使用python的plot绘制loss、acc曲线,并存储成图片
使用 python的plot 绘制网络训练过程中的的 loss 曲线以及准确率变化曲线,这里的主要思想就时先把想要的损失值以及准确率值保存下来,保存到 .txt 文件中,待网络训练结束,我们再拿这存储的数据绘制各种曲线。
其大致步骤为:数据读取与存储 - > loss曲线绘制 - > 准确率曲线绘制
一、数据读取与存储部分
我们首先要得到训练时的数据,以损失值为例,网络每迭代一次都会产生相应的 loss,那么我们就把每一次的损失值都存储下来,存储到列表,保存到 .txt 文件中。
1.3817585706710815,
1.8422836065292358,
1.1619832515716553,
0.5217241644859314,
0.5221078991889954,
1.3544578552246094,
1.3334463834762573,
1.3866571187973022,
0.7603049278259277
上图为部分损失值,根据迭代次数而异,要是迭代了1万次,这里就会有1万个损失值。
而准确率值是每一个 epoch 产生一个值,要是训练100个epoch,就有100个准确率值。
这里的损失值是怎么保存到文件中的呢?首先,找到网络训练代码,就是项目中的 main.py,或者 train.py ,在文件里先找到训练部分,里面经常会有这样一行代码:
for epoch in range(resume_epoch, num_epochs): # 就是这一行
####
...
loss = criterion(outputs, labels.long()) # 损失样例
...
epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / trainval_sizes[phase] # 准确率样例
...
###
从这一行开始就是训练部分了,往下会找到类似的这两句代码,就是损失值和准确率值了。
这时候将以下代码加入源代码就可以了:
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
for epoch in range(resume_epoch, num_epochs): # 就是这一行
###
...
loss = criterion(outputs, labels.long()) # 损失样例
train_loss.append(loss.item()) # 损失加入到列表中
...
epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / trainval_sizes[phase] # 准确率样例
train_acc.append(epoch_acc.item()) # 准确率加入到列表中
...
with open("./train_loss.txt", 'w') as train_los:
train_los.write(str(train_loss))
with open("./train_acc.txt", 'w') as train_ac:
train_ac.write(str(train_acc))
这样就算完成了损失值和准确率值的数据存储了!
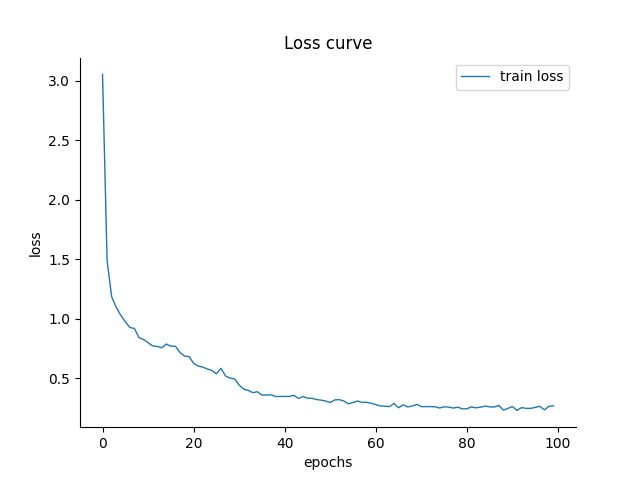
二、绘制 loss 曲线
主要需要 numpy 库和 matplotlib 库。
pip install numpy malplotlib
首先,将 .txt 文件中的存储的数据读取进来,以下是读取函数:
import numpy as np
# 读取存储为txt文件的数据
def data_read(dir_path):
with open(dir_path, "r") as f:
raw_data = f.read()
data = raw_data[1:-1].split(", ") # [-1:1]是为了去除文件中的前后中括号"[]"
return np.asfarray(data, float)
然后,就是绘制 loss 曲线部分:
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_loss_path = r"/train_loss.txt" # 存储文件路径
y_train_loss = data_read(train_loss_path) # loss值,即y轴
x_train_loss = range(len(y_train_loss)) # loss的数量,即x轴
plt.figure()
# 去除顶部和右边框框
ax = plt.axes()
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.xlabel('iters') # x轴标签
plt.ylabel('loss') # y轴标签
# 以x_train_loss为横坐标,y_train_loss为纵坐标,曲线宽度为1,实线,增加标签,训练损失,
# 默认颜色,如果想更改颜色,可以增加参数color='red',这是红色。
plt.plot(x_train_loss, y_train_loss, linewidth=1, linestyle="solid", label="train loss")
plt.legend()
plt.title('Loss curve')
plt.show()
pit.savefig("loss.png")
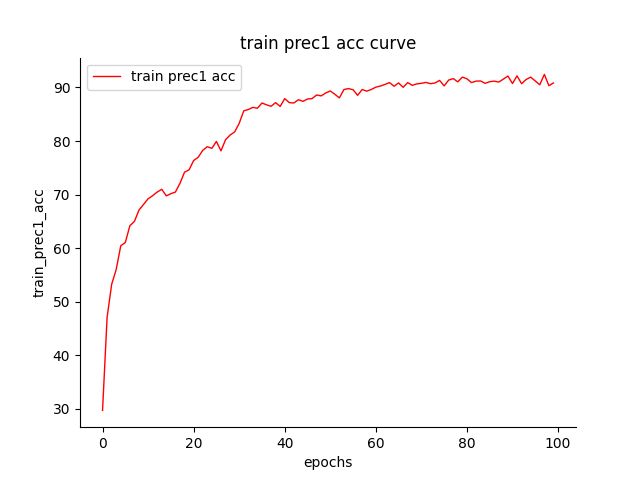
三、绘制准确率曲线
有了上面的基础,这就简单很多了。
只是有一点要记住,上面的x轴是迭代次数,这里的是训练轮次 epoch。
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_acc_path = r"/train_acc.txt" # 存储文件路径
y_train_acc = data_read(train_acc_path) # 训练准确率值,即y轴
x_train_acc = range(len(y_train_acc)) # 训练阶段准确率的数量,即x轴
plt.figure()
# 去除顶部和右边框框
ax = plt.axes()
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.xlabel('epochs') # x轴标签
plt.ylabel('accuracy') # y轴标签
# 以x_train_acc为横坐标,y_train_acc为纵坐标,曲线宽度为1,实线,增加标签,训练损失,
# 增加参数color='red',这是红色。
plt.plot(x_train_acc, y_train_acc, color='red',linewidth=1, linestyle="solid", label="train acc")
plt.legend()
plt.title('Accuracy curve')
plt.show()
pit.savefig("acc.png")
以下是完整代码,以绘制准确率曲线为例,并且将x轴换成了iters,和损失曲线保持一致,供参考:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读取存储为txt文件的数据
def data_read(dir_path):
with open(dir_path, "r") as f:
raw_data = f.read()
data = raw_data[1:-1].split(", ")
return np.asfarray(data, float)
# 不同长度数据,统一为一个标准,倍乘x轴
def multiple_equal(x, y):
x_len = len(x)
y_len = len(y)
times = x_len/y_len
y_times = [i * times for i in y]
return y_times
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_loss_path = r"/train_loss.txt"
train_acc_path = r"/train_acc.txt"
y_train_loss = data_read(train_loss_path)
y_train_acc = data_read(train_acc_path)
x_train_loss = range(len(y_train_loss))
x_train_acc = multiple_equal(x_train_loss, range(len(y_train_acc)))
plt.figure()
# 去除顶部和右边框框
ax = plt.axes()
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
plt.xlabel('iters')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
# plt.plot(x_train_loss, y_train_loss, linewidth=1, linestyle="solid", label="train loss")
plt.plot(x_train_acc, y_train_acc, color='red', linestyle="solid", label="train accuracy")
plt.legend()
plt.title('Accuracy curve')
plt.show()
pit.savefig("acc.png")