RaspberryPi 4B 使用 libgpiod 操作 gpio
RaspberryPi OS 是 Linux 的一个发行版,基于 Debian 制作。因此我们熟悉的基于 sysfs 方式控制 GPIO(/sys/class/gpio)都是可以使用的。但是嵌入式 Linux 系统下之前被广泛应用的 GPIO 工具 sysfs GPIO 接口,目前这个项目已经处于 deprecated 状态,经 Linux Kernel Community 确定其替代者就是 GPIO 字符设备 API Libgpiod。
libgpiod —— 与Linux GPIO 交互的 C 库和工具,字符设备(gpiod 代表 GPIO 设备)
从 Linux 4.8 开始,GPIO sysfs 接口已被弃用。用户空间应该使用取而代之的是字符设备。这个库简单的 API 实现封装了 ioctl 调用和数据结构。
一、硬件接线
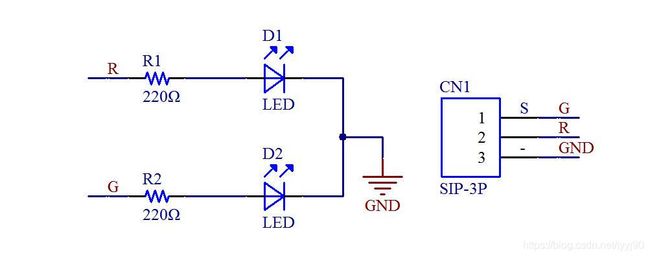
通过控制 gpio 引脚输出高电平就可以控制 LED 灯的点亮。使用树莓派传感器套件里的双色 LED 灯模块。原理图如下:
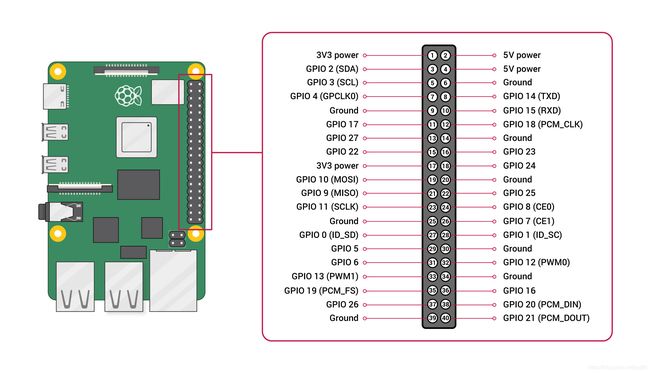
现在再来看树莓派的 gpio 引脚图:
我这里使用 GPIO 17 和 GPIO 18 引脚去控制双色 LED 灯模块的红灯(R)或绿灯(G)点亮。
接线如下:
| 树莓派引脚 | 双色 LED 灯模块引脚 |
|---|---|
| GPIO 17 | R |
| GPIO 18 | S(G) |
| GND | GND |
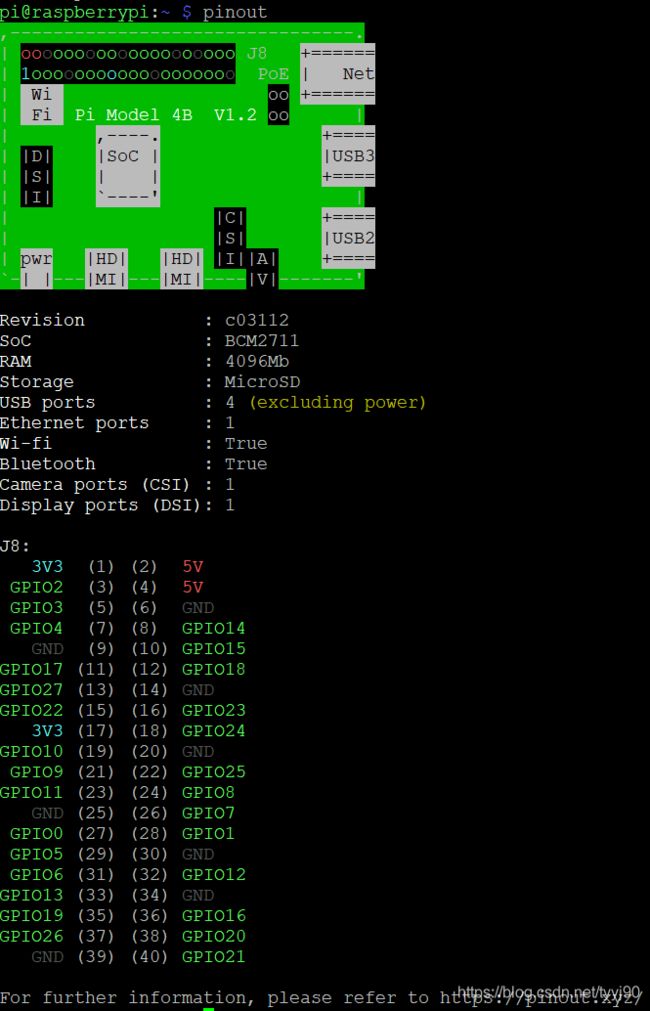
查看树莓派的 gpio 引脚图还有一个快捷方式,在树莓派命令行窗口直接输入命令:
pinout
显示如下:
二、使用 GPIO sysfs 接口
- sysfs 导出 GPIO 17 和 GPIO 18
echo 17 > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo 18 > /sys/class/gpio/export
现在再去 ls /sys/class/gpio/ 目录,就会多出来 gpio17 和 gpio18 目录。
- 设置 gpio 模式为输出
echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio17/direction
echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio18/direction
- 设置 gpio 高电平点亮 LED,点亮绿色(G)灯。
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio18/value
熄灭写 0 即可。
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio18/value
三、使用 libgpiod
3.1 安装
首先安装 libgpiod,先查找一下。
pi@raspberrypi:~/Package $ sudo apt-cache search libgpiod
gpiod - Tools for interacting with Linux GPIO character device - binary
libgpiod-dev - C library for interacting with Linux GPIO device - static libraries and headers
libgpiod-doc - C library for interacting with Linux GPIO device - library documentation
libgpiod2 - C library for interacting with Linux GPIO device - shared libraries
python3-libgpiod - Python bindings for libgpiod (Python 3)
gpiod —— 与 Linux GPIO 字符设备交互的工具 - bin 二进制
libgpiod-dev —— 用于与 Linux GPIO 设备交互的 C 库 - 静态库和头文件
libgpiod-doc —— 库文档
libgpiod2 —— 用于与 Linux GPIO 设备交互的 C 库 - 共享库
python3-libgpiod —— libgpiod 的 Python 绑定(Python 3)
直接 install libgpiod-dev
sudo apt-get install libgpiod-dev
可以看到实际上安装了 libgpiod-dev 的同时也安装了 libgpiod2,也就是其静态库和动态库都安装了。
3.2 使用
写一个程序验证一下,红绿灯交替闪烁一共 20 次。
下面的程序用到了 libgpiod 以下 API:
- gpiod_chip 结构体
它代表支持 gpio 的芯片。包括每个 gpio 口 gpiod_line 数组 lines,数组的个数用 num_lines 指出。还包含了 fd 设备句柄,以及名称和标签。
struct gpiod_chip {
struct gpiod_line **lines;
unsigned int num_lines;
int fd;
char name[32];
char label[32];
};
- gpiod_line 结构体
direction —— GPIO 的方向
active_state —— 活动状态配置
output_value —— 最后写入 GPIO 的逻辑值
info_flags —— GPIO_GET_LINEINFO_IOCTL 返回的 GPIOLINE_FLAGs
req_flags —— 提供 GPIOD_LINE_REQUEST_FLAGs 来请求 GPIO
state —— LINE_FREE,LINE_REQUESTED_VALUES 或 LINE_REQUESTED_EVENTS
struct line_fd_handle {
int fd;
int refcount;
};
struct gpiod_line {
unsigned int offset;
/* The direction of the GPIO line. */
int direction;
/* The active-state configuration. */
int active_state;
/* The logical value last written to the line. */
int output_value;
/* The GPIOLINE_FLAGs returned by GPIO_GET_LINEINFO_IOCTL. */
__u32 info_flags;
/* The GPIOD_LINE_REQUEST_FLAGs provided to request the line. */
__u32 req_flags;
/*
* Indicator of LINE_FREE, LINE_REQUESTED_VALUES or
* LINE_REQUESTED_EVENTS.
*/
int state;
struct gpiod_chip *chip;
struct line_fd_handle *fd_handle;
char name[32];
char consumer[32];
};
- gpiod_chip_open_by_name
按名称打开 gpiochip。
- gpiod_chip_get_line
在给定的偏移量处获取 GPIO 的句柄。
offset —— GPIO偏移量
- gpiod_line_request_output
设置输出方向。
consumer —— 使用者的名称
default_val —— 初始值
- gpiod_line_set_value
设置单个 GPIO 的值。
例程代码
#include 编译程序
gcc RG_LED.c -o RG_LED -lgpiod
运行
./RG_LED
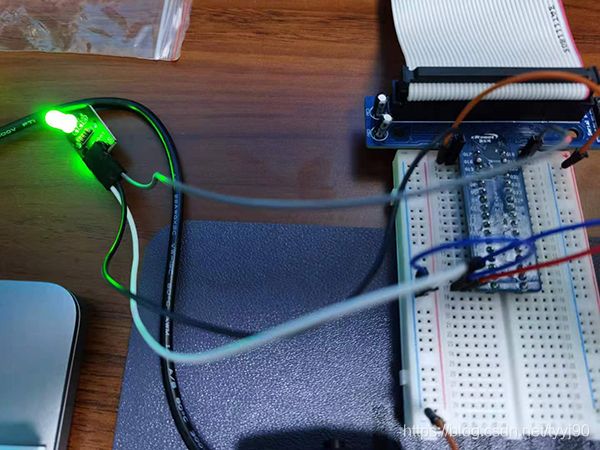
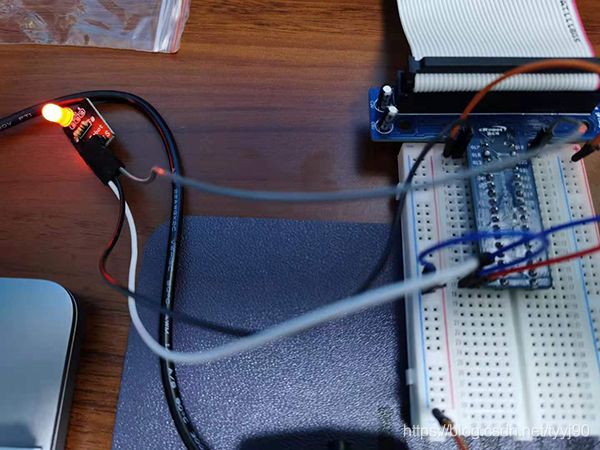
效果图如下,实际情况是红绿交替闪烁。
3.3 点亮 RGB 三色 LED
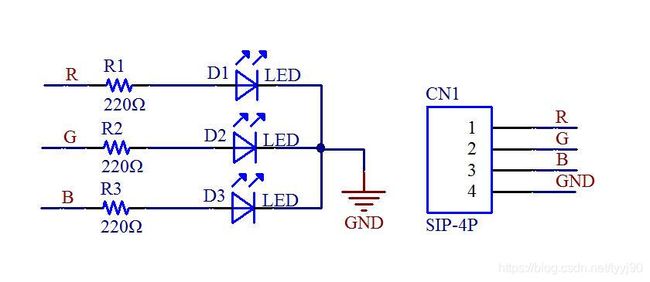
三色 LED 模块原理图如下,可以控制三原色混合。
| 树莓派引脚 | RGB 三色 LED 灯模块引脚 |
|---|---|
| GPIO 16 | R |
| GPIO 17 | B |
| GPIO 18 | G |
| GND | GND |
例程代码如下,在上面的代码的基础上抽离出公共方法 blend_led 。
#include 编译运行即可看到结果,R、G、B…的颜色顺序闪烁,间隔一秒。
gcc rgb_led.c -o rgb_led -lgpiod
./rgb_led