Mybatis 源码 ∞ :杂七杂八
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、TypeHandler
- 三、KeyGenerator
- 四、Plugin
-
- 1 Interceptor
- 2 org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin
- 3. 调用场景
- 五、Mybatis 嵌套映射 BUG
-
- 1. 示例
- 2. 原因
- 3. 解决方案
- 六、discriminator 标签
- 七、其他
-
- 1. RowBounds
- 2. ResultHandler
- 3. @MapKey
一、前言
Mybatis 官网 以及 本系列文章地址:
- Mybatis 源码 ① :开篇
- Mybatis 源码 ② :流程分析
- Mybatis 源码 ③ :SqlSession
- Mybatis 源码 ④ :TypeHandler
- Mybatis 源码 ∞ :杂七杂八
主要是 Mybatis 的一些杂七杂八的内容,用于自己可以快速定位一些问题,所以部分内容写比较随性
二、TypeHandler
关于 TypeHandler 的使用,各处都是文章,这里就不再贴出完整的项目,仅对关键内容进行说明。
- 注册或声明 TypeHandler :
-
通过 mybatis.type-handlers-package 直接指定包路径 :该路径下的 TypeHandler 实现类都会被自动注册,并且只要是符合转换类型无论是入参还是出参都会经过转换
mybatis.type-handlers-package=com.kingfish.config.handler -
Xml 中 通过如下标签注册,可以指定注册哪些 TypeHandler,并且只要是符合转换类型无论是入参还是出参都会经过转换。
<configuration> <typeHandlers> <typeHandler handler="com.kingfish.config.handler.PwdTypeHandler"/> typeHandlers> configuration> -
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.kingfish.entity.SysUser"> <result property="password" column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" typeHandler="com.kingfish.config.handler.PwdTypeHandler"/> resultMap>
-
-
定义密码加解密类型转换器 : PwdTypeHandler。密码不能明文存储在库中,所以当我们需要对DB 中的密码进行加密处理。这里便可以通过 TypeHandler 来实现(在新增、更新、删除时自动加密,在查询时自动解密)
public class PwdTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<String> { private static final SymmetricCrypto AES = new SymmetricCrypto( SymmetricAlgorithm.AES, "1234567890123456".getBytes()); @Override public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, String parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException { ps.setString(i, AES.encryptBase64(parameter)); } @Override public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException { return AES.decryptStr(rs.getString(columnName)); } @Override public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { return AES.decryptStr(rs.getString(columnIndex)); } @Override public String getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { return AES.decryptStr(cs.getString(columnIndex)); } }
需要注意的是
-
如果以注册的方式(mybatis.type-handlers-package 或者
-
如果是通过 标签的 typeHandler 属性指定,则只会在查询返回结果时对指定结果集中的指定字段进行处理。
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.kingfish.entity.SysUser"> <result property="password" column="password" jdbcType="VARCHAR" typeHandler="com.kingfish.config.handler.PwdTypeHandler"/> resultMap> <insert id="insert" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true" > insert into sys_user(create_time, modify_time, user_name, password, status, is_delete, nick_name, phone, extend) values (#{createTime}, #{modifyTime}, #{userName}, #{password, typeHandler=com.kingfish.config.handler.PwdTypeHandler}, #{status}, #{isDelete}, #{nickName}, #{phone}, #{extend}) insert> <update id="update"> update sys_user <set> <if test="password != null and password != ''"> password = #{password, typeHandler=com.kingfish.config.handler.PwdTypeHandler} if> set> where id = #{id} update>
三、KeyGenerator
在Mybatis中,执行insert操作时,如果我们希望返回数据库生成的自增主键值,那么就需要使用到KeyGenerator对象。
关于 KeyGenerator 的内容,这里直接摘取 Mybatis之KeyGenerator 的部分内容,详细部分请阅读原文
KeyGenerator 定义如下:
public interface KeyGenerator {
// BaseStatementHandler 构造函数中调用,在sql 执行前调用
void processBefore(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter);
// StatementHandler#update 中会调用,在sql 执行后调用
void processAfter(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter);
}
存在如下三个实现类:
- Jdbc3KeyGenerator:用于处理数据库支持自增主键的情况,如MySQL的auto_increment。
- NoKeyGenerator:空实现,不需要处理主键。
- SelectKeyGenerator:用于处理数据库不支持自增主键的情况,比如Oracle的sequence序列。
下面以 Jdbc3KeyGenerator 为例简单看下
@Override
public void processAfter(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter) {
processBatch(ms, stmt, parameter);
}
public void processBatch(MappedStatement ms, Statement stmt, Object parameter) {
// 获取key属性名,一般来说即 id,说明 key 就是属性名为 id 的字段
final String[] keyProperties = ms.getKeyProperties();
if (keyProperties == null || keyProperties.length == 0) {
return;
}
try (ResultSet rs = stmt.getGeneratedKeys()) {
final ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
final Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 如果列的长度小于 key的长度则不处理
if (rsmd.getColumnCount() < keyProperties.length) {
// Error?
} else {
// 赋值key
assignKeys(configuration, rs, rsmd, keyProperties, parameter);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExecutorException("Error getting generated key or setting result to parameter object. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private void assignKeys(Configuration configuration, ResultSet rs, ResultSetMetaData rsmd, String[] keyProperties,
Object parameter) throws SQLException {
if (parameter instanceof ParamMap || parameter instanceof StrictMap) {
// Multi-param or single param with @Param
// 多个参数或单一参数 使用 @Param 场景
assignKeysToParamMap(configuration, rs, rsmd, keyProperties, (Map<String, ?>) parameter);
} else if (parameter instanceof ArrayList && !((ArrayList<?>) parameter).isEmpty()
&& ((ArrayList<?>) parameter).get(0) instanceof ParamMap) {
// Multi-param or single param with @Param in batch operation
// 多个参数或单一参数 使用 @Param 批量操作的场景
assignKeysToParamMapList(configuration, rs, rsmd, keyProperties, (ArrayList<ParamMap<?>>) parameter);
} else {
// Single param without @Param
// 单个参数未使用 @Param 的场景
assignKeysToParam(configuration, rs, rsmd, keyProperties, parameter);
}
}
下面以单个参数未使用 @Param 场景为例
private void assignKeysToParam(Configuration configuration, ResultSet rs, ResultSetMetaData rsmd,
String[] keyProperties, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
// 将对象转换为 集合,就是简单封装
Collection<?> params = collectionize(parameter);
if (params.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
List<KeyAssigner> assignerList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < keyProperties.length; i++) {
assignerList.add(new KeyAssigner(configuration, rsmd, i + 1, null, keyProperties[i]));
}
Iterator<?> iterator = params.iterator();
// 遍历参数
while (rs.next()) {
if (!iterator.hasNext()) {
throw new ExecutorException(String.format(MSG_TOO_MANY_KEYS, params.size()));
}
// 获取参数
Object param = iterator.next();
// 反射将Key 值映射到 参数对应的属性上 (即将id的值映射到 param 的id 属性上)
assignerList.forEach(x -> x.assign(rs, param));
}
}
四、Plugin
Mybatis支持我们通过插件的方式扩展具体的过程,我们可以通过如下方式:
// 声明当前类是个拦截器,拦截的类型是 StatementHandler,方法名是 prepare,该方法的入参 Connection 和 Integer 类型。
// 当 StatementHandler 的 prepare 方法执行时会被该拦截器拦截
@Component
@Intercepts({ @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = { Connection.class, Integer.class}) })
public class DemoPlugins implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("invocation = " + invocation);
return null;
}
}
下面我们来看看代码的具体实现
在上面我们提到负责执行Sql的 Executor 被 Interceptor 包装了,实际上并非仅仅只有 执行器会被拦截器拦截,因此我们这里来看看 Mybatis 拦截器的具体实现。
如下是 InterceptorChain#pluginAll 的实现,当创建 Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler 时都会调用该方法:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
可以看到,该方法会通过 Interceptor#plugin 方法对 target 进行包装,具体如下:
1 Interceptor
org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor 定义如下:
public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
default Object plugin(Object target) {
// 使用当前对象包装 target
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
// XML 解析 interceptor 时会调用该方法进行属性赋值,具体看实现
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}
这里可以看到,Mybatis 通过 Plugin#wrap 方法代理并返回了一个新的对象。下面我们来看下 org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin 的具体实现。
2 org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin
org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin#wrap 实现如下:
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 1. 获取方法签名
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 获取 type 的所有实现接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 创建新的代理对象,这里看到,处理器实际上是Plugin
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
// 解析Intercepts注解并获取方法签名
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取 @Intercepts 注解信息
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
// 获取 @Intercepts 注解的 @Signature 签名信息
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
// 创建 代理方法集合,被代理的方法会保存到该 Set 中
Set<Method> methods = MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(signatureMap, sig.type(), k -> new HashSet<>());
try {
// 获取 @Signature.type 指定的类,方法名为 sig.method(),参数为 sig.args() 的方法
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 返回代理方法签名
return signatureMap;
}
可以看到,这里会为 target 创建一个代理对象,代理处理器由 Plugin 来担任,Plugin#invoke 方法如下:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 从代理方法签名中获取当前类的代理方法,如果当前方法需要代理则进行代理,否则执行调用
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 执行代理拦截器,这里 interceptor 实际上是 Interceptor 的实现类,也就是 Mybatis 的插件类
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
3. 调用场景
在 Mybatis 中,插件的包装调用都在 Configuration 中,如下
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
这里可以看到Mybatis Plugin 的实现还是比较简单的,通过注解解析,来创建对应类的对应方法的拦截器,(如 PageHelper 的实现核心就是通过 com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor 来完成的。)
五、Mybatis 嵌套映射 BUG
1. 示例
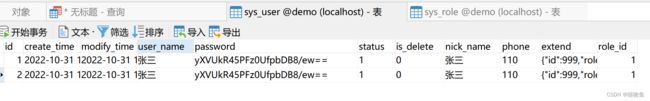
Mybatis 嵌套映射在行数据完全相同时 (这里的行数据完全相同指的是sql 查询出来的数据万完全相同,而非 Mybatis 的ResultMap 映射的字段的值完全相同)会丢失的缺陷,以下面为例子 :
-
执行如下SQL, 该 Sql 目的是为了查询有几个用户具有admin 权限,这里可以看到使用了Left join 所以会返回两条完全相同的数据:
SELECT sr.*, su.user_name user_user_name, su.PASSWORD user_password FROM sys_role sr LEFT JOIN sys_user su ON sr.id = su.role_id where sr.id = 1 -
但实际上如果通过Mybatis 执行上述逻辑则会出现错误结果如下:
SysRoleDto 如下,这里不再贴出SysUser:
public class SysRoleDto { /** * 自增主键ID */ private Long id; /** * 用户名 */ private String roleName; /** * 状态 */ private String status; /** * 用户 */ private List<SysUser> sysUsers; }Mapper 如下:
<mapper namespace="com.kingfish.dao.SysRoleDao"> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.kingfish.entity.SysRole"> <result property="id" column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER"/> <result property="roleName" column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/> <result property="status" column="status" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /> resultMap> <resultMap id="InnerNestMap" type="com.kingfish.entity.dto.SysRoleDto" extends="BaseResultMap"> <collection property="sysUsers" columnPrefix="user_" resultMap="com.kingfish.dao.SysUserDao.BaseResultMap">collection> resultMap> <select id="selectRoleUser" resultMap="InnerNestMap"> SELECT sr.*, su.user_name user_user_name, su.PASSWORD user_password FROM sys_role sr LEFT JOIN sys_user su ON sr.id = su.role_id where sr.id = 1 select> mapper> -
执行结果如下,可以发现 sysUsers 属性少了一条记录,因为这里两条查询的记录相同 在nestedResultObjects 中被判断已经存在。
-
如果我们把其中一个【张三】改成【李四】,其余全都不动,那么sysUsers两条记录数据就不相同,则不会出现这种问题,如下:
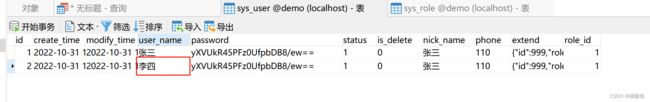
执行结果如下:
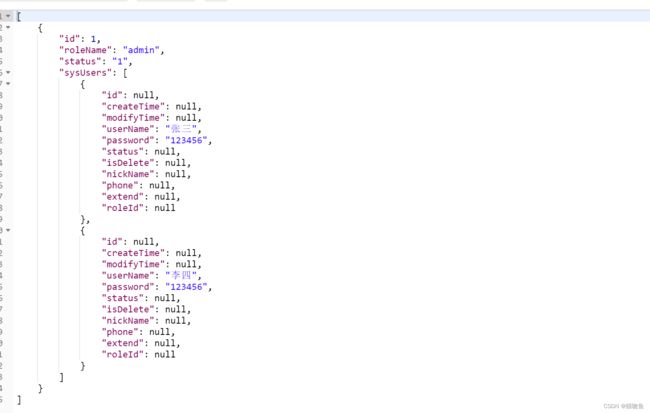
2. 原因
该缺陷的原因在于在 Mybatis 中会缓存嵌套对象到 DefaultResultSetHandler#nestedResultObjects 中,而缓存的key 的生成策略可以简单理解为 resultMapid + 属性名 + 属性值。而上面的例子中 Sql正常执行是如下数据,可以看到查出来的两行数据完全相同:

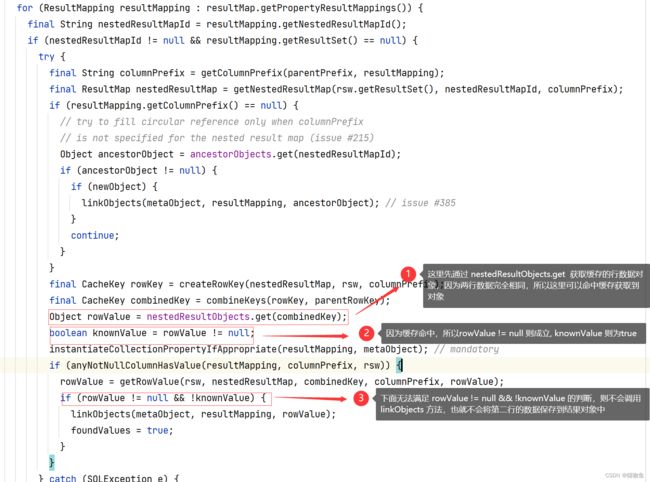
当处理第一条数据时一切正常,而因为是嵌套映射则会将当前行数据缓存到 DefaultResultSetHandler#nestedResultObjects 中。当处理到第二条数据时,
在 DefaultResultSetHandler#applyNestedResultMappings 方法中从 nestedResultObjects 获取到了缓存,从而不会将该行数据保存, 如下图:
3. 解决方案
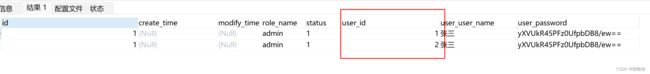
解决方案就是保证两行数据不完全相同,比如这里可以通过增加 sys_user 的id 查询保证数据的唯一性, 如下:
SELECT
sr.*,
su.id user_id,
su.user_name user_user_name,
su.PASSWORD user_password
FROM
sys_role sr
LEFT JOIN sys_user su ON sr.id = su.role_id
where sr.id = 1
六、discriminator 标签
我们以下面的情况为例:
<resultMap id="CollectionBaseResultMap" type="com.kingfish.entity.dto.SysUserDto" extends="BaseResultMap">
<discriminator javaType="java.lang.Integer" column="id">
<case value="1" resultType="com.kingfish.entity.dto.SysUserDto">
<result column="user_name" property="extend1"/>
case>
<case value="2" resultMap="CollectionBaseResultMap">
<result column="nick_name" property="extend1"/>
case>
discriminator>
resultMap>
这里需要注意 :
- discriminator 标签中 case 中使用 resultType 和 resultMap 的 discriminatedMapId 并不相同, 返回类型是 resultType 时 则会自动生成一个 ResultMap,
- resultType情况下需要自己重新对名字进行转换,因为没有 ResultMap 的转换,变量名无法对应。resultMap情况下会忽略 case 条件下的Result ,因为直接从缓存中获取之前加载好的 CollectionBaseResultMap结构了。
七、其他
1. RowBounds
Mybatis可以通过传参中的 RowBounds 可以完成逻辑分页,但不推荐,因为所有的数据都是查询到内存中再筛选。如下:
// 逻辑分页查询 :入参中有 RowBounds 参数
List<SysMenuDto> selectByParam(RowBounds rowBounds);
2. ResultHandler
Mybatis可以通过传参中的 ResultHandler 可以结果集处理,而不再通过 Mapper Method 方法再返回结果,如果不指定,则默认是通过 DefaultResultHandler 来处理。如下:
// 无返回值 && 入参中有 ResultHandler 实例
void selectByParam(ResultHandler resultHandler);
官方对 ResultHandler 的说明【ResultHandler 参数允许自定义每行结果的处理过程。你可以将它添加到 List 中、创建 Map 和 Set,甚至丢弃每个返回值,只保留计算后的统计结果。你可以使用 ResultHandler 做很多事,这其实就是 MyBatis 构建 结果列表的内部实现办法。】
需要注意的是
-
DefaultResultSetHandler#handleResultSet 中判断了如果指定了 ResultHandler 则使用指定的,否则使用 DefaultResultHandler:
3. @MapKey
官方描述 :供返回值为 Map 的方法使用的注解。它使用对象的某个属性作为 key,将对象 List 转化为 Map。属性:value,指定作为 Map 的 key 值的对象属性名。
即: 当一个查询方法想要返回 Map 时,可以通过 @MapKey 来指定用来聚合的key 是什么字段,如下:
<select id="selectRoleForMap" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select *
from sys_role
@MapKey("id")
Map<Long, SysRoleDto> selectRoleForMap();
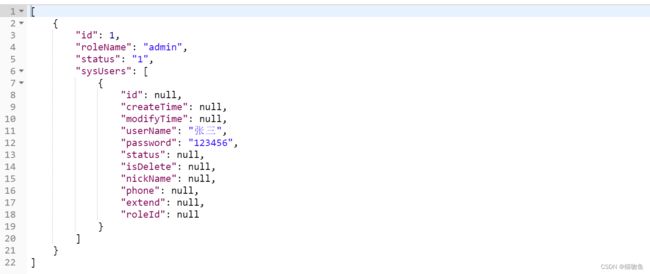
查询结果会把 id 当做 Map 的key 字段来聚合,返回如下:

源码处理逻辑在 :org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod#executeForMap 中,调用 DefaultSqlSession#selectMap 方法来处理,这里会交由 DefaultMapResultHandler 来处理结果, 将结果封装成对应的 Map。
以上:内容部分参考
https://www.jianshu.com/p/05f643f27246
https://juejin.cn/post/6844904127818891278
如有侵扰,联系删除。 内容仅用于自我记录学习使用。如有错误,欢迎指正