【链表】经典链表题LeetCode
文章目录
-
-
- 160. 相交链表 简单
- 206. 反转链表 简单
- 876. 链表的中间结点 简单
- 234. 回文链表 简单
- 141. 环形链表 简单
- 142. 环形链表 II 中等
- 21. 合并两个有序链表 简单
- 2. 两数相加 中等
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 中等
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 中等
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表 困难
- 92. 反转链表 II 中等
- 138. 复制带随机指针的链表
- 148. 排序链表 中等
- 23. 合并 K 个升序链表 困难
- 143. 重排链表 中等
- 328. 奇偶链表
-
:LeetCode Hot100题
160. 相交链表 简单
题目链接
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
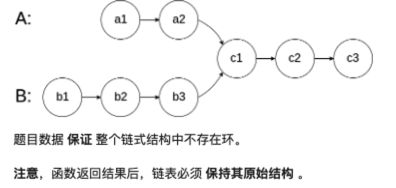
链表A与链表B如下如下所示,目标是找到c1。
A: a1-a2-c1-c2-c3
B: b1-b2-b3-c1-c2-c3
将A链表与B链表相连,B链表与A链表相连。
A: a1-a2-c1-c2-c3-b1-b2-b3-c1-c2-c4
B: b1-b2-b3-c1-c2-c4-a1-a2-c1-c2-c3
可以看到相交的那段链表重合了
同时遍历A和B,直到相同。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode h1 = headA;
ListNode h2 = headB;
while(h1!=h2){
if(h1==null){
h1 = headB;
}else{
h1 = h1.next;
}
if(h2==null){
h2 = headA;
}else{
h2 = h2.next;
}
}
return h1;
}
}
206. 反转链表 简单
题目链接
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
递归思路:
原链表:
a1->a2->a3-a4->null
第1步
a1->reverse(a2->a3-a4->null)
a1->a2<-a3<-a4
第2步
a1<->a2<-a3<-a4
第3步
null<-a1<-a2<-a3<-a4
代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 注意base case
if(head==null || head.next == null) return head;
// 第1步
ListNode node = reverseList(head.next); // 返回头节点
// 第2步
head.next.next = head;
// 第3步
head.next = null;
return node;
}
}
876. 链表的中间结点 简单
给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[3,4,5]
解释:链表只有一个中间结点,值为 3 。
示例 2:
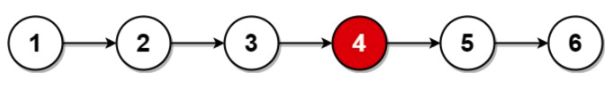
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:[4,5,6]
解释:该链表有两个中间结点,值分别为 3 和 4 ,返回第二个结点。
思路:快慢指针。
代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
// base case
if(head ==null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next!=null){
slow = slow.next; // 慢指针走1步
fast = fast.next.next;// 快指针走2步
}
return slow;
}
}
234. 回文链表 简单
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
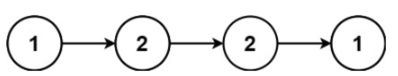
输入:head = [1,2,2,1]
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:false
思路:
找到中间节点
对中间节点(链表后半部分)反转
同时遍历原head和反转后的链表head2
代码:
class Solution {
// 判断回文链表 leetcode 234
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null) return true;
ListNode m = getMid(head);
ListNode l2 = reverseList(m);
ListNode l1 = head;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val==l2.val){
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 求中间节点 leetcode 876
public ListNode getMid(ListNode head){
if(head==null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head,fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 反转链表 leetcode 206
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode node = reverseList(head.next); // 返回头节点
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return node;
}
}
141. 环形链表 简单
题目链接
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:

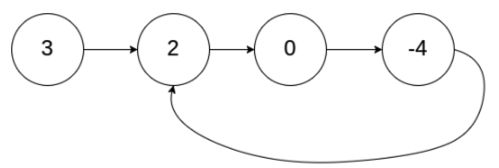
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
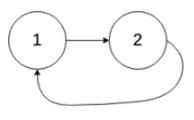
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
思路:快慢指针,如果有环,快指针会套圈慢指针,产生快慢在相同位置的情况。
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null) return false;
ListNode slow = head,fast = head;
do{
if(fast==null || fast.next==null) return false; // 没有环
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}while(slow != fast); // 相同则跳出循环
return true;
}
}
142. 环形链表 II 中等
题目链接
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
⚠️不允许修改链表。
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
思路:Krahets的题解思路链接。
抛开数学证明,就是当快慢指针第一次相遇时,此位置再走【头节点-环首节点】这段距离的步数即走到环首节点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null) return null;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
do{
if(fast==null || fast.next == null)return null; // 没有环
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}while(fast!=slow);
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
仅供娱乐的第二种方法: 每走一个node将其val改为一个特殊值,直到发现该值已被改过。
21. 合并两个有序链表 简单
题目链接
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode l1 = list1,l2 = list2;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode h = newHead;
while(l1!=null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val>=l2.val){
h.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
else if(l1.val<l2.val){
h.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
h = h.next;
}
if(l1!=null){
h.next = l1;
}
if(l2!=null){
h.next = l2;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
2. 两数相加 中等
题目链接
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
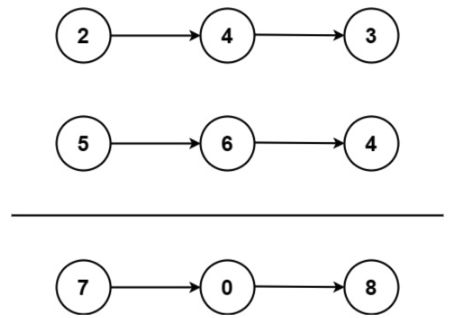
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();// 构建新的链表
ListNode cur = newHead;
int j = 0;// 初始进位
while(l1!=null || l2 != null || j != 0){ // 注意 或 的关系
if(l1 != null){
j += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if(l2 != null){
j += l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
int y = j%10;
int z = j/10; // 进位
cur.next = new ListNode(y);
j = z;
cur = cur.next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 中等
题目链接
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
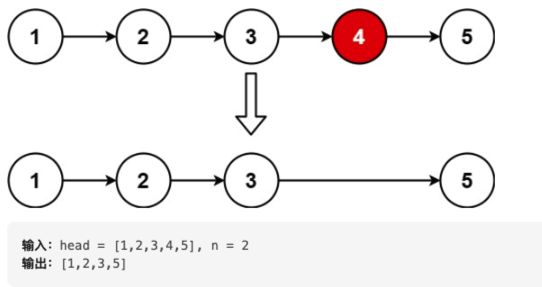
思路:
- 因为涉及删除头节点问题,因此创建一个新节点指向头节点。
- 快慢指针法找到倒数第n个节点
- 寻找倒数第n+1个节点,便于删除第n个
代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if(head==null || head.next == null)return null;
// 因为可能涉及删除第一个节点,所以我们创建一个新节点,指向头节点
ListNode newHead =new ListNode(-1);
newHead.next = head;
// 寻找倒数n+1的节点
ListNode x = getNthFromEnd(newHead,n+1);
// 删除
x.next = x.next.next;
// 返回newHead的下一个
return newHead.next;
}
// 快慢指针找到倒数某个节点
public ListNode getNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n){
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast!=null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点 中等
题目链接
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
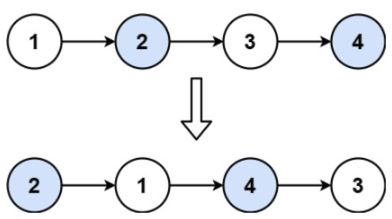
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
思路:与反转链表的递归相似。
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// base case
if(head==null||head.next==null)return head;
// 递归下下个节点
ListNode node = swapPairs(head.next.next);
// 调换前两个节点
ListNode x = head.next;
x.next= head;
head.next = node;
return x;
}
}
25. K 个一组翻转链表 困难
题目链接
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
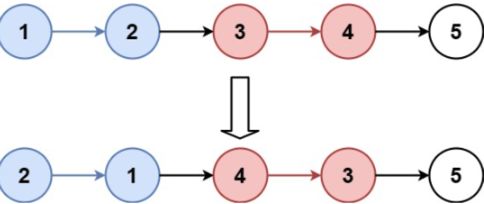
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head;
for(int i = 0;i < k;i++){
if(cur==null) return head;
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode newHead = reverse(head,cur); // 返回头节点
ListNode p = reverseKGroup(cur,k); // 对下一组进行反转递归
head.next = p; // 将上面两部分连接
return newHead;
}
ListNode node;
// 对该区间[head,wnode)反转,注意左闭右开区间
ListNode reverse(ListNode head,ListNode wnode){
if(head.next == wnode){
node = head.next;
return head;
}
ListNode n = reverse(head.next,wnode);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = node;
return n;
}
}
92. 反转链表 II 中等
题目链接
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:
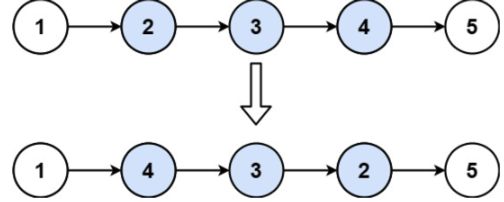
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
class Solution {
// 注意链表下标从1 开始
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
// 提前处理base case(此题可加可不加,建议添加)
if(head==null||head.next==null)return head;
if(left==right)return head;
// 递归处理
if(left == 1){ // 注意此处是1行
return reverse(head,right);
}
ListNode node = reverseBetween(head.next,left-1,right-1);
head.next = node; // 注意此行
return head;
}
ListNode w; // 注意此节点
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head,int k){
if(k == 1){
w = head.next;
return head;
}
ListNode node = reverse(head.next,k-1);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = w;
return node;
}
}
138. 复制带随机指针的链表
题目链接LC138
剑指Offer 35
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
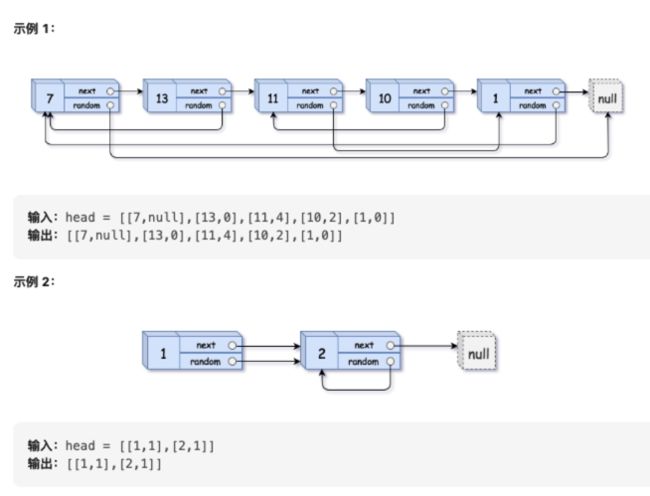
思路:采用DFS深度优先搜索遍历每一个节点,同时为每一个原始节点创建(拷贝)一个新节点,将对应关系放入Map中。然后在每一次递归DFS的后序位置,将新拷贝的节点与其下一个节点相连接。
代码:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
// 原始节点与克隆节点的对应关系
Map<Node,Node> originToCopyMap = new HashMap<>();
// 已经走过的点
Set<Node> visited = new HashSet<>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
DFS(head);
return originToCopyMap.get(head);// 返回克隆节点head
}
void DFS(Node head){
if(head==null)return;
if(visited.contains(head))return;
// 将原始节点和克隆节点放入Map
originToCopyMap.put(head,new Node(head.val));
visited.add(head);
DFS(head.next);
// 后序位置
originToCopyMap.get(head).next = originToCopyMap.get(head.next);
DFS(head.random);
// 后序位置
originToCopyMap.get(head).random = originToCopyMap.get(head.random);
}
}
148. 排序链表 中等
找到中间节点(876题 寻找中间节点);
利用分治法递归调用左右链表;
然后在合并两个链表(21题 合并两个有序链表)。
代码:
class Solution {
// 分治法
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return sortList(head,null);
}
/**
左闭右开区间
*/
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head,ListNode tail){
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.next == tail) {
head.next = null; // 注意此处
return head;
}
// 876题 寻找链表的中间节点
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != tail && fast.next != tail) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode mid = slow;
ListNode list1 = sortList(head, mid);// 分
ListNode list2 = sortList(mid, tail);// 分
ListNode sorted = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2);// 合并
return sorted;
}
// 21题 合并两个有序链接
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode l1 = list1,l2 = list2;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode h = newHead;
while(l1!=null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val>=l2.val){
h.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
else if(l1.val<l2.val){
h.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
h = h.next;
}
if(l1!=null){
h.next = l1;
}
if(l2!=null){
h.next = l2;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
23. 合并 K 个升序链表 困难
题目链接
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
思路:使用优先队列。
- 将所有非null的链表头节点add到queue中。
- 创建一个新节点newHead
- 循环poll出queue中的节点node,将其添加到newhead后,并将node.next添加到queue
代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists.length==0)return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a1,a2)->{
return a1.val - a2.val;
});
for(ListNode node : lists){
if(node!=null){
queue.add(node);// 入队列使用add
}
}
ListNode newhead = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = newhead;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ListNode q = queue.poll(); // 出队列使用poll
cur.next = q;
cur = cur.next;
if(q.next!=null){
queue.add(q.next);
}
}
return newhead.next;
}
}
143. 重排链表 中等
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[1,4,2,3]
示例 2:
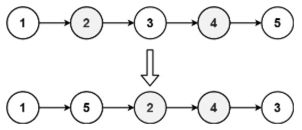
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[1,5,2,4,3]
思路:找到中间节点,反转后半段,然后依次更改指针指向。
代码:
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null) return;
ListNode mid = getMid(head);
ListNode l2 = reverse(mid);
ListNode l1 = head;
while(l2.next!=null){ // 注意此行
ListNode c1 = l1.next;
ListNode c2 = l2.next;
l1.next = l2;
l2.next = c1;
l1 = c1;
l2 = c2;
}
}
// 原题 获取中间节点 (4个节点时返回第3个,5个节点时返回第3个)
public ListNode getMid(ListNode head){
if(head==null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 原题 反转链表
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
if(head==null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode node = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return node;
}
}
为什么是 while(l2.next!=null){呢?
假如原链表有四个节点(偶数个):
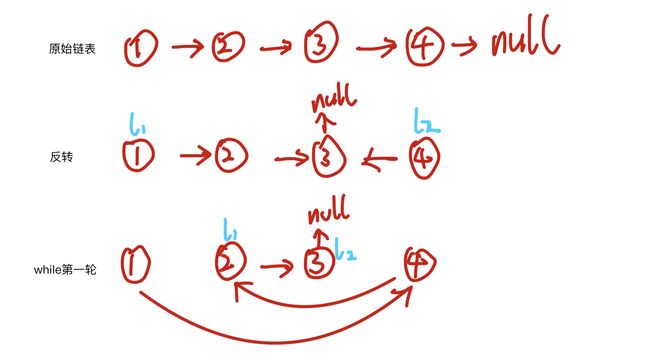
假如原链表有五个节点(奇数个):
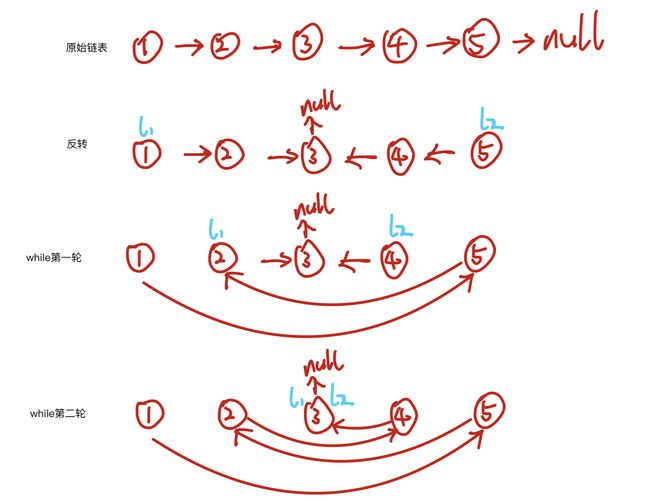
每当l2.next==null时,即已完成。
328. 奇偶链表
题目链接
给定单链表的头节点 head ,将所有索引为奇数的节点和索引为偶数的节点分别组合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。
第一个节点的索引被认为是 奇数 , 第二个节点的索引为 偶数 ,以此类推。
请注意,偶数组和奇数组内部的相对顺序应该与输入时保持一致。
你必须在 O(1) 的额外空间复杂度和 O(n) 的时间复杂度下解决这个问题。
示例 1:
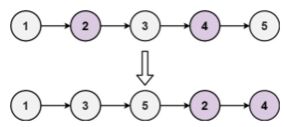
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [1,3,5,2,4]
示例 2:
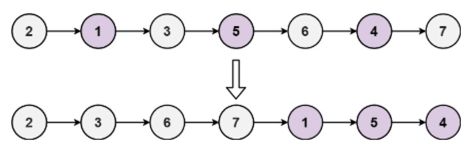
输入: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
输出: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]
代码:
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null || head.next.next == null)return head;
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = head.next;
ListNode l2head = l2;
while(l1.next!=null && l2.next!=null){
l1.next = l1.next.next; // l1 每次夸一个连接
l2.next = l2.next.next; // l2 每次夸一个连接
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
l1.next = l2head; // l1的末尾连上l2的头
return head;
}
}