react源码-debuger解析- createRoot阶段1
看懂这个之后https://react.iamkasong.com开始debugger源码
CreateRoot
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById(''))
craeteRoot主要调用了createContainer创建rootFiber和FiberRoot,并且将它们联系起来。
createContainer调用了createFiberRoot
const root: FiberRoot = new FiberRootNode(...) //FiberRoot
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(...) //rootFiber
// 连接rootFiber和fiberRottNode
root.current = uninitializedFiber;
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;
initializeUpdateQueue(uninitializedFiber);// 初始化rootFiber的updateQueue
最后createRoot返回一个ReactDOMRoot实例
return new ReactDOMRoot(root);
render方法就在ReactDOMRoot的原型上。
所以craeteRoot做的事情就是:
- 创建rootFiber和FiberRoot,将他们连接起来,并且初始化rootFiber的updateQueue
- 返回一个ReactDOMRoot的实例.`
render
ReactDOM.createRoot(xx).render(render里面主要调用了updateContainer方法(updateContiner属于Reconciler模块的)
updateContainer(children, root, null, null);
updateConinter:
1 创建update对象; 2 update对象插入fiber.UpdateQueue; 3 scheduleUpdateOnFiber开启调度;
- 创建update对象(createUpdate)
// 创建第一次的update
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
// update.payload为需要挂载在根节点的组件
//对应hostComponent的update的paylad就是Render的第一个参数,createRoot().render(xx)的xx
update.payload = {element}; // - 将生成的update对象插入updateQueue(enqueueUpdate)
// 将生成的update加入updateQueue
enqueueUpdate(current, update, lane);
- 开启第一次调度更新(scheduleUpdateOnFiber)
/ 开始第一次调度更新, 找到rootfiber => render阶段 => commit阶段
const root = scheduleUpdateOnFiber(current, lane, eventTime);
createUpdate
// 创建update对象export function createUpdate(eventTime: number, lane: Lane): Update<*> { const update: Update<*> = { eventTime, // 任务时间,通过performance.now()获取的毫秒数 lane, //优先级 tag: UpdateState, // 更新的类型,包括UpdateState | ReplaceState | ForceUpdate | CaptureUpdate // 对于ClassComponent,payload为this.setState的第一个传参。对于HostRoot,payload为ReactDOM.render的第一个传参。 payload: null, //更新挂在的数据 callback: null, // 更新的回调函数,比如ReactDOM.render(xx,xx,()=>{}),或是this.setState的第二个参数。 next: null, //与其他update连成指针 }; return update;}
enqueueUpdate
通过update的next指针,形成环状链表,挂在fiber.UpdateQueue.shard.pending上。
//update顺序:u1=>u2=>u3// fiber.UpdateQueue.shard.pending = u3=>u2=>u1 | | -------
ScheduleUpdateOnFiber
- 通过带有update的fiber往上查找,找到rootFiber。 markUpdateLaneFormFIberToRoot
- 通过找到的rootFiber,开始调度更新, ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime)
ensureRootIsScheduled
-
获取当前任务的优先级,判断有没有任务,没有的话重置root.callbackNode,并且退出。有的话往下判断
-
判断是否有正在工作的任务,有的话比对一下两者优先级,如果一样,表示正在工作的任务优先级也很高,直接返回null,让当前正在工作的任务继续工作。如果当前任务优先级较高,就会中断正在工作的任务,优先调度当前任务。
-
根据当前的优先级判断是执行scheduleCallback注册performSyncWorkOnRoot还是performConcurrentWorkOnRoot。(同步or异步)
-
更高级的任务task对象会被赋值到root.callbackNode上。
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root,didTimout)
-
schedule会将工作的fiber和是否过期作为参数传入,然后通过didTImeout等参数,判断是否过期,执行renderRootConcurrent或者是renderRootSync函数
-
这个函数会被作为注册进scheduleCallback的方法,那么它必须满足scheduleCallback的规定,每次执行完毕后都需要有一个返回值。
-
并且这个函数每次执行完毕后,都会调用
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());,就是重新判断是否有更高级的任务,通过上面我们知道如果有更高级的任务,那么会被赋值到root.callbackNode上。当ensureRootIsScheduled调用完毕后,会判断const originalCallbackNode = root.callbackNode; //现在调度的任务 task对象 .... ..... // 每次执行完一次任务之后,需要继续调度,查看是否有更高优先级的 ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now()); // 如果有优先级更高的任务,root.callbackNode !== originalCallbackNode if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) { // 只是因为档期桢不够时间,还是原本的work,继续返回给Schedule调度 return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root); } return null如果经过调用
ensureRootIsScheduled后,四种情况-
root.callbackNode还是等于原来的originalCallbackNode,表示没有新的任务需要调度,所以直接返回当前的任务作为下一个scheduleCallback调度的任务。
-
如果有新的任务,但是新的任务跟当前的任务优先级相关,通过上面
ensureRootIsScheduled的介绍也知道,如果任务优先级一样,那么直接return null,而root.callbackNode也不会被改变。 -
有新的任务,并且优先级更高,那么
ensureRootIsScheduled会调用通scheduleCallback注册performSyncWorkOnRoot或者performConcurrentWorkOnRoot函数,返回新的task对象,赋值root.callbackNode,那么等ensureRootIsScheduled执行完毕后,就不满足root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode,所以直接返回null,那么scheduleCallback如果收到一个null,就会将当前的任务取消掉,准备执行优先级更高的任务了。 -
没有新的任务,并且当前任务执行完毕。
ensureRootIsScheduled判断到没有任务,将root.callbackNode置为Null,那么也不满足条件,所以performConcurrentWokrOnRoot会返回null,该任务会在scheduleCallback被取消。
-
renderRootConcurrent
- 顾名思义i,异步执行root。
- 先将react hooks对象全部置为抛错的对象。 pushDIspatcher()
- 首先第一次进来,会根据root.current也就是rootFiber创建workInprogress fiber树,调用
prepareFreshStack调用createWorkInprogress
workInporgress.stateNode = current.stateNode // workInprogress也跟FIberRoot有关联。workInprogress.alternate = currentcurrent.alternate = workInprogress
-
workInprogress fiber通过alternate属性跟current fiber树关联起来。react使用双缓存机制进行更新的。FiberRoot,有且只有一个,但是rootFiber有很多个,比如第一个workInprogress就是另一个rootFiber。
-
调用workLoopConcurrent,准备进入render阶段。
-
workLoopConcurrent执行完毕之后,会判断当前任务是否执行完毕,是的话清除全局变量,比如workInProgressRoot = null;返回退出的状态给```performConcurrentWOrkOnRoot的``的exitStatus使用。
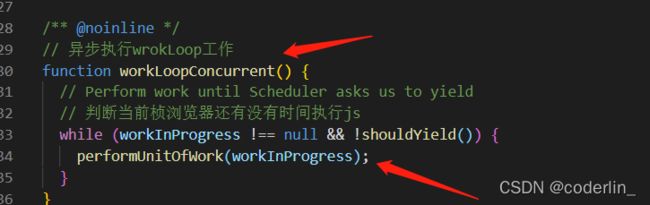
workLoopConcurrent
function workLoopConcurrent() { // Perform work until Scheduler asks us to yield // 判断当前桢浏览器还有没有时间执行js while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) { performUnitOfWork(workInProgress); }}
*shouldYield是schedule提供的,用来判断当前帧是否有剩余时间,如果有就执行performUnitOfWork,若没有,就退出循环。继续走renderRootConcurrent接下来的步骤。等待scheduleCallback继续执行performConcurrentWorkOnRoot调度。
这样,createRoot到render阶段的流程就走完了。
render阶段-commit阶段
render阶段开始于performConcurrentWorkOnRoot/perfromSyncWorkOnRoot;
- 我们知道performConcurrentWorkOnRoot调用renderRootConcurrent,renderRootConcurrent调用workLoopConcurrent执行任务,而renderRootConcurrent在执行完workLoopCOncurrent之后,会判断当前是否还有任务没有render。返回一个状态给exitStatus。
- 而如果任务执行都执行了render阶段之后,就会调用
finishConcurrentRender,判断exitStatus的值,调用commitRoot(root),正式开启commit阶段。 - 从这里就可以看出,render阶段,是可以中断的,它通过不断地调用注册performConcurrentWornOnRoot,去执行render阶段,每当浏览器帧时间不够就暂停退出,等到下一帧继续执行performConcurrentWornOnRoot。
- 而只有当全部的fiber执行完render阶段之后,才会调用commitRoot执行commit阶段。commit阶段主要是对dom的操作,而这一步是必须同步的。这里先了解。
render阶段
render阶段开始于performConcurrentWorkOnRoot/perfromSyncWorkOnRoot。最终都会调用performUnitOfWork,去执行每一个fiber。
function workLoopConcurrent() { // Perform work until Scheduler asks us to yield // 判断当前桢浏览器还有没有时间执行js while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) { performUnitOfWork(workInProgress); }}
第一个开始工作的是刚才创建的workInprogress。
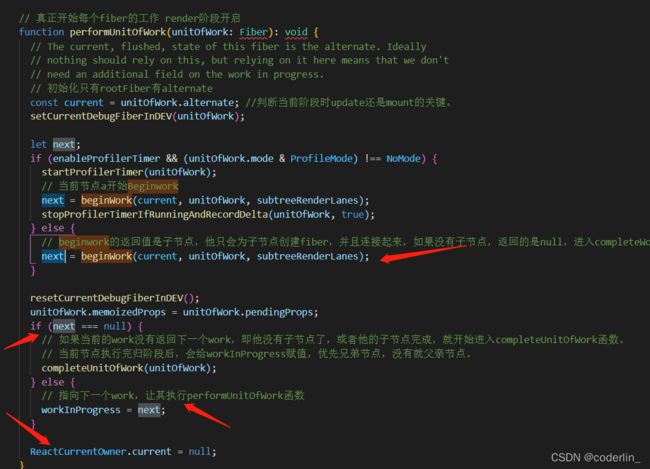
performUnitOfWork
- 通过unitOfWork.alterant判断当前处于mount阶段还是update阶段(rootFiber是唯一一个在mount的时候有alterant)
- 调用beginWork执行该fiber的递阶段。
beginWOrk(current, workInprogress, renderLanes) - 对完成递阶段的fiber,执行completeUnitOfWork。
- 对于还有子孙节点的fiber,将workInprogress设置为子fiber节点,退出。等待下一帧执行,继续调度workInprogress的beginWork阶段。
beginWork
-
对于一开始进入的rootFIber的workInprogress,他有altername
-
对于rootFiber,根据workInProgress.tag判断,调用
updateHostRoot -
而其他fiber,进入的时候unitOfWork.alternate为null,表示处于mount阶段。
render阶段HostRoot的处理
对于HostRoot,调用updateHostRoot
updateHostRoot
- 1 cloneUpdateQueue(current, workInprogress),将current fiber上的updateQueue复制到了workInprogress.updateQueue
- 2 调用
processUpdateQueue(workInprogress, nextProps,null, renderLanes)消费updateQueue.shard.pending上所有的update环状链表。 - 3 执行完processUpdateQueue之后,获取最新的state上面的element元素
const nextChildren = nextState.element;最后调用reconcileChildren(current,workInprogress,nextChildren,renderLanes)最后返回return workInprgress.child,返回值作为此次beginWork需要一个返回值,render阶段的beginWork是深度优先遍历的。返回值会继续执行beginWork。
processUpdateQueue
processUpdateQueue是一个非常重要的方法
- update对象分为两种,函数组件一种,放在fiber上的hooks对象上,fiber.memoizedState存放hooks对象的链表,而函数的Update存放在hooks对象上的hooks.queue.shard.pending上
- 类组件和hostRootComponent公用的一种,他们的update都是放在fiber.updateQueue.shard.pendign上,用环状链表存储这,
- 而processUpdateQueue,就是用来消费类组件这一类的update的。
执行逻辑:
-
将updateQueue上的firstBaseUpdate和lastBaseUpdate取出,将shard.pending上的update环状链表剪开,插入到lastBaseUpdate上。
firstBaseUpdate: u1,lastBaseUpdate: u2shard.pending: u5 -> u4 -> u3 -> u5所以这一次的update顺序: u1 -> u2 -> u3 -> u4 -> u5 -
为了防止update丢失,会将当前,存放到current fiber.update.lastBaseUpdate上
-
接着开始遍历Update链表,执行update。(do while遍历update链表)
update优先级
-
判断update优先级,如果当前update优先级较低,就会跳过,重新插入到一条新的链表中。
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) { newFirstBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate = clone; newBaseState = newState; //有update需要跳过,那么下次fiber.baseState需要停留在此次更新前的state。即这 } else { newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone;}保存在newFirstBaseUpdate和newLastBaseUpdate上,前者永远指向第一个update,后者永远指向最后一个Update。
-
如果有跳过的update,那么此时fiber的state应该停留在跳过的update时候的状态,而不应该只计算优先级高的几个update后就拿来当新的state。
-
所以
// 计算最新的state let newState = queue.baseState // 赋值当前fiber的状态的变量 let newBaseState = null;newState是用来计算每个Update执行之后的状态,newBaseState是所有的update执行过后,赋值到fiber上的state的状态。一旦有Update跳过,newState和newBaseState就不一样。如上,当发现一个
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) { // 优先级比较低的,不执行。以链表的形式存储到新的firstBaseUpdate上, const clone: Update= { eventTime: updateEventTime, lane: updateLane, tag: update.tag, payload: update.payload, callback: update.callback, next: null, }; if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) { newFirstBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate = clone; newBaseState = newState; //有update需要跳过,那么下次fiber.baseState需要停留在此次更新前的state。即这 } else { newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone; } // Update the remaining priority in the queue. newLanes = mergeLanes(newLanes, updateLane); } update优先级比较低,并且他是当前第一个跳过的update,就会执行
newBaseState = newState,而第二个跳过的update不会执行,所以newBaseState的状态永远的停留在了当前跳过的update的状态。 -
如果优先级高的,那么不会被跳过,但是为了保证状态的连续性,如果有跳过的Update,那么当前执行的update即使优先级很高,也要预留一份继续插入lastBaseUpdate上
if (newLastBaseUpdate !== null) { // 如果已经有update被逃过,当前update也必须保存在链表后面 const clone: Update= { eventTime: updateEventTime, // This update is going to be committed so we never want uncommit // it. Using NoLane works because 0 is a subset of all bitmasks, so // this will never be skipped by the check above. lane: NoLane, tag: update.tag, payload: update.payload, callback: update.callback, next: null, }; newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone; } 如,当执行高优先级的update的时候,会判断是否有跳过的update,有就会clone一份,放入lastBaseUpdate后面。
小总结:为了保证优先级update被跳过后状态的连续性,做了什么处理?
- 1 首先是,workInprogress fiber上的update链表,会保存一份在current fiber.updateQUeue上
- 2 有跳过的update,Fiber的state跟遍历update之后计算的state不同,永远停留在跳过update时候的状态
- 3 有跳过的update,那么他之后所有的update,即使优先级高被执行了,但还是会保留一份,插在lastBaseUpdate后面
执行优先级高的update
-
上面说过,每次消费fiber上的update链表的时候,都会先进行一系列处理,对跳过的update复制,等等。然后才会执行本次render阶段优先级高的update。
-
而,newState变量是用来存放update最新计算的state,存放在fiber.memoizedState,newBaseState是存放本次计算update之后,当前fiber使用的值,存放在updateQueue.baseState上,他们会因为是否有跳过的update而不同
-
每个update的执行如下:
// Process this update. 执行当前的update,获取state
newState = getStateFromUpdate(
workInProgress,
queue,
update,
newState,
props,
instance,
);
// setState或者ReactDOM.render的第三个参数
const callback = update.callback;
它会根据update.tag来进行不同的处理,在创建update的时候,就有,
// 创建update对象
export function createUpdate(eventTime: number, lane: Lane): Update<*> {
const update: Update<*> = {
eventTime, // 任务时间,通过performance.now()获取的毫秒数
lane, //优先级
tag: UpdateState, // 更新的类型,包括UpdateState | ReplaceState | ForceUpdate | CaptureUpdate
// 对于ClassComponent,payload为this.setState的第一个传参。对于HostRoot,payload为ReactDOM.render的第一个传参。
payload: null, //更新挂在的数据
callback: null, // 更新的回调函数,比如ReactDOM.render(xx,xx,()=>{}),或是this.setState的第二个参数。
next: null, //与其他update连成指针
};
return update;
}
createRoot对应的tag是UpdateState。看一下getStateFormUpdate是怎么处理的。
// Intentional fallthrough
case UpdateState: {
const payload = update.payload;
let partialState;
if (typeof payload === 'function') {
// Updater function
partialState = payload.call(instance, prevState, nextProps);
} else {
// Partial state object
partialState = payload;
}
if (partialState === null || partialState === undefined) {
// Null and undefined are treated as no-ops.
return prevState;
}
// Merge the partial state and the previous state.
return Object.assign({}, prevState, partialState);
}
上面说过,对于HostRoot,update.playload就是{element},一般就是App组件,他不是函数,所以直接 partialState = payload,返回了App组件,那么此时的newState就是App组件(react element,也就是虚拟dom)。最后还有个合并prevState的操作
-
处理完update之后,newState的值得到更新,并且指针往下移动。update = update.next,如果没有Update了,就会退出do while循环。
-
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) { // 如果没有跳过的update,那么下次的baseState就等于这次更新的state。 newBaseState = newState; }可以看到,newLastBaseUpdate表示的是当前跳过的update,如果没有跳过的update,那么newBaseState的值等于newState
-
进行一些赋值操作
// 更新updateQueue上的baseState queue.baseState = ((newBaseState: any): State); queue.firstBaseUpdate = newFirstBaseUpdate; queue.lastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate; //最新的state保存在当前fiber的memoizedState上 workInProgress.memoizedState = newState;最新的值保存在了memoizedState,当前fiber使用的值保存在了updateQueue.baseState上。
自此,processUpdateQueue执行完毕,rootFiber的update处理完毕。
reconcileChildren
processUpdateQueue执行完毕之后,会
const nextChildren = nextState.element;
...
reconcileChildren(current, workInProgress, nextChildren, renderLanes);
resetHydrationState();
....
return workInProgress.child;
重点看reconcilechilren,我们知道render阶段的beginwork,不仅会消费update,还会将生成子节点的fiber并且将他们关联起来。
reconcilerChilren做的事情很简单,
export function reconcileChildren(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
nextChildren: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
// 对于mount的组件
if (current === null) {
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
//不会为fiber创建dom,
workInProgress,
null, //与reconcileChildFibers的区别
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
} else {
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
}
}
-
对于mount的组件,调用mountChildFibers,创建新的子fiber节点,并且将它与父结点关联起来。
-
对于update的组件,调用reconcileChildFibers,他会将当前组件与该组件在上次更新时对应的Fiber节点比较(也就是俗称的Diff算法),将比较的结果映射到fiber节点上去,产生effectTag。
-
所以diff算法是在render阶段的递阶段完成的,计算完update得到最新的State之后即开始diff,判断是否加上effectTag。
-
这两个方法都是调用同一个方法
export const reconcileChildFibers = ChildReconciler(true); export const mountChildFibers = ChildReconciler(false)
mountChildFibers
即ChildReconciler(false)的返回值reconcileChildFibers但是对于rooFiber,他的current是有值得,所以调用的是reconcileChildFibers,
也就是ChildReconciler(true)
function ChildReconciler(shouldTrackSideEffects){
function xx(){}
....
function reconcileChildFibers(){}
return reconcileChildFibers
}
mountChildFibers和reconcileChildFIbers都是这个函数。
reconcileChildFibers(returnFiber, currentFirstChild, newCHild, lanes)
-
第一件事,处理<>,< Fragment >< /Fragment>这些,把他们当作数组,直接处理第一个children就可以了。
const isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment = typeof newChild === 'object' && newChild !== null && newChild.type === REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE && newChild.key === null; if (isUnkeyedTopLevelFragment) { newChild = newChild.props.children; } -
对于不同的newChild,如果是对象,表示是虚拟dom,如果是字符串,数字,就要进行优化。
-
如果是对象,根据虚拟dom.$$typeof来处理。有三种,如REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE, REACT_PORTAL_TYPE, REACT_LAZY_TYPE,通常的就是第一种,REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,来看怎么处理的。
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE: // 对于普通的react元素 return placeSingleChild( reconcileSingleElement( returnFiber, currentFirstChild, newChild, lanes, ), );placeSingleChild(reconcileSingleElement(xxx))
reconcileSingleElement,创建子fiber,关联父fiber
下面是这个函数的主要逻辑:
根据element创建子节点fiber。第一次是根据App组件创建App fiber
const created = createFiberFromElement(element, returnFiber.mode, lanes);
created.ref = coerceRef(returnFiber, currentFirstChild, element);
created.return = returnFiber; //与父级fiber关联。
return created;
placeSingleChild
-
如果说reconcileSingleElement是创建子fiber,那么placeSingleChild,就是为rootFiber打上effectTag标记,
-
而我们知道,rootFiebr是唯一一个在mount阶段有alterNate属性的值,所以刚才进来传递得shouldTrackSideEffects是true,并且新的newFiber就是App组件得fiber,他的alternate为null,所以会为其打上一个Placement标记,打在app fiber上。
-
到下一次,下一个fiber来的时候,因为处于mount阶段,他们不像rootFiber一样,有alterNate,所以shouldTrackSideEffects为false,所以不会打上标记,这里也对应了,mount阶段只有rootFiber会为他的子节点打上placeMent标记,而其他fiber不会打上标记。
// 给根节点加入effectag属性,shouldTrackSideEffects是update传入的true
function placeSingleChild(newFiber: Fiber): Fiber {
// This is simpler for the single child case. We only need to do a
// placement for inserting new children.
if (shouldTrackSideEffects && newFiber.alternate === null) {
newFiber.flags |= Placement;
}
return newFiber;
}
自此,workInporgress.child创建完毕。rootFiber的beginWork阶段正式完成。
rooFiber的递阶段就是,消费第一次创建的update,然后调用reconcileChildren去创建第一个儿子App组件的fiber,然后关联起来,返回App fiber>
然后
这里返回的next就是App fiber,而next还有值,所以不会走commit的逻辑。将App fiber赋值给workInprogress。结束performUnitOfWork
接着
while循环继续判断当前是否还有任务,当前App fiber赋值给了workInprogress,所以还有任务,并且浏览器是否还有时间?
有多余时间就会继续执行下一个fiber的递阶段。无多余时间的话就结束运行。等下schedule下一帧调度的时候,继续调用我们注册的performConcurrentWorkOnRoot,然后由他继续调用performUnitOfWork,继续执行下一个fiber的递阶段。
现在关系就是
FiberRoot.current = rootFiber(当前ui使用的fiber树)
rootFiber.stateNode = FIberRoot
workINprogress.stateNode = FiberRoot(当前正在构建的fiber树)
workInprogress.child = AppFiber (AppFiber被创建完毕