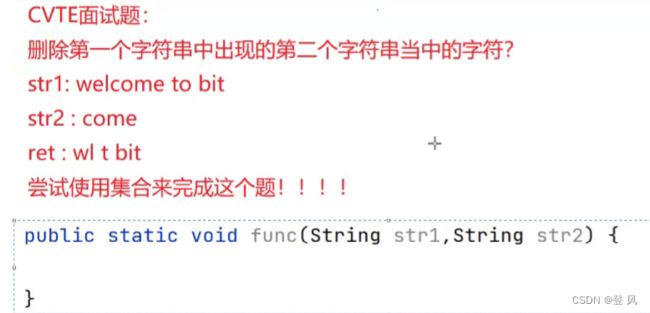
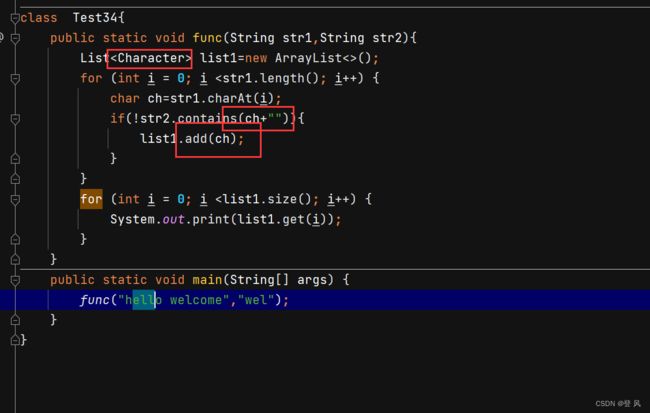
数据结构(Java实现)-ArrayList与顺序表
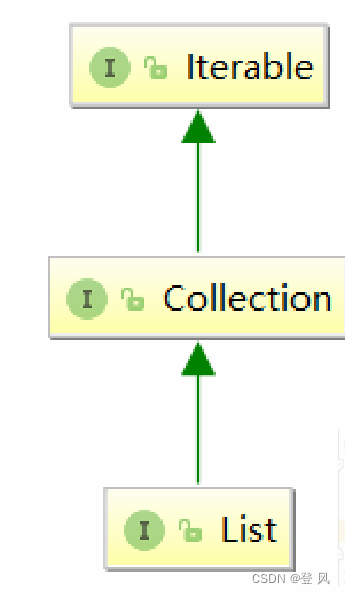
什么是List
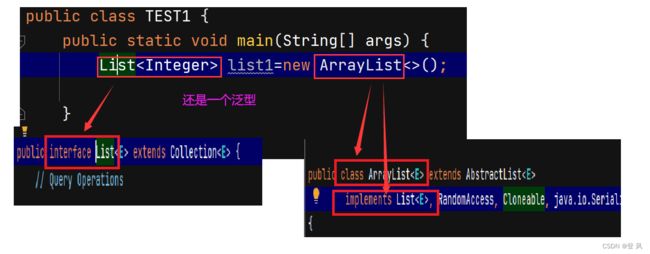
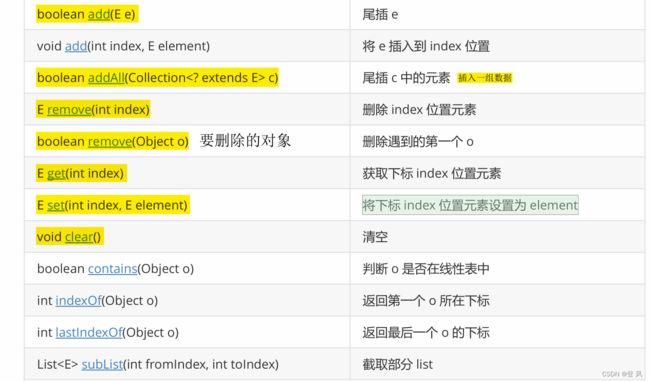
List是一个接口,继承自Collection。

List的使用
List是个接口,并不能直接用来实例化。
如果要使用,必须去实例化List的实现类。在集合框架中,ArrayList和LinkedList都实现了List接口。
线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。
常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线
顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成
数据的增删查改

所有代码如下
PosOutBoundsException
public class PosOutBoundsException extends RuntimeException{
public PosOutBoundsException() {
}
public PosOutBoundsException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
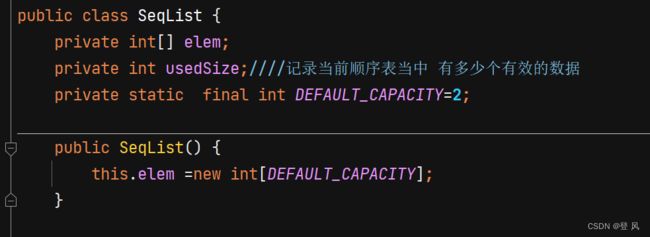
SeqList
public class SeqList {
private int[] elem;
private int usedSize;记录当前顺序表当中 有多少个有效的数据
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY=2;
public SeqList() {
this.elem =new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}
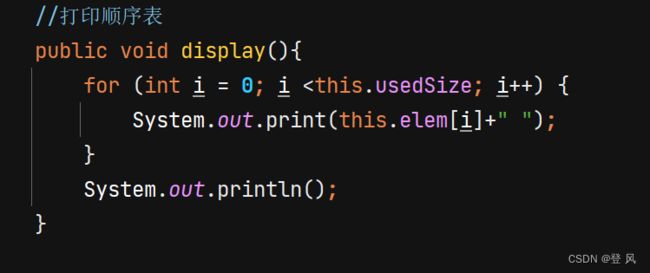
//打印顺序表
public void display(){
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
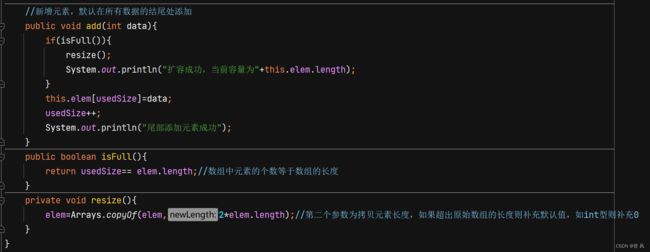
//新增元素,默认在所有数据的结尾处添加
public void add(int data){
if(isFull()){
resize();
System.out.println("扩容成功,当前容量为"+this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[usedSize]=data;
usedSize++;
System.out.println("尾部添加元素成功");
}
public boolean isFull(){
return usedSize== elem.length;//数组中元素的个数等于数组的长度
}
private void resize(){
elem=Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);//第二个参数为拷贝元素长度,如果超出原始数组的长度则补充默认值,如int型则补充0
}
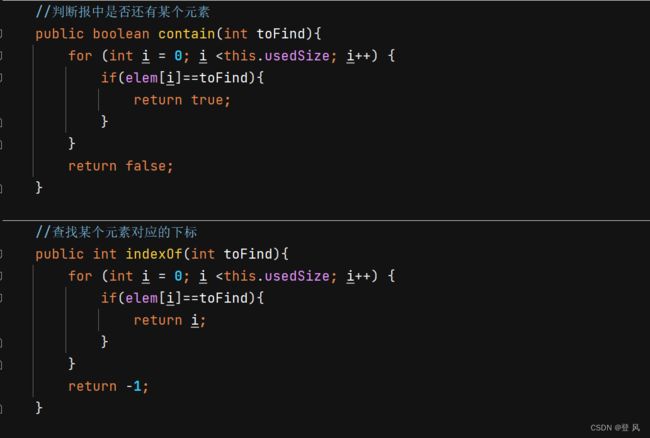
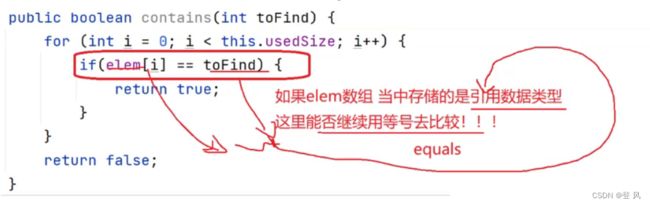
//判断报中是否还有某个元素
public boolean contain(int toFind){
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i]==toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//查找某个元素对应的下标
public int indexOf(int toFind){
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize; i++) {
if(elem[i]==toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
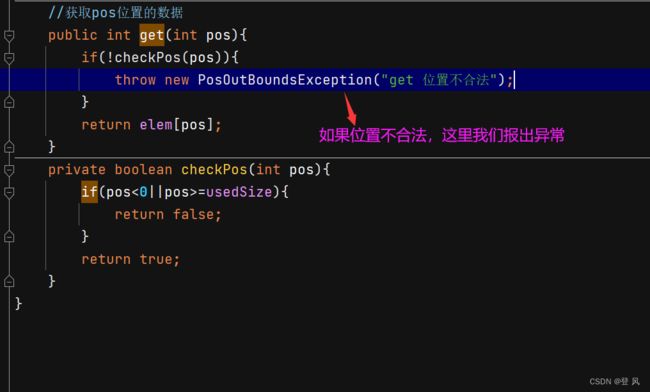
//获取pos位置的数据
public int get(int pos){
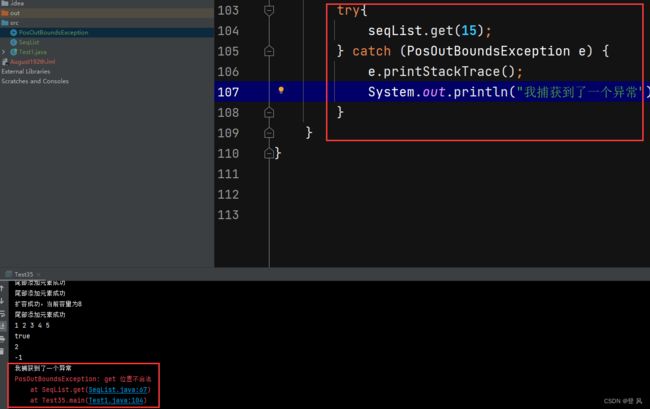
if(!checkPos(pos)){
throw new PosOutBoundsException("get 位置不合法");
}
return elem[pos];
}
private boolean checkPos(int pos){
if(pos<0||pos>=usedSize){
return false;
}
return true;
}
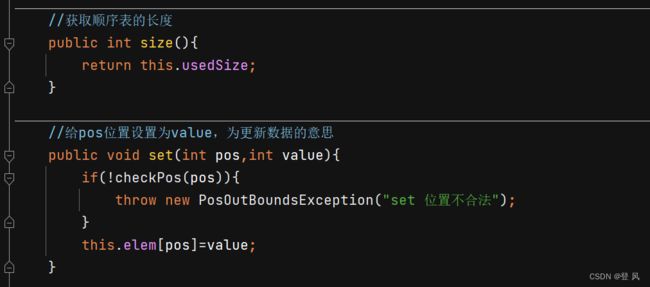
//获取顺序表的长度
public int size(){
return this.usedSize;
}
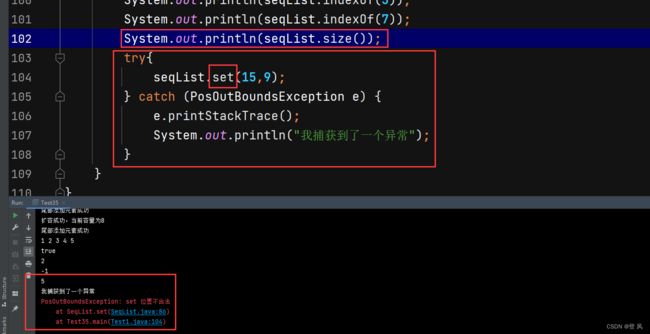
//给pos位置设置为value,为更新数据的意思
public void set(int pos,int value){
if(!checkPos(pos)){
throw new PosOutBoundsException("set 位置不合法");
}
this.elem[pos]=value;
}
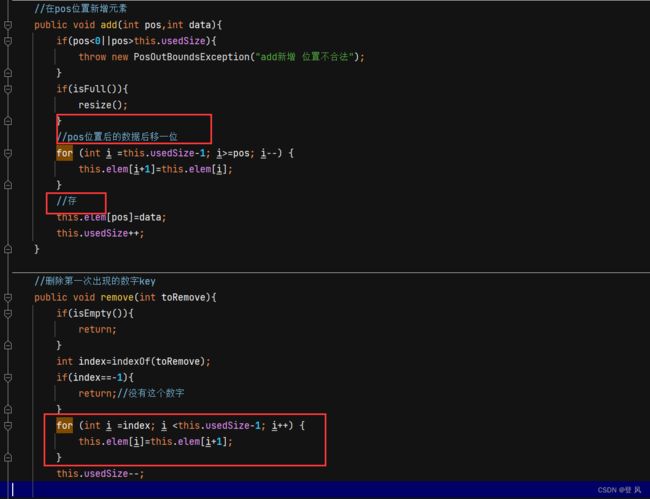
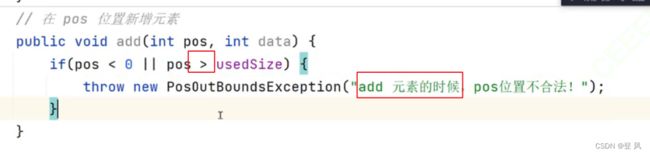
//在pos位置新增元素
public void add(int pos,int data){
if(pos<0||pos>this.usedSize){
throw new PosOutBoundsException("add新增 位置不合法");
}
if(isFull()){
resize();
}
//pos位置后的数据后移一位
for (int i =this.usedSize-1; i>=pos; i--) {
this.elem[i+1]=this.elem[i];
}
//存
this.elem[pos]=data;
this.usedSize++;
}
//删除第一次出现的数字key
public void remove(int toRemove){
if(isEmpty()){
return;
}
int index=indexOf(toRemove);
if(index==-1){
return;//没有这个数字
}
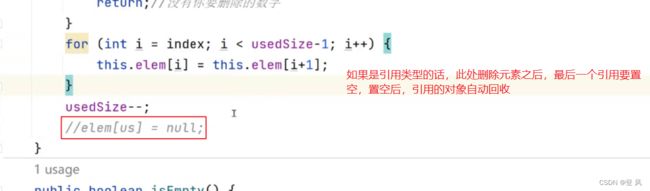
for (int i =index; i <this.usedSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i]=this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize==0;
}
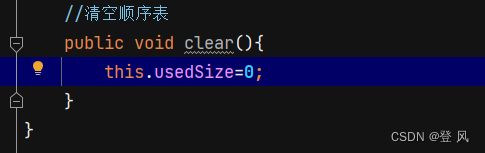
//清空顺序表
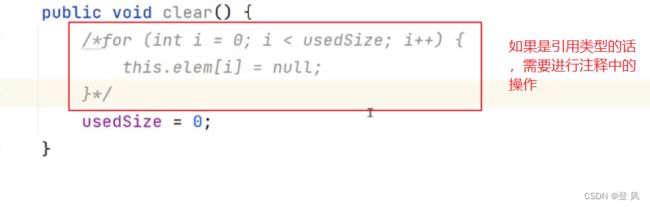
public void clear(){
this.usedSize=0;
}
}
Test1.java
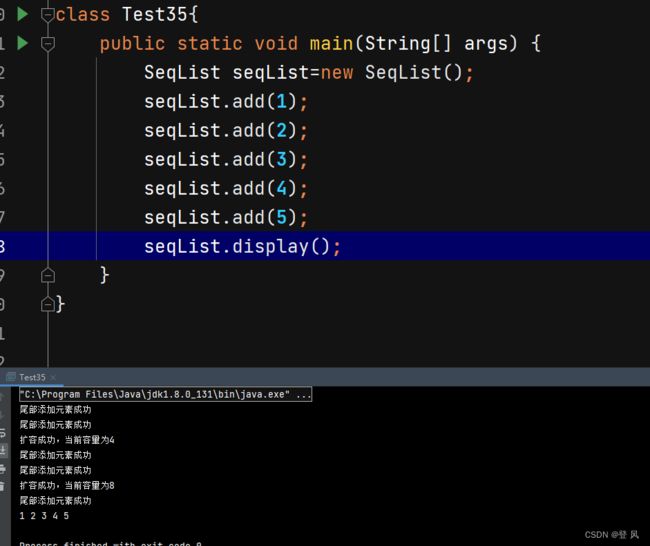
class Test35{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SeqList seqList=new SeqList();
seqList.add(1);
seqList.add(2);
seqList.add(3);
seqList.add(4);
seqList.add(5);
seqList.display();
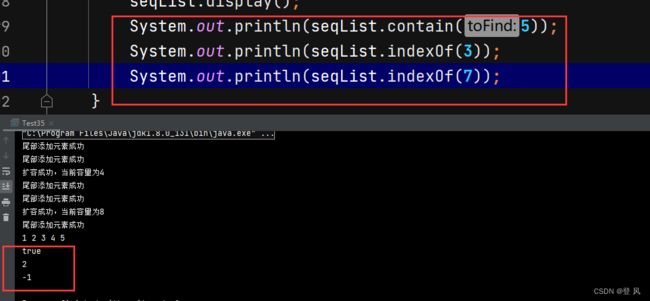
System.out.println(seqList.contain(5));
System.out.println(seqList.indexOf(3));
System.out.println(seqList.indexOf(7));
/* System.out.println(seqList.size());
try{
seqList.set(15,9);
} catch (PosOutBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("我捕获到了一个异常");
}*/
seqList.display();
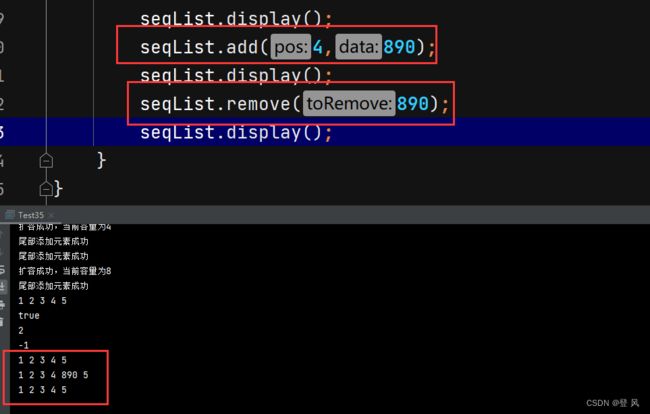
seqList.add(4,890);
seqList.display();
seqList.remove(890);
seqList.display();
}
}
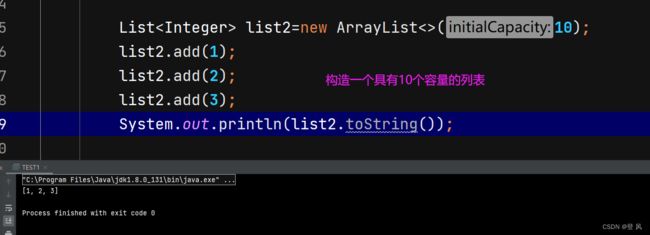
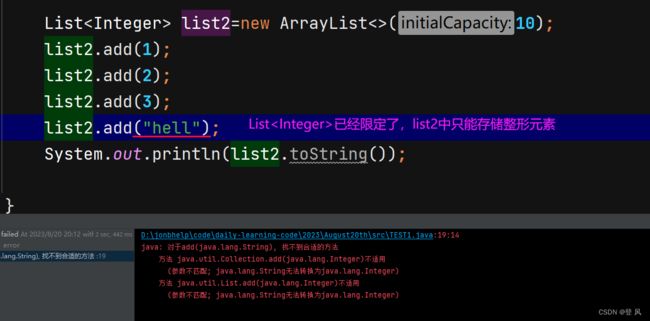
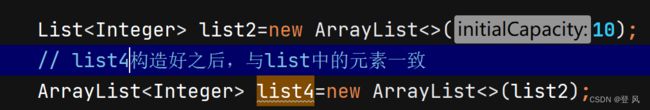
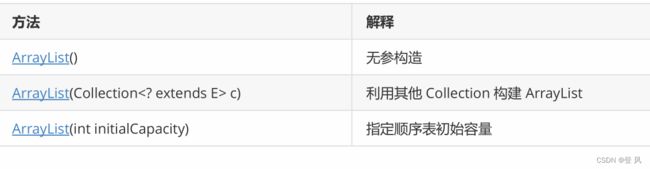
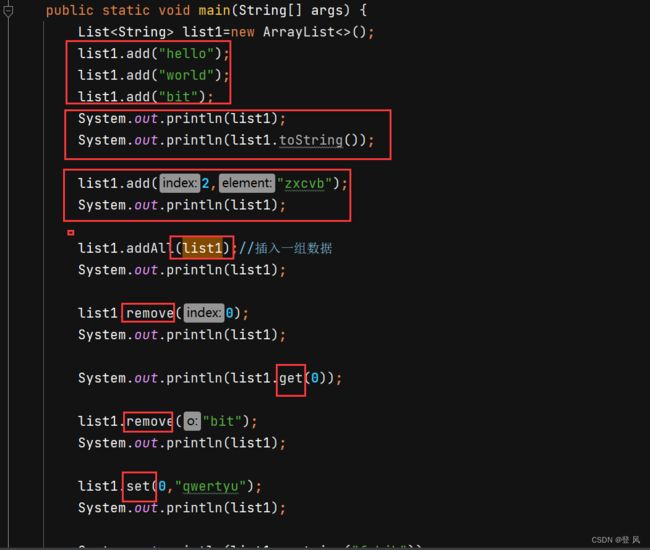
ArrayList简介
ArrayList是以泛型方式实现的,使用时必须要先实例化
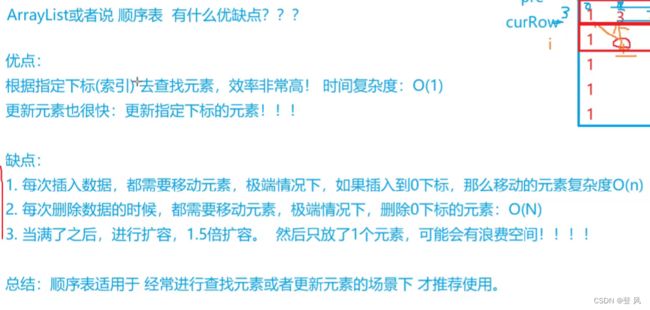
ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
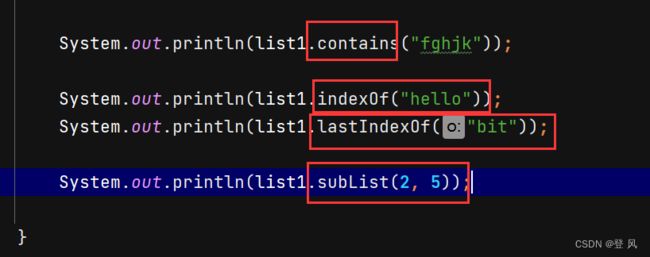
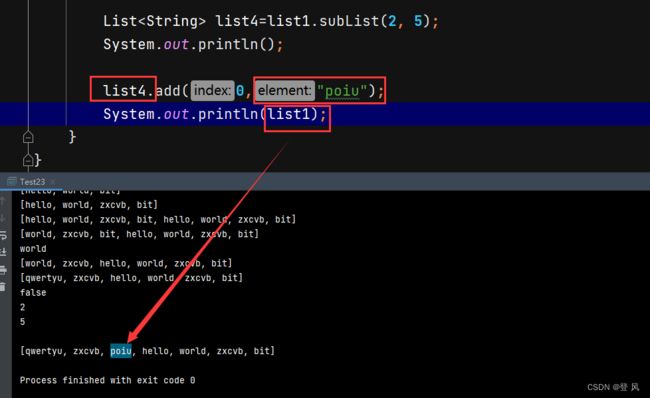
subList方法,会改变原来对象中0位置处的数据,截取拿到的是地址
ArrayList的遍历
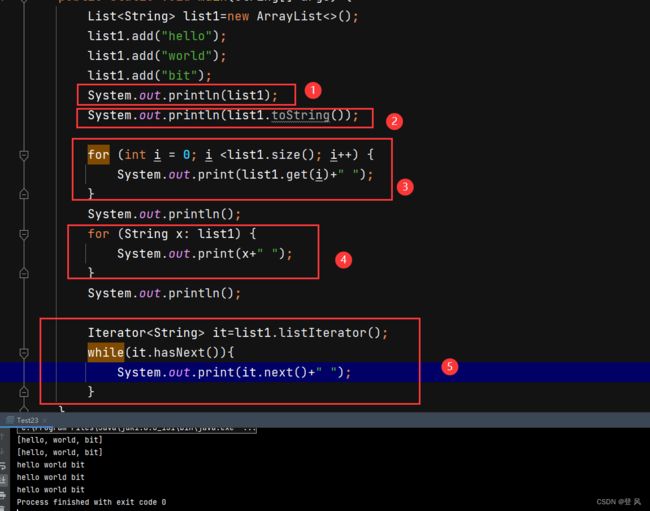
ArrayList 可以使用3种方式遍历:for循环+下标、foreach、使用迭代器
ArrayList的扩容机制
按照1.5倍方式扩容
如果用户需要扩容大小 超过 原空间1.5倍,按照用户所需大小扩容
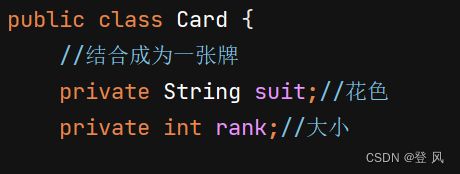
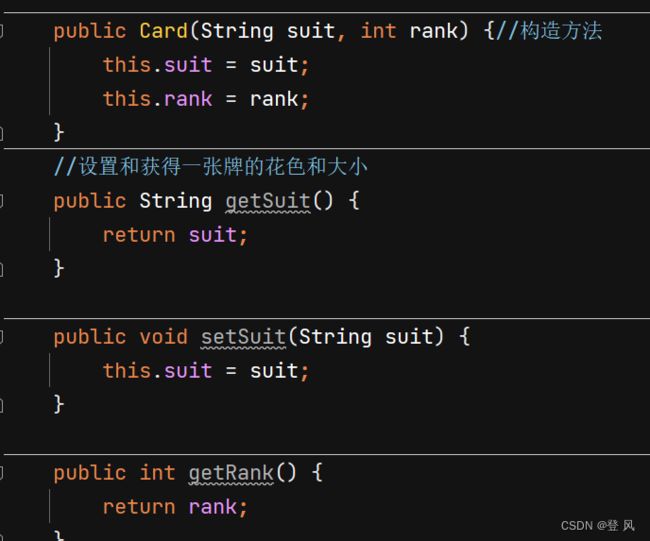
public class Card {
//结合成为一张牌
private String suit;//花色
private int rank;//大小
public Card(String suit, int rank) {//构造方法
this.suit = suit;
this.rank = rank;
}
//设置和获得一张牌的花色和大小
public String getSuit() {
return suit;
}
public void setSuit(String suit) {
this.suit = suit;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
public void setRank(int rank) {
this.rank = rank;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "【" +
suit +
", " + rank +
'】';
}
}
Test
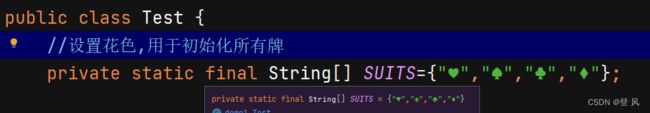
public class Test {
//设置花色,用于初始化所有牌
private static final String[] SUITS={"♥","♠","♣","♦"};
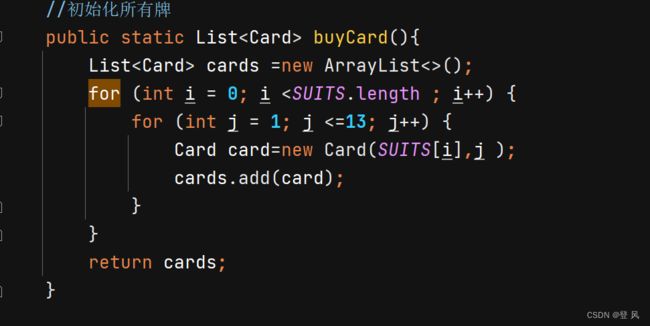
//初始化所有牌
public static List<Card> buyCard(){
List<Card> cards =new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <SUITS.length ; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <=13; j++) {
Card card=new Card(SUITS[i],j );
cards.add(card);
}
}
return cards;
}
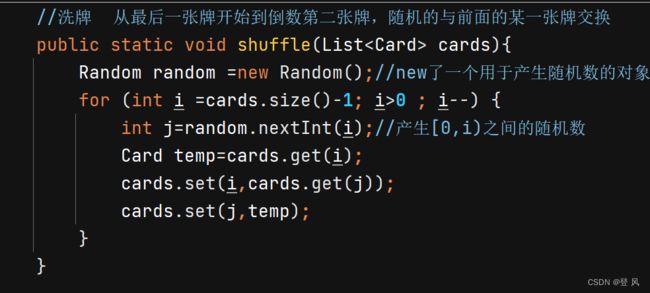
//洗牌 从最后一张牌开始到倒数第二张牌,随机的与前面的某一张牌交换
public static void shuffle(List<Card> cards){
Random random =new Random();//new了一个用于产生随机数的对象
for (int i =cards.size()-1; i>0 ; i--) {
int j=random.nextInt(i);//产生[0,i)之间的随机数
Card temp=cards.get(i);
cards.set(i,cards.get(j));
cards.set(j,temp);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Card> cards =buyCard();
System.out.println(cards);
shuffle(cards);
System.out.println(cards);
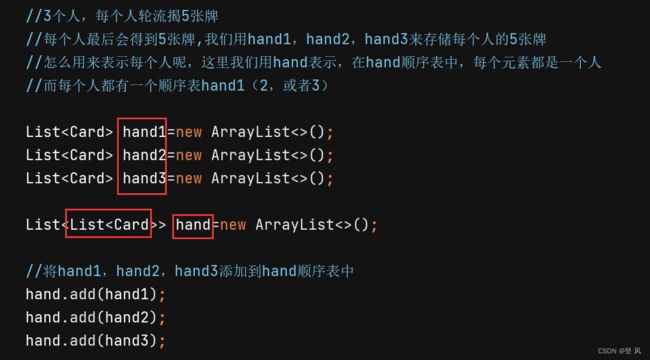
//3个人,每个人轮流揭5张牌
//每个人最后会得到5张牌,我们用hand1,hand2,hand3来存储每个人的5张牌
//怎么用来表示每个人呢,这里我们用hand表示,在hand顺序表中,每个元素都是一个人
//而每个人都有一个顺序表hand1(2,或者3)
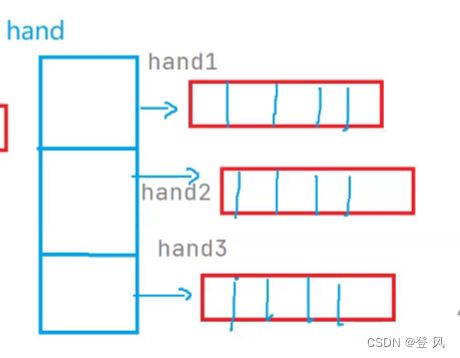
List<Card> hand1=new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand2=new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> hand3=new ArrayList<>();
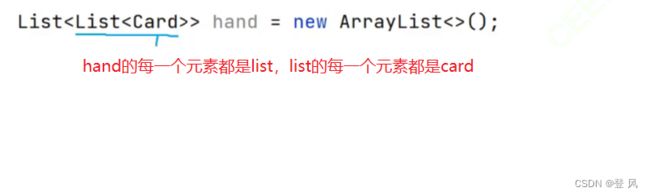
List<List<Card>> hand=new ArrayList<>();
//将hand1,hand2,hand3添加到hand顺序表中
hand.add(hand1);
hand.add(hand2);
hand.add(hand3);
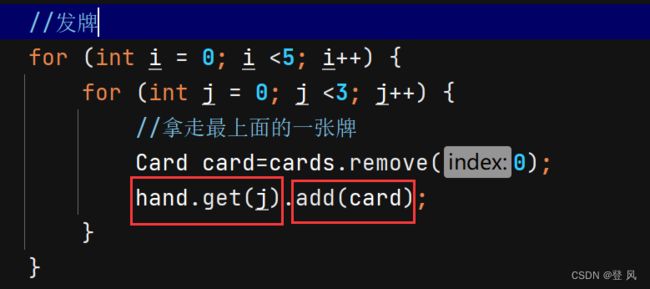
//发牌
for (int i = 0; i <5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <3; j++) {
//拿走最上面的一张牌
Card card=cards.remove(0);
hand.get(j).add(card);
}
}
System.out.println("第1个人得到的牌");
System.out.println(hand1);
System.out.println("第2个人得到的牌");
System.out.println(hand2);
System.out.println("第3个人得到的牌");
System.out.println(hand3);
System.out.println("剩余的牌");
System.out.println(cards);
}
}
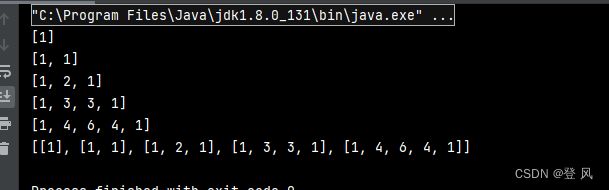
利用ArraryList构造出杨辉三角(采用直角三角形的样式)
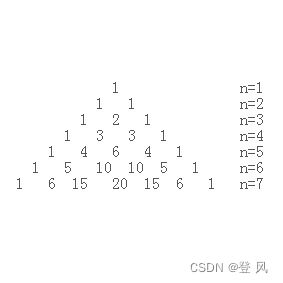
同3个人玩扑克牌一样,这里我们也构造出一个二维的顺序表
用ret来存储所有的行,list用来存储每一行的元素
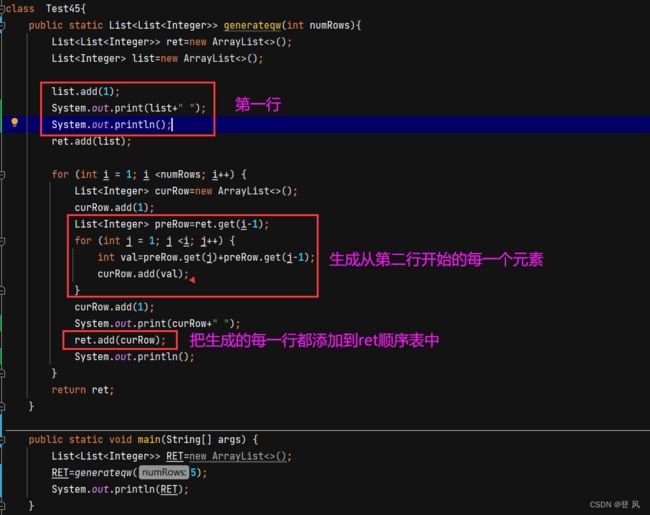
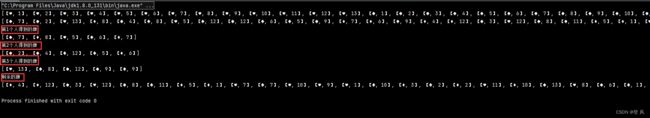
运行结果如下