开源工具fit-cache
一、引言
github地址:https://github.com/SongTing0711/fit-cache
目前业内对于本地缓存、Redis、Es、Ck等缓存的使用处于比较随意的状态,一方面是资源的浪费,另外一方面如果是本地缓存可能是导致oom的最后一根稻草。
作者创作的fit-cache提供key是否适合缓存,适合缓存的时间,解决缓存滥用、缓存同时失效等问题。
二、架构
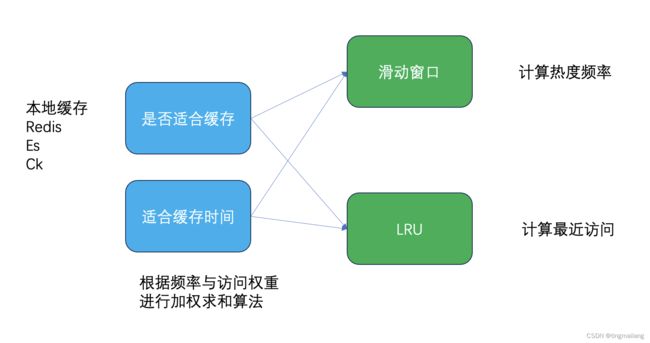
1、工具定位
fit-cahe要实现两个功能:key是否适合缓存、如果适合缓存,应该缓存多久。
作者参考了Mysql的Innodb存储引擎(innodb用有百分比的LRU进行mysql的缓冲池,避免频繁的磁盘读写)和京东的HotKey(京东用于商城的热点数据及时缓存,防止大促下打爆redis)。
作者认为可以使用滑动窗口+LRU列表的方式进行计算,也就是频率和最近访问时间。
2、实现
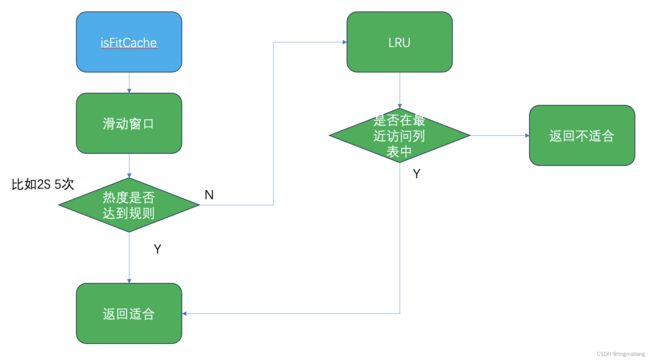
实现的话,作者认为频率的权重在最近访问之上因此是否适合缓存应该是先判断key对应的滑动窗口是否达到设定的热度规则,如果达不到再看LRU列表,但是LRU的长度是需要限定的,不然就不是非常有可能被很快被再次访问。
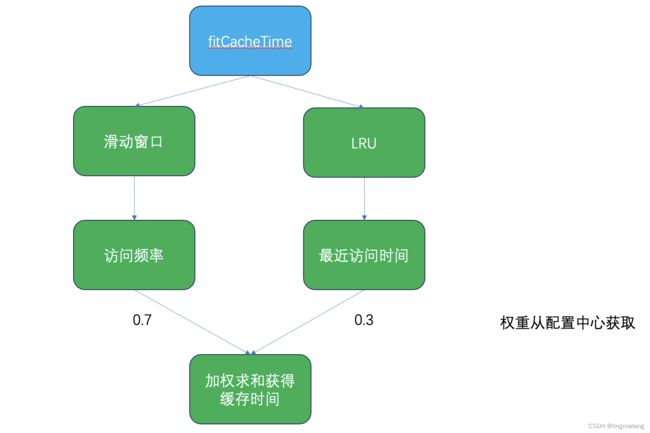
适合缓存的时间就需要通过频率和最近访问时间分配权重,进行加权计算,最近访问时间还需要进行指数衰减,因为访问时间离现在越久,很明显优先级越低。
3、封装
对于开源工具的封装无非两种方式,一种是封装成独立的Client放到maven给服务引用,这种是针对单体服务纬度的,优点是使用的时候引入简单,不用像很多中间件工具一样划分客户端服务端,导致引入成本巨大。
另外一种是封装成客户端服务端的模式,这样的话就可以计算到集群纬度,从而从整体上判断是否适合缓存,以及相应的缓存时间。
作者目前封装了第一种,第二种还在封装中。
三、源代码
这里讲一下fit-cache的核心代码
1、core
FitCacheStore对外暴露的核心api:是否适合缓存和适合缓存时间
可以把适合缓存的key的值通过set存入,作者底层是用的caffeine
DispatcherConfig是一个阻塞队列,key的访问事件被存储到这里,然后被异步线程取出进行计算频率和最近访问
public class FitCacheStore {
/**
* 判断是否适合缓存
*/
public static boolean isFitCache(String key) {
try {
// 先看滑动窗口的热度,判断适不适合缓存
boolean fit = CaffeineCacheHolder.getFitCache().getIfPresent(key) != null;
if (!fit) {
fit = CaffeineCacheHolder.getLruCache().get(key) != null;
}
DispatcherConfig.QUEUE.put(key);
return fit;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
public static int fitCacheTime(String key) {
try {
SlidingWindow window = (SlidingWindow) CaffeineCacheHolder.getWindowCache().getIfPresent(key);
long lastTime = (long) CaffeineCacheHolder.getLruCache().get(key);
if (window == null && lastTime == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (window == null && lastTime != 0) {
return FitCacheTime.calculateStorageTime(0, lastTime);
}
if (window != null && lastTime == 0) {
return FitCacheTime.calculateStorageTime(window.getCount(), 0);
}
int res = FitCacheTime.calculateStorageTime(window.getCount(), lastTime);
DispatcherConfig.QUEUE.put(key);
return res;
} catch (Exception e) {
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 从本地caffeine取值
*/
public static Object get(String key) {
return CaffeineCacheHolder.getFitCache().getIfPresent(key);
}
/**
* 设置缓存
*/
public static boolean set(String key, Object value) {
Object object = CaffeineCacheHolder.getFitCache().getIfPresent(key);
Object lru = CaffeineCacheHolder.getLruCache().get(key);
if (object == null && lru == null) {
return false;
}
CaffeineCacheHolder.getFitCache().put(key, value);
return true;
}
//
// private static ExecutorService threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1,
// 2,
// 5,
// TimeUnit.SECONDS,
// new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100),
// new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
// public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// KeyRule rule = new KeyRule("test", true, 2,5);
// KeyRuleHolder.KEY_RULES.add(rule);
// IKeyListener iKeyListener = new KeyListener();
// KeyConsumer keyConsumer = new KeyConsumer();
// keyConsumer.setKeyListener(iKeyListener);
//
// threadPoolExecutor.submit(keyConsumer::beginConsume);
// boolean fit = isFitCache("test");
// System.out.println("第一次访问test是否适合" + fit);
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// fit = isFitCache("test");
// System.out.println("第2次访问test是否适合" + fit);
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// fit = isFitCache("test666");
// System.out.println("第一次访问test666是否适合" + fit);
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// fit = isFitCache("test");
// System.out.println("第3次访问test是否适合" + fit);
// Thread.sleep(1000);
// int time = fitCacheTime("test");
// System.out.println("第1次访问test适合时间" + time);
// }
}2、config
这里主要是做了一个分发的作用,将消费事件的线程放入线程池启动
@Configuration
public class DispatcherConfig {
private ExecutorService threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1,
2,
5,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
/**
* 队列
*/
public static BlockingQueue QUEUE = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(200);
@Bean
public Consumer consumer() {
List consumerList = new ArrayList<>();
KeyConsumer keyConsumer = new KeyConsumer();
consumerList.add(keyConsumer);
threadPoolExecutor.submit(keyConsumer::beginConsume);
return new Consumer(consumerList);
}
}
public class KeyConsumer {
@Resource
private IKeyListener iKeyListener;
public void setKeyListener(IKeyListener iKeyListener) {
this.iKeyListener = iKeyListener;
}
public void beginConsume() {
while (true) {
try {
String key = DispatcherConfig.QUEUE.take();
iKeyListener.newKey(key);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} 3、listen
消费事件,在滑动窗口和LRU列表走一遍
@Component
public class KeyListener implements IKeyListener {
@Override
public void newKey(String key) {
SlidingWindow slidingWindow = checkWindow(key);
// 被访问,进入最近访问列表
CaffeineCacheHolder.getLruCache().put(key, System.currentTimeMillis());
//看看达到匹配规则没有
boolean fit = slidingWindow.addCount(1);
CaffeineCacheHolder.getWindowCache().put(key, slidingWindow);
if (fit && CaffeineCacheHolder.getFitCache().getIfPresent(key) == null) {
//数据变热,适合缓存
CaffeineCacheHolder.getFitCache().put(key, System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
/**
* 生成或返回该key的滑窗
*/
private SlidingWindow checkWindow(String key) {
// 取该key的滑窗
return (SlidingWindow) CaffeineCacheHolder.getWindowCache().get(key, (Function) s -> {
// 是个新key,获取它的规则
KeyRule keyRule = KeyRuleHolder.findRule(key);
return new SlidingWindow(keyRule.getInterval(), keyRule.getThreshold());
});
}
} 4、工具类
首先就是LRU列表,这里使用双向链表存储key的访问时间,列表容量可设置,mysql的innodb的lru特殊一点,它设置了一个比例,第一次访问的时候不会放到头部,而是放在30%左右的if,因为它的数据访问很大量,不是key维度。如果全表扫描很容易把lru列表原有内容全部顶掉。
作者这里不需要像他这样,因为是key维度的。
public class LruCache {
class Node {
String key;
Object value;
Node prev;
Node next;
public Node(String key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private final int capacity;
private final Map cache;
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public LruCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.cache = new HashMap<>();
this.head = new Node("head", 0);
this.tail = new Node("tail", 0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public Object get(String key) {
Node node = cache.get(key);
if (node != null) {
// l列表里面有就转到头部
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
return null;
}
public synchronized void put(String key, Object value) {
Node node = cache.get(key);
if (node != null) {
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
} else {
node = new Node(key, value);
cache.put(key, node);
addToHead(node);
if (cache.size() > capacity) {
// 超过容量就删除尾部节点
Node removedNode = removeTail();
cache.remove(removedNode.key);
}
}
}
private synchronized void moveToHead(Node node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private synchronized void addToHead(Node node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private synchronized void removeNode(Node node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private synchronized Node removeTail() {
Node removedNode = tail.prev;
removeNode(removedNode);
return removedNode;
}
} 然后是滑动窗口,管理的是频率
public class SlidingWindow {
/**
* 循环队列,就是装多个窗口用,该数量是windowSize的2倍
*/
private AtomicLong[] timeSlices;
/**
* 队列的总长度
*/
private int timeSliceSize;
/**
* 每个时间片的时长,以毫秒为单位
*/
private int timeMillisPerSlice;
/**
* 共有多少个时间片(即窗口长度)
*/
private int windowSize;
/**
* 在一个完整窗口期内允许通过的最大阈值
*/
private int threshold;
/**
* 该滑窗的起始创建时间,也就是第一个数据
*/
private long beginTimestamp;
/**
* 最后一个数据的时间戳
*/
private long lastAddTimestamp;
public SlidingWindow(int duration, int threshold) {
//超过10分钟的按10分钟
if (duration > 600) {
duration = 600;
}
//要求5秒内探测出来的,
if (duration <= 5) {
this.windowSize = 5;
this.timeMillisPerSlice = duration * 200;
} else {
this.windowSize = 10;
this.timeMillisPerSlice = duration * 100;
}
this.threshold = threshold;
// 保证存储在至少两个window
this.timeSliceSize = windowSize * 2;
reset();
}
public SlidingWindow(int timeMillisPerSlice, int windowSize, int threshold) {
this.timeMillisPerSlice = timeMillisPerSlice;
this.windowSize = windowSize;
this.threshold = threshold;
// 保证存储在至少两个window
this.timeSliceSize = windowSize * 2;
reset();
}
/**
* 初始化
*/
private void reset() {
beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
//窗口个数
AtomicLong[] localTimeSlices = new AtomicLong[timeSliceSize];
for (int i = 0; i < timeSliceSize; i++) {
localTimeSlices[i] = new AtomicLong(0);
}
timeSlices = localTimeSlices;
}
/**
* 计算当前所在的时间片的位置
*/
private int locationIndex() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
//如果当前的key已经超出一整个时间片了,那么就直接初始化就行了,不用去计算了
if (now - lastAddTimestamp > timeMillisPerSlice * windowSize) {
reset();
}
int index = (int) (((now - beginTimestamp) / timeMillisPerSlice) % timeSliceSize);
if (index < 0) {
return 0;
}
return index;
}
/**
* 增加count个数量
*/
public synchronized boolean addCount(int count) {
//当前自己所在的位置,是哪个小时间窗
int index = locationIndex();
clearFromIndex(index);
int sum = 0;
// 在当前时间片里继续+1
sum += timeSlices[index].addAndGet(count);
for (int i = 1; i < windowSize; i++) {
sum += timeSlices[(index - i + timeSliceSize) % timeSliceSize].get();
}
lastAddTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
return sum >= threshold;
}
public int getCount() {
int sum = 0;
//加上前面几个时间片
for (int i = 1; i < windowSize; i++) {
sum += timeSlices[i].get();
}
return sum;
}
private void clearFromIndex(int index) {
for (int i = 1; i <= windowSize; i++) {
int j = index + i;
if (j >= windowSize * 2) {
j -= windowSize * 2;
}
timeSlices[j].set(0);
}
}
}然后是适合缓存时间的计算,根据频率和最近访问时间进行计算
public class FitCacheTime {
/**
* 加权递减求和算法,计算数据的评分
*
* @param frequency
* @param lastTime
* @return
*/
private static double calculateScore(double frequency, long lastTime) {
// 根据业务需求和数据的重要性,给访问频率和最近访问时间分配不同的权重
// 这里可以从配置中心拿
double frequencyWeight = 0.7;
double timeWeight = 0.3;
// 计算访问频率和最近访问时间的值
double time = (System.currentTimeMillis() - lastTime) / 1000.0;
// 使用递减函数计算时间权重,越近访问的时间权重越高
double timeDecay = Math.exp(-time);
// 加权求和,得到评分
double score = frequencyWeight * frequency + timeWeight * timeDecay;
return score;
}
/**
* 计算数据适合被存储的时间
*
* @param frequency
* @param lastTime
* @return
*/
public static int calculateStorageTime(double frequency, long lastTime) {
// 根据评分确定数据适合被存储的时间
double score = calculateScore(frequency, lastTime);
int storageTime = (int) Math.ceil(score);
return storageTime;
}
}5、缓存
public class CaffeineCacheHolder {
/**
* key是appName,value是caffeine
*/
private static final ConcurrentHashMap CACHE_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final String FIT = "fit";
private static final String WINDOW = "window";
private static final String LRU = "lru";
public static Cache getFitCache() {
if (CACHE_MAP.get(FIT) == null) {
// todo 这里要从配置中心拿
CACHE_MAP.put(FIT, CaffeineBuilder.cache(60, 100, 60));
}
return (Cache) CACHE_MAP.get(FIT);
}
public static Cache getWindowCache() {
if (CACHE_MAP.get(WINDOW) == null) {
// todo 这里要从配置中心拿
CACHE_MAP.put(WINDOW, CaffeineBuilder.cache(60, 100, 60));
}
return (Cache) CACHE_MAP.get(WINDOW);
}
public static LruCache getLruCache() {
if (CACHE_MAP.get(LRU) == null) {
// todo 这里要从配置中心拿
CACHE_MAP.put(LRU, new LruCache(1));
}
return (LruCache) CACHE_MAP.get(LRU);
}
}
public class CaffeineBuilder {
/**
* 构建所有来的要缓存的key getCache
*/
public static Cache cache(int minSize, int maxSize, int expireSeconds) {
return Caffeine.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(minSize)
.maximumSize(maxSize)
.expireAfterWrite(expireSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
}
} 四、总结
fit-cache目前实现了客户端的是否适合缓存、适合缓存时间,还有很多拓展功能思路,比如缓存的失效,数据被更改的时候展示给用户的还是旧的数据;比如缓存的优先序列,低优先级的缓存侵占高优先级缓存的空间等等。作者有了一些方案,需要实践。
目前作者还在创作完善中,有兴趣的同学欢迎加入。