毫米波雷达成像论文阅读笔记: IEEE TPAMI 2023 | CoIR: Compressive Implicit Radar
原始笔记链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg4MjgxMjgyMg==&mid=2247486680&idx=1&sn=edf41d4f95395d7294bc958ea68d3a68&chksm=cf51be21f826373790bc6d79bcea6eb2cb3d09bb1860bba0af0fd5e60c448ca006976503e460#rd
↑ \uparrow ↑点击上述链接即可阅读全文
IEEE TPAMI 2023 | CoIR: Compressive Implicit Radar
毫米波雷达成像论文阅读笔记: IEEE TPAMI 2023 | CoIR: Compressive Implicit Radar
Abstract
-
背景
- mmWave radars suffer from low angular resolution due to small apertures and conventional signal processing
- 稀疏阵列雷达 can increase aperture size while minimizing power consumption and readout bandwidth
-
方法 :提出 Compressive Implicit Radar (CoIR)
-
目标: high accuracy sparse radar imaging using a single radar chip
-
Leverages : CNN decoder and compressed sensing
-
贡献:
✅ 设计稀疏线阵: with 5.5x fewer antennas than conventional MIMO arrays
✅ 提出ComDecoder :a fully convolutional implicit neural network architecture
✅ 证明了CoIR的有效性 :in both simulation and real-world experiments,且 不需要 auxiliary sensors
-
-
实验结果
1 INTRODUCTION
基于光学的Depth imaging及其缺点
- Depth imaging
- crucial for applications like SLAM, autonomous driving, security monitoring
- Typical sensors: cameras, LiDAR
- Cameras: high-resolution near-field depth imaging
- LiDAR: directly outputs dense point cloud with high range/angular resolution
- Limitation : degraded performance in visually degraded environments like fog, smoke
毫米波雷达成像的优点和挑战
- 优点
- penetrate through fog/smoke without performance degradation
- 挑战
- low angular resolution δ ≈ λ / d \delta ≈ \lambda/d δ≈λ/d
- Increasing d d d increases cost, power consumption and readout bandwidth
已有提高角分辨率的工作和缺陷
- 已有思路
- Large physical arrays
- MIMO arrays
- SAR
- Sensor fusion
- Optimization with handcrafted priors
- Deep learning
- 不足
- Slow acquisition
- Increased hardware complexity
- Require large datasets
- Limited generalizability
The proposed CoIR:
-
Key observation:
- INR provides inductive bias towards natural solutions for imaging inverse problems
-
方法
- Leverages implicit neural representations (INRs) + compressed sensing
-
贡献
- Designed sparse linear array with 5.5x fewer antennas
- Proposed convolutional decoder architecture ComDecoder
- Demonstrated improved performance over standard mmWave radars and competitive untrained methods
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 mmWave Imaging Systems
-
提高角度分辨率的方法及其缺点
- Large physical arrays: expensive, large data volumes
- MIMO arrays: requires many radar chips to synthesize large aperture
- SAR techniques:slow imaging, bulky scanners
- Sensor fusion: fails if one modality fails
- Deep learning: requires large labeled datasets, limited generalizability
-
proposed CoIR 的不同:
-
仅使用 single chip sparse MIMO array
-
使用 未经训练 的 神经网络
✅ 无需训练数据
-
2.2 Sparse Radar Imaging
-
稀疏雷达成像技术:
- 1 Sparse aperture array designs
- 2 Sparse reconstruction methods
-
1 Sparse aperture array designs
-
使用欠奈奎斯特采样 减少 天线数
-
优化方法:
✅ Convex relaxations
✅ Prior knowledge of number of reflectors
-
-
2 Sparse reconstruction methods
-
Super-resolution algorithms
✅ MUSIC, ESPRIT
✅ Require incoherent signals, known number of targets
-
Compressed sensing (CS) optimization:
✅ 使用稀疏先验,如 spatial sparsity, TV norm
✅ Challenging to design priors, scene dependent
-
-
proposed CoIR 的不同:
-
Sparse array design
inspired by prior work but modified due to hardware constraints
-
Uses untrained neural network
as complex prior instead of handcrafted prior
✅ Neural network prior shows affinity for natural features and noise robustness
-
2.3 Implicit Neural Representations
-
两类INR architectures:
- 1 Convolutional methods
- 2 Coordinate-based MLP methods
-
1 Convolutional methods ,适合:
- Compressed sensing
- Image super-resolution
- Image denoising
- Accelerated MRI
-
2 Coordinate-based MLP methods ,适合:
- Novel view synthesis
- Dynamic illumination
- PDE solutions
- Image deconvolution
-
CoIR中的ComDecoder:
-
属于 Convolutional methods
-
tailored for sparse radar imaging
-
Key properties:
Convolutional operations capture local spatial information
Upsampling induces notion of resolution per layer
Residual blocks smooth optimization and propagate information between layers
Together these inductive biases improve performance on sparse radar imaging
-
Differences from prior works:
✅ CoIR uses untrained INR as complex prior for sparse radar imaging
✅ Prior works use INR for natural images or other imaging modalities
-
3 RADAR IMAGING BACKGROUND
-
发射信号模型
- y t x ( t ) = e j 2 π ( f 0 t + 1 2 B τ t 2 ) , 0 ≤ t ≤ T y_{tx}(t) = e^{j2π(f_0t + \frac{1}{2}Bτt^2)}, 0 \leq t \leq T ytx(t)=ej2π(f0t+21Bτt2),0≤t≤T
- f 0 f_0 f0: carrier frequency
- B B B: chirp bandwidth
- T T T: pulse duration
-
场景模型 (离散反射体分布)
- x ‾ [ n r , n θ ] ∈ C K × L \overline{x}[n_r, n_\theta] \in \mathbb{C}^{K\times L} x[nr,nθ]∈CK×L
- n r n_r nr: range bin index
- n θ n_\theta nθ: angle bin index
-
回波信号模型
- z [ n , m ] = ∑ n r = 0 K − 1 ∑ n θ = 0 L − 1 x ‾ [ n r , n θ ] e j 2 π ψ θ ( n θ ) m e j 2 π ψ r ( n r ) n + w [ n , m ] z[n,m] = \sum_{n_r=0}^{K-1} \sum_{n_\theta=0}^{L-1} \overline{x}[n_r, n_\theta] e^{j2π\psi_\theta(n_\theta)m} e^{j2π\psi_r(n_r)n} + w[n,m] z[n,m]=∑nr=0K−1∑nθ=0L−1x[nr,nθ]ej2πψθ(nθ)mej2πψr(nr)n+w[n,m]
- ψ θ ( n θ ) = f 0 d c sin ( b θ [ n θ ] ) \psi_\theta(n_\theta) = \frac{f_0 d}{c}\sin(b_\theta[n_\theta]) ψθ(nθ)=cf0dsin(bθ[nθ]): spatial frequency
- ψ r ( n r ) = B N 2 b r [ n r ] c \psi_r(n_r) = \frac{B}{N}\frac{2b_r[n_r]}{c} ψr(nr)=NBc2br[nr]: normalized temporal frequency
- w [ n , m ] w[n,m] w[n,m]: noise
-
Compact matrix form
-
z = F ( x ‾ ) + w z = F(\overline{x}) + w z=F(x)+w
-
F F F: 2D FFT
-
Goal: recover x ‾ \overline{x} x from under-sampled measurements z z z
-
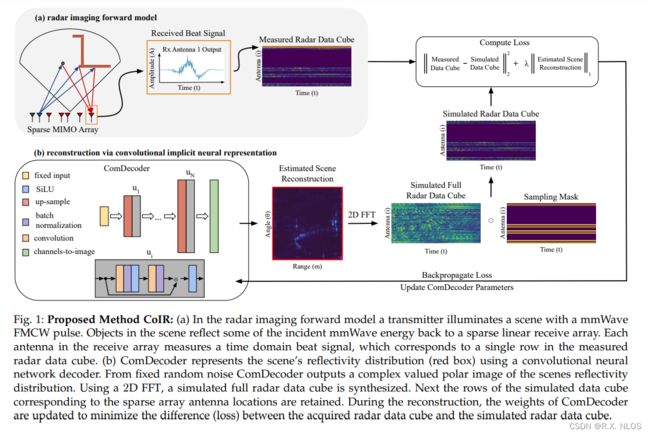
4 PROPOSED METHOD
-
目标 :
- Recover scene reflectivity x ‾ \overline{x} x from under-sampled measurements z z z
-
Measurements :
-
z = M ⊙ F ( x ‾ ) + w z = M\odot F(\overline{x}) + w z=M⊙F(x)+w
-
M M M: binary mask implementing under-sampling
-
w w w: noise
-
-
困难 :
- under-sampling causes grating lobes in sparse array PSF leading to aliasing in image
-
解决方法
-
Optimize weights of untrained deep CNN G ( C ; p ) G(C;p) G(C;p) to solve inverse problem
✅ G G G: untrained CNN,
✅ C C C: fixed noise input,
✅ p p p: CNN parameters
-
Optimization objective:
p ^ = arg min p ∣ ∣ z − M ⊙ F ( G ( C ; p ) ) ∣ ∣ 2 + λ L ∣ ∣ G ( C ; p ) ∣ ∣ 1 \hat{p} = \argmin_p ||z - M\odot F(G(C;p))||_2 + \lambda_L||G(C;p)||_1 p^=argminp∣∣z−M⊙F(G(C;p))∣∣2+λL∣∣G(C;p)∣∣1
λ L \lambda_L λL: sparsity regularization strength
-
Key observation:
INR provides inductive bias towards natural solutions for imaging inverse problems
-
-
优点 :
-
CNN architecture has high impedance to noise
-
Learned solution balances fitting salient features and suppressing artifacts
-
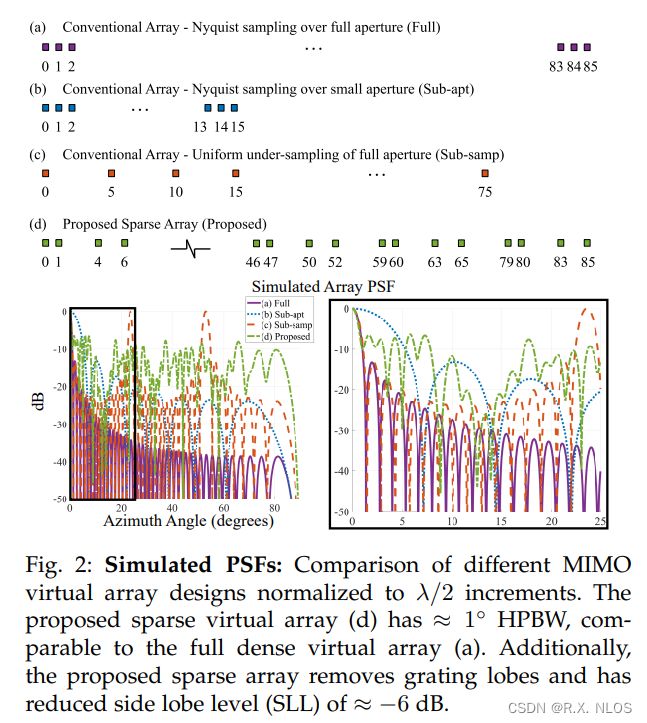
4.1 Sparse Aperture Design
- 目标
- Design a sparse MIMO virtual array that improves imaging accuracy when used with ComDecoder
- 设计准测 (metrics)
- PSF main lobe half-power beamwidth (HPBW)
- Peak sidelobe level (SLL)
- Presence of grating lobes
- 硬件约束
- Max aperture 86λ/2
- Limited to 4 TX and 4 RX due to commercial single radar chip
- 设计方法
- Select 4-element minimum redundancy array for RX to avoid grating lobes
- Grid search over TX positions to minimize SLL
- 比较对象(baselines)
- Full: Ideal full Nyquist sampled array
- Sub-apt: Largest Nyquist sampled MIMO array given constraints
- Sub-samp: Largest sub-Nyquist array given constraints
- 设计结果
- RX: [0, 1, 4, 6] λ/2
- TX: [0, 46, 59, 79] λ/2
- Gives 5.5x fewer antennas than conventional MIMO array
- 优点 :
- Avoids grating lobes
- Minimizes HPBW
- Minimizes SLL
- Satisfies hardware constraints
4.2 Neural Network Architecture
提出 ComDecoder:convolutional decoder architecture
-
ComDecoder :
- Maps latent variables C to image G(C;p)
- 优化:Parameters p optimized to reconstruct image
-
网络结构 :
- Series of upsampling and residual convolution blocks
- Use SiLU activation instead of ReLU
- No upsampling in last layer, uses 1x1 conv instead
-
超参数 :
- 6 layers (including last layer)
- 128 channels per layer
- Fixed input C sampled from uniform distribution
-
优化过程 :
- Update network weights p using backpropagation and Adam
- Takes <50 s per 256x256 image using 2000 iterations
-
优点 :
- SiLU increased expressivity over ReLU
- Upsampling reinforces multi-resolution nature
- Residual blocks enable information flow between layers
- Inductive biases improve performance on sparse radar imaging
5 COMPETING UNTRAINED METHODS
7个baselines: Compared CoIR against several untrained methods
-
1 Delay-and-Sum (DAS)
- Standard beamforming method
-
2 Sparse DAS
- DAS with under-sampled measurements
-
3 Gradient Descent with L1 Regularization (GD+L1 Reg)
- Directly optimizes reflectivity distribution with sparsity prior
-
4 Implicit Neural Representations:
-
4.1 INR-ReLU
✅ MLP-based, uses Fourier feature encoding
-
4.2 SIREN
✅ MLP-based, uses sinusoidal activation functions
-
-
5 Deep Image Prior (DIP)
- U-Net style convolutional autoencoder
-
6 DeepDecoder
- Decoder-only convolutional network
-
7 ConvDecoder
- Variant of DeepDecoder with some modifications
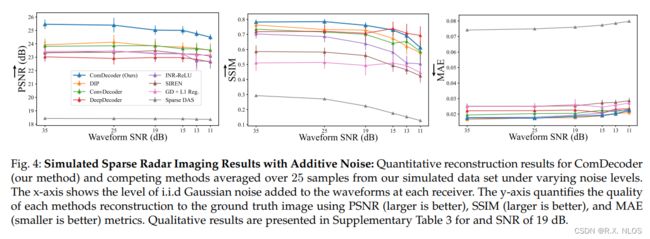
6 SIMULATION RESULTS
在仿真数据上评估所提出的CoIR
-
仿真数据生成:
- Synthesizes radar data cube from 2D reflectivity images
- Uses LiDAR point clouds to generate realistic reflectivity distributions
-
评估标准:
- PSNR, SSIM, MAE between reconstruction and ground truth image
-
实验:
-
1 Vary SNR from 35dB to 11dB
✅ ComDecoder gave superior PSNR over all methods at all SNRs
✅ ComDecoder and DIP gave comparable SSIM
-
2 Visualize reconstructions at 19dB SNR
✅ ComDecoder gave most accurate recovery of extended reflectors
✅ Other CNN methods also improved over Sparse DAS
✅ SIREN struggled to distinguish clutter and true reflectors

-
3 Additional analyses:
✅ Compared different CNN decoder architectures
✅ Evaluated computational complexity (in supplementary)
-
-
总结:
- ComDecoder 在 simulated data 上 SOTA
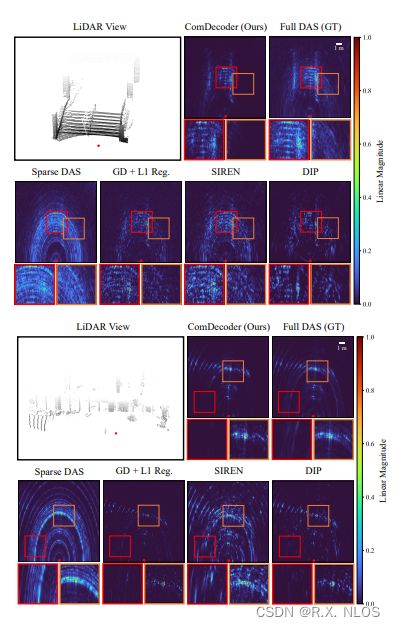
7 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
在真实采集的Coloradar dataset上评估所有方法
-
Radar system:
-
77 GHz FMCW with 1.282 GHz bandwidth
-
86λ/2 uniform linear array
-
-
Metrics :
- 与 full array DAS reconstruction 进行对比
-
Experiments :
-
1 不同场景下的重建效果
✅ ComDecoder accurately recovered dominant features
✅ DIP also performed well but more artifacts than ComDecoder
-
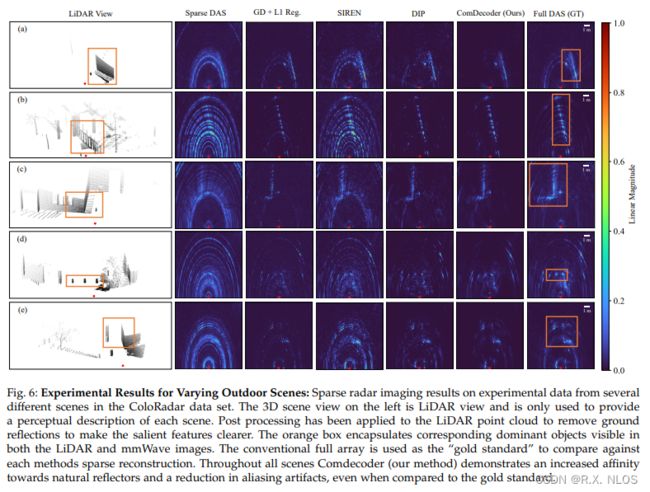
2 Evaluate 鲁棒性 across multiple outdoor scenes
✅ ComDecoder gave high fidelity reconstructions closest to DAS
✅ SIREN fit strong reflectors but also artifacts
✅ GD+L1 located dominant reflectors but artifacts remained
✅ DIP performed well but more artifacts than ComDecoder
-
- 总结:
- ComDecoder 在 real data 上 SOTA
- 显著好于其他untrained methods
8 DISCUSSION & LIMITATIONS
Limitations
- 1 Assume static scene in forward model
- Cannot handle moving objects
- 2 Single bounce scattering model may not match real-world
- 3 Slow optimization time (tens of seconds)
- Explore different initialization strategies
Future work
- 1 Demonstrated 2D range-angle slices due to linear array
- 2D array needed for full 3D, but increases complexity
- 2 CoIR could benefit other array-based imaging modalities:
- SAR, ultrasound, etc.
9 CONCLUSION
Proposed CoIR
-
1 Designed sparse linear array with 5.5x fewer antennas
-
2 Proposed convolutional decoder architecture ComDecoder
-
3 Demonstrated superior performance on simulated and real mmWave radar data