二叉树的迭代遍历
二叉树的迭代遍历
前序遍历
基本思路
基本思路其实很简单, 使用递归遍历的时候, 一直是系统帮我们把其他数据压栈, 举个例子
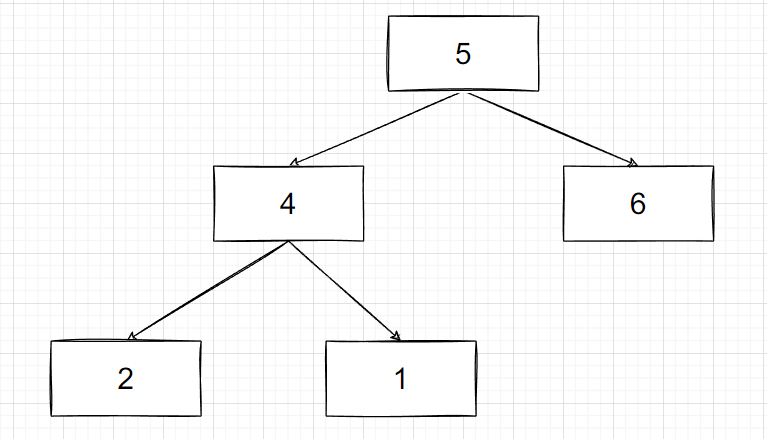
=> ans = [5,4,6,2,1,null,null]
前序遍历的序列是: [5,4,2,1,6] , 栈的出入顺序是, 先入, 后出, 假如我们想要一个元素先出, 就要让它后入栈
基本思路就是 : 先把 root = 5 入栈 , 然后出栈, 访问 5 , 然后把 5 的 右子树 和 左子树节点(注意是右子树和左子树)分别入栈
此时栈内 : {6, 4} 栈顶是 4, 然后我们再把栈顶元素 4 出栈, 访问 4, 再把 4的右子树和左子树的节点入栈
此时栈内容 : {6, 1, 2} 再把栈顶元素 2出栈, 重复上面的过程,

在这个过程中, 因为我们是先把右子树入栈, 再入栈的左子树, 所以保证了左子树在栈顶, 所以在出栈时, 左子树先出栈, 右子树后出栈
算法流程 :
- 将root入栈
- 将栈顶元素出栈, node = stack.pop() , 将node.val 存入结果数组, 将node.right和node.left放入栈
- 重复上面过程
- stack.isEmpty() 算法结束
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private LinkedList<Integer> ans = new LinkedList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ans;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
stack.add(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
// 访问节点
ans.add(node.val);
// 将其右子树和左子树节点放入
if(node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
if(node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
中序遍历
基本思路
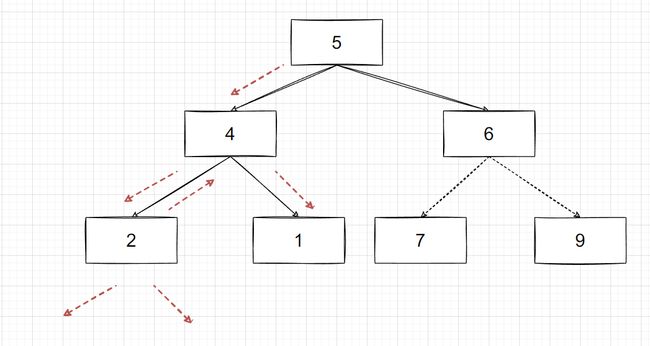
使用一个指针 p 一直向左走, 将走过的节点放入栈中, 这里注意, 栈是先入后出的, 所以出栈时的顺序正好是我们中序遍历的顺序, 当指针走到叶子节点时,
继续向左走就会指向null, 如上图 :
此时栈中 {5,4,2} , p 此时指向 2 的左子树, 但是左子树是null, 我们就需要将栈顶元素出栈 2 , 此时指针再指向 2 的右子树, 以此类推,
继续向左走,
算法流程 :
- p 指向 root
- p != null p 一直向左边移动 : p = p.left
- p == null , node = stack.pop() 出栈, 将栈顶元素放入结果集, p = node.right;
- p == null || stack.isEmpty , 算法结束
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ans;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// 让指针一直向左走
if(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
// 为空, 说明走到最左边了
// 元素出栈
// cur 之前一直是指向左边, 此时为null, 说明左边没有
// 取出根节点
cur = stack.pop();
ans.add(cur.val);
// 向右移动
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
后续遍历
和前序遍历思路一样, 但是需要简单调整下, 前序遍历是 中左右, 后序是左右中, 我们只需要让前序遍历添加左右子树时先添加 左子树, 后添加右子树
得到 中右左的顺序, 然后再逆序即可.
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ans;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
// 出栈
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
ans.add(node.val);
// 前序是 中左右, 后续是 左右中
// 前序逆序后 右左中, 我们只要在添加的时候
// 让顺序是 中右左, 这样逆序后就是 左右中, 就是后序的顺序了
if(node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
}
// 将左子树和右子树入栈
if(node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
// 反转结果
Collections.reverse(ans);
return ans;
}
}
层序遍历
基本思路
层序的遍历思路很简单, 借助队列先入先出的思想, 我们只需要不断的把根节点存入, 然后按照队列顺序取出, 取出时再把它们的子树节点存入, 以此类推
关键点是 :
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
LinkedList<Integer> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
ans.add(tmp);
}
在循环内部, 我们先获取 当前队列的size, 然后再用for循环, 去将当前队列中当前层的元素取出
代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return ans;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
LinkedList<Integer> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.remove();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
ans.add(tmp);
}
return ans;
}
}