java-读取配置文件自定义字段(yml、properties)
一、概述
在springboot项目配置文件中设置自定义字段,项目代码按需读取,想换重要参数时直接更改配置文件即可,这篇文章说一说配置文件自定义字段的方法。
二、实现方法
方法1 @Value
使用org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation包下的@Value注解读取yml文件里面的字段,代码如下:
yml文件
server:
port: 8080
#自定义参数字段
student:
name: Simon
age: 23
sex: male
height: 185
读取
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Value("${student.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${student.age}")
private String age;
@Value("${student.sex}")
private String sex;
@Value("${student.height}")
private String height;
@RequestMapping("/1")
public Object test(){
log.info("我叫"+name+",性别是:"+sex+",今年"+age+"岁,我还是个"+height+"cm大高个的帅小伙!");
return "我叫"+name+",性别是:"+sex+",今年"+age+"岁,我还是个"+height+"cm大高个的帅小伙!";
}
}
测试结果
方法2:Environment
与@value类似,注入Environment通过配置参数的前缀拿到任何配置文件里配置参数的值,优点是随时随地,便捷,但是配置参数数量多的时候,会造成代码冗余。
/**
* @ClassName TestController
* @Author
* @Date 2023/2/28 0028 16:52
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private Environment environmentConfig;
@PostMapping("/environment")
public String testEnvironment(){
String number = environmentConfig.getProperty("school.role.teacher.number");
String age = environmentConfig.getProperty("student.age");
System.out.println("number = " + number);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
return null;
}
}
方法3:@PropertySource()、@ConfigurationProperties()
组合使用@PropertySource()、@ConfigurationProperties()两个注解对springboot项目的properties配置文件的的读取。
properties文件
student.name=simon
student.age=23
student.sex=male
student.height= 185
student.self-assessment=handsome!!!注意:这里与方法一yml文件采取@Value的方式读取不同,读取properties文件需要建一个读取类(Studentconfig),将properties文件中想读取得字段都注入进去作为该类的属性,再将Student通过@Configuration注解将其当作Bean交给容器管理,需要用的时候将Student整个类注入,在调用get方法得到其属性(即配置文件中的自定义字段)
StudentConfig类
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")//读取配置文件
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="student")//读取节点
@Data
public class StudentConfig {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
private int height;
private String selfAssessment;
}细节注意
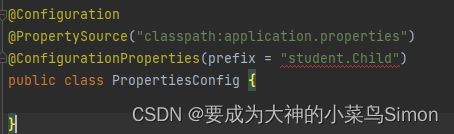
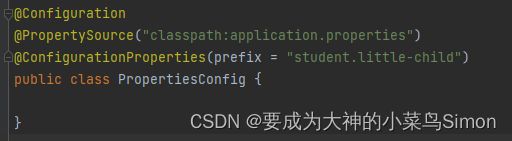
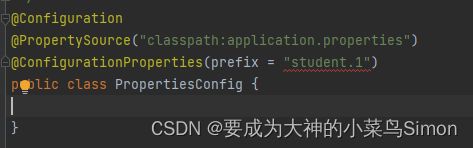
Configuration注解的prefix有书写规范,据我本人经验总结
不可用大写字母
不可写下划线,两个单词需隔开的话使用横线
不能使用数字(有博主说可以用数字我自己试了下是不可以的,希望大家避坑)
读取(将StudentConfig整个类注入,再使用get方法调用)
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private StudentConfig student;
@RequestMapping("/properties")
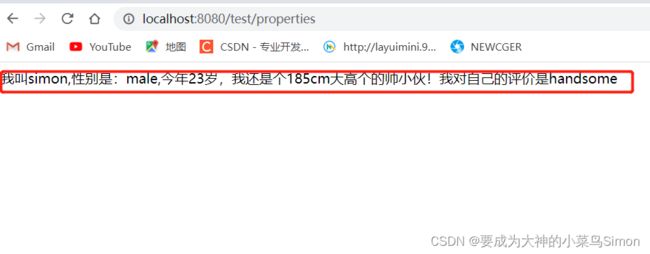
public Object test2(){
return "我叫"+student.getName()+"" +
",性别是:"+student.getSex()+
",今年"+student.getAge()+
"岁,我还是个"+student.getHeight()+"cm大高个的帅小伙!" +
"我对自己的评价是"+student.getSelfAssessment();
}得到结果
三、使用@value注解读取yml失效的场景及解决办法(下次更新)
四、嵌套读取properties文件的方法(读取类继承HashMap类)(下次更新)
在项目中有时候需要接入许多不同的企业,每个企业需要不同的配置参数,将不同的配置参数写到配置文件,通过企业传递来的值取得不同的配置参数。
这里以学校的老师和学生为例,在不同角色和不同科目下得到的参数信息
配置文件
#老师
##人数
school.role.teacher.number=50
##老师着装
school.role.teacher.wearing=suit
##职责
school.role.teacher.job=teach
##科目
###数学老师的stereotype
####性格
school.role.teacher.subject.math.character=serious
####性别
school.role.teacher.subject.math.sex=male
####年龄
school.role.teacher.subject.math.age=old
###英语老师的imagination
####性格
school.role.teacher.subject.english.character= optimistic
####性别
school.role.teacher.subject.english.sex=female
####年龄
school.role.teacher.subject.english.age=young
#学生
#数量
school.role.student.number=1000
#学生着装
school.role.student.wearing=uniform
#任务
school.role.student.job=study
##科目
###数学课上表现
school.role.student.subject.math.performance=cautious
###英语课上表现
school.role.student.subject.english.performance=happy
配置类
package com.example.test.config;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @ClassName TestConfig
* @Author
* @Date 2023/2/28 0028 15:26
*/
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school.role")
public class TestConfig extends HashMap {
}
角色层
package com.example.test.config;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @ClassName TestConfigItem
* @Author
* @Date 2023/2/28 0028 15:27
*/
@Data
public class TestConfigItem {
/**
* 数量
*/
private int number;
/**
* 穿着
*/
private String wearing;
/**
* 职责
*/
private String job;
/**
* 科目
*/
private InnerConfig subject;
}
package com.example.test.config;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @ClassName InnerConfig
* @Author
* @Date 2023/2/28 0028 15:48
*/
@Data
public class InnerConfig extends HashMap {
}
科目层
package com.example.test.config;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @ClassName InnerConfigItem
* @Author
* @Date 2023/2/28 0028 15:49
*/
@Data
public class InnerConfigItem {
/**
* 性格
*/
private String character;
/**
*性别
*/
private String sex;
/**
*年龄
*/
private String age;
/**
*学生表现
*/
private String performance;
}读取
package com.example.test.controller;
import com.example.test.config.InnerConfigItem;
import com.example.test.config.TestConfig;
import com.example.test.config.TestConfigItem;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* @ClassName TestController
* @Author
* @Date 2023/2/28 0028 16:52
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private TestConfig config;
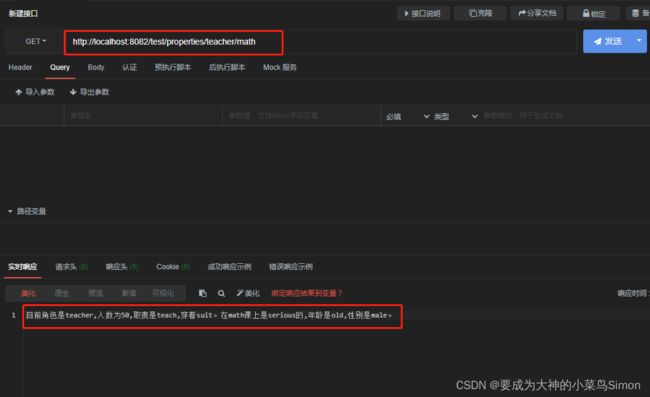
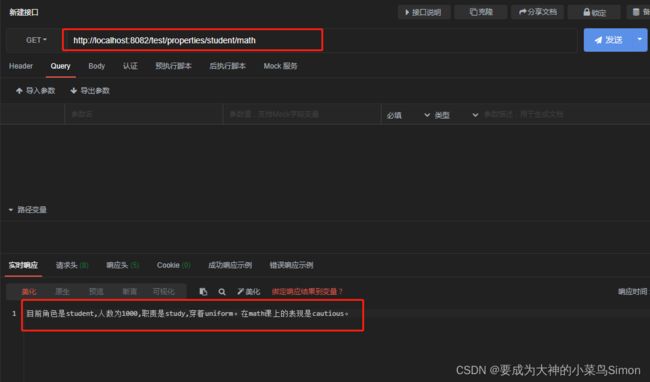
@GetMapping("/properties/{role}/{subject}")
public String testProperties(@PathVariable String role,@PathVariable String subject){
String result= null;
TestConfigItem testConfigItem = config.get(role);
int number = testConfigItem.getNumber();
String wearing = testConfigItem.getWearing();
String job = testConfigItem.getJob();
InnerConfigItem innerConfigItem = testConfigItem.getSubject().get(subject);
String age = innerConfigItem.getAge();
String character = innerConfigItem.getCharacter();
String sex = innerConfigItem.getSex();
if ("student".equals(role)){
String performance = innerConfigItem.getPerformance();
result = "目前角色是"+role+",人数为"+number+",职责是"+job+",穿着"+wearing+"。在"+subject+"课上的表现是"+performance+"。";
return result;
}
result = "目前角色是"+role+",人数为"+number+",职责是"+job+",穿着"+wearing+"。" +
"在"+subject+"课上是"+character+"的,年龄是"+age+",性别是"+sex+"。";
return result;
}
}