Spring事务和事务传播机制
1. Spring中事务的实现
- 编程式事务(手动写代码操作事务)
- 声明式事务(利用注解自动开启和提交事务)
2. 编程式事务
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import mybatis.model.User;
import mybatis.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//编程式事务(手动写代码操作事务)
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/trans")
public class TransactionalController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
//数据库事务管理器
@Autowired
private DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager;
//关于事务的一些配置,用默认的即可
@Autowired
private TransactionDefinition transactionDefinition;
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
public Integer addUser(String username,String password){
//~获取事务
TransactionStatus transaction = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);
User user = new User(username,password);
Integer result = userService.insert(user);
log.info("插入操作");
//回滚到当时事务的状态
// dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(transaction);
// log.info("回滚操作");
//事务的提交
dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(transaction);
log.info("事务提交");
return result;
}
}3. 声明式事务@Transactional
加上@Transactional即可自动处理事务
另外这个注解可以加到方法上也可以加到类上
- 修饰方法时: 需要注意只能应用到
public方法上,否则不生效。推荐此种用法。 - 修饰类时: 表明该注解对该类中所有的
public方法都生效
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import mybatis.model.User;
import mybatis.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/trans2")
public class TransactionalController2 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Transactional
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
public Integer addUser(String username,String password){
User user = new User(username,password);
Integer result = userService.insert(user);
log.info("影响行数:"+result);
// int a=10/0; //当发生了异常,事务会自动回滚
return result;
}
}3.1. 可能遇到的问题
①@Transactional默认只在遇到运行时异常(RuntimeException及其子类)和Error时才会回滚, 其他的(例如IOException)不回滚, 具体可以看异常的分类
②@Transactional在异常被捕获的情况下(try-catch),不会进行事务自动回滚
③在测试类里总是会回滚
3.2. @Transactional参数说明
3.2.1. 示例
①noRollbackFor
参数设置为@Transactional(noRollbackFor = ArithmeticException.class), 当出现了算术运算异常(ArithmeticException), 例如int a=10/0, 虽然会抛异常, 但并不会回滚
②rollbackFor
对于上面的问题@Transactional默认只在遇到运行时异常的时候才回滚, 所以为了所有异常都要回滚, 可以设置@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)让他所有异常都会回滚.
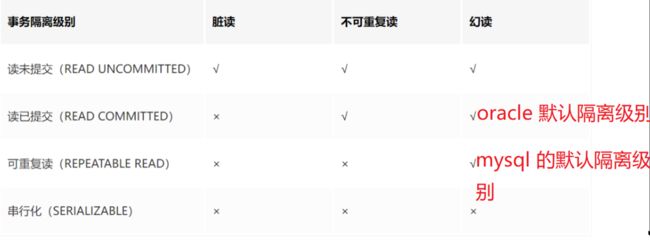
4. 事务的隔离级别
- 脏读: 一个事务读取到了另一个事务修改的数据之后,后一个事务又进行了回滚操作,从而导致第一个事务读取的数据是错误的。
- 不可重复读: 一个事务两次查询得到的结果不同,因为在两次查询中间,有另一个事务把数据修改了。
- 幻读: 一个事务两次查询中得到的结果集不同,因为在两次查询中另一个事务有新增了一部分数据。
4.1. Spring事务的隔离级别
在@Transactional注解里设置
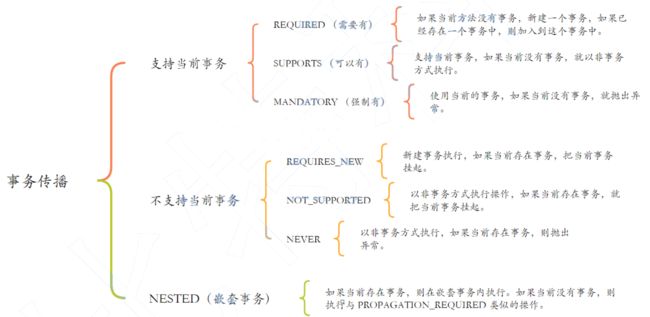
5. 事务的传播机制
5.1. Spring事务的传播机制
5.1.1. 示例
如果C事务执行失败,B事务执行成功, 那么B和A最终是否能够成功?
不同的事务传播机制, 结果是不同的
5.1.1.1. REQUIRED
Propagation.REQUIRED: 默认的事务传播级别,它表示如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务,如果
当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务。
对于上面的例子, B,C被加入到A事务, 如果C事务执行失败, 代表整个事务失败, 则会回滚
5.1.1.2. SUPPORTS
Propagation.SUPPORTS: 如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则以非事务的
方式继续运行。
如果A不是事务, B是事务, 那么B事务会取消
5.1.1.3. MANDATORY
Propagation.MANDATORY: (mandatory: 强制性) 如果当前存在事务, 则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务, 则抛出异常
5.1.1.4. REQUIRES_NEW
Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW: 表示创建一个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂
起。也就是说不管外部方法是否开启事务,Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW 修饰的内部方法会新开
启自己的事务,且开启的事务相互独立,互不干扰。
5.1.1.5. NOT_SUPPORTED
Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED: 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起
5.1.1.6. NEVER
Propagation.NEVER: 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
5.1.1.7. NESTED
Propagation.NESTED: 如果当前存在事务,则创建一个事务作为当前事务的嵌套事务来运行;如
果当前没有事务,则该取值等价于 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED。
6. 使用演示
数据库准备
drop table if exists userlog;
create table userlog(
id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(100) not null,
createtime datetime default now(),
updatetime datetime default now()
) default charset 'utf8mb4';6.1. 支持当前事务(required)
新建UserLog类方便传参数
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class UserLog {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Date createtime;
private Date updatetime;
public UserLog() {
}
public UserLog(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
}定义UserLogMapper接口
import mybatis.model.UserLog;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface UserLogMapper {
@Insert("insert into userlog (username) values (#{username})")
public Integer insertLog(UserLog userLog);
}实现UserLogService
import mybatis.mapper.UserLogMapper;
import mybatis.model.UserLog;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service
public class UserLogService {
@Autowired
private UserLogMapper userLogMapper;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public Integer insertLog(UserLog userLog){
return userLogMapper.insertLog(userLog);
}
}定义Controller, 记得给addUser方法加上@Transactional, 还有UserLogService和UserService都加上@Transactional, 这样就可以演示Propagation.REQUIRED: 默认的事务传播级别,它表示如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务,如果当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务. 当UserLogService和UserService和Controller都有@Transactional, 会默认把UserLogService和UserService事务合并到Controller的事务
import mybatis.model.User;
import mybatis.model.UserLog;
import mybatis.service.UserLogService;
import mybatis.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/trans3")
public class TransactionalController3 {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private UserLogService userLogService;
@Transactional
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
public boolean addUser(String username,String password){
//1.插入用户表
User user = new User(username,password);
userService.insert(user);
//2.插入日志表
UserLog userLog = new UserLog(username);
userLogService.insertLog(userLog);
return true;
}
}当我们主动让UserLogService和UserService其中一个出现异常, 那么网页会返回错误码500, 然后另外一个操作并不会成功, 而是会事务回滚
6.2. requires_new
当我们把UserLogService和UserService的@Transactional都设置为@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW). 即创建一个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起, 不用他的事务, 用自己新的事务.
让UserLogService出现异常, 此时, 网页错误码500, userInfo成功被插入数据, 但userLog没有被插入内容
6.3. never
给UserService设置一个@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NEVER), 会报错, 因为不该有事务却发现了一个事务, 结果是数据库并没有被插入数据
6.4. nested
UserLogService和UserService都改成@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NESTED). 两个都成功都成功, 其中一个失败, 都失败.
当我们将异常捕获, 并用下面的方法回滚, 那么没错的会插入到数据库, 出现异常的不会插入.
try {
int a=1/0;
}catch (Exception e){
TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();
}嵌套事务, 允许部分回滚. 而required只能全部回滚, 同样的情况, 两个都不能插入成功. (required表示如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务, 相当于把这个回滚也整体加入到了上层事务里, 导致全部回滚)