GPS软件应用 Geometry 对象浅析
GPS软件应用 Geometry 对象浅析
来源:GPS之家-导航之家 作者:www.gpsuu.com 时间:2008-01-18
GPS软件应用 Geometry 对象浅析
ArcEngine Geometry库定义了基本几何图形的矢量表达形式,顶级的几何图形有Points、Multipoints、Polylines、Polygons、 Multipatches,Geodatabase和绘图系统使用这些几何图形来定义其他各种形状的特征和图形,提供了编辑图形的操作方法和地图符号系统 符号化特征数据的途径。
Geometry库中几个核心类和接口构成了Geometry对象的基本框架。
GeometryEnvironment
GeometryEnvironment提供了从不同的输入、设置或获取全局变量来创建几何图形的方法,以便控制geometry方法的行为。GeometryEnvironment对象是一个单例对象。
 public IPolyline TestGeometryEnvironment()
public IPolyline TestGeometryEnvironment()

 {
{ ISpatialReferenceFactory spatialReferenceFactory = new SpatialReferenceEnvironmentClass();
ISpatialReferenceFactory spatialReferenceFactory = new SpatialReferenceEnvironmentClass();
 //Create a projected coordinate system and define its domain, resolution, and x,y tolerance.
//Create a projected coordinate system and define its domain, resolution, and x,y tolerance. ISpatialReferenceResolution spatialReferenceResolution = spatialReferenceFactory.CreateProjectedCoordinateSystem((int)esriSRProjCSType.esriSRProjCS_NAD1983UTM_11N) as ISpatialReferenceResolution;
ISpatialReferenceResolution spatialReferenceResolution = spatialReferenceFactory.CreateProjectedCoordinateSystem((int)esriSRProjCSType.esriSRProjCS_NAD1983UTM_11N) as ISpatialReferenceResolution; spatialReferenceResolution.ConstructFromHorizon();
spatialReferenceResolution.ConstructFromHorizon(); ISpatialReferenceTolerance spatialReferenceTolerance = spatialReferenceResolution as ISpatialReferenceTolerance;
ISpatialReferenceTolerance spatialReferenceTolerance = spatialReferenceResolution as ISpatialReferenceTolerance; spatialReferenceTolerance.SetDefaultXYTolerance();
spatialReferenceTolerance.SetDefaultXYTolerance(); ISpatialReference spatialReference = spatialReferenceResolution as ISpatialReference;
ISpatialReference spatialReference = spatialReferenceResolution as ISpatialReference;
 //Create an array of WKSPoint structures starting in the middle of the x,y domain of the
//Create an array of WKSPoint structures starting in the middle of the x,y domain of the  //projected coordinate system.
//projected coordinate system.
 double xMin;
double xMin; double xMax;
double xMax; double yMin;
double yMin; double yMax;
double yMax; spatialReference.GetDomain(out xMin, out xMax, out yMin, out yMax);
spatialReference.GetDomain(out xMin, out xMax, out yMin, out yMax);
 double xFactor = (xMin + xMax) * 0.5;
double xFactor = (xMin + xMax) * 0.5; double yFactor = (yMin + yMax) * 0.5;
double yFactor = (yMin + yMax) * 0.5;
 WKSPoint[] wksPoints = new WKSPoint[10];
WKSPoint[] wksPoints = new WKSPoint[10]; for (int i = 0; i < wksPoints.Length; i++)
for (int i = 0; i < wksPoints.Length; i++) {
{ wksPoints[i].X = xFactor + i;
wksPoints[i].X = xFactor + i; wksPoints[i].Y = yFactor + i;
wksPoints[i].Y = yFactor + i; }
}
 IPointCollection4 pointCollection = new PolylineClass();
IPointCollection4 pointCollection = new PolylineClass();
 IGeometryBridge2 geometryBridge = new GeometryEnvironmentClass();
IGeometryBridge2 geometryBridge = new GeometryEnvironmentClass(); geometryBridge.AddWKSPoints(pointCollection, ref wksPoints);
geometryBridge.AddWKSPoints(pointCollection, ref wksPoints);
 IPolyline polyline = pointCollection as IPolyline;
IPolyline polyline = pointCollection as IPolyline; polyline.SpatialReference = spatialReference;
polyline.SpatialReference = spatialReference;
 return polyline;
return polyline; }
}
new GeometryEnvironmentClass仅仅是创建了一个指向已存在的GeometryEnvironmentClass的引用。注意 IGeometryBridge2接口的使用,addWKSPoints方法将WKSPoint二维点添加到PointCollection中,用于构建 path、ring、polyline、polygon,或增加新点到Multipoint、TriangleFan、TriangleStrip。在 Geometry库中,除了IGeometryBridge2还有IGeometryBridge接口,后者继承了前者,增加了一些编辑功能(添加点、插 入点、重置点、分段等)。
GeometryBag
GeometryBag是支持IGeometry接口的几何对象引用的集合,任何几何对象都可以通过IGeometryCollection接口添加到 GeometryBag中,但是在使用拓扑操作的时候,需要注意不同类型的几何类型可能会有相互不兼容的情况。在向GeometryBag中添加几何对象 的时候,GeometryBag对象需要指定空间参考,添加到其中的几何对象均拥有和GeometryBag对象一样的空间参考。
 private IPolygon GeometryBag_Example(IFeatureClass featureClass)
private IPolygon GeometryBag_Example(IFeatureClass featureClass)


 {
{
 //Check input objects.
//Check input objects. if (featureClass == null)
if (featureClass == null)

 {
{ return null;
return null; }
}
 IGeoDataset geoDataset = featureClass as IGeoDataset;
IGeoDataset geoDataset = featureClass as IGeoDataset; ISpatialFilter queryFilter = new SpatialFilterClass();
ISpatialFilter queryFilter = new SpatialFilterClass();
 //Set the properties of the spatial filter here.
//Set the properties of the spatial filter here. IGeometry geometryBag = new GeometryBagClass();
IGeometry geometryBag = new GeometryBagClass();
 //Define the spatial reference of the bag before adding geometries to it.
//Define the spatial reference of the bag before adding geometries to it. geometryBag.SpatialReference = geoDataset.SpatialReference;
geometryBag.SpatialReference = geoDataset.SpatialReference;
 //Use a nonrecycling cursor so each returned geometry is a separate object.
//Use a nonrecycling cursor so each returned geometry is a separate object.  IFeatureCursor featureCursor = featureClass.Search(queryFilter, false);
IFeatureCursor featureCursor = featureClass.Search(queryFilter, false);
 IGeometryCollection geometryCollection = geometryBag as IGeometryCollection;
IGeometryCollection geometryCollection = geometryBag as IGeometryCollection; IFeature currentFeature = featureCursor.NextFeature();
IFeature currentFeature = featureCursor.NextFeature();
 while (currentFeature != null)
while (currentFeature != null)

 {
{ //Add a reference to this feature's geometry into the bag.
//Add a reference to this feature's geometry into the bag. //You don't specify the before or after geometry (missing),
//You don't specify the before or after geometry (missing), //so the currentFeature.Shape IGeometry is added to the end of the geometryCollection.
//so the currentFeature.Shape IGeometry is added to the end of the geometryCollection. object missing = Type.Missing;
object missing = Type.Missing; geometryCollection.AddGeometry(currentFeature.Shape, ref missing, ref missing);
geometryCollection.AddGeometry(currentFeature.Shape, ref missing, ref missing);
 currentFeature = featureCursor.NextFeature();
currentFeature = featureCursor.NextFeature(); }
}
 // Create the polygon that will be the union of the features returned from the search cursor.
// Create the polygon that will be the union of the features returned from the search cursor. // The spatial reference of this feature does not need to be set ahead of time. The
// The spatial reference of this feature does not need to be set ahead of time. The  // ConstructUnion method defines the constructed polygon's spatial reference to be the same as
// ConstructUnion method defines the constructed polygon's spatial reference to be the same as  // the input geometry bag.
// the input geometry bag. ITopologicalOperator unionedPolygon = new PolygonClass();
ITopologicalOperator unionedPolygon = new PolygonClass(); unionedPolygon.ConstructUnion(geometryBag as IEnumGeometry);
unionedPolygon.ConstructUnion(geometryBag as IEnumGeometry);
 return unionedPolygon as IPolygon;
return unionedPolygon as IPolygon; }
}
Points
一个点包括X、Y坐标,同时可以增加M、Z值及ID属性来扩展点的功能。
Multipoints
点的集合,多点组成Multipoint几何类型,使用multipoint对象实现了的IPointCollection接口可以访问所有的点元素,这些点同样可以拥有M、Z值及ID属性来获得更多的地理空间内涵。
下面列举一个例子,通过一个已知的polyline来定义一个新的multipart polyline。
 public IPolyline ConstructMultiPartPolyline(IPolyline inputPolyline)
public IPolyline ConstructMultiPartPolyline(IPolyline inputPolyline)


 {
{ IGeometry outGeometry = new PolylineClass();
IGeometry outGeometry = new PolylineClass();
 //Always associate new, top-level geometries with an appropriate spatial reference.
//Always associate new, top-level geometries with an appropriate spatial reference. outGeometry.SpatialReference = inputPolyline.SpatialReference;
outGeometry.SpatialReference = inputPolyline.SpatialReference; 
 IGeometryCollection geometryCollection = outGeometry as IGeometryCollection;
IGeometryCollection geometryCollection = outGeometry as IGeometryCollection;
 ISegmentCollection segmentCollection = inputPolyline as ISegmentCollection;
ISegmentCollection segmentCollection = inputPolyline as ISegmentCollection;
 //Iterate over existing polyline segments using a segment enumerator.
//Iterate over existing polyline segments using a segment enumerator. IEnumSegment segments = segmentCollection.EnumSegments;
IEnumSegment segments = segmentCollection.EnumSegments;
 ISegment currentSegment;
ISegment currentSegment; int partIndex = 0;;
int partIndex = 0;; int segmentIndex = 0;;
int segmentIndex = 0;;  segments.Next(out currentSegment,ref partIndex, ref segmentIndex);
segments.Next(out currentSegment,ref partIndex, ref segmentIndex); while(currentSegment != null)
while(currentSegment != null)

 {
{ ILine normal = new LineClass();
ILine normal = new LineClass();
 //Geometry methods with _Query_ in their name expect to modify existing geometries.
//Geometry methods with _Query_ in their name expect to modify existing geometries.  //In this case, the QueryNormal method modifies an existing line
//In this case, the QueryNormal method modifies an existing line //segment (normal) to be the normal vector to
//segment (normal) to be the normal vector to  //currentSegment at the specified location along currentSegment.
//currentSegment at the specified location along currentSegment. currentSegment.QueryNormal(esriSegmentExtension.esriNoExtension, 0.5, true, currentSegment.Length / 3, normal);
currentSegment.QueryNormal(esriSegmentExtension.esriNoExtension, 0.5, true, currentSegment.Length / 3, normal); 
 //Since each normal vector is not connected to others, create a new path for each one.
//Since each normal vector is not connected to others, create a new path for each one. ISegmentCollection newPath = new PathClass();
ISegmentCollection newPath = new PathClass(); object missing = Type.Missing;
object missing = Type.Missing; newPath.AddSegment(normal as ISegment, ref missing, ref missing);
newPath.AddSegment(normal as ISegment, ref missing, ref missing); //The spatial reference associated with geometryCollection will be assigned to all incoming paths and segments.
//The spatial reference associated with geometryCollection will be assigned to all incoming paths and segments. geometryCollection.AddGeometry(newPath as IGeometry, ref missing, ref missing);
geometryCollection.AddGeometry(newPath as IGeometry, ref missing, ref missing);
 segments.Next(out currentSegment,ref partIndex, ref segmentIndex);
segments.Next(out currentSegment,ref partIndex, ref segmentIndex); }
} //The geometryCollection now contains the new, multipart polyline.
//The geometryCollection now contains the new, multipart polyline. return geometryCollection as IPolyline;
return geometryCollection as IPolyline; }
}
ISegment接口的QueryNormal方法用来在弧段上的某一点生成该弧段的法线,指定其长度,这样就生成了新的segment,并且多个path添加到geometryCollection中,以IPolyline的形式返回。
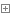
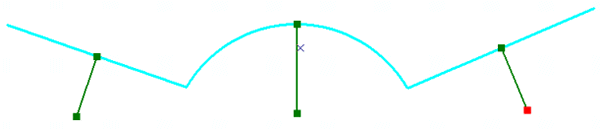
Polylines
Polylines是有序path组成的集合,可以拥有M、Z和ID属性值。Polyline对象的IPointCollection接口包含了所有节点 的复制,IGeometryCollection接口可以获取polyline的paths,ISegmentCollection接口可以获取 polyline的segments。
Polyline结构图
Polygons
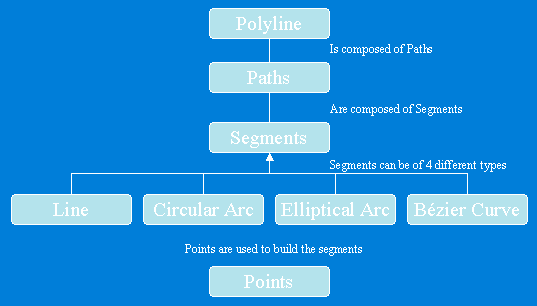
Polygon是一系列rings组成的集合,可以拥有M、Z和ID属性值。每一个ring由一个或多个segment组成,Polygon或ring对 象的IPointCollection接口包含了所有节点的复制,IGeometryCollection接口可以获取polygon的 rings,ISegmentCollection接口可以获取polygon的segments。
Polygon结构图
Multipatch
Multipatch用于描述3D面状几何类型,由一系列的矢量三角形构成,如果其中的part是一个ring,那么它必须是封闭的,第一个节点和最后一 个节点相同,另外每个part所包含节点的顺序非常重要,Inner Rings在Outer Rings之后,代表单个表面patch的一系列rings必须由第一个ring开始。
在9.0以后的开发包中,使用IGeneralMultiPatchCreator创建新的Multipatch,IGeometryMaterial进行材质贴图。
 public IMultiPatch CreateMultipatch()
public IMultiPatch CreateMultipatch()


 {
{ //Prepare the geometry material list.
//Prepare the geometry material list. IGeometryMaterial texture = new GeometryMaterialClass();
IGeometryMaterial texture = new GeometryMaterialClass(); texture.TextureImage = C:TempMyImage.bmp;
texture.TextureImage = C:TempMyImage.bmp;
 IGeometryMaterialList materialList = new GeometryMaterialListClass();
IGeometryMaterialList materialList = new GeometryMaterialListClass(); materialList.AddMaterial(texture);
materialList.AddMaterial(texture);
 //Create the multipatch.
//Create the multipatch. IGeneralMultiPatchCreator multiPatchCreator = new GeneralMultiPatchCreatorClass();
IGeneralMultiPatchCreator multiPatchCreator = new GeneralMultiPatchCreatorClass(); multiPatchCreator.Init(4, 1, false, false, false, 4, materialList);
multiPatchCreator.Init(4, 1, false, false, false, 4, materialList);
 //Set up part.
//Set up part.
 //Could also use a Ring or a TriangleFan.
//Could also use a Ring or a TriangleFan. multiPatchCreator.SetPatchType(0, esriPatchType.esriPatchTypeTriangleStrip);
multiPatchCreator.SetPatchType(0, esriPatchType.esriPatchTypeTriangleStrip); multiPatchCreator.SetMaterialIndex(0, 0);
multiPatchCreator.SetMaterialIndex(0, 0); multiPatchCreator.SetPatchPointIndex(0, 0);
multiPatchCreator.SetPatchPointIndex(0, 0); multiPatchCreator.SetPatchTexturePointIndex(0, 0);
multiPatchCreator.SetPatchTexturePointIndex(0, 0);
 //Set real-world points.
//Set real-world points. WKSPointZ upperLeft = new WKSPointZ();
WKSPointZ upperLeft = new WKSPointZ(); WKSPointZ lowerLeft = new WKSPointZ();
WKSPointZ lowerLeft = new WKSPointZ(); WKSPointZ upperRight = new WKSPointZ();
WKSPointZ upperRight = new WKSPointZ(); WKSPointZ lowerRight = new WKSPointZ();
WKSPointZ lowerRight = new WKSPointZ();
 upperLeft.X = 0;
upperLeft.X = 0; upperLeft.Y = 0;
upperLeft.Y = 0; upperLeft.Z = 0;
upperLeft.Z = 0; upperRight.X = 300;
upperRight.X = 300; upperRight.Y = 0;
upperRight.Y = 0; upperRight.Z = 0;
upperRight.Z = 0; lowerLeft.X = 0;
lowerLeft.X = 0; lowerLeft.Y = 0;
lowerLeft.Y = 0; lowerLeft.Z = -100;
lowerLeft.Z = -100; lowerRight.X = 300;
lowerRight.X = 300; lowerRight.Y = 1;
lowerRight.Y = 1; lowerRight.Z = -100;
lowerRight.Z = -100;
 multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(0, ref upperRight);
multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(0, ref upperRight); multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(1, ref lowerRight);
multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(1, ref lowerRight); multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(2, ref upperLeft);
multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(2, ref upperLeft); multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(3, ref lowerLeft);
multiPatchCreator.SetWKSPointZ(3, ref lowerLeft);
 //Set texture points.
//Set texture points. //Set the texture coordinates for a panel.
//Set the texture coordinates for a panel. WKSPoint textureUpperLeft = new WKSPoint();
WKSPoint textureUpperLeft = new WKSPoint(); WKSPoint textureLowerLeft = new WKSPoint();
WKSPoint textureLowerLeft = new WKSPoint(); WKSPoint textureUpperRight = new WKSPoint();
WKSPoint textureUpperRight = new WKSPoint(); WKSPoint textureLowerRight = new WKSPoint();
WKSPoint textureLowerRight = new WKSPoint();
 textureUpperLeft.X = 0;
textureUpperLeft.X = 0; textureUpperLeft.Y = 0;
textureUpperLeft.Y = 0; textureUpperRight.X = 1;
textureUpperRight.X = 1; textureUpperRight.Y = 0;
textureUpperRight.Y = 0; textureLowerLeft.X = 0;
textureLowerLeft.X = 0; textureLowerLeft.Y = 1;
textureLowerLeft.Y = 1; textureLowerRight.X = 1;
textureLowerRight.X = 1; textureLowerRight.Y = 1;
textureLowerRight.Y = 1;
 multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(0, ref textureUpperRight);
multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(0, ref textureUpperRight); multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(1, ref textureLowerRight);
multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(1, ref textureLowerRight); multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(2, ref textureUpperLeft);
multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(2, ref textureUpperLeft); multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(3, ref textureLowerLeft);
multiPatchCreator.SetTextureWKSPoint(3, ref textureLowerLeft); IMultiPatch multiPatch = multiPatchCreator.CreateMultiPatch() as IMultiPatch;
IMultiPatch multiPatch = multiPatchCreator.CreateMultiPatch() as IMultiPatch;
 return multiPatch;
return multiPatch; }
}