springboot 基础
巩固基础,砥砺前行 。
只有不断重复,才能做到超越自己。
能坚持把简单的事情做到极致,也是不容易的。
SpringBoot JavaEE 简介
JavaEE的局限性:
1、过于复杂,JavaEE正对的是复杂的分布式企业应用,然而现实情况是大部分应用都是比较简单,复杂的架构带来了复杂的开发方式和部署方式。
2、最求分布式,大部分引用并非都是JavaEE 嘉定的分布式系统,Spring曾经反对过这种分布式架构,并只提供了容器管理,名词获得了成功,大型应用采用分布式架构不可避免,Spring提供了其他的技术支持,eg:RestFul架构
3、不能及时和流行开源技术整合,比如消息处理,除了有了标准的JMS支持,现在还有新能更好的RabbitMQ和kalfa。JavaEE 并没有与之相对应的标准,方二十Spring,具有统一的实现消息处理模式
4、JavaEE 应用服务器都有商业公司提供价格不菲,少有公司采用管理引用服务器和部署应用对初学者和自学者有一定门槛
Spring
Spring通过ioc管理bean,通过Aop方式增强bean功能,它没有像JavaEE那样纤细规定容器提供的是何种服务和容器运行的具体组件类型。
Spring的缺点
尽管Spring很强大,但是他也有JavaEE的缺点:
1、使用门槛升高,要入门spring需要较长时间
2、对过时技术支持,导致使用复杂度升高
3、xml配置已经不再是流行的系统配置方式
4、集成第三方工具的时候,程序员还要考虑工具之间的兼容性
5、系统启动慢,不具备热部署功能,完全依赖虚拟机或者web服务器的热部署
SpringBoot
springboot简化了spring应用配置,不需要配置就能就能运行spring应用,springboot管理spring容器、第三方插件,并提供了许多默认系统级的服务。大部分的spring应用,无论是简单还是复杂,都只需要少量的配置和代码就能完成。springboot通过starter来提供系统级别的服务。在使用的时候,在pom.xml中引入对应的starter即可使用。
相比于spring,springboot优点:
1、实现约定大于配置,是一个低配置的应用系统架构,不像spring那样需要大量的配置。仅仅需要少量的配置就能完成大量的功能
2、提供了内置的tomcat或者jetty功能
3、通过加载jar包管理、自动装配技术,容易支持与其他技术体系、工具集成
4、支持热加载,开发体检好,也支持springboot监控,方便了解系统运行情况。
springboot 配置、加载
加载外部类的几种方式
- 使用@Configuration + @Bean 的方式引入
- 使用@Configuration + @ImportResource 方式引入
- 使用@Configuration + @Import 方式引入
加载配置文件中的属性的方式
- @Value(“${}”) 加载单一的配置文件
person.last-name=张三3333333333${random.uuid}
application.properties 文件中
@Value("${person.last-name}")
private String lastName;
- 使用@Component、@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”) 从全局的默认配置文件中加载属性
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
}
application.properties文件中
person.last-name=张三3333333333${random.uuid}
person.age=${random.int}
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=${person.hello:hello}_dog
person.dog.age=15
- 使用 @Component、@ConfigurationProperties 、@PropertySource 三个注解 从指定位置加载属性
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map maps;
private List profiles
application.yml 中的文档块模式
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: prod # 激活指定配置文件
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod # 该文件被激活
在启动jar包的时候 动态指定jar的端口号
java -jar demo.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev
配置虚拟机参数
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev
在启动jar的时候指定外部的配置文件
java -jar demo.jar --spring.config.location=G:/application.properties
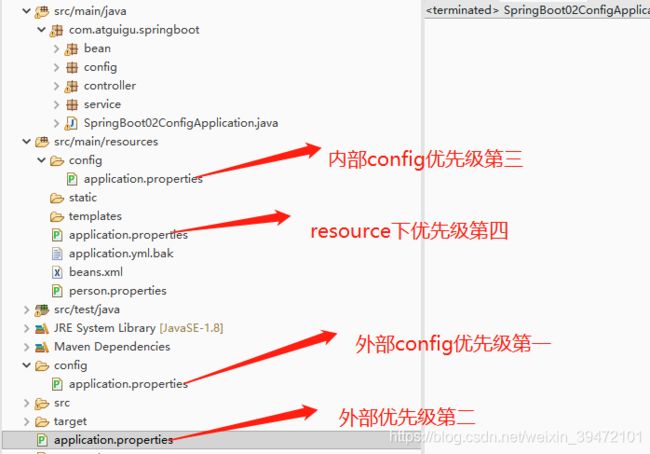
配置文件的加载顺序
- 在相同位置的application.properties 和application.yml 配置文件的加载顺序:从上到下加载,谁在上就加载谁
application.properties
server.port=8082
application.yml
server:
port: 8081
application.properties 在 application.yml 之上,所以启动的端口号 是8082
maven简介
maven实现的目标
- 是构建项目变得同意,maven屏蔽了构建的复杂过程
- 统一了构建下项目的方式,不同人、不同公司的羡慕都有同样的描述和构建项目的方式。maven通过pom.xml来描述项目,并提供了一系列插件来构建项目。
- 提出了一套开发项目的最佳实践。而不用每个项目都有不同机构和构建方式。比如源代码出现在scr/main/java中,测试代码出现在scr/main/test中,项目需要的配置文件放在scr/main/resources中
- 包含不同环境项目的构建方式
- 解决了依赖的问题,只要申明使用的类库,maven会自动冲仓库下载依赖的jar包,并能协助你管理jar之间的冲突
pom中元素介绍
groupId
表示项目所属的组,通常是一个公司或者组织的名称。如。org.springframework
artifactId
项目的唯一标识,如。spring-boot-start-web。groupId 和 artifactId 能唯一标识一个项目或者一个库,通常称之为项目坐标。
packaging
项目类型,常用的有jar和war两种
version
项目的版本号。通常来说,项目版本号分为三段,主版本、此版本、修订版本
主版本:代表脚骨变动或者不见同实现
次版本:是兼容性修改,功能增强
修订版:bug修复
modelVersion
代表pom文件的maven版本。
scope
scope 代表次类库和项目的关系,默认是compile,也就是编译和打包都需要此类库。
test:仅仅在单元测试的时候需要
provided:标识在编译阶段需要词此类库,但是打包不需要,因为项目的目标环境已经提供了
runtime:标识在编译和打包的时候都不需要,但是在运行的时候需要
build
此项目在pom中可选,build包含多个插件plugin,用来辅助构建项目
面试的时候,问过scope
spring boot 发送邮件
1.引入jar
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-mail
2.application.yml配置
spring:
mail:
#发送消息的邮箱配置
username: [email protected]
#password是QQ邮箱的授权码
password: snnaaprastgfdebg
host: smtp.qq.com
properties:
mail:
smtp:
ssl:
enable: true
3.发送简单文本信息
@Autowired
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
public void testContext() {
SimpleMailMessage message = new SimpleMailMessage();
//邮件设置
message.setSubject("Topic主题");
message.setText("Message……");
//发送到哪里
message.setTo("[email protected]");
//从哪里发送
message.setFrom("[email protected]");
mailSender.send(message);
}
4.发送带有附件的
public void testAA() throws Exception{
//1、创建一个复杂的消息邮件
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true);
//邮件设置
helper.setSubject("XXXX");
helper.setText("CCCC",true);
helper.setTo("[email protected]");
helper.setFrom("[email protected]");
//上传文件
helper.addAttachment("1.jpg",new File("C:\\Users\\DELL\\Pictures\\1.jpg"));
helper.addAttachment("2.mp4",new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\DELL\\\\Pictures\\\\2.mp4"));
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}
springboot和redis缓存
redis缓存
1)在pom中新增
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2)在application.yml中新增redis配置.ookk
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
3)配置redis序列化
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize 替换默认序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
// 设置value的序列化规则和 key的序列化规则
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
- java操作redis工具类
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.BoundSetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@SuppressWarnings(value = { "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
@Component
public class RedisCache
{
@Autowired
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
* @param timeout 时间
* @param timeUnit 时间颗粒度
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value, final Integer timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit)
{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeout, timeUnit);
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout)
{
return expire(key, timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout, final TimeUnit unit)
{
return redisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit);
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象。
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> T getCacheObject(final String key)
{
ValueOperations<String, T> operation = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
return operation.get(key);
}
/**
* 删除单个对象
*
* @param key
*/
public void deleteObject(final String key)
{
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
/**
* 删除集合对象
*
* @param collection 多个对象
* @return
*/
public void deleteObject(final Collection collection)
{
redisTemplate.delete(collection);
}
/**
* 缓存List数据
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param dataList 待缓存的List数据
* @return 缓存的对象
*/
public <T> long setCacheList(final String key, final List<T> dataList)
{
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, dataList);
return count == null ? 0 : count;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的list对象
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> List<T> getCacheList(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, 0, -1);
}
/**
* 缓存Set
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @param dataSet 缓存的数据
* @return 缓存数据的对象
*/
public <T> BoundSetOperations<String, T> setCacheSet(final String key, final Set<T> dataSet)
{
BoundSetOperations<String, T> setOperation = redisTemplate.boundSetOps(key);
Iterator<T> it = dataSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
setOperation.add(it.next());
}
return setOperation;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的set
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Set<T> getCacheSet(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
}
/**
* 缓存Map
*
* @param key
* @param dataMap
*/
public <T> void setCacheMap(final String key, final Map<String, T> dataMap)
{
if (dataMap != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, dataMap);
}
}
/**
* 获得缓存的Map
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Map<String, T> getCacheMap(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
}
/**
* 往Hash中存入数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @param value 值
*/
public <T> void setCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hKey, value);
}
/**
* 获取Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @return Hash中的对象
*/
public <T> T getCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey)
{
HashOperations<String, String, T> opsForHash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return opsForHash.get(key, hKey);
}
/**
* 获取多个Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKeys Hash键集合
* @return Hash对象集合
*/
public <T> List<T> getMultiCacheMapValue(final String key, final Collection<Object> hKeys)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, hKeys);
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象列表
*
* @param pattern 字符串前缀
* @return 对象列表
*/
public Collection<String> keys(final String pattern)
{
return redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
}
}
springboot本地缓存
缓存
本地缓存
1)启动类增加注解 @EnableCaching // 开启缓存
2)在service层代码中增加注解,进行测试
本地缓存使用的是currentHashMap
```
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.ttzz.bean.Dog;
import com.ttzz.mapper.DataDemo;
@Service
/**
* @CacheConfig(cacheNames = {},cacheManager=AAAA,cacheResolver = {})
*/
public class DogService {
@Autowired
private DataDemo dataDemo;
/**
* @Cacheable:先在缓存中查找,如果没有该缓存,则创建,查询数据,放入缓存,并返回数据
* 参数:1)cacheNames/value:
* 2)key:
* 3)keyGenerator:
* 4)cacheManager:
* 5)condition:
* 6)unless:
* 7)sync:
*/
@Cacheable(value = "dog",/*cacheNames = ,keyGenerator = ,condition = ,unless = ,sync = true*/key = "#id")
public Dog getById(String id) {
return dataDemo.getById(id);
}
/**
* @CachePut: 先调用目标方法,然后调用缓存信息
*/
@CachePut(value = "dog",key="#dog.id")
public void save(Dog dog) {
dataDemo.save(dog);
}
@CachePut(value = "dog",key="#dog.id")
public void update(Dog dog) {
dataDemo.update(dog);
}
/**
* @CacheEvict:
* allEntries:删除整个缓存中的数据
* beforeInvocation:执行方法前删除还是执行方法后删除
*/
@CacheEvict(value = "dog" /* allEntries = true, beforeInvocation = true*/,key="#id")
public void delete(String id) {
dataDemo.delete(id);
}
/**
* @Caching:复合注解
* @Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value = )
},
put = {
@CachePut()
}
)
*/
}
```
SpringBoot以jar启动加载外部配置文件
SpringBoot以jar启动加载外部配置文件
通常需要将SpringBoot打成jar的方式来启动,有时候也需要将配置文件放到项目(jar)外。如何访问外部的配置文件呢?
使用以下命令来操作
命令1
java -jar XXX.jar -Dspring.config.location=D:\workspace-test\work02\seed-java\seed-framework\target\_config\application.yml
命令2
java -jar D:\workspace-test\work02\seed-java\seed-framework\target\XXX.jar -Dspring.config.location=D:\workspace-test\work02\seed-java\seed-framework\target\_config\application.yml -Dspring.profiles.active=test
SpringBoot 读取应用配置文件
springboot读取配置文件有三种方式
- 使用environment类,可以通过key-value的方式读取到application.properties中的数据
- 使用@value注解,使用spel表达式,注入属性值
- 使用@configurationProperties注解
environment
environment是一个通用的读取应用运行时的环境变量的类,可以读取application。properties,命令函输入参数、系统属性、操作系统环境变量等
@Autowired
private Environment env;
使用方法:env.getProperty(XXXX)
@value
直接通过@value注入一个配置信息到bean
@configurationProperties
该注解可以将同样类型的配置映射成为一个类,方便使用。一般和@Configuration注解配合使用。它和@value功能差不多,它不能读取yml文件中的属性信息,@value可以,@value支持spel表达式。
SpringBoot之Jackson注解
Jackson有多个注解,用来在序列化和反序列化操作
@JsonProperty("XXXX") //为key指定一个别名
private String aa;
@JsonIgnore("XXXX") //忽略此属性
private String aa;
@JsonIgnoreProperties({"XXXX","BBBB"}) //忽略多个属性,作用在类上
private class aa{}
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd") //忽略此属性
private Date aa;
Jackson支持三种序列化和反序列化的方式
- 使用JsonParser来解析json,解析结果是一串tokens,采用jsonGenerator来生成json,这是最底层的方式
- 采用树遍历的方式 json被读入到jsonnode对象中,可以像操作xmldom那样读取json
- 采用dataBind方式,将实体类对象序列化成json,或者反序列化成实体对象,这是最简单的一种。对于应用程序来说最常用的是第三种。
SpringBoot Mock代码测试
增删改查代码
import java.net.URI;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = XXXX.class)
@WebAppConfiguration
//配置事务的回滚,对数据库的增删改都会回滚,便于测试用例的循环利用
@Transactional(transactionManager = "transactionManager")
@Rollback(value = true)
public class BySpecimenControllerTest {
@Autowired
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
private MockMvc mockMvc;
public String token;
@Resource
private SysLoginService loginService;
@Before
public void setupMockMvc() {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(webApplicationContext).build();
// token =
}
@Test
public void testDeleteBySpecimen () throws Exception{
String id = "1";
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.delete("/bySpecimens/delete/"+id)
// .header("Authorization", "Bearer "+token+"")
)
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
}
@Test
public void testFindBySpecimenById() throws Exception {
String id = "1";
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get(new URI("/bySpecimens/info"))
.param("opertationId", id)
)
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
}
@Test
public void testFindBySpecimens () throws Exception{
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/bySpecimens/list")
// .header("Authorization", "Bearer "+token+"")
)
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
}
@Test
public void testSaveBySpecimen() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/bySpecimens/save")
// .header("Authorization", "Bearer "+token+"")
// 标本标识
.param("specimenId", "value")
.param("status", "0")
)
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
}
@Test
public void testUpdateBySpecimen () throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.put("/bySpecimens/save")
// .header("Authorization", "Bearer "+token+"")
// 标本标识
.param("specimenId", "1")
.param("status", "1")
)
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
}
}
使用实体作为参数,需要在Controller 的参数 使用@RequestBody 标记
A domain = new A();
//设置参数
//domain.set
String jsonStr = JSONObject.toJSONString(domain);
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.put("/As/save")
.header("Authorization", "Bearer "+token+"")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.content(jsonStr)
)
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print());
SpringBoot+Mybatis 实现多数据源配置(基于分包管理)、Swagger配置
1.本文主要是基于分包管理来实现多数据源的方式,简单易用
2.Swagger配置
pom.xml配置
4.0.0
XXX
XXX
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
sXXX
XXX
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.13.RELEASE
1.8
3.1.2
1.2.5
1.1.17
0.9.1
1.2.60
2.9.2
2.6
1.19
26.0-jre
2.5
3.9.1
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
12.1.0.2
org.apache.clerezza.ext
org.json.simple
0.4
org.apache.commons
commons-lang3
commons-io
commons-io
org.apache.poi
poi
3.15
org.apache.poi
poi-ooxml
3.15
eu.bitwalker
UserAgentUtils
com.github.oshi
oshi-core
net.java.dev.jna
jna
net.java.dev.jna
jna-platform
org.springframework
spring-context-support
com.github.pagehelper
pagehelper-spring-boot-starter
org.mybatis
mybatis
org.mybatis
mybatis-spring
com.oracle
ojdbc7
12.1.0.2
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.46
org.springframework.security
spring-security-core
5.1.8.RELEASE
compile
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-freemarker
net.hasor
hasor-spring
4.1.3
net.hasor
hasor-dataway
4.1.3-fix20200414
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
${mybatis-plus.version}
com.alibaba
druid-spring-boot-starter
${druid.version}
com.alibaba
fastjson
${fastjson.version}
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
${swagger.version}
io.swagger
swagger-annotations
io.swagger
swagger-models
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
${swagger.version}
io.springfox
springfox-bean-validators
${swagger.version}
io.swagger
swagger-annotations
1.5.22
io.swagger
swagger-models
1.5.22
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
com.github.pagehelper
pagehelper-spring-boot-starter
${pagehelper.spring.boot.starter.version}
commons-io
commons-io
${commons.io.version}
eu.bitwalker
UserAgentUtils
${bitwalker.version}
com.github.oshi
oshi-core
${oshi.version}
多数据源配置代码
1.主数据源配置
@Primary 标注的是主数据源
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = {
"包路径.mapper.数据库标识1mapper" },
annotationClass = Mapper.class,
sqlSessionFactoryRef = "数据库标识1SqlSessionFactory")
public class 数据库标识1MybatisConfig {
/**
* @return 返回DataSource对象
*/
@Bean(name = "数据库标识1DataSource")
@Qualifier("数据库标识1DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.数据库标识1")
@Primary
public DataSource cmsDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "数据库标识1SqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("数据库标识1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocati数据库标识1(
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mapper/数据库标识1mapper/*.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "数据库标识1PlatformTransactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("数据库标识1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean("数据库标识1SqlSessionTemplate")
// 表示这个数据源是默认数据源
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate test1sqlsessiontemplate(
@Qualifier("数据库标识1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionfactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionfactory);
}
}
2.第二个数据源配置
如何扩展 第三、第四数据源呢?
(1)复制第二数据源配置类,简单修改注解中的名称
(2)在resource的mapper文件夹下创建XXXmapper,用来存放XXXXMapper.xml文件
特别注意没有primary修饰了哦
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = {
"包路径.mapper.数据库标识2mapper" },
annotationClass = Mapper.class,
sqlSessionFactoryRef = "数据库标识2SqlSessionFactory")
public class 数据库标识2MybatisConfig {
/**
* @return 返回DataSource对象
*/
@Bean(name = "数据库标识2DataSource")
@Qualifier("数据库标识2DataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.数据库标识2")
public DataSource cmsDataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "数据库标识2SqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("数据库标识2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocati数据库标识2(
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mapper/数据库标识2mapper/*.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "数据库标识2PlatformTransactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("数据库标识2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean("数据库标识2SqlSessionTemplate")
// 表示这个数据源是默认数据源
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate test1sqlsessiontemplate(
@Qualifier("数据库标识2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionfactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionfactory);
}
}
resource下application.yml 中的数据源信息配置信息
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /**
resource:
static-locations: classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/
datasource:
#数据库标识1数据源配置
数据库标识1:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://ip:3306/d1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username: XXX
password: XXX
maxActive: 50
initialSize: 10
maxWait: 60000
minIdle: 1
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
maxOpenPreparedStatements: 2
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
filters: stat
validationQuery: select version()
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#数据库标识2数据源配置
数据库标识2:
jdbc-url: jdbc:oracle:thin:@ip:1521:XXX
username: XXX
password: XXX
maxActive: 50
initialSize: 5
maxWait: 60000
minIdle: 1
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
maxOpenPreparedStatements: 2
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
filters: stat
validationQuery: select * from dual
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
Swagger类配置 SwaggerConfig.java
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiKey;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.service.AuthorizationScope;
import springfox.documentation.service.SecurityReference;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spi.service.contexts.SecurityContext;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
/**
* 创建API
*/
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.enable(true)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(ApiOperation.class))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build()
/* 设置安全模式,swagger可以设置访问token */
.securitySchemes(securitySchemes())
.securityContexts(securityContexts());
}
/**
* 安全模式,这里指定token通过Authorization头请求头传递
*/
private List securitySchemes() {
List apiKeyList = new ArrayList();
apiKeyList.add(new ApiKey("Authorization", "Authorization", "header"));
return apiKeyList;
}
/**
* 安全上下文
*/
private List securityContexts() {
List securityContexts = new ArrayList<>();
securityContexts.add(
SecurityContext.builder()
.securityReferences(defaultAuth())
.forPaths(PathSelectors.regex("^(?!auth).*$"))
.build());
return securityContexts;
}
/**
* 默认的安全上引用
*/
private List defaultAuth() {
AuthorizationScope authorizationScope = new AuthorizationScope("global", "accessEverything");
AuthorizationScope[] authorizationScopes = new AuthorizationScope[1];
authorizationScopes[0] = authorizationScope;
List securityReferences = new ArrayList<>();
securityReferences.add(new SecurityReference("Authorization", authorizationScopes));
return securityReferences;
}
/**
* 添加摘要信息
*/
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
// 用ApiInfoBuilder进行定制
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
// 设置标题
.title("XXXX_接口文档")
// 描述
.description("XXXX所有API接口")
// 作者信息
.contact(new Contact("XXXX", null, null))
// 版本
.version("版本号:1.0" )
.build();
}
}
SpringBoot引入外部jar,并将项目打包成jar包,引发项目运行失败的问题
SpringBoot引入外部jar,并将项目打包成jar包
正常打包操作
- 在src/main/resource 目录下创建一个lib文件夹,将需要打如到项目中的jar放在这里
- 通过build path 将这些jar加入到工程中,以方便调用
- 在pom.xml中增加,其中xxx看实际情况而定
XXX
XXX
XXX
system
${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/lib/XXX.jar
- 在pom.xml中增加build 逻辑
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
true
lib
BOOT-INF/lib/
**/*.jar
src/main/resources
BOOT-INF/classes/
特别注意: 上面的build中的代码仅仅是在打包的时候打开,在运行项目的时候,需要将上面的代码注释掉。不然会报错:找不到XXXMapper.xml mybatis对应的xml文件。
【转载】springboot引入外部依赖jar包
今天项目(springboot项目)中需要导入外部的jar包,在打包的时候需要将外部jar打到项目中。就这一个问题,CSDN中有好多的提示的文章。真TM傻逼啊,发文章之前,自己就不测试一下吗?自己在网上随便找一个案例,正好满足自己的要求,就直接用了,标题都TM不调整一下,也不看看人家的标题和你自己写的是不是一个意思。误人子弟。
正解文件连接:
springboot引入外部依赖jar包_springboot引入外部jar包_半山惊竹的博客-CSDN博客
RestTemplateUtil 工具类
两个系统之间做数据交互,一般都是使用接口的方式,在SpringBoot中提供了一个RestTemplate类,方便调用。
以下是一个简单封装,方便使用
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class RestTemplateUtil {
/**
* restTemplate 发送post请求
* @param restTemplate
* @param url
* @param json
* @return
*/
public static ResponseEntity getRestTemplatePost(RestTemplate restTemplate,String url,String json){
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setAccept(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON));
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8);
HttpEntity requestEntity = new HttpEntity(json,headers);
ResponseEntity entity = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, requestEntity, String.class);
return entity;
}
/**
* restTemplate 发送get请求
* @param restTemplate
* @param url
* @param json
* @return
*/
public static ResponseEntity getRestTemplateGet(RestTemplate restTemplate,String url,String json){
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setAccept(Arrays.asList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON));
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8);
HttpEntity requestEntity = new HttpEntity(json,headers);
ResponseEntity entity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class,json);
return entity;
}
public static Map parseResponseEntity(ResponseEntity entity) {
Map map = new HashMap();
log.info("ResponseEntity="+JSONObject.toJSONString(entity));
Integer code = entity.getStatusCodeValue();
if(entity.getStatusCodeValue()==200) {
JSONObject obj = JSONObject.parseObject(entity.getBody());
map.put("code", code+"");
map.put("data", obj.getString("data").toString());
}
log.info(JSONObject.toJSONString(map));
return map;
}
}
关于@Transactional 的sao操作
关于@Transactional 作用的一些测试
-
- SpringBoot JavaEE 简介
- springboot 配置、加载
-
- 加载外部类的几种方式
- 加载配置文件中的属性的方式
- profiles
-
- 在启动jar包的时候 动态指定jar的端口号
- 配置虚拟机参数
- 在启动jar的时候指定外部的配置文件
- 配置文件的加载顺序
- maven简介
-
-
- maven实现的目标
- pom中元素介绍
-
- groupId
- artifactId
- packaging
- version
- modelVersion
- scope
- build
-
- spring boot 发送邮件
-
- 1.引入jar
- 2.application.yml配置
- 3.发送简单文本信息
- 4.发送带有附件的
- springboot和redis缓存
-
- redis缓存
- springboot本地缓存
-
- 缓存
- SpringBoot以jar启动加载外部配置文件
- SpringBoot以jar启动加载外部配置文件
-
-
-
-
- 使用以下命令来操作
-
- 命令1
- 命令2
-
-
- SpringBoot 读取应用配置文件
-
-
-
- springboot读取配置文件有三种方式
-
- environment
- @value
- @configurationProperties
-
-
- SpringBoot之Jackson注解
-
-
- Jackson支持三种序列化和反序列化的方式
-
- SpringBoot Mock代码测试
- SpringBoot+Mybatis 实现多数据源配置(基于分包管理)、Swagger配置
-
- pom.xml配置
- 多数据源配置代码
-
- 1.主数据源配置
- 2.第二个数据源配置
- resource下application.yml 中的数据源信息配置信息
- Swagger类配置 SwaggerConfig.java
- SpringBoot引入外部jar,并将项目打包成jar包,引发项目运行失败的问题
-
-
-
-
- 正常打包操作
- **特别注意:** 上面的build中的代码仅仅是在打包的时候打开,在运行项目的时候,需要将上面的代码注释掉。不然会报错:找不到XXXMapper.xml mybatis对应的xml文件。
-
-
-
- 【转载】springboot引入外部依赖jar包
- RestTemplateUtil 工具类
-
-
-
-
- 以下是一个简单封装,方便使用
-
-
-
- 关于@Transactional 的sao操作
-
- case1 无try catch、无嵌套,没有加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务正常回滚
- case2 无try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务正常回滚
- case3 没有加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务没有回滚
- case4 有try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务没有回滚
- case5 有try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class ,抛出异常 。 事务正常回滚
- case6 有try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class ,抛出异常。方法调用,事务没有回滚
- case7 事务没有回滚
- case8 事务回滚
- case9 事务回滚
- case10 事务未回滚
- case11 事务回滚
- case12 事务未回滚
- case13 事务回滚
- case14 事务回滚
- case15 事务回滚
- dynamic-datasource 使用
-
在使用@Transactional 关键字的时候,总会有这样 或者 那有的问题。
一下做一些测试来验证问题
case1 无try catch、无嵌套,没有加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务正常回滚
@Transactional
public int testSave() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
}
case2 无try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务正常回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
}
case3 没有加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务没有回滚
@Transactional
public int testSave() {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
return 0;
}
case4 有try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class 事务没有回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
return 0;
}
case5 有try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class ,抛出异常 。 事务正常回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception(e.getMessage());
}
}
case6 有try catch、无嵌套,加 rollbackFor = Exception.class ,抛出异常。方法调用,事务没有回滚
public int testSave() throws Exception {
return testSave2();
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave2() throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new Exception(e.getMessage());
}
}
case7 事务没有回滚
@Transactional
public int testSave() throws Exception {
return testSave2();
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave2() throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new Exception(e.getMessage());
}
}
case8 事务回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
return testSave2();
}
public int testSave2() throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new Exception(e.getMessage());
}
}
case9 事务回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
return testSave2();
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave2() throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new Exception(e.getMessage());
}
}
case10 事务未回滚
@Transactional
public int testSave() throws Exception {
return testSave2();
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave2() throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new Exception(e.getMessage());
}
}
case11 事务回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
return testSave2();
}
@Transactional
public int testSave2() throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
throw new Exception(e.getMessage());
}
}
case12 事务未回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
return testSave2();
}
@Transactional
public int testSave2() {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
int m = 1/0;
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return 0;
}
case13 事务回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
int m = testSave2();
int n = 1/0;
return m;
}
@Transactional
public int testSave2() {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return 0;
}
case14 事务回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
int m = testSave2();
int n = 1/0;
return m;
}
public int testSave2() {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return 0;
}
case15 事务回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave() throws Exception {
int m = testSave2();
int n = 1/0;
return m;
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int testSave2() {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("岳不群2");
user.setAge(70);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.insert(user);
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return 0;
}
dynamic-datasource 使用
1)在项目中引入dynamic-datasource该modul
2)在application.yml中添加
dynamic:
datasource:
slave1:
driver-class-name: oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
url: jdbc:oracle:thin:XXX:orcl_tjh
username: XX
password: XX
validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
slave2:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/XXX?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: XXXX
password: XXXX
- 在项目中使用,dynamic 配置的都是子数据源。
在访问的service 方法上 使用@DataSource(数据源表示);如上的slave1
【临渊羡鱼不如退而结网】