import torch
from IPython import display
from d2l import torch as d2l
batach_size=256
train_iter,test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batach_size)
num_input = 784
num_output = 10
W = torch.normal(0,0.01,size=(num_input,num_output),requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(num_output,requires_grad=True)
def softmax(X):
X_exp = torch.exp(X)
partition = X_exp.sum(1,keepdim=True)
return X_exp/partition
def net(X):
return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape((-1,W.shape[0])),W)+b)
def cross_entropy(y_hat,y):
return -torch.log(y_hat[range(len(y_hat)),y])
def accuracy(y_hat,y):
if len(y_hat.shape)>1 and y_hat.shape[1]>1:
y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y
return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())
class Accumulator:
def __init__(self,n):
self.data = [0.0] * n
def add(self, *args):
self.data = [a+float(b) for a,b in zip(self.data, args)]
def reset(self):
self.data = [0.0] * len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.data[idx]
def evaluate_accuracy(net,data_iter):
if isinstance(net,torch.nn.Module):
net.eval()
metric = Accumulator(2)
with torch.no_grad():
for X,y in data_iter:
metric.add(accuracy(net(X),y),y.numel())
return metric[0]/metric[1]
def train_epoch(net,train_iter,loss,updater):
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.train()
metric = Accumulator(3)
for X,y in train_iter:
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat,y)
if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer):
updater.zero_grad()
l.mean().backward()
updater.setp()
else:
l.sum().backward()
updater(X.shape[0])
metric.add(float(l.sum()), accuracy(y_hat, y), y.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2]
class Animator:
"""在动画中绘制数据"""
def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None,
ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear',
fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1,
figsize=(3.5, 2.5)):
if legend is None:
legend = []
d2l.use_svg_display()
self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize)
if nrows * ncols == 1:
self.axes = [self.axes, ]
self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes(
self.axes[0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend)
self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts
def add(self, x, y):
if not hasattr(y, "__len__"):
y = [y]
n = len(y)
if not hasattr(x, "__len__"):
x = [x] * n
if not self.X:
self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)]
if not self.Y:
self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i, (a, b) in enumerate(zip(x, y)):
if a is not None and b is not None:
self.X[i].append(a)
self.Y[i].append(b)
self.axes[0].cla()
for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts):
self.axes[0].plot(x, y, fmt)
self.config_axes()
display.display(self.fig)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
def train(net,train_iter,test_iter,loss,num_epoch,updater):
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0.3, 0.9],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_metrics = train_epoch(net, train_iter, loss, updater)
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, train_metrics + (test_acc,))
train_loss, train_acc = train_metrics
assert train_loss < 0.5, train_loss
assert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7, train_acc
assert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7, test_acc
lr = 0.1
def updater(batch_size):
return d2l.sgd([W,b],lr,batch_size)
num_epochs = 10
train(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, updater)
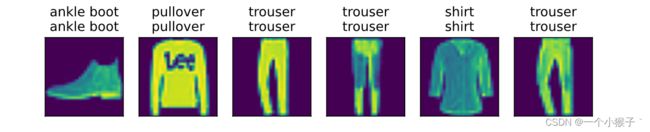
def predict(net,test_iter,n=6):
for X,y in test_iter:
break
trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y)
preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1))
titles = [true+'\n'+pred for true,pred in zip(trues,preds)]
d2l.show_images(
X[0:n].reshape((n, 28, 28)), 1, n, titles=titles[0:n])
predict(net,test_iter)
训练图像

测试