lesson9: C++多线程
1.线程库
1.1 thread类的简单介绍
C++11 中引入了对 线程的支持 了,使得 C++ 在 并行编程时 不需要依赖第三方库
而且在原子操作中还引入了 原子类 的概念。要使用标准库中的线程,必须包含 < thread > 头文件
|
函数名
|
功能
|
|
thread()
|
构造一个线程对象,没有关联任何线程函数,即没有启动任何线程
|
|
thread(fn, args1, args2, ...)
|
构造一个线程对象,并关联线程函数fn,args1,args2,...为线程函数的
参数
|
|
get_id()
|
获取线程id
|
|
jionable()
|
线程是否还在执行,joinable代表的是一个正在执行中的线程。
|
|
jion()
|
该函数调用后会 阻塞住线程 ,当该线程结束后,主线程继续执行
|
|
detach()
|
在创建线程对象后马上调用,用于把被创建线程与线程对象分离开,分离
的线程变为后台线程,创建的线程的"死活"就与主线程无关
|
-
线程是操作系统中的一个概念,线程对象可以关联一个线程,用来控制线程以及获取线程的状态。
-
当创建一个线程对象后,没有提供线程函数,该对象实际没有对应任何线程
1.2 线程对象关联线程函数
#include
using namespace std;
#include
void ThreadFunc(int a)
{
cout << "Thread1" << a << endl;
}
class TF
{
public:
void operator()()
{
cout << "Thread3" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
// 线程函数为函数指针
thread t1(ThreadFunc, 10);
// 线程函数为lambda表达式
thread t2([](){cout << "Thread2" << endl; });
// 线程函数为函数对象
TF tf;
thread t3(tf);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
cout << "Main thread!" << endl;
return 0;
} - 线程对象可以关联1.函数指针2.lambda表达式3.函数对象
- 当创建一个线程对象后,没有提供线程函数,该对象实际没有对应任何线程
1.2.1 注意
-
thread类是防拷贝的,不允许拷贝构造以及赋值,但是可以 移动构造 和 移动赋值 ,即将一个线程对象关联线程的状态转移给其他线程对象,转移期间不意向线程的执行。
- 可以通过jionable()函数判断线程是否是有效的,如果是以下任意情况,则线程无效
- 采用无参构造函数构造的线程对象
- 线程对象的状态已经转移给其他线程对象
-
线程已经调用jion或者detach结束
1.3 线程函数参数
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void Print(int n, int& x,mutex& mtx)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
mtx.lock();
cout < - 线程函数的参数是先传递给thread的,并以值拷贝的方式拷贝到线程栈空间中的
-
如果不给线程函数的参数不借助 ref函数
-
即使线程参数为 引用类型 ,在线程中修改后也 不能修改外部实参 ,
-
因为其实际引用的是线程栈中的拷贝,而不是外部实参
-
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
mutex mtx;
int x = 0;
int n = 10;
int m;
cin >> m;
vector v(m);
//v.resize(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
// 移动赋值给vector中线程对象
v[i] = thread([&](){
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
mtx.lock();
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ":" << i << endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
++x;
mtx.unlock();
}
});
}
for (auto& t : v)
{
t.join();
}
cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}
- 借助lambda表达式中的引用捕捉也可以实现上面那个函数,就可以不用借助ref函数
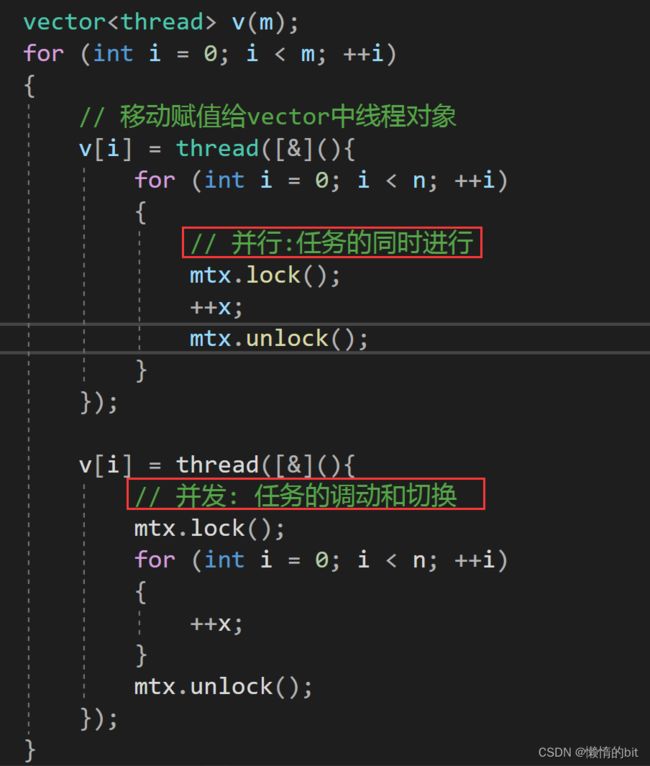
1.3.1 线程并行 && 并发的讨论
- 并行:任务的同时进行
- 并发: 任务的调动和切换
- 在这个函数中其实是并行的速度更快,因为线程切换十分耗时间
1.4 原子性操作库(atomic)
多线程最主要的问题是共享数据带来的问题 ( 即线程安全 )
当一个或多个线程要 修改 共享数据时,就会产生很多潜在的麻烦
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
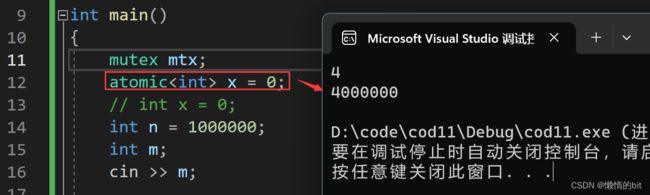
int main()
{
mutex mtx;
atomic x = 0;
// int x = 0;
int n = 1000000;
int m;
cin >> m;
vector v(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
// 移动赋值给vector中线程对象
v[i] = thread([&](){
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
// t1 t2 t3 t4
++x;
}
});
}
for (auto& t : v)
{
t.join();
}
cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}
- C++98中传统的解决方式:可以对共享修改的数据加锁保护
- 加锁的问题: 这个线程执行的时候, 其他线程就会被阻塞,会影响程序运行的效率,而且锁如果控制不好,还容易造成死锁。
-
C++11 中使用atomic类模板,定义出需要的任意原子类型
-
程序员 不需要 对原子类型变量进行 加锁解锁 操作,线程能够对原子类型变量互斥的访问。
-
1.4.1 注意
#include
int main()
{
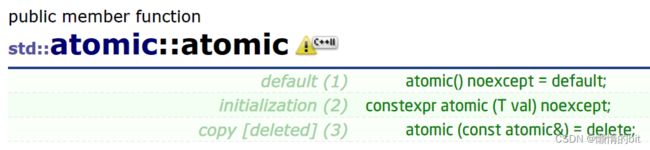
atomic a1(0);
//atomic a2(a1); // 编译失败
atomic a2(0);
//a2 = a1; // 编译失败
return 0;
} - 原子类型通常属于"资源型"数据,多个线程只能访问单个原子类型的拷贝,
- 因此在C++11 中,原子类型只能从其模板参数中进行构造,不允许原子类型进行拷贝构造、移动构造以及 operator=等,为了防止意外,标准库已经将atmoic模板类中的拷贝构造、移动构造、赋值运算符重载默认删除掉了
1.5 lock_guard与unique_lock
在 多线程 环境下, 原子性 只能保证 某个变量的安全性
在多线程环境下,而需要保证一段代码的安全性,就只能通过加锁的方式实现
1.5.1 lock_guard
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//RAII
template
class LockGuard
{
public:
LockGuard(Lock& lk)
:_lock(lk)
{
_lock.lock();
cout << "thread:" << this_thread::get_id() << "加锁" << endl;
}
~LockGuard()
{
cout << "thread:" << this_thread::get_id() << "解锁" << endl << endl;
_lock.unlock();
}
private:
Lock& _lock;// 成员变量是引用
};
int main()
{
mutex mtx;
atomic x = 0;
//int x = 0;
int n = 100;
int m;
cin >> m;
vector v(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
// 移动赋值给vector中线程对象
v[i] = thread([&](){
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
{
lock_guard lk(mtx);
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ":" << i << endl;
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
});
}
for (auto& t : v)
{
t.join();
}
cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}
- lock_guard类模板主要是通过RAII的方式,对其管理的互斥量进行了封装
-
调用构造函数成功上锁,出作用域前,lock_guard对象要被销毁,调用析构函数自动解锁,可以有效避免死锁问题。
-
lock_guard 的 缺陷 :太单一,用户没有办法对该锁进行控制
1.5.2 unique_lock
与 lock_guard 不同的是, unique_lock 更加的灵活,提供了更多的成员函数:
- 上锁/解锁操作:lock、try_lock、try_lock_for、try_lock_until和unlock
- 修改操作:移动赋值、交换(swap:与另一个unique_lock对象互换所管理的互斥量所有 权)、释放(release:返回它所管理的互斥量对象的指针,并释放所有权)
- 获取属性:owns_lock(返回当前对象是否上了锁)、operator bool()(与owns_lock()的功能相 同)、mutex(返回当前unique_lock所管理的互斥量的指针)。
1.6 支持两个线程交替打印,一个打印奇数,一个打印偶数
1.6.1 错误案例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int n = 100;
mutex mtx;
thread t1([&](){
while (i < n)
{
mtx.lock();
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ":" << i << endl;
i += 1;
mtx.unlock();
}
});
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(100));
thread t2([&](){
while (i < n)
{
mtx.lock();
cout << this_thread::get_id() << ":" << i << endl;
i += 1;
mtx.unlock();
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
return 0;
} - 在线程切换的中间时间也会发现线程竞争抢锁的问题
1.6.2 正确案例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int n = 100;
mutex mtx;
condition_variable cv;// 条件变量
bool ready = true;
// t1打印奇数
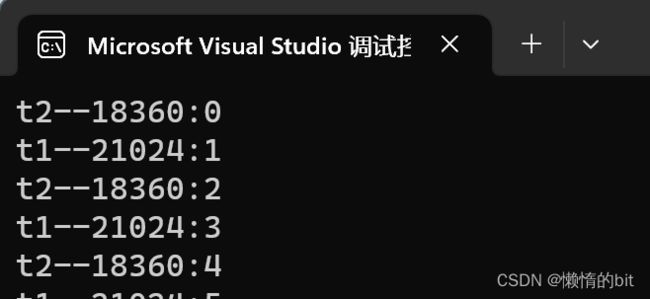
thread t1([&](){
while (i < n)
{
{
unique_lock lock(mtx);
cv.wait(lock, [&ready](){return !ready; });// 等待线程
cout << "t1--" << this_thread::get_id() << ":" << i << endl;
i += 1;
ready = true;
cv.notify_one();// 解除线程等待
}
//this_thread::yield();
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(100));
}
});
// t2打印偶数
thread t2([&]() {
while (i < n)
{
unique_lock lock(mtx);
cv.wait(lock, [&ready](){return ready; });
cout <<"t2--"< - cv.wait(lock, [&ready]() {return !ready; });
- 当ready返回的是false时,这个线程就会阻塞
- 阻塞当前线程,并自动调用lock.unlock(),允许其他锁定的线程继续执行
- cv.notify_one();
- 唤醒当前线程并自动调用lock.lock();就只允许自己一个线程执行
1.7 shared_ptr的多线程问题
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace bit
{
template
class shared_ptr
{
public:
shared_ptr(T* ptr = nullptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
, _pRefCount(new int(1))
, _pMutex(new mutex)
{}
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr& sp)
:_ptr(sp._ptr)
, _pRefCount(sp._pRefCount)
, _pMutex(sp._pMutex)
{
AddRef();
}
void Release()
{
bool flag = false;
_pMutex->lock();
if (--(*_pRefCount) == 0 && _ptr)
{
cout << "delete:" << _ptr << endl;
delete _ptr;
delete _pRefCount;
flag = true;
}
_pMutex->unlock();
if (flag)
delete _pMutex;
}
void AddRef()
{
_pMutex->lock();
++(*_pRefCount);
_pMutex->unlock();
}
shared_ptr& operator=(const shared_ptr& sp)
{
if (_ptr != sp._ptr)
{
Release();
_ptr = sp._ptr;
_pRefCount = sp._pRefCount;
_pMutex = sp._pMutex;
AddRef();
}
return *this;
}
int use_count()
{
return *_pRefCount;
}
~shared_ptr()
{
Release();
}
// 像指针一样使用
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
T* get() const
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
int* _pRefCount;// 使用时需要加锁
mutex* _pMutex;// 锁指针
};
}
int main()
{
// shared_ptr是线程安全的吗?
bit::shared_ptr sp1(new double(1.11));
bit::shared_ptr sp2(sp1);
mutex mtx;
vector v(2);
int n = 100000;
for (auto& t : v)
{
t = thread([&](){
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
// 拷贝是线程安全的
bit::shared_ptr sp(sp1);
// 访问资源不是
mtx.lock();
(*sp)++;
mtx.unlock();
}
});
}
for (auto& t : v)
{
t.join();
}
cout << sp1.use_count() << endl;
cout << *sp1 << endl;
return 0;
} -
在多线程中,shared_ptr也应该对自己的引用计数进行加锁处理
- 在多线程中, shared_ptr的拷贝是线程安全的,但访问资源不是,所以访问资源也需要加锁
1.8 单例模式的多线程问题
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton* GetInstance()
{
// 保护第一次,后续不需要加锁
// 双检查加锁
if (_pInstance == nullptr)
{
unique_lock lock(_mtx);
if (_pInstance == nullptr)
{
_pInstance = new Singleton;
}
}
return _pInstance;
}
private:
// 构造函数私有
Singleton(){};
// C++11
Singleton(Singleton const&) = delete;
Singleton& operator=(Singleton const&) = delete;
static Singleton* _pInstance;
static mutex _mtx;
};
Singleton* Singleton::_pInstance = nullptr;
mutex Singleton::_mtx;
int main()
{
Singleton::GetInstance();
Singleton::GetInstance();
return 0;
} - 在多线程的情况下, 第一次创建对象时也是需要加锁保护的
1.8.1 巧妙的解决方案
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Singleton
{
public:
static Singleton* GetInstance()
{
static Singleton _s;// 局部的静态对象,第一次调用时初始化
return &_s;
}
private:
// 构造函数私有
Singleton() {};
// C++11
Singleton(Singleton const&) = delete;
Singleton& operator=(Singleton const&) = delete;
};
int main()
{
Singleton::GetInstance();
Singleton::GetInstance();
return 0;
} - 局部的静态对象,第一次调用时初始化
- 在C++11之前是不能保证线程安全的
静态对象的构造函数调用初始化并不能保证线程安全的原子性 - C++11的时候修复了这个问题,所以这种写法,只能在支持C++11以后的编译器上玩