注册字符设备
五、注册字符设备
struct cdev
{
struct kobject kobj;//表示该类型实体是一种内核对象
struct module *owner;//填THIS_MODULE,表示该字符设备从属于哪个内核模块
const struct file_operations *ops;//指向空间存放着针对该设备的各种操作函数地址
struct list_head list;//链表指针域
dev_t dev;//设备号
unsigned int count;//设备数量
};
自己定义的结构体中必须有一个成员为 struct cdev cdev,两种方法定义一个设备:
-
直接定义:定义结构体全局变量
-
动态申请:
struct cdev * cdev_alloc()
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev,const struct file_operations *fops)
struct file_operations
{
struct module *owner; //填THIS_MODULE,表示该结构体对象从属于哪个内核模块
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); //打开设备
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); //关闭设备
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); //读设备
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); //写设备
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); //定位
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);//读写设备参数,读设备状态、控制设备
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); //POLL机制,实现多路复用的支持
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); //映射内核空间到用户层
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int); //信号驱动
//......
};
该对象各个函数指针成员都对应相应的系统调用函数,应用层通过调用系统函数来间接调用这些函数指针成员指向的设备驱动函数:
一般定义一个struct file_operations类型的全局变量并用自己实现各种操作函数名对其进行初始化
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p,dev_t dev,unsigned int count)
功能:将指定字符设备添加到内核
参数:
p:指向被添加的设备
dev:设备号
count:设备数量,一般填1
void cdev_del(struct cdev *p)
功能:从内核中移除一个字符设备
参数:
p:指向被移除的字符设备
小结:
字符设备驱动开发步骤:
- 如果设备有自己的一些控制数据,则定义一个包含struct cdev cdev成员的结构体struct mydev,其它成员根据设备需求,设备简单则直接用struct cdev
- 定义一个struct mydev或struct cdev的全局变量来表示本设备;也可以定义一个struct mydev或struct cdev的全局指针(记得在init时动态分配)
- 定义三个全局变量分别来表示主设备号、次设备号、设备数
- 定义一个struct file_operations结构体变量,其owner成员置成THIS_MODULE
- module init函数流程:a. 申请设备号 b. 如果是全局设备指针则动态分配代表本设备的结构体元素 c. 初始化struct cdev成员 d. 设置struct cdev的owner成员为THIS_MODULE e. 添加字符设备到内核
- module exit函数:a. 注销设备号 b. 从内核中移除struct cdev c. 如果如果是全局设备指针则释放其指向空间
- 编写各个操作函数并将函数名初始化给struct file_operations结构体变量
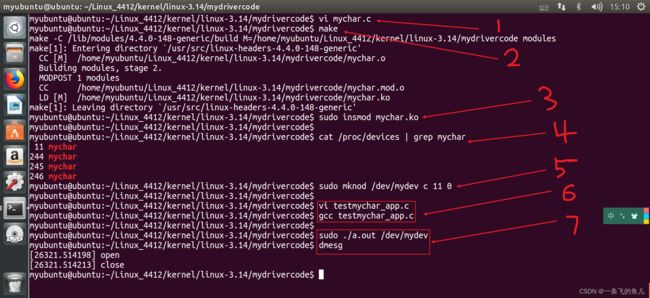
验证操作步骤:
- 编写驱动代码mychar.c
- make 生成ko文件
- sudo insmod mychar.ko 插入内核模块
- 查阅字符设备用到的设备号(主设备号):cat /proc/devices | grep <申请设备号时用的名字 (mychar)>
- 创建设备文件(设备节点) : mknod /dev/mydev c 上一步查询到的主设备号 代码中指定初始次设备号
- 编写app验证驱动(testmychar_app.c)
- 编译运行app,dmesg命令查看内核打印信息
代码实现:
mychar.c
#include testmychar_app.c
#include Makefile
ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
ifeq ($(ARCH),arm)
KERNELDIR ?= /home/linux/fs4412/linux-3.14
ROOTFS ?= /opt/4412/rootfs
else
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
endif
PWD := $(shell pwd)
modules:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
modules_install:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules INSTALL_MOD_PATH=$(ROOTFS) modules_install
clean:
rm -rf *.o *.ko .*.cmd *.mod.* modules.order Module.symvers .tmp_versions
else
xtt-objs = test.o func.o
endif