使用grep做文本的过滤
常与 管道符(|)结合在一起使用
管道符 piping:用于前一个命令的输出当作后一个命令的输入。常用于连接多个命令
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ps aux | grep apache2
root 41946 0.0 0.2 6568 2304 pts/1 S+ 17:26 0:00 grep --color=auto apache2
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─#
netstat -tunlp 查看端口
──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam] 查看端口 -t tcp -u udp -n 数字形式显示 -l 显示当前正在监听的端口 -p 哪个程序在使用这个端口
└─# netstat -tunlp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
ps aux 显示系统正在运行的所有进程
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam] 显示所有系统正在运行进程
└─# ps aux
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.9 20776 8524 ? Ss 16:04 0:02 /sbin/init splash
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:04 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 16:04 0:00 [rcu_gp]
root 4 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 16:04 0:00 [rcu_par_gp]
root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 16:04 0:00 [slub_flushwq]
root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 16:04 0:00 [netns]
root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I 16:04 0:03 [kworker/u256:0-events_unbou
root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I< 16:04 0:00 [mm_percpu_wq]
root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I 16:04 0:00 [rcu_tasks_kthread]
root 12 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I 16:04 0:00 [rcu_tasks_rude_kthread]
root 13 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? I 16:04 0:00 [rcu_tasks_trace_kthread]
root 14 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:04 0:02 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 15 0.1 0.0 0 0 ? I 16:04 0:04 [rcu_preempt]
root 16 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 16:04 0:00 [migration/0]
systemctl 系统服务控制工具
systemctl 命令 服务名称
常用命令:start :启动 stop:停止 restart :重启
──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam] 系统服务控制工具
└─# systemctl -h
systemctl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND ...
Query or send control commands to the system manager.
Unit Commands:
list-units [PATTERN...] List units currently in memory
list-automounts [PATTERN...] List automount units currently in memory,
ordered by path
list-paths [PATTERN...] List path units currently in memory,
ordered by path
list-sockets [PATTERN...] List socket units currently in memory,
ordered by address
list-timers [PATTERN...] List timer units currently in memory,
ordered by next elapse
is-active PATTERN... Check whether units are active
is-failed PATTERN... Check whether units are failed
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
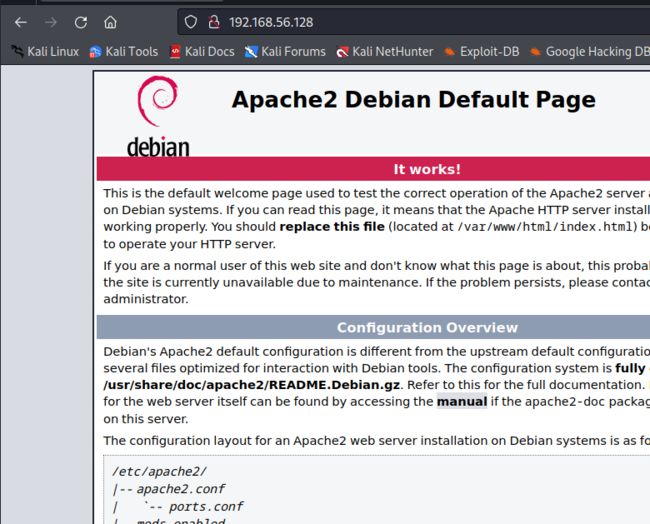
└─# systemctl start apache2
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ps aux | grep apache2
root 44345 0.9 2.1 205256 19992 ? Ss 17:31 0:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
www-data 44348 0.0 1.0 205968 9952 ? S 17:31 0:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
www-data 44349 0.0 1.0 205968 9952 ? S 17:31 0:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
www-data 44350 0.0 1.0 205968 9952 ? S 17:31 0:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
www-data 44351 0.0 1.0 205968 9952 ? S 17:31 0:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
www-data 44352 0.0 1.0 205968 9952 ? S 17:31 0:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
root 44394 0.0 0.2 6568 2304 pts/1 S+ 17:31 0:00 grep --color=auto apache2
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─#
echo $? 查看命令的执行状态
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam] 正确执行为 0
└─# echo $?
0
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# netstat -tunlp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 44345/apache2
ifconfig 查看ip 地址
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ifconfig
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.56.128 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.56.255
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:feb3:7991 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:b3:79:91 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 1272 bytes 89992 (87.8 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 89 bytes 16008 (15.6 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 4 bytes 240 (240.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 4 bytes 240 (240.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
SSH服务:常用于远程连接(安全)
端口号 tcp/22
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ps aux | grep ssh
kali 1219 0.0 0.1 7912 1012 ? Ss 16:05 0:00 /usr/bin/ssh-agent x-session-manager
root 48394 0.0 0.2 6568 2304 pts/1 S+ 17:38 0:00 grep --color=auto ssh
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ps aux | grep -w ssh
kali 1219 0.0 0.1 7912 1012 ? Ss 16:05 0:00 /usr/bin/ssh-agent x-session-manager
root 48665 0.0 0.2 6568 2176 pts/1 S+ 17:38 0:00 grep --color=auto -w ssh
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# systemctl start ssh
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# echo $?
0
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# netstat -tunlp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 48831/sshd: /usr/sb
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 48831/sshd: /usr/sb
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 44345/apache2
!n 调用最近一次以n打头的指令
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# !n
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# netstat -tunlp
grep 例子
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# grep --help
用法:grep [选项]... 模式 [文件]...
在每个 <文件> 中查找指定的 <模式>。
例如:grep -i 'hello world' menu.h main.c
<模式> 可以包含多个模式字符串,使用换行符进行分隔。
模式选择与解释:
-E, --extended-regexp <模式> 是扩展正则表达式
-F, --fixed-strings <模式> 是字符串
-G, --basic-regexp <模式> 是基本正则表达式
-P, --perl-regexp <模式> 是 Perl 正则表达式
-e, --regexp=模式 使用指定的 <模式> 进行匹配
-f, --file=文件 从指定的 <文件> 中获得 <模式>
-i, --ignore-case 对于模式和数据,忽略大小写
--no-ignore-case 不要忽略大小写(默认)
-w, --word-regexp 仅匹配整个单词
-x, --line-regexp 仅匹配整行
-z, --null-data 数据行以 0 字节 (NUL) 结束,而非换行符
杂项:
-s, --no-messages 不显示错误信息
-v, --invert-match 选中不匹配的行
-V, --version 显示版本信息并退出
--help 显示此帮助信息并退出
输出控制:
-m, --max-count=数值 选中 <数值> 行后停止执行
-b, --byte-offset 输出的同时打印字节偏移量
-n, --line-number 输出的同时打印行号
--line-buffered 每行输出后排空输出缓冲区
-H, --with-filename 输出的同时打印文件名
-h, --no-filename 输出时不显示文件名前缀
--label=标签 使用指定 <标签> 作为标准输入文件名前缀
-o, --only-matching 只显示行中非空的匹配部分
-q, --quiet, --silent 不显示所有常规输出
--binary-files=类型 假定二进制文件是 <类型>;
<类型> 可以是 "binary"、"text" 或 "without-match"
-a, --text 等价于 --binary-files=text
-I 等价于 --binary-files=without-match
-d, --directories=动作 处理目录的方式;
<动作> 可以是 "read"、"recurse" 或 "skip"
-D, --devices=动作 处理设备、FIFO 和套接字的方式;
<动作> 可以是 "read" 或 "skip"
-r, --recursive 等价于 --directories=recurse
-R, --dereference-recursive 同上,但跟随所有符号链接
--include=GLOB 只查找匹配 GLOB(含通配符的文件模式)的文件
--exclude=GLOB 跳过匹配 GLOB 的文件
--exclude-from=文件 跳过匹配 <文件> 内容中任一文件模式的文件
--exclude-dir=GLOB 跳过匹配 GLOB 的目录
-L, --files-without-match 只打印没有被选中的行的 <文件> 的名称
-l, --files-with-matches 只打印有被选中的行的 <文件> 的名称
-c, --count 只打印每个 <文件> 的被选中的行的数量
-T, --initial-tab 使制表符对齐(如有必要)
-Z, --null 在 <文件> 名后打印 0 字节 (NUL)
文件控制:
-B, --before-context=数值 打印前面 <数值> 行上下文
-A, --after-context=数值 打印后面 <数值> 行上下文
-C, --context=数值 打印前后 <数值> 行上下文
-数值 等价于 --context=数值
--group-separator=分隔符 在带有上下文的匹配块之间打印 <分隔符>
--no-group-separator 不要在带有上下文的匹配块之间打印分隔符
--color[=何时],
--colour[=何时] 使用标记高亮匹配的字符串;
<何时> 可以是 "always"、"never" 或 "auto"
-U, --binary 不要清除行尾的 CR 字符 (MSDOS/Windows)
若 <文件> 为 "-",则从标准输入读取。若没有指定 <文件>,则递归模式
下从 "." 读取,其他情况下从 "-" 读取。若指定的 <文件> 数量少于两个,
则默认启用 -h 选项。如果有任意行被选中,则退出状态为 0,否则
退出状态为 1;如果有错误发生,且未指定 -q 选项,则退出状态为 2。
──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ls /usr/bin | grep zip
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# pwd
/root/work/exam
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# cd a
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# pwd
/root/work/exam/a
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# mkdir -pv 01/001/0001
mkdir: 已创建目录 '01'
mkdir: 已创建目录 '01/001'
mkdir: 已创建目录 '01/001/0001'
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo depressiom is very great
depressiom is very great
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo depressiom is very great > test.txt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# cat test.txt
depressiom is very great
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# ls
01 test.txt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo depressiom is very great >01/test.txt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# ls 01
001 test.txt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo depressiom is very great >01/001/test.txtt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo depressiom is very great >01/001/001/test.txtt
zsh: 没有那个文件或目录: 01/001/001/test.txtt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo depressiom is very great >01/001/0001/test.txtt
// 递归查询
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# grep depressiom 01
grep: 01: 是一个目录
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# grep -r depressiom 01
01/001/0001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/test.txt:depressiom is very great
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─#
-i 忽略大小写
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo DPRESSIOM is very great >01/001/test01.txtt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# grep -r depressiom 01
01/001/0001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/test.txt:depressiom is very great
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# grep -r -i depressiom 01
01/001/0001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/test.txt:depressiom is very great
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# echo DEPRESSIOM is very great >01/001/test01.txtt
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─# grep -r -i depressiom 01
01/001/0001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/001/test.txtt:depressiom is very great
01/001/test01.txtt:DEPRESSIOM is very great
01/test.txt:depressiom is very great
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam/a]
└─#