Servlet3.0
Servlet3.0是基于注解配置的理论基础。
Servlet3.0引入了基于注解配置Servlet的规范,提出了可拔插的ServletContext初始化方式,引入了一个叫ServletContainerInitializer的接口。
An instance of the ServletContainerInitializer is looked up via the jar services API by the container at container / application startup time. The framework providing an implementation of the ServletContainerInitializer MUST bundle in the META-INF/services directory of the jar file a file called javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer, as per the jar services API, that points to the implementation class of the ServletContainerInitializer.
Servlet3.0规范约定:WEB容器(比如tomcat)要通过SPI的方式检查应用jar包的META-INF/services目录下的Servlet容器的初始化类(ServletContainerInitializer接口的实现类),通过调用该实现类的onStartup方法完成Servlet容器的初始化。
此外,Servlet3.0还引入了@HandlesTypes注解,用来指定Servlet容器初始化过程中,WEB容器会认为应用中的哪些类(由@HandlesTypes指定)会参与到Servlet容器的初始化过程中来。
SpringMVC正是通过以上方式实现Servlet容器的初始化的!!!
SpringMVC Servlet容器初始化过程
按照上述理论的指引,探究注解方式配置Spring MVC的原理就没那么困难了。
先看下图: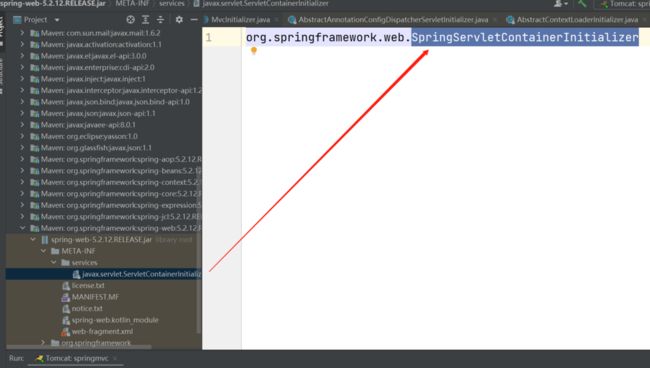
很容易的,我们发现SpringMVC指定的Servlet容器初始化的实现类为org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer。
所以我们找到他看看:
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
}确实是ServletContainerInitializer接口的实现类,@HandlesTypes指定的是WebApplicationInitializer,这个WebApplicationInitializer究竟是个啥东东,我们先放放,我们先来研究一下 SpringServletContainerInitializer类的onStartup方法。
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
} 代码逻辑也不算复杂,检查传入的参数webAppInitializerClasses,如果是实现类的话(不是接口或抽象类)则通过反射机制实例化webAppInitializerClasses并强转为WebApplicationInitializer,然后调用WebApplicationInitializer的onStartup方法。
这里有一个小问题:参数webAppInitializerClasses实例化之后,为什么能强转为WebApplicationInitializer?
其实这也是Servlet3.0规范约定的,WEB容器会根据@HandlesTypes的设置,从当前类加载器中查找符合条件的类,当前@HandlesTypes指定的正是WebApplicationInitializer。
之后的操作就都交给WebApplicationInitializer了。
WebApplicationInitializer
WebApplicationInitializer是承担起Servlet3.0规范约定的初始化Servlet容器的那个人:
Interface to be implemented in Servlet 3.0+ environments in order to configure the ServletContext programmatically -- as opposed to (or possibly in conjunction with) the traditional web.xml-based approach.
Implementations of this SPI will be detected automatically by SpringServletContainerInitializer, which itself is bootstrapped automatically by any Servlet 3.0 container. See its Javadoc for details on this bootstrapping mechanism.
我们先看一下他的类结构: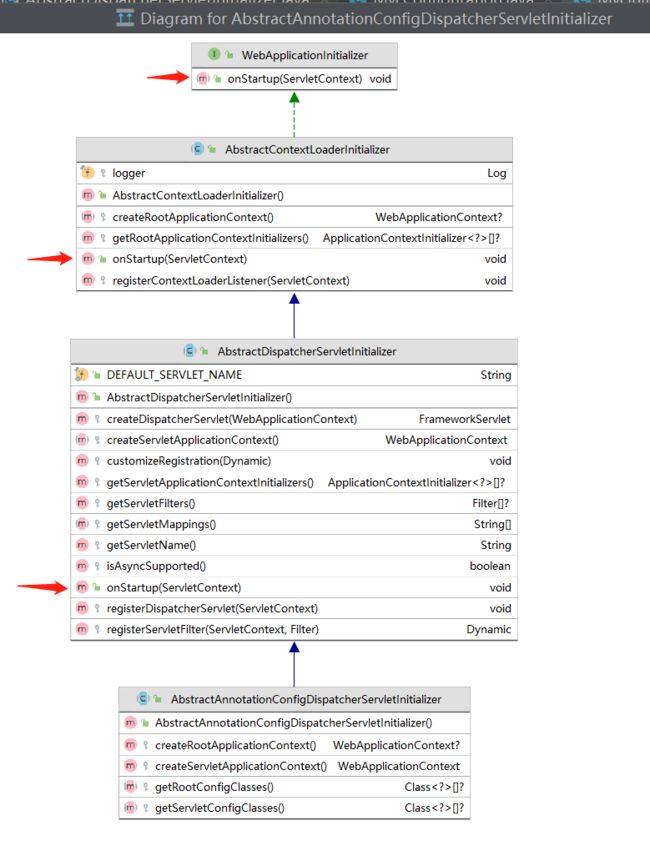
Spring框架实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口的3个抽象类,最后一个抽象类AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer没有onStartup方法,onStartup方法是他的父类实现的。
我们看一下他的父类AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer的onStartup方法:
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext);
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}可以发现他其实是一个模板方法,首先调用了父类的onStartup,之后调用registerDispatcherServlet方法。父类的onStartup方法是实现rootApplicationContext调用的,至于什么是rootApplicationContext我们暂时不管,我们先看一下registerDispatcherServlet方法:
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.notNull(dispatcherServlet, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
...省略代码首先调用createServletApplicationContext创建ServletApplicationContext(Servlet容器),之后创建DispathcerServlet并且把创建好的Servlet容器传递给DispatcherServlet(DispatcherServlet要记录他所在的ServletApplicationContext)。
关键代码出现了,Servlet容器的创建过程应该就在这个createServletApplicationContext方法中,是在AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer中实现的:
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
Class[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
context.register(configClasses);
}
return context;
}创建了一个新的AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext对象,然后调用getServletConfigClasses()方法获取配置类,之后把配置类注册到了新创建的AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext对象中。这个getServletConfigClasses()方法是没有实现的(应该是我们的实现类需要实现的)。
至此,Spring通过Servlet3.0规范进行初始化的过程应该已经很清晰了:
1.Spring Framework通过WebApplicationInitializer接口的onStartup方法完成Servlet上下文的初始化。
2.Spring Framework已经完成了WebApplicationInitializer接口的大部分实现(提供了3个抽象类),已经通过模板方法完成了大部分的初始化操作。
3. 猜测:应用层只需要扩展AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer类实现getServletConfigClasses()方法、返回Servlet的配置类,即可完成初始化。
接下来我们就验证一下上述猜测。
创建基于注解的Spring MVC应用
按照上述猜测,我们只需要扩展AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer、实现getServletConfigClasses()方法即可。
我们还是用上篇文章中用过的例子来验证,在动手之前,由于注解方式和web.xml配置方式是冲突的(配置方式会覆盖掉注解方式),所以我们需要删掉web.xml文件(copy出去即可)。
创建一个configuration包,并创建配置类(只要配置Controller的扫描路径即可):
package org.example.configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example.controller")
public class MvcConfiguration {
}然后再创建initializer的实现类:
package org.example.configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class MvcInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[0];
}
@Override
protected Class[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] {MvcConfiguration.class};
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] {"/"};
}
}其中RootConfigClasse()方法是为RootApplicationContext服务的,我们前面说过了,展示不管这个RootApplicationContext是什么,现在依然也不管他。
getServletConfigClasses方法,返回我们创建的初始化类。
还有一个getServletMappings方法,上面没有提到过,其实是起到web.xml中的servlet-mapping配置的作用的,所以我们直接返回"/" - 默认匹配规则。
启动项目,访问:
大功告成!