SQL力扣练习(十一)
目录
1.树节点(608)
示例 1
解法一(case when)
解法二(not in)
2.判断三角形(610)
示例 1
解法一(case when)
解法二(if)
解法三(嵌套if)
3.只出现一次的最大数字(619)
示例 1
解法一(count limit)
解法二(max)
4.有趣的电影(620)
解法一
5.换座位(626)
示例 1
解法一(case when)
解法二(count mod case-when)
解法三(union)
解法四(Lag/Lead)
6.变更性别(627)
示例 1
解法一(case when)
解法二(if)
7.买下所以产品的客户(1045)
示例 1
解法一(count)
解法二(嵌套select)
1.树节点(608)
表:Tree
+-------------+------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+------+ | id | int | | p_id | int | +-------------+------+ id 是该表中具有唯一值的列。 该表的每行包含树中节点的 id 及其父节点的 id 信息。 给定的结构总是一个有效的树。
树中的每个节点可以是以下三种类型之一:
- "Leaf":节点是叶子节点。
- "Root":节点是树的根节点。
- "lnner":节点既不是叶子节点也不是根节点。
编写一个解决方案来报告树中每个节点的类型。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
结果格式如下所示。
示例 1
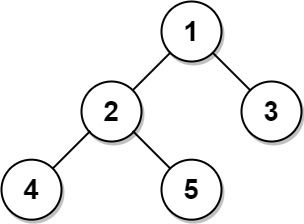
输入: Tree table: +----+------+ | id | p_id | +----+------+ | 1 | null | | 2 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | | 5 | 2 | +----+------+ 输出: +----+-------+ | id | type | +----+-------+ | 1 | Root | | 2 | Inner | | 3 | Leaf | | 4 | Leaf | | 5 | Leaf | +----+-------+ 解释: 节点 1 是根节点,因为它的父节点为空,并且它有子节点 2 和 3。 节点 2 是一个内部节点,因为它有父节点 1 和子节点 4 和 5。 节点 3、4 和 5 是叶子节点,因为它们有父节点而没有子节点。
解法一(case when)
首先根节点很好判断,先用一个flag 区分出根和非根,然后用p_id是否含有id,根据这个标准判断是否叶节点.
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select id,case
when flag=0 then 'Root'
when p_id is not null then 'Inner'
else 'Leaf'
end as type
from (select id,if((p_id is null),0,1) flag from tree ) a
left join
(select p_id from tree where p_id is not null group by p_id) b
on a.id=b.p_id解法二(not in)
用case when,先判断是否根节点,然后根据一个内查询再区分是否叶节点,这个方法虽然简单点,但not in 较为损耗性能,总体速度与解法一差不多.
SELECT
id,
(
CASE
WHEN p_id IS NULL THEN 'Root'
WHEN id NOT IN(
SELECT
p_id
FROM tree
WHERE p_id IS NOT NULL
) THEN 'Leaf'
ELSE 'Inner'
END
)as type
FROM tree2.判断三角形(610)
表: Triangle
+-------------+------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+------+ | x | int | | y | int | | z | int | +-------------+------+ 在 SQL 中,(x, y, z)是该表的主键列。 该表的每一行包含三个线段的长度。
对每三个线段报告它们是否可以形成一个三角形。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
查询结果格式如下所示。
示例 1
输入: Triangle 表: +----+----+----+ | x | y | z | +----+----+----+ | 13 | 15 | 30 | | 10 | 20 | 15 | +----+----+----+ 输出: +----+----+----+----------+ | x | y | z | triangle | +----+----+----+----------+ | 13 | 15 | 30 | No | | 10 | 20 | 15 | Yes | +----+----+----+----------+
解法一(case when)
利用三角形两边之和大于第三边性质.
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select *,
case when (x+y)>z and (x+z)>y and (y+z)>x then 'Yes'
else 'No'
end as triangle
from triangle解法二(if)
Select *,IF(x+y>z and x+z>y and y+z>x, "Yes", "No") AS triangle
FROM triangle解法三(嵌套if)
这个是力扣上的友友写的,他的速度是最快的.
原理:x + y + z > 2 * max(x, y, z) [x + y + z > z + z, 三条件组合]
select x, y, z,
if(x + y + z > 2 * if(x > y and x > z, x, if(y > x and y > z, y, z)), 'Yes', 'No') triangle
from Triangle3.只出现一次的最大数字(619)
MyNumbers 表:
+-------------+------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+------+ | num | int | +-------------+------+ 该表可能包含重复项(换句话说,在SQL中,该表没有主键)。 这张表的每一行都含有一个整数。
单一数字 是在 MyNumbers 表中只出现一次的数字。
找出最大的 单一数字 。如果不存在 单一数字 ,则返回 null 。
查询结果如下例所示。
示例 1
输入: MyNumbers 表: +-----+ | num | +-----+ | 8 | | 8 | | 3 | | 3 | | 1 | | 4 | | 5 | | 6 | +-----+ 输出: +-----+ | num | +-----+ | 6 | +-----+ 解释:单一数字有 1、4、5 和 6 。 6 是最大的单一数字,返回 6 。
解法一(count limit)
首先根据count()选出只出现一次的数,然后排序加分页选出最大一个.
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select
case
when count(*)=1 then num
when num is null then null
end as 'num' from MyNumbers group by num order by num desc limit 1解法二(max)
因为本题出现了null.所以我们需要null的数据,下面是从网上找的一些总结,发现,原来一些聚合函数自带null.本方法较快
# Write your MySQL query statement below
# 表格为空,加入任何SUM/AVG/MAX/MIN函数,都可以得到null值的结果。
# 可以使用聚合函数进行空值null值的转换,具体的聚合函数包括SUM/AVG/MAX/MIN
# 可以使用select语句进行转换,但空值应直接写在select中而非from中
# limit语句无法出现新的null值
# where和having同样无法出现新的null值
# ifnull函数定位:用于判断第一个表达式是否为 NULL,如果为 NULL 则返回第二个参数的值,如果不为 NULL 则返回第一个参数的值。
# IFNULL(expression, alt_value)
SELECT
MAX(num) AS num
FROM
(SELECT
num
FROM
MyNumbers
GROUP BY num
HAVING COUNT(num) = 1) AS t
;4.有趣的电影(620)
某城市开了一家新的电影院,吸引了很多人过来看电影。该电影院特别注意用户体验,专门有个 LED显示板做电影推荐,上面公布着影评和相关电影描述。
作为该电影院的信息部主管,您需要编写一个 SQL查询,找出所有影片描述为非 boring (不无聊) 的并且 id 为奇数 的影片,结果请按等级 rating 排列。
例如,下表 cinema:
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+ | id | movie | description | rating | +---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+ | 1 | War | great 3D | 8.9 | | 2 | Science | fiction | 8.5 | | 3 | irish | boring | 6.2 | | 4 | Ice song | Fantacy | 8.6 | | 5 | House card| Interesting| 9.1 | +---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
对于上面的例子,则正确的输出是为:
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+ | id | movie | description | rating | +---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+ | 5 | House card| Interesting| 9.1 | | 1 | War | great 3D | 8.9 | +---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
解法一
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select * from cinema where description !='boring' and id%2=1 order by rating desc5.换座位(626)
表: Seat
+-------------+---------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+---------+ | id | int | | name | varchar | +-------------+---------+ id是该表的主键(唯一值)列。 该表的每一行都表示学生的姓名和 ID。 id 是一个连续的增量。
编写解决方案来交换每两个连续的学生的座位号。如果学生的数量是奇数,则最后一个学生的id不交换。
按 id 升序 返回结果表。
查询结果格式如下所示。
示例 1
输入: Seat 表: +----+---------+ | id | student | +----+---------+ | 1 | Abbot | | 2 | Doris | | 3 | Emerson | | 4 | Green | | 5 | Jeames | +----+---------+ 输出: +----+---------+ | id | student | +----+---------+ | 1 | Doris | | 2 | Abbot | | 3 | Green | | 4 | Emerson | | 5 | Jeames | +----+---------+ 解释: 请注意,如果学生人数为奇数,则不需要更换最后一名学生的座位。
解法一(case when)
用左连接将三个表连接起来,然后用case when判断是否空就行.这个是修改名字
select a.id,case when b.student is not null then b.student
when c.student is not null then c.student
else a.student
end as 'student' from seat a left join seat b on a.id=b.id-1 and a.id%2=1
left join seat c on a.id=c.id+1 and a.id%2=0解法二(count mod case-when)
用count区分总数是单还是双,然后用case判断id,这个是变相修改id
SELECT
(CASE
WHEN MOD(id, 2) != 0 AND counts != id THEN id + 1
WHEN MOD(id, 2) != 0 AND counts = id THEN id
ELSE id - 1
END) AS id,
student
FROM
seat,
(SELECT
COUNT(*) AS counts
FROM
seat) AS seat_counts
ORDER BY id ASC;解法三(union)
使用left join和union实现 先改奇数id学生的名字,再改偶数id学生的名字,全改过来后,
再union合并所有的id
select a.id as id,ifnull(b.student,a.student) as student from Seat as a
left join (
select * from Seat
where mod(id,2) = 0
) as b
on (a.id+1) = b.id
where mod(a.id,2) = 1
union
select c.id as id,d.student as student from Seat as c
left join (
select * from Seat
where mod(id,2) = 1
) as d
on (c.id-1) = d.id
where mod(c.id,2) = 0
order by id asc;
解法四(Lag/Lead)
Lag/Lead(col,n,DEFAULT) 用于统计窗口内当前行往前或者往后第n行值
- 第一个参数为列名,
- 第二个参数为往后/前第n行(可选,默认为1),
- 第三个参数为默认值(当往上第n行为NULL时候,取默认值,如不指定,则为NULL)
需要注意的是lag 取得是当前行之前的数据,lead 取的实当前行之后的数据
SELECT
id,
IF(id % 2 = 0, last, next) student
FROM (
SELECT
id,student,
lag(student,1,student) over(order by id) last,
lead(student,1,student) over(order by id) next
FROM seat
) t;6.变更性别(627)
Salary 表:
+-------------+----------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+----------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
| sex | ENUM |
| salary | int |
+-------------+----------+
id 是这个表的主键。
sex 这一列的值是 ENUM 类型,只能从 ('m', 'f') 中取。
本表包含公司雇员的信息。
请你编写一个 SQL 查询来交换所有的 'f' 和 'm' (即,将所有 'f' 变为 'm' ,反之亦然),仅使用 单个 update 语句 ,且不产生中间临时表。
注意,你必须仅使用一条 update 语句,且 不能 使用 select 语句。
查询结果如下例所示。
示例 1
输入: Salary 表: +----+------+-----+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+-----+--------+ | 1 | A | m | 2500 | | 2 | B | f | 1500 | | 3 | C | m | 5500 | | 4 | D | f | 500 | +----+------+-----+--------+ 输出: +----+------+-----+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+-----+--------+ | 1 | A | f | 2500 | | 2 | B | m | 1500 | | 3 | C | f | 5500 | | 4 | D | m | 500 | +----+------+-----+--------+ 解释: (1, A) 和 (3, C) 从 'm' 变为 'f' 。 (2, B) 和 (4, D) 从 'f' 变为 'm' 。
解法一(case when)
# Write your MySQL query statement below
update salary set sex=(
case when sex='m' then 'f'
else 'm'
end
)解法二(if)
# Write your MySQL query statement below
update salary set sex=(if(sex='m','f','m'))解法三(replace)
最快
# replace(‘总字符串’,要下场的字符,要上场的字符)
update salary set sex = replace("fm", sex, "")7.买下所以产品的客户(1045)
Customer 表:
+-------------+---------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+---------+ | customer_id | int | | product_key | int | +-------------+---------+ 该表可能包含重复的行。 customer_id 不为 NULL。 product_key 是 Product 表的外键(reference 列)。
Product 表:
+-------------+---------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+---------+ | product_key | int | +-------------+---------+ product_key 是这张表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。
编写解决方案,报告 Customer 表中购买了 Product 表中所有产品的客户的 id。
返回结果表 无顺序要求 。
返回结果格式如下所示。
示例 1
输入: Customer 表: +-------------+-------------+ | customer_id | product_key | +-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 5 | | 2 | 6 | | 3 | 5 | | 3 | 6 | | 1 | 6 | +-------------+-------------+ Product 表: +-------------+ | product_key | +-------------+ | 5 | | 6 | +-------------+ 输出: +-------------+ | customer_id | +-------------+ | 1 | | 3 | +-------------+ 解释: 购买了所有产品(5 和 6)的客户的 id 是 1 和 3 。
解法一(count)
根据数量判断
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select customer_id from customer group by customer_id
having count(distinct product_key)=(select count(*) from product)解法二(嵌套select)
SELECT customer_id, product_key
FROM Customer GROUP BY customer_id, product_key
这段用来去重,然后从这里再分组count,最后根据产品数量比较
# Write your MySQL query statement below
SELECT customer_id
FROM (SELECT customer_id, COUNT(*) AS 'number'
FROM (SELECT customer_id, product_key
FROM Customer GROUP BY customer_id, product_key) a
GROUP BY customer_id) b
WHERE number = (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT product_key) FROM Product);