数据结构:力扣刷题
目录
题一:反转链表
思路一:
思路二:
题二:移除链表元素
思路一:
思路二:
题三:链表的中间节点
思路一:
题四:链表中倒数第k个结点
思路一:
题五:合并两个有序链表
思路一:
简化后:
本人实力有限可能对一些地方解释的不够清晰,可以自己尝试读代码,望海涵!
题一:反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
思路一:
三个变量n1=NULL,n2=head,n3,如果n2不为NULL,则n3=n2->next,循环如果n2为NULL,就停下来,当n3为空时n3就不进行变化,最后n1会停在最后一个位置,这个时候逆置完成。
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;
n1 = NULL;
n2 = head;
if(n2)
n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1;
}思路二:
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
//头插新节点,更新头
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}
题二:移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
思路一:
分别定义结构体指针类型的n1=head,n2=NULL,在链表上进行n1->val == val,不同则不改变,相同则跳过这个结构体指针地址,指向下一个结构体的地址,然后free释放值相同的地址,循环操作到指向NULL地址,当然,如果第一个位置就与val相同,则,跳过这个地址,指向下一个地址。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* n1 = head, * n2 = NULL;
while (n1)
{
if (n1->val == val)
{
if (head == n1)
{
head = n1->next;
free(n1);
n1 = head;
}
else
{
n2->next = n1->next;
free(n1);
n1 = n2->next;
}
}
else
{
n2 = n1;
n1 = n1->next;
}
}
return head;
}思路二:
新开辟一个newnode,n1=head,n2=NULL;让原链表中与val不相同的位置放到新开辟的结构体指针中,依次放入,最后将newnode的最后一个地址的next==NULL,完成移除。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* n1 = head;
struct ListNode* newnode = NULL;
struct ListNode* n2 = NULL;
while (n1)
{
if (n1->val == val)
{
struct ListNode* tail = n1->next;
free(n1);
n1 = tail;
}
else
{
if (n2 == NULL)
{
n2 = n1;
newnode = n2;
}
else
{
n2->next = n1;
n2 = n2->next;
}
n1 = n1->next;
}
}
if (n2)
n2->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}题三:链表的中间节点
给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
示例 1:
思路一:
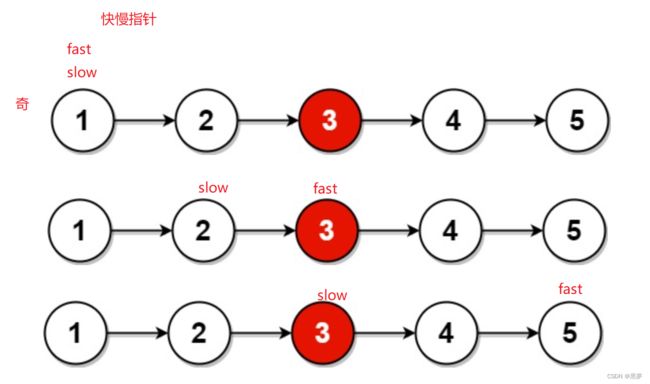
分别定义快慢两个指针,快指针一次前进两个地址,慢指针一次前进一个地址,当奇数时快指针的next为NULL时,当链表为偶数时判断条件为地址为NULL,停下来,此时慢指针就在链表中间节点上。
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}题四:链表中倒数第k个结点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
思路一:
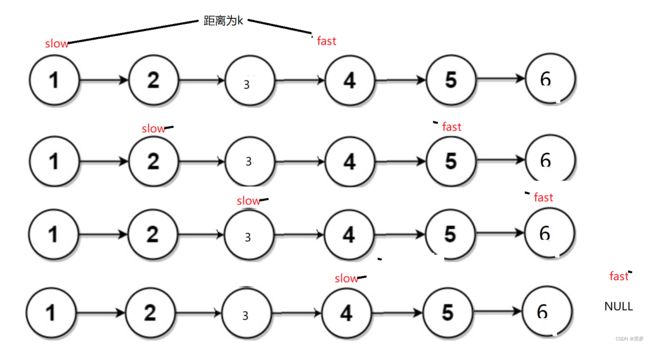
分别定义快慢两个指针,快指针fast先前进k个地址,然后fast和slow开始同时每次前进一个地址,一直到fast的地址为NULL时,停下来,这时的slow就是倒数第k个节点。排除倒数第0个和传递的指针为NULL的两种情况,直接return NULL。
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{
struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;
struct ListNode* slow = pListHead;
//方法一:
while(k--)
{
if(fast)
fast = fast->next;
else
return NULL;
}
//方法二:
//if (pListHead == NULL)
//{
// return NULL;
//}
//if (k == 0)
//{
// return NULL;
//}
//for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
//{
// if (fast == NULL)
// {
// return NULL;
// }
// fast = fast->next;
//
//}
while(fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}题五:合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
思路一:
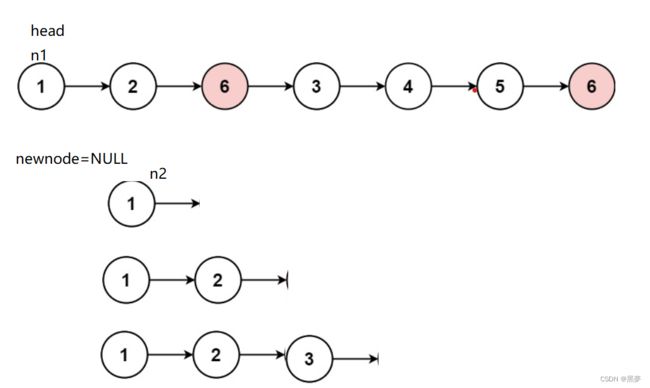
创建一个新的结构体指针newnode=NULL,n1=list1,n2=list2,写一个tail=NUL来遍历newnode,先判断list1和list2是否为空,为空则返回另一方,均不为空则,则按如下图循环放入newnode,循环到有一方为NULL,做一个判断将另一方在newnode后接上。
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if (list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if (list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode* n1 = list1;
struct ListNode* n2 = list2;
struct ListNode* newnode = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
while(n1 && n2)
{
if(n1->val >= n2->val)
{
if(tail == NULL)
{
tail = n2;
newnode = tail;
n2 = n2->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = n2;
tail = tail->next;
n2 = n2->next;
}
}
else
{
if(tail == NULL)
{
tail = n1;
newnode = tail;
n1 = n1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = n1;
tail = tail->next;
n1 = n1->next;
}
}
}
if(n1)
{
tail->next = n1;
}
if(n2)
{
else
tail->next = n2;
}
return newnode;
}简化后:
/*
解题思路:
此题可以先创建一个空链表,然后依次从两个有序链表中选取最小的进行尾插操作进行合并。
*/
typedef struct ListNode Node;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2){
if(l1 == NULL)
return l2;
else if(l2 == NULL)
return l1;
Node* head = NULL, *tail = NULL;
//创建空链表
head = tail = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
tail->next = NULL;
while(l1 && l2)
{
// 取小的进行尾插
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
tail->next = l1;
tail = tail->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = l2;
tail = tail->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
//剩余元素直接拼接
if(l1)
tail->next = l1;
else
tail->next = l2;
Node* list = head->next;
free(head);
return list;
}