:13
B 192.168.24.0/24[200/0] via 192.168.12.2, 00:23:36
B 192.168.34.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.13.2, 00:08:06
2#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B- BGP
D - EIGRP,EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPFNSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPFexternal type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS,su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-ISinter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P -periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
1.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.1[200/0] via 192.168.12.1, 00:23:16
B 192.168.13.0/24 [200/0] via 192.168.12.1, 00:23:16
2.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
C 2.2.2.2 isdirectly connected, Loopback0
3.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 3.3.3.3[200/0] via 192.168.12.1, 00:03:25
4.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.4[20/0] via 192.168.24.2, 00:02:54
C 192.168.24.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
B 192.168.34.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.24.2, 00:02:55
我们要实现R3与R4到网络1.1.1.1走R3,R3与R4到网络2.2.2.2走R4,也能够使用改动MED的方法。可是我们还有还有一种方法就是BGP的Local Pref 即本地优先。查看R3的路由表:
R3#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B- BGP
D - EIGRP,EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPFNSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPFexternal type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS,su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-ISinter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P -periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 192.168.12.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.13.1, 00:35:57
1.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.1[20/0] via 192.168.13.1, 00:35:57
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
2.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 2.2.2.2[20/0] via 192.168.13.1, 00:35:57
3.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
C 3.3.3.3 isdirectly connected, Loopback0
4.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.4[200/0] via 192.168.34.2, 00:31:05
B 192.168.24.0/24 [200/0] via 192.168.34.2, 00:31:06
C 192.168.34.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
然后进行例如以下改动改变选路:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#access-list 2 permit 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
R3(config)#route-map no2 permit 22
R3(config-route-map)#match ip address 2
R3(config-route-map)#set local-preference 200
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#route-map no2 permit 23
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 65502
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.2 route-map no2 out
R3(config-router)#end
R3# clear ip bgp * soft out
R4#conf t
R4(config)#access-list 2 permit 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255
R4(config)#route-map no1 permit 22
R4(config-route-map)#match ip address 2
R4(config-route-map)#set local-preference 200
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#route-map no1 permit 23
R4(config-route-map)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 65502
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.1 route-map no1 out
R4(config-router)#end
R4#clear ip bgp * soft out
配置完毕后R3和R已经达到我们的目的,此时查看R3的路由表:
R3#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B- BGP
D - EIGRP,EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPFNSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPFexternal type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS,su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-ISinter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P -periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
B 192.168.12.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.13.1, 00:08:32
1.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.1[20/0] via 192.168.13.1, 00:08:32
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1/0
2.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 2.2.2.2[200/0] via 192.168.34.2, 00:02:08
3.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
C 3.3.3.3 isdirectly connected, Loopback0
4.0.0.0/32 issubnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.4[200/0] via 192.168.34.2, 00:08:32
B 192.168.24.0/24 [200/0] via 192.168.34.2, 00:08:34
C 192.168.34.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
总结:
MED属性可选非传递,相当于IGP中的Metic值,它告诉另外一个邻居AS中的BGP Router,从哪个入口进来我本地AS的才是最优的:邻居AS中的BGP Router依据这个MED值来选择到达某个网络的最佳路径,MED值越小越好。另外邻居AS不会再将这个MED属性值通告给邻居AS,当邻居AS中的BGP Router将那些网络条目通告给它另外的EBGP邻居时,会将这个MED值删掉MED属性值默觉得0,值越低优先级越高。谨记MED是影响他人的AS。
Local_Pref属性是公认自由决定,仅仅用在和IBGP邻居间 的Update分组更新中,这个属性字段是不会传递给EBGP邻居的,它告诉本地AS中的BGP Router,从哪个出口出去才是最优的:同一个AS中的BGP Router依据这个Local_Pref值来选择到达某个网络的最佳路径当Router要将路由条目通告给其EBGP邻居的时候,会将这个Local_Pref属性删掉。Local-pref属性的默认值为100,值越高优先级越高。谨记Local_Pref是影响自己的AS。
实验七、AS-PATH属性
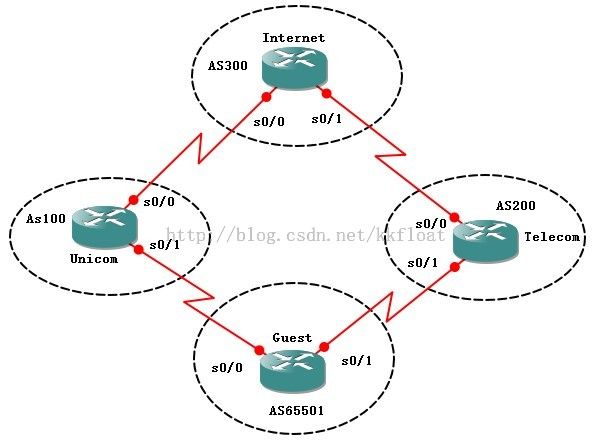
Internet配置:
Internet#conf t
Internet(config)#int lo0
Internet(config-if)#ip add 202.100.100.1255.255.255.0
Internet(config-if)#exit
Internet(config)#int s0/0
Internet(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Internet(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
Internet(config-if)#no sh
Internet(config-if)#exit
Internet(config)#int s0/1
Internet(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Internet(config-if)#ip add 192.168.13.1255.255.255.0
Internet(config-if)#no sh
Internet(config-if)#exit
Internet(config)#router bgp 300
Internet(config-router)#bgp router-id1.1.1.1
Internet(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0mask 255.255.255.0
Internet(config-router)#net 192.168.13.0mask 255.255.255.0
Internet(config-router)#net202.100.100.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Internet(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2remote-as 100
Internet(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.2remote-as 100
Unicom配置:
Unicom#conf t
Unicom(config)#int s0/0
Unicom(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Unicom(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.2255.255.255.0
Unicom(config-if)#no sh
Unicom(config-if)#exit
Unicom(config)#int s0/1
Unicom(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Unicom(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.1255.255.255.0
Unicom(config-if)#no sh
Unicom(config-if)#exit
Unicom(config)#router bgp 100
Unicom(config-router)#bgp router-id2.2.2.2
Unicom(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0mask 255.255.255.0
Unicom(config-router)#net 192.168.23.0mask 255.255.255.0
Unicom(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1remote-as 300
Unicom(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.2remote-as 65501
Telecom配置:
Telecom#conf t
Telecom(config)#int s0/0
Telecom(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Telecom(config-if)#ip add 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.0
Telecom(config-if)#no sh
Telecom(config-if)#exit
Telecom(config)#int s0/1
Telecom(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Telecom(config-if)#ip add 192.168.34.1 255.255.255.0
Telecom(config-if)#no sh
Telecom(config-if)#exit
Telecom(config)#router bgp 100
Telecom(config-router)#bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
Telecom(config-router)#net 192.168.13.0 mask255.255.255.0
Telecom(config-router)#net 192.168.34.0 mask255.255.255.0
Telecom(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.1 remote-as 300
Telecom(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.2 remote-as 65501
Guest配置:
Guest#conf t
Guest(config)#int lo0
Guest(config-if)#ip add 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
Guest(config-if)#exit
Guest(config)#int s0/0
Guest(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Guest(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
Guest(config-if)#no sh
Guest(config-if)#exit
Guest(config)#int s0/1
Guest(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Guest(config-if)#ip add 192.168.34.2 255.255.255.0
Guest(config-if)#no sh
Guest(config-if)#exit
Guest(config)#router bgp 65501
Guest(config-router)#bgp router-id 4.4.4.4
Guest(config-router)#net 192.168.24.0 mask255.255.255.0
Guest(config-router)#net 192.168.34.0 mask255.255.255.0
Guest(config-router)#net 4.4.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Guest(config-router)#nei 192.168.24.1 remote-as 100
Guest(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.1 remote-as 100
完毕配置后,我们来看看Unicom的BGP路由表,你会发现根本学习不到Telecom的 AS 100路由条目,同一时候查看Telecom的BGP路由表也会找不到Unicom的AS100路由条目。
Unicom#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, *valid, > best, i - internal,
rRIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 4.4.4.0/24 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
* 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.13.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i
* 192.168.24.0 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.34.0 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
*> 202.100.100.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i
事实上这是由于Unicom与Telecom的AS号同样,触犯了BGP的防环机制。即当某台BGP路由器从其外部对等体接收到的某条路由的AS-Path中包括已有的自己的AS号,那么该路由器就知道该路由出现了环路,须要丢包处理。此时我们改动Telecom的AS为200,并又一次与其它路由建立关系.然后再次查看Unicom的BGP路由表
Telecom#conf t
Telecom(config)#no router bgp 100
Telecom(config)#router bgp 200
Telecom(config-router)#bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
Telecom(config-router)#net 192.168.13.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Telecom(config-router)#net 192.168.34.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Telecom(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.1 remote-as 300
Telecom(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.2 remote-as 65501
Internet# conf t
Internet(config)#router bgp 300
Internet(config-router)#no nei 192.
Internet(config-router)#no nei 192.168.13.2 remote-as 100
Internet(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.2 remote-as 200
Guest#conft
Guest(config)#routerbgp 65501
Guest(config-router)#nonei 192.168.34.1 remote-as 100
Guest(config-router)#nei192.168.34.1 remote-as 200
Unicom#sh ipbgp
BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, *valid, > best, i - internal,
rRIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 4.4.4.0/24 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
* 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.13.0 192.168.24.2 0 65501 200i
*> 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i //最优
* 192.168.24.0 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.34.0 192.168.12.1 0 300 200 i
*> 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 I //最优
*> 202.100.100.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i
如今全网已经正常了,我们最好还是看一看Unicom 的BGP路由表中的Path属性,即AS-PATH属性,它是公认必遵属性,该属性用一串AS号来描写叙述去往的指定目的地AS间路径或路由,当BGP speaker发起一条路由,将在AS_Path中添加自己的AS号。也就是说,这条路由每经过一个AS区域,就会加上一个AS号,用来标示路径的优先级。当weight值同样,Local Pre同样,Metric同样时,As号叠加得越多,说明经过的AS越多,那么这个路由的优先级也越低。相反,经过的AS越少,那么说明路由越优先.越优先的路由,最先进入路由表,以下用Unicom的路由表表明
Unicom#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRPexternal, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA externaltype 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-ISsummary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area,* - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodicdownloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 isdirectly connected, Serial0/0
B 192.168.13.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.12.1, 00:37:52
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted,1 subnets
B 4.4.4.0 [20/0] via192.168.24.2, 00:31:12
B 202.100.100.0/24 [20/0]via 192.168.12.1, 00:47:34
C 192.168.24.0/24 isdirectly connected, Serial0/1
B 192.168.34.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.24.2, 00:31:12
那么我们能否够改动AS—PATH属性,达到调整选路的目的呢?请看以下,这里我们改变一条试试效果:
Unicom#conf t
Unicom(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.13.00.0.0.255 //创建訪问控制网络
Unicom(config)#route-map net13 permit 10 //创建策略
Unicom(config-route-map)#match ip add 1 //将訪问控制列表应用到策略
Unicom(config-route-map)#set as-path prepend 400 500 //对符合策略网络追加AS号
Unicom(config-route-map)#exit
Unicom(config)#route-map net13 permit 11 //创建同意其它不变的策略
Unicom(config-route-map)#exit
Unicom(config)#router bgp 100
Unicom(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1 route-map net13in //将策略应用到邻居的进方向
Unicom(config-router)#do clear ip bgp * soft in //不中断邻居关系,请求邻居更新bgp路由信息
Unicom#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, *valid, > best, i - internal,
rRIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 4.4.4.0/24 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
* 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.13.0 192.168.24.2 0 65501 200 i
* 192.168.12.1 0 0 400 500 300 i
* 192.168.24.0 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.34.0 192.168.12.1 0 300 200 i
*> 192.168.24.2 0 0 65501 i
*> 202.100.100.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 300 i
Unicom#sh ip rou
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile,B - BGP
D -EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPFNSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPFexternal type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i -IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-ISinter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR,P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.12.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0
B 192.168.13.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.24.2, 00:01:38
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.0[20/0] via 192.168.24.2, 01:02:45
B 202.100.100.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.12.1, 01:19:08
C 192.168.24.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/1
B 192.168.34.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.24.2, 01:02:45
这次我们来看看Internet AS中的BGP路由表
Internet#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, *valid, > best, i - internal,
rRIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 4.4.4.0/24 192.168.13.2 0 200 65501 i
*> 192.168.12.2 0 100 65501 i
* 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.2 0 0 100 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.13.0 192.168.12.2 0 100 65501 200 i
* 192.168.13.2 0 0 200 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.24.0 192.168.13.2 0 200 65501 i
*> 192.168.12.2 0 0 100 i
*> 192.168.34.0 192.168.13.2 0 0 200 i
* 192.168.12.2 0 100 65501 i
*> 202.100.100.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
对于Internet它根本不用知道Guest的网络,假设须要过滤掉Guest的网络传送到Intetnet。这是就要使用AS_PATH过滤列表,它是一种相似于ACL的列表,仅仅是它匹配的不是网络,而是AS号。编写AS_PATH的ACL要利用正則表達式,这是从linux中发展出来的命令系统。以下进行配置,并观察Internet的BGP路由是否还有4.4.4.0网络。
Internet#conft
Internet(config)#ipas-path access-list 1 deny 65501$ //创建AS-PATH过滤列表,拒绝由AS65501发起的路由
Internet(config)#ipas-path access-list 1 permit .* //创建AS-PATH同意其它路由
Internet(config)#routerbgp 300
Internet(config-router)#nei192.168.12.2 filter-list 1 in //将AS-PATH策略应用到邻居的进方向
Internet(config-router)#nei192.168.13.2 filter-list 1 in//将AS-PATH策略应用到邻居的进方向
Internet(config-router)#doclear ip bgp * soft in//不中断邻居关系,更新BGP路由
Internet#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 12, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, *valid, > best, i - internal,
rRIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.2 0 0 100 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.13.0 192.168.12.2 0 100 65501 200 i
* 192.168.13.2 0 0 200 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.24.0 192.168.12.2 0 0 100 i
*> 192.168.34.0 192.168.13.2 0 0 200 i
*> 202.100.100.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
注意:AS_PATH的ACL,依据BGP路由的AS_PATH属性决定路由的接受与拒绝。正則表達式经常使用操作符:
| 符号 |
说明 |
| 。 |
匹配随意字符,包括特殊字符,空格。 |
| * |
匹配*前面字符中0次或多次。 |
| + |
匹配+前面字符中1次或多次。 |
| ? |
匹配?前面字符中0次或1次。 |
| ^ |
匹配字符串的開始。 |
| $ |
匹配字符串的结束。 |
| _ |
匹配一个符号,如逗号、左大括号、右大括号、左括号、右括号和空格等符号,在表达式的开头或结尾时还可作起始符、结束符(同^ ,$)。 |
| ( ) |
匹配一个变化的字符或一个独立的匹配,通常和"|"一起使用。 |
| | |
逻辑或,交替匹配 |
| [ ] |
表示一组字符的集合,假设集合中第一个字符为"^",则表示补集 |
| - |
连接符 |
| \ |
转义操作符,去除特殊字符的特殊意义 |
实验八、BGP的origin属性
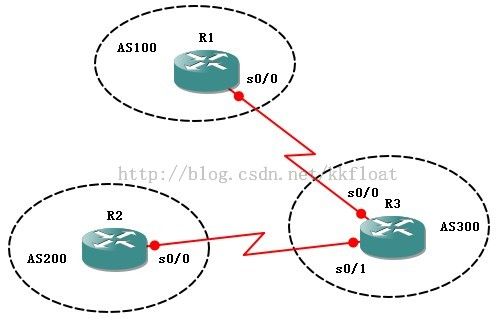
R1配置:
R1#CONF T
R1(config)#int s0/0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip add192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#bgprouter-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)#net192.168.12.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#nei192.168.12.2 remote-as 300
R2配置:
R2#conf t
R2(config)#int s0/0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#int lo0
R2(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#net192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#nei192.168.23.2 remote-as 300
R3配置:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#int s0/0
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#ip add192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int s0/1
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#ip add192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#net192.168.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei192.168.12.1 remote-as 100
R3(config-router)#nei192.168.23.1 remote-as 200
查看一下R3的BGP路由表:
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 5, localrouter ID is 192.168.23.2
Status codes: s suppressed, ddamped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e -EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 100 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
接着分别在R1和R2上进行例如以下改动:
R1(config)#conf t
R1(config)#iproute 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 null0 //创建指向空port的静态路由
R1(config)#routerbgp 100
R1(config-router)#redistributestatic //将静态路由重分发到BGP进程
R1(config-router)#doclear ip bgp * soft out
R2#conf t
R2(config)#routerbgp 200
R2(config-router)#net1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0//将Loopback0网络宣告到BGP中
R2(config-router)#do clear ip bgp * soft out
再次观察R3的BGP路由表:
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table versionis 7, local router ID is 192.168.23.2
Status codes: ssuppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i -IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>1.1.1.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i //最优
* 192.168.12.1 0 0 100 ?
* 192.168.12.0 192.168.12.1 0 0 100 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R3#sh ip bgp1.1.1.1
BGP routing tableentry for 1.1.1.0/24, version 7
Paths: (2available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
200
192.168.23.1 from 192.168.23.1(192.168.23.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100,valid, external, best
100
192.168.12.1 from 192.168.12.1 (1.1.1.1)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref100, valid, external
这里引出了BGP路由的origin属性。这个属性有3个值,分别为:
IGP:当使用 bgp network 命令宣告进BGP中。在BGP路由表中起源于IGP的路由用“i”表示
EGP:通过BGP学习到的路由。在BGP路由表中起源于EGP的路由用“e”表示(淘汰了)
incomplete:当路由重分布进BGP时,即无法确定路由的始发者时,在BGP路由表中用“?”表示
这三个值得优先级是:IGP>EGP>Incompelete。
实验九、BGP的路由过滤prefix-list和Distribute-list
R1配置:
R1#conf t
R1(config)#int lo0
R1(config-if)#ip add 172.168.0.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int lo1
R1(config-if)#ip add 172.168.1.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int lo2
R1(config-if)#ip add 172.168.2.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int lo3
R1(config-if)#ip add 172.168.3.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int s0/0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 172.168.0.0 mask255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 172.168.1.0 mask255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 172.168.2.0 mask255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#net 172.168.3.0 mask255.255.255.0
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2remote-as 200
R2配置:
R2#conf t
R2(config)#int s0/0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.2255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int s0/1
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.1255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.12.0 mask255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#net 192.168.23.0 mask255.255.255.0
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.1remote-as 100
R2(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.2remote-as 300
R3配置:
R3#conf t
R3(config)#int s0/0
R3(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.2255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#net 192.168.23.0 mask255.255.255.0
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.1remote-as 200
完毕以上配置后,查看R3的BGP路由表
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 8, localrouter ID is 192.168.23.2
Status codes: s suppressed, ddamped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>172.168.0.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 172.168.1.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 172.168.2.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 172.168.3.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 192.168.12.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
* 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
此时我们使用prefix-list让R3学不到172.168.0.0网段,然后再次查看R3的路由表
R2#conf t
R2(config)#ip prefix-list bgpbldeny 172.168.0.0/24 //创建拒绝的前缀过滤列表
R2(config)#ip prefix-list bgpblpermit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32//创建同意其它的前缀列表
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei192.168.23.2 prefix-list bgpbl out//将前缀列表应用到邻居的出方向
R2(config-router)#do clear ipbgp * soft out//不中段邻居关系,更新BGP路由信息
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 9, localrouter ID is 192.168.23.2
Status codes: s suppressed, ddamped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.168.1.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 172.168.2.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 172.168.3.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 192.168.12.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
* 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
我们还能够使用Prefix-list过滤掉R1发起172.168.1.0的路由,可是我想使用还有一个方法就是Distribute-list,配置例如以下
R1(config)#conf t
R1(config)#access-list 10 deny 172.168.1.00.0.0.255//创建訪问控制列表拒绝指定网络
R1(config)#access-list 10 permit any//设置訪问控制列表同意其它网络
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#nei 192.168.12.2distribute-list 10 out//将控制列表应用到邻居的出方向
R1(config-router)#do clear ip bgp * softout//不中断邻居关系,更新BGP路由
配置完毕后R2和R3的BGP路由表中就不会有172.168.1.0网段了
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is192.168.23.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, hhistory, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? -incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.168.2.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 172.168.3.0/24 192.168.23.1 0 200 100 i
*> 192.168.12.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
* 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 0 0 200 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
实验十、BGP路由汇聚
在BGP下有三种生成汇聚地址的方法:谨记BGP宣告网络的前提是该路由条目存在路由表中
第一种,自己主动汇总(默觉得关闭状态),BGP的自己主动路由汇总特性,并不是像RIP这些普通距离矢量协议或EIGRP高级距离矢量协议一样在主类的边界进行汇总,其主要是将本地多个同样主类网络下的无类路由向主类网络进行汇总,并且向邻居路由器通告此条路由。而无论其本身是否处于主类边界。auto-summary命令作用的对象:重分布进bgp的igp或直连或静态路由.假设这些路由是子网路由,在进bgp表时将被自己主动汇总成有类路由条目.auto-summary命令不作用的对象:network通告的路由,ibgp或ebgp邻居通告的路由.假设是此类产生的路由,在showip bgp表中将是子网路由,这些路由再通过ibgp或ebgp通告给邻居时,依据此原则,无论邻居是否启用auto-summary,接收到的都将是子网路由条目.仅仅要在showip bgp表中存在的路由,都会不变地传给ibgp或ebgp的邻居,而无论邻居或自己是否启用auto-summary命令.
另外一种,在路由表中为聚合路由建立一条静态路由条目后使用network命令将它公布出去。通过用静态路由指一条汇总地址到null0当中去,让这条路由条目存在于路由表中再去通告一个汇总地址这样的方式去做汇总。可是其它的BGP路由器并不知道是在哪里汇总的,导致不easy排错,且不能对汇总路由做策略。仅仅能在产生明细路由的路由器上做。
第三种,使用 aggregate-address 命令生成聚合地址。此方式为BGP真正的路由汇总,它须要在本路由器上通过network命令先通告明细路由加入到BGP表中,也能够通过重分发来完毕。aggregate-address 汇聚命令的选项
summary-only :该命令加入后,aggregate-address 宣告的路由中,明细路由将不会宣告。
supress-map :该命令用来抑制aggregate-address 宣告的路由中不包括某条明细路由。
attribute-map: 该命令能够改变聚合路由的属性,比如能够改变聚合路由的ORIGIN属性,
AS-Set :不写该命令时,聚合路由的as-path是基于生成聚合路由的as-path,而不是明细路由的as-path,加入该命令后,聚合路由将继承明细路由的全部属性,包括as-path。
Advertise Map:设置汇聚路由的组成不包括特定明细路由,这样聚合路由就不会继承特定明细路由的属性。当在对BGP路由进行聚合的时候,用AS-SET属性对被聚合的路由将携带明细路由的AS号,利用advertise-map