Android 9.0 Vold挂载流程解析(下)
Android 9.0 Vold挂载流程解析(上)
前言
上一篇介绍了Android 文件系统中Vold挂载机制的总体框架,我们分析了vod进程的main.cpp.接下来我们分析下存储卡挂载和卸载的流程。
存储卡挂载
在上篇文章文章提到,监听驱动层挂载和卸载最终会回调VolumeManager.cpp中的handleBlockEvent(NetlinkEvent *evt)方法。我们先看下面挂载的时序图,再来分析具体的挂载流程
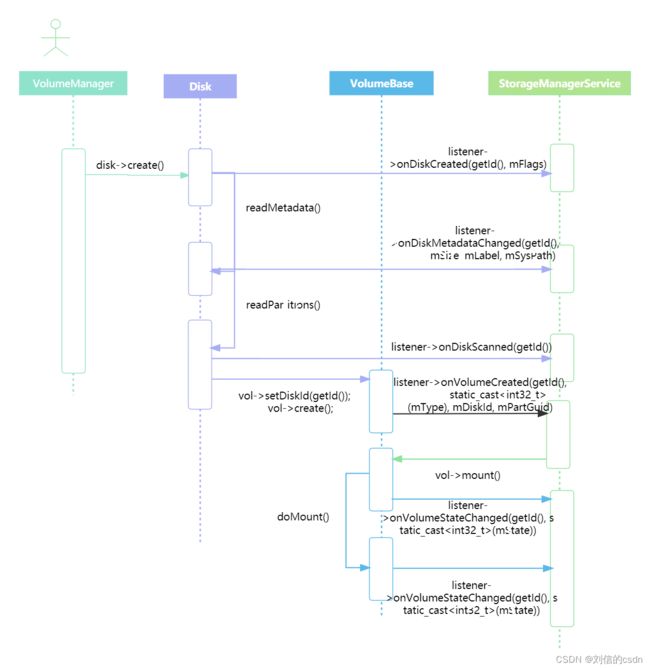
从时序图中我们得知挂载相关联的类有VolumeManager、Disk、VolumeBase、StorageManagerService。挂载步骤如下:
1.到VolumeManager中接收到驱动层中的挂载信息后,会创建Disk对象并且调用其Create方法。
2.Disk中的Create方法会先通过binder方式调用onDiskCreated(getId(), mFlags)通知framework层的StorageManagerService,告诉其创建了Disk;r然后调用其成员方法 readMetadata()获取存储卡大小和标签告知framework层的StorageManagerService;再调用其成员方法readPartitions()解析存储卡类型创建Volume对象,通知framework层的StorageManagerService解析完成。
3.VolumeBase是基类,有三种卷,一个是PublicVolume是上面第二步骤解析的存储卡类型为mbr,一种事PrivateVolume解析的是gpt类型,还有一种是内部存储卡EmulatedVolume;中三种都是继承自BaseVolume。我们以PublicVolume为例,创建完volume对象后会调用其create方法,然后通知通知framework层的StorageManagerService volume创建完成。
4.StorageManagerService收到创建volume完成的消息后,会通过binder的方式回调mount的方法,这里首先会回调Binder服务端VoldNativeService中的mount方法,然后再调用VolumeBase中的mount方法。
5.VolumeBase收到mount方法后先发送准备挂载kChecking信息给StorageManagerService、执行挂载方法doMount,挂载成功后发送kMounted消息给StorageManagerService。
接下来我们结合源码详细分析下流程
system\vold\VolumeManager.cpp
void VolumeManager::handleBlockEvent(NetlinkEvent *evt) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mLock);
if (mDebug) {
LOG(VERBOSE) << "----------------";
LOG(VERBOSE) << "handleBlockEvent with action " << (int) evt->getAction();
evt->dump();
}
std::string eventPath(evt->findParam("DEVPATH")?evt->findParam("DEVPATH"):"");
std::string devType(evt->findParam("DEVTYPE")?evt->findParam("DEVTYPE"):"");
if (devType != "disk") return;
int major = std::stoi(evt->findParam("MAJOR"));
int minor = std::stoi(evt->findParam("MINOR"));
dev_t device = makedev(major, minor);
switch (evt->getAction()) {
//挂载
case NetlinkEvent::Action::kAdd: {
//这个在上一篇文章中讲过,解析fstab文件创建了DiskSource
for (const auto& source : mDiskSources) {
//匹配eventPath,是不是挂载路径
if (source->matches(eventPath)) {
// For now, assume that MMC and virtio-blk (the latter is
// emulator-specific; see Disk.cpp for details) devices are SD,
// and that everything else is USB
int flags = source->getFlags();
//设置时SD卡还是Usb
if (major == kMajorBlockMmc
|| (android::vold::IsRunningInEmulator()
&& major >= (int) kMajorBlockExperimentalMin
&& major <= (int) kMajorBlockExperimentalMax)) {
flags |= android::vold::Disk::Flags::kSd;
} else {
flags |= android::vold::Disk::Flags::kUsb;
}
LOG(DEBUG) << "VolumeManager::handleBlockEvent="<<eventPath<<", nickname="<<source->getNickname()<<"dev_t"<<device;
//创建Disk类
auto disk = new android::vold::Disk(eventPath, device,
source->getNickname(), flags);
//调用handleDiskAdded方法
handleDiskAdded(std::shared_ptr<android::vold::Disk>(disk));
break;
}
}
break;
}
//Disk信息改变
case NetlinkEvent::Action::kChange: {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Disk at " << major << ":" << minor << " changed"<<"device"<<device;
handleDiskChanged(device);
break;
}
//移除
case NetlinkEvent::Action::kRemove: {
handleDiskRemoved(device);
break;
}
default: {
LOG(WARNING) << "Unexpected block event action " << (int) evt->getAction();
break;
}
}
}
这里主要看下怎么匹配的eventPah,我们看下打印
![]()
从日志中可以看到eventPath为:/devices/Mstar-ehci-2/usb1/1-1/1-1:1.0/host0/target0:0:0/0:0:0:0/block/sda
nick为usb deviceId为2048
与fstable中的 /devices/Mstar-ehci*是匹配的
接下来我们分析handleDiskAdded方法:
system\vold\VolumeManager.cpp
void VolumeManager::handleDiskAdded(const std::shared_ptr<android::vold::Disk>& disk) {
// For security reasons, if secure keyguard is showing, wait
// until the user unlocks the device to actually touch it
//如果锁屏,先存储进队列
if (mSecureKeyguardShowing) {
LOG(INFO) << "Found disk at " << disk->getEventPath()
<< " but delaying scan due to secure keyguard";
mPendingDisks.push_back(disk);
} else {
//调用Disk中的create方法
disk->create();
mDisks.push_back(disk);
}
}
上面代码很简单主要调用Disk中的Create方法,接下来看Disk中的构造方法和create方法。
system\vold\Disk.cpp
Disk::Disk(const std::string& eventPath, dev_t device,
const std::string& nickname, int flags) :
mDevice(device), mSize(-1), mNickname(nickname), mFlags(flags), mCreated(
false), mJustPartitioned(false) {
//解析主次设备号,我这是8,0
mId = StringPrintf("disk:%u,%u", major(device), minor(device));
mEventPath = eventPath;
mSysPath = StringPrintf("/sys/%s", eventPath.c_str());
mDevPath = StringPrintf("/dev/block/vold/%s", mId.c_str());
//创建DevPath节点,如/dev/block/vold/disk:8,0
CreateDeviceNode(mDevPath, mDevice);
}
再看create方法:
system\vold\Disk.cpp
status_t Disk::create() {
CHECK(!mCreated);
mCreated = true;
//回调到Framework层创建DiskInfo
auto listener = VolumeManager::Instance()->getListener();
if (listener) listener->onDiskCreated(getId(), mFlags);
readMetadata();
readPartitions();
return OK;
}
先看Framewok层服务中收到消息的处理
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\StorageManagerService.java
@Override
public void onDiskCreated(String diskId, int flags) {
synchronized (mLock) {
final String value = SystemProperties.get(StorageManager.PROP_ADOPTABLE);
switch (value) {
case "force_on":
flags |= DiskInfo.FLAG_ADOPTABLE;
break;
case "force_off":
flags &= ~DiskInfo.FLAG_ADOPTABLE;
break;
}
//创建一个DiskInfo,加入到map里
mDisks.put(diskId, new DiskInfo(diskId, flags));
}
}
再分析readMetadata()方法
system\vold\Disk.cpp
status_t Disk::readMetadata() {
mSize = -1;
mLabel.clear();
//打开/dev/block/vold/disk:8,0节点获取存储卡大小
int fd = open(mDevPath.c_str(), O_RDONLY | O_CLOEXEC);
if (fd != -1) {
if (ioctl(fd, BLKGETSIZE64, &mSize)) {
mSize = -1;
}
close(fd);
}
unsigned int majorId = major(mDevice);
switch (majorId) {
case kMajorBlockLoop: {
mLabel = "Virtual";
break;
}
case kMajorBlockScsiA: case kMajorBlockScsiB: case kMajorBlockScsiC: case kMajorBlockScsiD:
case kMajorBlockScsiE: case kMajorBlockScsiF: case kMajorBlockScsiG: case kMajorBlockScsiH:
case kMajorBlockScsiI: case kMajorBlockScsiJ: case kMajorBlockScsiK: case kMajorBlockScsiL:
case kMajorBlockScsiM: case kMajorBlockScsiN: case kMajorBlockScsiO: case kMajorBlockScsiP: {
//读文件获取存储卡标签
std::string path(mSysPath + "/device/vendor");
std::string tmp;
if (!ReadFileToString(path, &tmp)) {
PLOG(WARNING) << "Failed to read vendor from " << path;
return -errno;
}
tmp = android::base::Trim(tmp);
mLabel = tmp;
break;
}
case kMajorBlockMmc: {
std::string path(mSysPath + "/device/manfid");
std::string tmp;
if (!ReadFileToString(path, &tmp)) {
PLOG(WARNING) << "Failed to read manufacturer from " << path;
return -errno;
}
tmp = android::base::Trim(tmp);
int64_t manfid;
if (!android::base::ParseInt(tmp, &manfid)) {
PLOG(WARNING) << "Failed to parse manufacturer " << tmp;
return -EINVAL;
}
// Our goal here is to give the user a meaningful label, ideally
// matching whatever is silk-screened on the card. To reduce
// user confusion, this list doesn't contain white-label manfid.
switch (manfid) {
case 0x000003: mLabel = "SanDisk"; break;
case 0x00001b: mLabel = "Samsung"; break;
case 0x000028: mLabel = "Lexar"; break;
case 0x000074: mLabel = "Transcend"; break;
}
break;
}
default: {
if (isVirtioBlkDevice(majorId)) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Recognized experimental block major ID " << majorId
<< " as virtio-blk (emulator's virtual SD card device)";
mLabel = "Virtual";
break;
}
LOG(WARNING) << "Unsupported block major type " << majorId;
return -ENOTSUP;
}
}
//把获取的信息回调到Framework层存储起来
auto listener = VolumeManager::Instance()->getListener();
if (listener) listener->onDiskMetadataChanged(getId(),
mSize, mLabel, mSysPath);
return OK;
}
上面方法解析获取了存储卡大小和标签并且回调到Framework层,我们接着看Framework收到消息后的处理
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\StorageManagerService.java
@Override
public void onDiskMetadataChanged(String diskId, long sizeBytes, String label,
String sysPath) {
synchronized (mLock) {
//直接保存对应的信息,简单
final DiskInfo disk = mDisks.get(diskId);
if (disk != null) {
disk.size = sizeBytes;
disk.label = label;
disk.sysPath = sysPath;
}
}
}
接着分析readPartitions方法干了什么
system\vold\Disk.cpp
status_t Disk::readPartitions() {
int maxMinors = getMaxMinors();
if (maxMinors < 0) {
return -ENOTSUP;
}
//销毁之前所有的卷Volume
destroyAllVolumes();
// Parse partition table
//执行sgdisk命令获取存储卡类型,卷的信息,如/system/bin/sgdisk --android-dump /dev/block/vold/disk:8,0
std::vector<std::string> cmd;
cmd.push_back(kSgdiskPath);
cmd.push_back("--android-dump");
cmd.push_back(mDevPath);
std::vector<std::string> output;
status_t res = ForkExecvp(cmd, output);
if (res != OK) {
LOG(WARNING) << "sgdisk failed to scan " << mDevPath;
auto listener = VolumeManager::Instance()->getListener();
if (listener) listener->onDiskScanned(getId());
mJustPartitioned = false;
return res;
}
Table table = Table::kUnknown;
bool foundParts = false;
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
bool filesystemInEntireDisk = false;
filesystemInEntireDisk = IsFilesystemInEntireDisk(mDevPath);
// Mediatek Android Patch End
//一行一行的解析,行内以空格区分如以下信息
/**
* DISK mbr
* PART 1 c
*/
for (const auto& line : output) {
auto split = android::base::Split(line, kSgdiskToken);
auto it = split.begin();
if (it == split.end()) continue;
if (*it == "DISK") {
if (++it == split.end()) continue;
if (*it == "mbr") {
table = Table::kMbr;
} else if (*it == "gpt") {
table = Table::kGpt;
} else {
LOG(WARNING) << "Invalid partition table " << *it;
continue;
}
} else if (*it == "PART") {
foundParts = true;
if (++it == split.end()) continue;
int i = 0;
if (!android::base::ParseInt(*it, &i, 1, maxMinors)) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Invalid partition number " << *it;
continue;
}
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
int majorNum = major(mDevice);
int minorNum = minor(mDevice) + i;//Disk的minor加i,如这里i=1
if (i >= kPartitionMax) {
majorNum = kMajorBlockExtended;
minorNum = minorNum % kPartitionMax + 1;
}
//创建卷的设备号如majorNum =8,minorNum=1
dev_t partDevice = makedev(majorNum, minorNum);
// Mediatek Android Patch End
if (table == Table::kMbr) {
if (++it == split.end()) continue;
int type = 0;
if (!android::base::ParseInt("0x" + *it, &type)) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Invalid partition type " << *it;
continue;
}
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
//如type=0x0c
if (type) {
//创建卷PublicVolume
createPublicVolume(partDevice);
}
// Mediatek Android Patch End
} else if (table == Table::kGpt) {
if (++it == split.end()) continue;
auto typeGuid = *it;
if (++it == split.end()) continue;
auto partGuid = *it;
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
if (android::base::EqualsIgnoreCase(typeGuid, kGptAndroidExpand)) {
//创建卷PrivateVolume
createPrivateVolume(partDevice, partGuid);
} else if (android::base::EqualsIgnoreCase(typeGuid, kGptAndroidMeta)) {
//Ignore kGptAndroidMeta partition
} else {
//创建卷PublicVolume
createPublicVolume(partDevice);
}
// Mediatek Android Patch End
}
}
}
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
LOG(INFO) << mId << " In case of invalid partition table, trying entire device, foundParts=" << foundParts << ", filesystemInEntireDisk=" << filesystemInEntireDisk;
// Ugly last ditch effort, treat entire disk as partition
if (table == Table::kUnknown || !foundParts || filesystemInEntireDisk) {
LOG(WARNING) << mId << " has unknown partition table; trying entire device";
std::string fsType;
std::string unused;
if (ReadMetadataUntrusted(mDevPath, &fsType, &unused, &unused) == OK) {
createPublicVolume(mDevice);
} else {
LOG(WARNING) << mId << " failed to identify, giving up";
}
}
// Mediatek Android Patch End
//回调framework卷信息扫描完成
auto listener = VolumeManager::Instance()->getListener();
if (listener) listener->onDiskScanned(getId());
mJustPartitioned = false;
return OK;
}
我们从上面代码分析得知会创建调用createPublicVolume方法或者 createPublicVolume方法,然后回调Framework层告知卷信息扫描完成,我们以createPublicVolume为例分析
system\vold\Disk.cpp
void Disk::createPublicVolume(dev_t device) {
//创建PublicVolume对象
auto vol = std::shared_ptr<VolumeBase>(new PublicVolume(device));
//正在格式化
if (mJustPartitioned) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Device just partitioned; silently formatting";
vol->setSilent(true);
vol->create();
vol->format("auto");
vol->destroy();
vol->setSilent(false);
}
//加入队列,设置diskId。调用vol的create方法
mVolumes.push_back(vol);
vol->setDiskId(getId());
vol->create();
}
接着看Framework收到卷扫描完成会做什么
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\StorageManagerService.java
@Override
public void onDiskScanned(String diskId) {
synchronized (mLock) {
final DiskInfo disk = mDisks.get(diskId);
if (disk != null) {
onDiskScannedLocked(disk);
}
}
}
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private void onDiskScannedLocked(DiskInfo disk) {
int volumeCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < mVolumes.size(); i++) {
final VolumeInfo vol = mVolumes.valueAt(i);
if (Objects.equals(disk.id, vol.getDiskId())) {
volumeCount++;
}
}
//主要发送"android.os.storage.action.DISK_SCANNED"广播;好像没啥卵用
//目前没发现有对这广播有处理啥
final Intent intent = new Intent(DiskInfo.ACTION_DISK_SCANNED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_INCLUDE_BACKGROUND);
intent.putExtra(DiskInfo.EXTRA_DISK_ID, disk.id);
intent.putExtra(DiskInfo.EXTRA_VOLUME_COUNT, volumeCount);
mHandler.obtainMessage(H_INTERNAL_BROADCAST, intent).sendToTarget();
final CountDownLatch latch = mDiskScanLatches.remove(disk.id);
if (latch != null) {
latch.countDown();
}
disk.volumeCount = volumeCount;
//这个Callbacks可以在StorageManager类注册回调
mCallbacks.notifyDiskScanned(disk, volumeCount);
}
我们接着回到PublicVolume.cpp中分析其构造方法和create方法
system\vold\PublicVolume.cpp
PublicVolume::PublicVolume(dev_t device) :
VolumeBase(Type::kPublic), mDevice(device), mFusePid(0) {
//设置Id,如:public:8,1
setId(StringPrintf("public:%u,%u", major(device), minor(device)));
//设置devPath 如:/dev/block/vold/public:8,1
mDevPath = StringPrintf("/dev/block/vold/%s", getId().c_str());
}
我们在看PublicVolume的create函数,create函数在其父类BaseVolume中实现
system\vold\BaseVolume.cpp
status_t VolumeBase::create() {
CHECK(!mCreated);
mCreated = true;
//子类实现
status_t res = doCreate();
auto listener = getListener();
//回到Framework层 卷创建成功
if (listener) listener->onVolumeCreated(getId(),
static_cast<int32_t>(mType), mDiskId, mPartGuid);
//设置状态未挂载回调到framework层
setState(State::kUnmounted);
return res;
}
再看子类doCreate实现了什么
system\vold\PublicVolume.cpp
status_t PublicVolume::doCreate() {
//只是创建了device节点,如刚刚的/dev/block/vold/public:8,1
return CreateDeviceNode(mDevPath, mDevice);
}
接着分析Framework层收到卷创建成功做了什么
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\StorageManagerService.java
@Override
public void onVolumeCreated(String volId, int type, String diskId, String partGuid) {
synchronized (mLock) {
final DiskInfo disk = mDisks.get(diskId);
//同样是创建卷加入到map中
final VolumeInfo vol = new VolumeInfo(volId, type, disk, partGuid);
mVolumes.put(volId, vol);
onVolumeCreatedLocked(vol);
}
}
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private void onVolumeCreatedLocked(VolumeInfo vol) {
if (mPms.isOnlyCoreApps()) {
Slog.d(TAG, "System booted in core-only mode; ignoring volume " + vol.getId());
return;
}
//如果是内部存储卡
if (vol.type == VolumeInfo.TYPE_EMULATED) {
final StorageManager storage = mContext.getSystemService(StorageManager.class);
//替换id private为emulated java层内部存储卡的id为private,vold中为emulated
final VolumeInfo privateVol = storage.findPrivateForEmulated(vol);
if (Objects.equals(StorageManager.UUID_PRIVATE_INTERNAL, mPrimaryStorageUuid)
&& VolumeInfo.ID_PRIVATE_INTERNAL.equals(privateVol.id)) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Found primary storage at " + vol);
vol.mountFlags |= VolumeInfo.MOUNT_FLAG_PRIMARY;
vol.mountFlags |= VolumeInfo.MOUNT_FLAG_VISIBLE;
//发送挂载信息
mHandler.obtainMessage(H_VOLUME_MOUNT, vol).sendToTarget();
} else if (Objects.equals(privateVol.fsUuid, mPrimaryStorageUuid)) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Found primary storage at " + vol);
vol.mountFlags |= VolumeInfo.MOUNT_FLAG_PRIMARY;
vol.mountFlags |= VolumeInfo.MOUNT_FLAG_VISIBLE;
//发送挂载信息
mHandler.obtainMessage(H_VOLUME_MOUNT, vol).sendToTarget();
}
//为public的即vold中的PublicVolume
} else if (vol.type == VolumeInfo.TYPE_PUBLIC) {
// TODO: only look at first public partition
//这里为false
if (Objects.equals(StorageManager.UUID_PRIMARY_PHYSICAL, mPrimaryStorageUuid)
&& vol.disk.isDefaultPrimary()) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Found primary storage at " + vol);
//MOUNT_FLAG_PRIMARY,是否为内部主存储卡
vol.mountFlags |= VolumeInfo.MOUNT_FLAG_PRIMARY;
vol.mountFlags |= VolumeInfo.MOUNT_FLAG_VISIBLE;
}
// Adoptable public disks are visible to apps, since they meet
// public API requirement of being in a stable location.
if (vol.disk.isAdoptable()) {
//是否对app可见
vol.mountFlags |= VolumeInfo.MOUNT_FLAG_VISIBLE;
}
//挂载用户Id 一般为0
vol.mountUserId = mCurrentUserId;
mHandler.obtainMessage(H_VOLUME_MOUNT, vol).sendToTarget();
//为private的即vold中的PrivateVolume
} else if (vol.type == VolumeInfo.TYPE_PRIVATE) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(H_VOLUME_MOUNT, vol).sendToTarget();
} else {
Slog.d(TAG, "Skipping automatic mounting of " + vol);
}
}
以上代码主要创建java层的VolumeInfo根据存储卡类型设置标志位,然后通过handle发送H_VOLUME_MOUNT消息,我们看下H_VOLUME_MOUNT消息中的处理
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\StorageManagerService.java
case H_VOLUME_MOUNT: {
final VolumeInfo vol = (VolumeInfo) msg.obj;
//UserManager中策略限制是否忽略掉这个卷
if (isMountDisallowed(vol)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Ignoring mount " + vol.getId() + " due to policy");
break;
}
try {
//调用Vold进程的mount方法挂载
mVold.mount(vol.id, vol.mountFlags, vol.mountUserId);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, e);
}
break;
}
通过以上代码分析调用了mVold.mount函数,回到vold进程binder服务端中的进行代码分析:
\system\vold\VoldNativeService.cpp
binder::Status VoldNativeService::mount(const std::string& volId, int32_t mountFlags,
int32_t mountUserId) {
ENFORCE_UID(AID_SYSTEM);
CHECK_ARGUMENT_ID(volId);
ACQUIRE_LOCK;
//获取卷Volume对象,如PublicVolume对象
auto vol = VolumeManager::Instance()->findVolume(volId);
if (vol == nullptr) {
return error("Failed to find volume " + volId);
}
//设置卷的标志和用户Id
vol->setMountFlags(mountFlags);
vol->setMountUserId(mountUserId);
//调用volume的mount方法进行挂载
int res = vol->mount();
//如果挂载的内部存储卡
if ((mountFlags & MOUNT_FLAG_PRIMARY) != 0) {
//设置一下标志
VolumeManager::Instance()->setPrimary(vol);
}
return translate(res);
}
接下来分析volume中的mount方法,mount方法在基类VolumeBase中实现
system\vold\VolumeBase.cpp
status_t VolumeBase::mount() {
if ((mState != State::kUnmounted) && (mState != State::kUnmountable)) {
LOG(WARNING) << getId() << " mount requires state unmounted or unmountable";
return -EBUSY;
}
//设置状态为checking,通知framework层
setState(State::kChecking);
//子类实现
status_t res = doMount();
if (res == OK) {
//挂载成功
setState(State::kMounted);
} else {
//挂载失败
setState(State::kUnmountable);
}
return res;
}
void VolumeBase::setState(State state) {
mState = state;
//通知framework层状态
auto listener = getListener();
if (listener) listener->onVolumeStateChanged(getId(), static_cast<int32_t>(mState));
}
我们先分析下framwork收到存储卡状态信息,做了什么,这个状态调用很多地方都有,接下来的卸载流程也有,这里分析了在卸载流程中我们就不分析了。
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\StorageManagerService.java
@Override
public void onVolumeStateChanged(String volId, int state) {
synchronized (mLock) {
final VolumeInfo vol = mVolumes.get(volId);
if (vol != null) {
final int oldState = vol.state;
final int newState = state;
//设置新状态
vol.state = newState;
onVolumeStateChangedLocked(vol, oldState, newState);
}
}
}
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private void onVolumeStateChangedLocked(VolumeInfo vol, int oldState, int newState) {
// Remember that we saw this volume so we're ready to accept user
// metadata, or so we can annoy them when a private volume is ejected
if (vol.isMountedReadable() && !TextUtils.isEmpty(vol.fsUuid)) {
VolumeRecord rec = mRecords.get(vol.fsUuid);
if (rec == null) {
rec = new VolumeRecord(vol.type, vol.fsUuid);
rec.partGuid = vol.partGuid;
rec.createdMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (vol.type == VolumeInfo.TYPE_PRIVATE) {
rec.nickname = vol.disk.getDescription();
}
mRecords.put(rec.fsUuid, rec);
writeSettingsLocked();
} else {
// Handle upgrade case where we didn't store partition GUID
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(rec.partGuid)) {
rec.partGuid = vol.partGuid;
writeSettingsLocked();
}
}
}
//callback通知
mCallbacks.notifyVolumeStateChanged(vol, oldState, newState);
// Do not broadcast before boot has completed to avoid launching the
// processes that receive the intent unnecessarily.
//开机后先发送 "android.os.storage.action.VOLUME_STATE_CHANGED"广播
if (mBootCompleted && isBroadcastWorthy(vol)) {
final Intent intent = new Intent(VolumeInfo.ACTION_VOLUME_STATE_CHANGED);
intent.putExtra(VolumeInfo.EXTRA_VOLUME_ID, vol.id);
intent.putExtra(VolumeInfo.EXTRA_VOLUME_STATE, newState);
intent.putExtra(VolumeRecord.EXTRA_FS_UUID, vol.fsUuid);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_INCLUDE_BACKGROUND);
mHandler.obtainMessage(H_INTERNAL_BROADCAST, intent).sendToTarget();
}
final String oldStateEnv = VolumeInfo.getEnvironmentForState(oldState);
final String newStateEnv = VolumeInfo.getEnvironmentForState(newState);
//如果和上次的状态不一致
if (!Objects.equals(oldStateEnv, newStateEnv)) {
// Kick state changed event towards all started users. Any users
// started after this point will trigger additional
// user-specific broadcasts.
for (int userId : mSystemUnlockedUsers) {
//对用户app可见
if (vol.isVisibleForRead(userId)) {
final StorageVolume userVol = vol.buildStorageVolume(mContext, userId, false);
//发送挂载卸载等广播
mHandler.obtainMessage(H_VOLUME_BROADCAST, userVol).sendToTarget();
//回调里通知
mCallbacks.notifyStorageStateChanged(userVol.getPath(), oldStateEnv,
newStateEnv);
}
}
}
if (vol.type == VolumeInfo.TYPE_PUBLIC && vol.state == VolumeInfo.STATE_EJECTING) {
// TODO: this should eventually be handled by new ObbVolume state changes
/*
* Some OBBs might have been unmounted when this volume was
* unmounted, so send a message to the handler to let it know to
* remove those from the list of mounted OBBS.
*/
mObbActionHandler.sendMessage(mObbActionHandler.obtainMessage(
OBB_FLUSH_MOUNT_STATE, vol.path));
}
maybeLogMediaMount(vol, newState);
}
通过以上代码分析我们得知收到状态通知后会发送挂载卸载等广播,方便App中监听。回到Vold进程中我们看volume中doMount函数是怎么挂载的
system\vold\PublicVolume.cpp
status_t PublicVolume::doMount() {
//这个方法中获取了卷的信息 fsType和mFsUuid
readMetadataWithoutNotify();
//判断文件系统类型,如果支持该文件系统先check
if (mFsType == "vfat" && vfat::IsSupported()) {
if (vfat::Check(mDevPath)) {
LOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed filesystem check";
return -EIO;
}
} else if (mFsType == "exfat" && exfat::IsSupported()) {
if (exfat::Check(mDevPath)) {
LOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed filesystem check";
return -EIO;
}
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
}else if (mFsType == "ntfs" && ntfs::IsSupported()) {
if (ntfs::Check(mDevPath)) {
LOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed filesystem check";
return -EIO;
}
// Mediatek Android Patch End
}else {
//不支持的文件系统直接挂载失败
LOG(ERROR) << getId() << " unsupported filesystem " << mFsType;
return -EIO;
}
// Use UUID as stable name, if available
//mFsUuid在前面步骤中通过工具命令获取的
std::string stableName = getId();
if (!mFsUuid.empty()) {
stableName = mFsUuid;
}
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
LOG(INFO) << "stableName = " << stableName << ", mFsType = " << mFsType;
dev_t check = -1;
const std::string prefix("xyzabcdefg");
LOG(DEBUG) << "Node duplication check.";
for (int idx = 0; (idx < 8) && (check != 0); ++idx) {
std::string tempName = stableName;
if (idx > 0) {
tempName = prefix[idx - 1] + tempName;
}
std::string tempPath = StringPrintf("/mnt/media_rw/%s", tempName.c_str());
std::string tempDefaultPath = StringPrintf("/mnt/runtime/default/%s", tempName.c_str());
std::string tempReadPath = StringPrintf("/mnt/runtime/read/%s", tempName.c_str());
std::string tempWritePath = StringPrintf("/mnt/runtime/write/%s", tempName.c_str());
check = GetDevice(tempPath);
if(check != 0) {
if (!checkMountedBeUsed(tempPath)) {
/* for default fuse mount point still in case */
LOG(ERROR) << "ForceUnmount(" << tempDefaultPath << "): "<< ForceUnmount(tempDefaultPath);
LOG(ERROR) << "ForceUnmount(" << tempReadPath << "): "<< ForceUnmount(tempReadPath);
LOG(ERROR) << "ForceUnmount(" << tempWritePath << "): "<< ForceUnmount(tempWritePath);
if (rmdir(tempPath.c_str()) && errno != ENOENT) {
LOG(ERROR) << "rmdir(" << tempPath << "), errno: " << strerror(errno);
continue;
}
if (rmdir(tempDefaultPath.c_str()) && errno != ENOENT) {
LOG(ERROR) << "rmdir(" << tempDefaultPath << "), errno: " << strerror(errno);
continue;
}
if (rmdir(tempReadPath.c_str()) && errno != ENOENT) {
LOG(ERROR) << "rmdir(" << tempReadPath << "), errno: " << strerror(errno);
continue;
}
if (rmdir(tempWritePath.c_str()) && errno != ENOENT) {
LOG(ERROR) << "rmdir(" << tempWritePath << "), errno: " << strerror(errno);
continue;
}
stableName = tempName;
mFsUuid = tempName;
setId(tempName);
check = 0;
}
LOG(ERROR) << "rawpath : " << tempPath << " already exists.";
} else if (idx > 0) {
stableName = tempName;
mFsUuid = tempName;
setId(tempName);
LOG(ERROR) << "Change uuid to " << stableName;
}
}
metaDataNotificaiton();
// Mediatek Android Patch End
//源路径
mRawPath = StringPrintf("/mnt/media_rw/%s", stableName.c_str());
//fuse默认路径,目前Android 9.0采用了sdcardfs文件系统,sdcardfs文件系统是一个包装类文件系统
//它包装了vfat、ntfs等底层文件系统,加入了权限管理等机制
mFuseDefault = StringPrintf("/mnt/runtime/default/%s", stableName.c_str());
mFuseRead = StringPrintf("/mnt/runtime/read/%s", stableName.c_str());
mFuseWrite = StringPrintf("/mnt/runtime/write/%s", stableName.c_str());
//设置内部路径,同样会回调到Framework层设置VolumeInfo的internalPath字段
setInternalPath(mRawPath);
//对用户可见
if (getMountFlags() & MountFlags::kVisible) {
//设置路径,同样会回调到Framework层设置VolumeInfo的path字段
setPath(StringPrintf("/storage/%s", stableName.c_str()));
} else {
//设置路径,同样会回调到Framework层设置VolumeInfo的path字段
setPath(mRawPath);
}
//创建mRawPath挂载点
if (fs_prepare_dir(mRawPath.c_str(), 0700, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed to create mount points";
return -errno;
}
//根据底层文件系统进行相应的挂载操作
if (mFsType == "vfat") {
if (vfat::Mount(mDevPath, mRawPath, false, false, false, AID_MEDIA_RW, AID_MEDIA_RW, 0007,
true)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed to mount " << mDevPath;
return -EIO;
}
} else if (mFsType == "exfat") {
if (exfat::Mount(mDevPath, mRawPath, AID_MEDIA_RW, AID_MEDIA_RW, 0007)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed to mount " << mDevPath;
return -EIO;
}
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
}else if (mFsType == "ntfs") {
if (ntfs::Mount(mDevPath, mRawPath, false, false, false, AID_MEDIA_RW, AID_MEDIA_RW, 0007,
true)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed to mount " << mDevPath;
return -EIO;
}
// Mediatek Android Patch End
}
if (getMountFlags() & MountFlags::kPrimary) {
initAsecStage();
}
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
// We get the fs label of the Volume at here
//回调到framework层,设置相关信息
getVolumeLabel(mDevPath.c_str(), mRawPath.c_str(), mFsType.c_str(), mFsLabel);
auto listener = getListener();
if (listener) listener->onVolumeMetadataChanged(getId(), mFsType, mFsUuid, mFsLabel);
// Mediatek Android Patch End
if (!(getMountFlags() & MountFlags::kVisible)) {
// Not visible to apps, so no need to spin up FUSE
return OK;
}
if (fs_prepare_dir(mFuseDefault.c_str(), 0700, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT) ||
fs_prepare_dir(mFuseRead.c_str(), 0700, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT) ||
fs_prepare_dir(mFuseWrite.c_str(), 0700, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed to create FUSE mount points";
return -errno;
}
dev_t before = GetDevice(mFuseWrite);
//fork一个新进程,执行sdcard的挂载操作,excel是执行了system/bin/sdcard程序,相关代码在sdcard.cpp
if (!(mFusePid = fork())) {
//内部存储卡
if (getMountFlags() & MountFlags::kPrimary) {
if (execl(kFusePath, kFusePath,
"-u", "1023", // AID_MEDIA_RW
"-g", "1023", // AID_MEDIA_RW
"-U", std::to_string(getMountUserId()).c_str(),
"-w",//可写
mRawPath.c_str(),
stableName.c_str(),
NULL)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to exec";
}
} else {
//其他
if (execl(kFusePath, kFusePath,
"-u", "1023", // AID_MEDIA_RW
"-g", "1023", // AID_MEDIA_RW
"-U", std::to_string(getMountUserId()).c_str(),
"-w",//可写
mRawPath.c_str(),
stableName.c_str(),
NULL)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to exec";
}
}
LOG(ERROR) << "FUSE exiting";
_exit(1);
}
if (mFusePid == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << getId() << " failed to fork";
return -errno;
}
nsecs_t start = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_BOOTTIME);
while (before == GetDevice(mFuseWrite)) {
LOG(VERBOSE) << "Waiting for FUSE to spin up...";
usleep(50000); // 50ms
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_BOOTTIME);
if (nanoseconds_to_milliseconds(now - start) > 5000) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Timed out while waiting for FUSE to spin up";
//force unmount here, otherwise this usb would mount fail next time.
doUnmount();
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}
}
/* sdcardfs will have exited already. FUSE will still be running */
if (TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(waitpid(mFusePid, nullptr, WNOHANG)) == mFusePid)
mFusePid = 0;
return OK;
}
以上代码逻辑主要调用相应的底层文件系统进行check,mount,操作,然后执行sdcard进程程序命令进行sdcardfs的挂载。APP是和sdcardfs文件系统进行操作的。到这里挂载流程就分析完成了,我们接下来分析卸载的操作流程
存储卡卸载

从时序图中我们得知卸载相关联的类有VolumeManager、Disk、VolumeBase、StorageManagerService。卸载步骤如下:
1.到VolumeManager中接收到驱动层中的卸载信息后,会调用Disk对象的destory方法。
2.Disk中destory方法中调用其destroyAllVolumes()销毁其所有的卷。
3Disk中destory方法中通过binder机制回调onDiskDestroyed(getId())方法告知framework层。
4.destroyAllVolumes()中调用卷VolumeBase中的destory()方法销毁卷
5.VolumeBase中destory()方法中,判断如果挂载了继续卸载操作,通知卸载过程中的状态到framework层。
前面分析了挂载,卸载其实一样的,我们也是从收到卸载消息开始分析
/system/vold/VolumeManager.cpp
void VolumeManager::handleDiskRemoved(dev_t device) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "VolumeManager::handleDiskRemoved"<<"dev_t"<<device;
//获取到对应的Disk执行其destory方法,并且移除队列
auto i = mDisks.begin();
while (i != mDisks.end()) {
if ((*i)->getDevice() == device) {
(*i)->destroy();
i = mDisks.erase(i);
} else {
++i;
}
}
auto j = mPendingDisks.begin();
while (j != mPendingDisks.end()) {
if ((*j)->getDevice() == device) {
j = mPendingDisks.erase(j);
} else {
++j;
}
}
}
接下来看Disk中的destory方法
/system/vold/Disk.cpp
status_t Disk::destroy() {
CHECK(mCreated);
//移除所包含的所有卷
destroyAllVolumes();
mCreated = false;
//通知到framework层,framework层也只是移除相应的java bean,这里不展开讲了
auto listener = VolumeManager::Instance()->getListener();
if (listener) listener->onDiskDestroyed(getId());
return OK;
}
我们看destroyAllVolumes()方法中的逻辑
/system/vold/Disk.cpp
void Disk::destroyAllVolumes() {
//遍历调用
for (const auto& vol : mVolumes) {
vol->destroy();
}
//清空
mVolumes.clear();
}
我们以PublicVolume为例看看destory方法,其destory方法实现在其父类VolumeBase中
/system/vold/VolumeBase.cpp
status_t VolumeBase::destroy() {
CHECK(mCreated);
//如果挂载了执行挂载操作
if (mState == State::kMounted) {
unmount();
setState(State::kBadRemoval);
} else {
//没有直接设置remove状态
setState(State::kRemoved);
}
//通知framework
auto listener = getListener();
if (listener) listener->onVolumeDestroyed(getId());
//子类调用
status_t res = doDestroy();
mCreated = false;
return res;
}
status_t VolumeBase::unmount() {
if (mState != State::kMounted) {
LOG(WARNING) << getId() << " unmount requires state mounted";
return -EBUSY;
}
setState(State::kEjecting);
//有没有卷中卷移除
for (const auto& vol : mVolumes) {
if (vol->destroy()) {
LOG(WARNING) << getId() << " failed to destroy " << vol->getId()
<< " stacked above";
}
}
mVolumes.clear();
// 子类调用
status_t res = doUnmount();
setState(State::kUnmounted);
return res;
}
通过以上代码分析,销毁的时候如果挂载了会继续卸载操作,卸载是通知framework存储卡相应的状态,卸载前是Ejecting卸载后Unmounted状态,卸载最终调用doUnmount()方法,卸载完后调用了doDestroy()方法。
/system/vold/PublicVolume.cpp
status_t PublicVolume::doUnmount() {
// Unmount the storage before we kill the FUSE process. If we kill
// the FUSE process first, most file system operations will return
// ENOTCONN until the unmount completes. This is an exotic and unusual
// error code and might cause broken behaviour in applications.
//杀掉使用了当前挂载路径的进程
KillProcessesUsingPath(getPath());
//卸载掉相关路径
ForceUnmount(kAsecPath);
ForceUnmount(mFuseDefault);
ForceUnmount(mFuseRead);
ForceUnmount(mFuseWrite);
ForceUnmount(mRawPath);
if (mFusePid > 0) {
kill(mFusePid, SIGTERM);
TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(waitpid(mFusePid, nullptr, 0));
mFusePid = 0;
}
//删除掉相关路径节点
rmdir(mFuseDefault.c_str());
rmdir(mFuseRead.c_str());
rmdir(mFuseWrite.c_str());
rmdir(mRawPath.c_str());
//清空路径信息
mFuseDefault.clear();
mFuseRead.clear();
mFuseWrite.clear();
mRawPath.clear();
return OK;
}
我们再看doDesotroy方法做了什么
status_t PublicVolume::doDestroy() {
//删除create中创建的设备节点
return DestroyDeviceNode(mDevPath);
}
到这里整个卸载流程就分析完了。
总结
挂载和卸载的流程还是比较简单,出了这2个功能外,Vold还提供了格式化、挂载卸载cifs文件系统(网上邻居的功能),大家如果感兴趣可以根据上面分析的思路去阅读源码;如果大家觉得这篇文章对你有帮助记得点赞收藏。