Springboot测试
目录
- 1.加载测试专用属性
- 2.加载测试专用配置
- 3.表现层测试
- 4.业务层测试回滚
- 5.测试用例使用随机值
- 总结
1.加载测试专用属性
主要为@SpringBootTest中properties属性和args属性
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
//添加临时属性,优先级大于application.yml中的属性
//properties为当前测试类添加临时属性
//@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"})
//args属性可以为当前测试用例添加临时的命令行参数
//@SpringBootTest(args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"})
//args的优先级最高
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"},args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"})
class Springboot02TestApplicationTests {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
void testProperties(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
2.加载测试专用配置
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MsgConfig {
@Bean
public String message(){
return "message";
}
}
ConfigurationTest.class
package com.example;
import com.example.config.MsgConfig;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@SpringBootTest
@Import(MsgConfig.class)
public class ConfigurationTest {
@Autowired
private String msg;
@Test
void testConfiguration(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
3.表现层测试
使用webEnvironment属性开启tomcat,具体代码如下:
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.domain.Book;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.xml.ws.RequestWrapper;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/book")
public class BookController {
/*@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("getById is running.....");
return "Springboot";
}*/
@GetMapping
public Book getById(){
Book book=new Book();
book.setId(1);
book.setName("流浪地球");
book.setType("科幻");
return book;
}
}
Book.class
package com.example.domain;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private String type;
}
WebTest.class
package com.example;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultMatcher;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.ContentResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.HeaderResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.StatusResultMatchers;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
//开启虚拟调用
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
@Test
void testWeb() throws Exception {
//创建一个虚拟的请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder build= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
mvc.perform(build);
}
//状态匹配
@Test
void testStatus() throws Exception {
//创建一个虚拟的请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder build= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(build);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过
//定义本次调用的预期值
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
//预期本次调用成功
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(ok);
}
//字符串匹配
@Test
void testBody() throws Exception {
//创建一个虚拟的请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder build= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(build);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过
//定义本次调用的预期值
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
//预期本次调用成功
ResultMatcher result = content.string("springboot");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(result);
}
//json匹配
@Test
void testJson() throws Exception {
//创建一个虚拟的请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder build= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(build);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过
//定义本次调用的预期值
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
//预期本次调用成功
ResultMatcher result = content.json("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"流浪地球\",\"type\":\"科幻\"}");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(result);
}
//ContentType匹配
@Test
void testContentType() throws Exception {
//创建一个虚拟的请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder build= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(build);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过
//定义本次调用的预期值
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
//预期本次调用成功
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type", "application/json");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(contentType);
}
@Test
void testGetById() throws Exception {
//创建一个虚拟的请求
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder build= MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/book");
ResultActions action = mvc.perform(build);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过
//定义本次调用的预期值
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
//预期本次调用成功
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(ok);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过
//定义本次调用的预期值
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
//预期本次调用成功
ResultMatcher result = content.json("{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"流浪地球\",\"type\":\"科幻\"}");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(result);
//设定预期值,与真实值进行比较,成功测试通过
//定义本次调用的预期值
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
//预期本次调用成功
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type", "application/json");
//添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
action.andExpect(contentType);
}
}
4.业务层测试回滚
想在Springboot中做业务层相关的测试,但是又不想留下数据在数据库中,则只需在测试类上添加@Transactional注解即可。
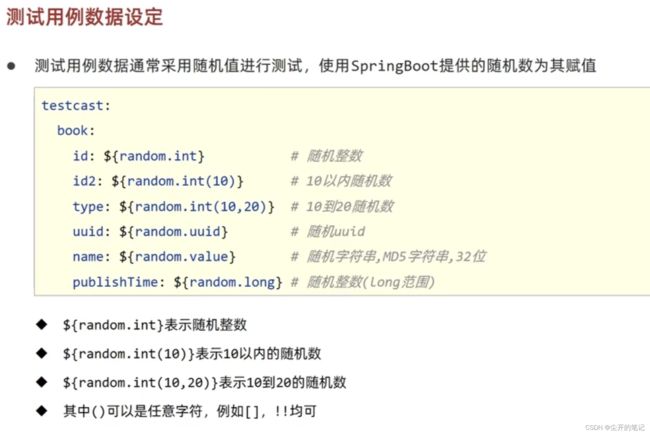
5.测试用例使用随机值
总结
参考视频
这部分内容作为了解使用。