设计模式之命令模式(C++实现)
更多设计模式参看: 设计模式之模式概述(模式汇总)(C++实现)
文章目录
- 介绍
-
- 意图:
- 解决问题:
- 实现概述:
- 要点:
- 应用场景:
-
- 生活中场景
- 优点:
- 缺点:
- 模式结构
-
- 角色
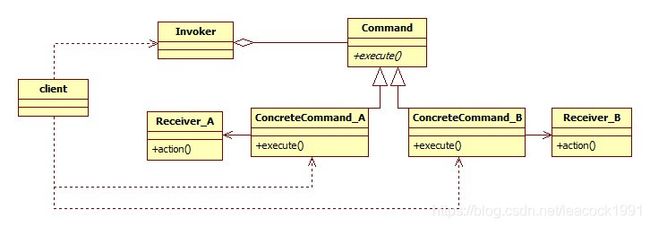
- 类图
- 代码示例
-
- GitHub
- Command(抽象命令类)
- Receiver(接收者)
- ConcreteCommand(具体命令类)
- Invoker(调用者)
- CommandVector 命令集合
- Invoker(调用者)命令集合
- 单命令
-
- 测试
- 输出
- 命令组合
-
- 测试
- 输出
介绍
在软件开发中,需要向某些对象发送请求(相当于调用其中的某个或某些方法),却并不知道请求的接收者是谁,也不知道被请求的操作是哪个,这时需要一种松耦合的方式来设计软件,来消除请求发送者与请求接收者之间的耦合。命令模式为此类问题提供了一个较为完美的解决方案。
意图:
命令模式(Command Pattern): 将一个请求(命令)封装为一个对象,从而让我们可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化(将不同请求依赖注入到其他对象);并且能支持对请求排队或者记录请求(命令)日志,以及支持可撤销的操作。
命令模式的本质是对请求进行封装,将发出命令的责任和执行命令的责任分割开,一个请求对应于一个命令。命令模式允许请求的一方和接收的一方独立开来,使得请求的一方不必知道接收请求的一方的接口,更不必知道请求如何被接收、操作是否被执行、何时被执行,以及是怎么被执行的。
解决问题:
解决行为请求者与行为实现者需要一种松耦合的关系,比如要对行为进行"记录、撤销/重做、事务"等处理。
实现概述:
命令模式可以将请求发送者和接收者完全解耦,发送者与接收者之间没有直接引用关系,发送请求的对象只需要知道如何发送请求,而不必知道如何完成请求。顺序:调用者→命令→接收者。
要点:
命令模式的核心在于引入了命令类,通过命令类来降低发送者和接收者的耦合度,请求发送者只需指定一个命令对象,再通过命令对象来调用请求接收者的处理方法。可以通过构造注入或者设值注入的方式在运行时传入具体命令类对象,并在业务方法中调用命令对象的execute()方法
应用场景:
- 需要将请求发送者和接收者解耦,使得发送者和接收者互不影响。请求调用者无须知道接收者的存在,也无须知道接收者是谁,接收者也无须关心何时被调用。
- 需要在不同时间指定请求、将请求排队和执行请求。
- 需要支持命令的撤销和恢复操作。
- 需要将一组操作组合在一起形成宏命令。
生活中场景
开关,未使用前并不知道它将来到底用于控制什么电器,开关与电器并无直接关系,它在安装之后可能用来控制电灯,也可能用来控制其他设备。
开关和电器之间并不存在直接耦合关系,它们通过电线连接在一起,使用不同的电线可以连接不同的请求接收者,只需更换一根电线,相同的发送者(开关)即可对应不同的接收者(电器)。
优点:
- 降低系统耦合度。请求发送者和接收者解耦,各自独立互不影响。
- 新的命令很容易加入到系统中,只需增加命令类不影响其他代码。
- 可以比较容易地设计一个命令队列或宏命令(组合命令)。
- 为请求的撤销(Undo)和恢复(Redo)操作提供了一种设计和实现方案。
缺点:
命令模式针对的是接收者不明确的情况,此时接收者是无法做到抽象的。所以才引入抽象命令的概念,通过抽象命令来封装接收者,以达到开闭原则、依赖倒转原则的目的。缺点也很明显,每个接收者都要对应一个具体命令,类的个数会增加。
模式结构
角色
Command(抽象命令类): 抽象命令类一般是一个抽象类或接口,声明了用于执行命令的接口execute()。
ConcreteCommand(具体命令类): 抽象命令类的子类,实现了在抽象命令类中声明的方法。它对应具体的接收者对象(类中包含),将接收者的动作绑定其中。在execu()方法中将调用接收者的动作action()。
Invoker(调用者): 请求的发送者,通过命令对象来执行请求。调用者不需要在设计时确定其接收者,它只与抽象命令类之间存在关联关系。具体实现中,可以将一个具体命令对象通过构造注入或者设值注入到调用者中,再通过调用具体命令对象的execute()方法,从而间接调用请求命令执行者(接收者)的操作。
Receiver(接收者): 实现处理请求的具体操作(action)。
类图
代码示例
使用命令模式,模拟开关控制电器,开关按钮Button,打开或者关闭灯Lamp(命令类 LampCommand),打开或者关闭风扇Fan(命令类 FanCommand),每次 Switch 开关发送命令执行对应操作。
Command(抽象命令类): Command
ConcreteCommand(具体命令类): LampCommand 、 FanCommand
Invoker(调用者):Switch 、SwitchVector(处理 CommandVector 命令集合)
Receiver(接收者): Lamp 、 Fan
命令集合 : CommandVector
GitHub
CommandPattern
Command(抽象命令类)
/// Command(抽象命令类): Command
class Command {
public:
virtual ~Command() = default;
// 声明抽象接口:执行命令
virtual void execute() = 0;
protected:
Command() = default;
};
Receiver(接收者)
/// Receiver(接收者): Lamp 、 Fan
class Lamp {
public:
Lamp() {
lampState = false;
std::cout << "Lamp Hello" << std::endl;
}
~Lamp() {
std::cout << "Lamp Bye" << std::endl;
}
void lampOn() {
lampState = true;
std::cout << "Lamp On" << std::endl;
}
void lampOff() {
lampState = false;
std::cout << "Lamp Off" << std::endl;
}
bool getLampState(){
return lampState;
}
private:
bool lampState;
};
class Fan {
public:
Fan() {
fanState = false;
std::cout << "Fan Hello" << std::endl;
}
~Fan() {
std::cout << "Fan Bye" << std::endl;
}
void fanOn() {
fanState = true;
std::cout << "Fan On" << std::endl;
}
void fanOff() {
fanState = false;
std::cout << "Fan Off" << std::endl;
}
bool getFanState(){
return fanState;
}
private:
bool fanState;
};
ConcreteCommand(具体命令类)
/// ConcreteCommand(具体命令类): LampCommand 、 FanCommand
class LampCommand : public Command {
public:
LampCommand() {
std::cout << "LampCommand Hello" << std::endl;
lamp = new Lamp();
}
~LampCommand() override {
std::cout << "LampCommand Bye" << std::endl;
delete lamp;
}
void execute() override{
if(lamp->getLampState()) { // true
lamp->lampOff(); // false
} else {
lamp->lampOn();
}
}
private:
Lamp *lamp;
};
class FanCommand : public Command {
public:
FanCommand() {
std::cout << "FanCommand Hello" << std::endl;
fan = new Fan();
}
~FanCommand() override {
std::cout << "FanCommand Bye" << std::endl;
delete fan;
}
void execute() override{
if(fan->getFanState()) { // true
fan->fanOff(); // false
} else {
fan->fanOn();
}
}
private:
Fan *fan;
};
Invoker(调用者)
/// Invoker(调用者):Switch
class Switch {
public:
Switch() {
std::cout << "Switch Hello" << std::endl;
command = nullptr;
}
~Switch() {
std::cout << "Switch Bye" << std::endl;
delete command;
}
// 设值注入具体命令类对象
void setCommand(Command *cmd){
delete command;// 删除之前命令
command = cmd;
}
// 发送命令:切换开关
void touch(){
std::cout << "切换开关:" << std::endl;
command->execute();
}
private:
Command *command;
};
CommandVector 命令集合
/// CommandVector 命令集合 示例
class CommandVector {
public:
CommandVector() {
std::cout << "CommandVector Hello" << std::endl;
}
~CommandVector() {
std::cout << "CommandVector Bye" << std::endl;
for(auto command : commandVector) {
delete command;
}
}
void addCommand(Command *cmd) {
commandVector.push_back(cmd);
}
void execute() { // 直接调用 commandVector 中元素 的 execute
for(auto command : commandVector) {
command->execute();
}
}
private:
std::vector<Command *> commandVector;
};
Invoker(调用者)命令集合
/// Invoker(调用者):SwitchVector 处理 CommandVector 命令集合
class SwitchVector {
public:
SwitchVector() {
std::cout << "SwitchVector Hello" << std::endl;
commandVector = nullptr;
}
~SwitchVector() {
std::cout << "SwitchVector Bye" << std::endl;
delete commandVector;
}
// 设值注入具体命令类对象
void setCommandVector(CommandVector *vector){
commandVector = vector;
}
// 发送命令:切换开关
void touch(){
if(nullptr!=commandVector) {
std::cout << "切换开关:" << std::endl;
commandVector->execute();
} else {
std::cout << "commandVector 为空" << std::endl;
}
}
private:
CommandVector *commandVector;
};
单命令
测试
int main() {
// 实例化调用者:开关 (调用者)
auto *pSwitch = new Switch();
// (具体命令) , Switch 中 函数 setCommand和析构 会处理 命令 Command
Command *lampCmd, *fanCmd;
std::cout << "====Lamp Test====" << std::endl;
// 按钮 控制 电灯 Lamp
lampCmd = new LampCommand(); // 具体命令
pSwitch->setCommand(lampCmd);
pSwitch->touch(); // 开
pSwitch->touch(); // 关
pSwitch->touch(); // 开
std::cout << "====Fan Test====" << std::endl;
// 按钮控制风扇
fanCmd = new FanCommand();
pSwitch->setCommand(fanCmd);
pSwitch->touch(); // 开
pSwitch->touch(); // 关
pSwitch->touch(); // 开
std::cout << "==============" << std::endl;
delete pSwitch;
return 0;
}
输出
命令组合
测试
int main() {
// 实例化调用者:开关 (调用者)
auto *pSwitchVector = new SwitchVector();
// (具体命令) , pSwitchVector 中 析构 会处理 commandVector
Command *lampCmd, *fanCmd;
// 命令集合
auto *commandVector = new CommandVector();
std::cout << "====CommandVector Test====" << std::endl;
// 按钮 控制 电灯 Lamp
lampCmd = new LampCommand(); // 具体命令
commandVector->addCommand(lampCmd);
// 按钮控制风扇
fanCmd = new FanCommand();
commandVector->addCommand(fanCmd);
pSwitchVector->setCommandVector(commandVector);
pSwitchVector->touch(); // 开
pSwitchVector->touch(); // 关
pSwitchVector->touch(); // 开
delete pSwitchVector;
return 0;
}
输出
个人能力有限,如有错误之处或者其他建议,敬请告知欢迎探讨,谢谢!