单链表oj题
1.反转链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/

思路一:遍历一遍的同时两两逆置
写法一:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode *cur,*ahead,*next;
cur=head;ahead=cur;
if(cur){
next=cur->next;
cur->next=NULL;
while(next){
cur=next;
next=cur->next;
cur->next=ahead;
ahead=cur;
}
head=cur;
}
return head;
}
写法二:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL;
n2=head;
if(n2){
n3=n2->next;
}
while(n2){
n2->next=n1;
n1=n2;n2=n3;
if(n3){
n3=n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
思路二:将原链表所有节点头插到一个空指针前
将原链表中的节点拿下来,头插到新链表,无需给每个节点都开辟新空间
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* newhead=NULL,*cur=head;
//最好在初始化节点时不要给节点赋有关某节点->next的值,
//万一该节点时空就会,是没有next的。
while(cur){
struct ListNode* next=cur->next;
cur->next=newhead;
newhead=cur;
cur=next;
}
return newhead;
}
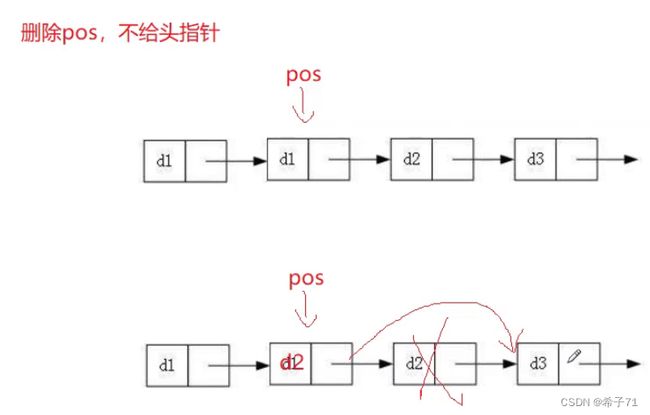
2.替换法删除
含义:不知道头结点的情况下删除给出的pos位置的结点
思路:将下一个节点的值赋给pos位置,删除下一个节点
代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include测试结果:
3.移除链表元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
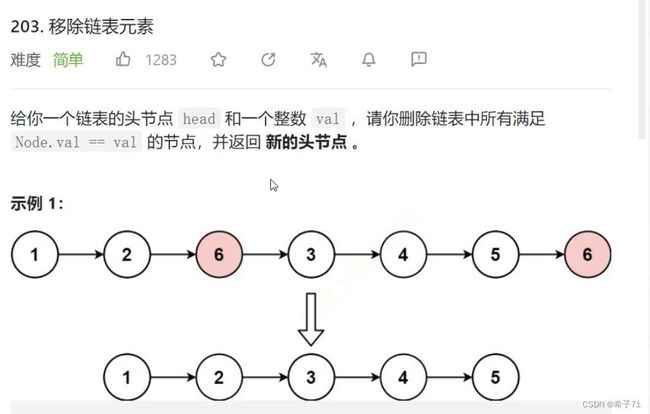
思路一:遍历链表,删除指定元素
第一个指针cur负责进入节点查看该节点是否需要删除,第二个指针prev紧跟第一个节点后面,方便删除节点。(不要用替换删除法,该方法删不了最后一个节点)。
写法一:通过等于val或不等于val,将节点分为两种情况
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode*prev=NULL,*cur=head;
while(cur){
if(cur->val==val){
if(cur==head){
head=head->next;
free(cur);
cur=head;
}
else{
prev->next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=prev->next;
}
}
else{
prev=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
写法二:将头节点和非头节点分开处理
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode*cur=head,*prev=head,*del=head;
while(cur){
if(head->val==val){
head=head->next;
free(del);
del=head;
prev=head;cur=head;
}
else {
cur=cur->next;
break;
}
}
while(cur){
if(cur->val!=val){
cur=cur->next;
prev=prev->next;
}
else{
prev->next=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=prev->next;
}
}
return head;
}
思路二:将值不是val的节点尾插到新链表中
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode*newhead=NULL,*tail=NULL;
while(cur){
if(cur->val==val){
struct ListNode*del=cur;
cur=cur->next;
free(del);
}
else{
if(tail==NULL){
newhead=tail=cur;
}
else{
tail->next=cur;
tail=tail->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
}
if(tail){
tail->next=NULL;
}
return newhead;
}
陷阱一:链表有可能是空链表,在将新链表的tail置空时要先判断tail是否为空。
陷阱二:遍历原链表的指针cur走向末尾的NULL停下时,尾插形成的新链表的尾节点的next要置空。
注意:
1.此方法不会使空间复杂度变高,因为链接的节点还是原链表中的,没有新开辟空间。
2.尾插一般都要再定义一个tail指针永远指向新链表的尾节点,是为了避免每次尾插时重新遍历链表找尾节点。
4.找到链表的中间节点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
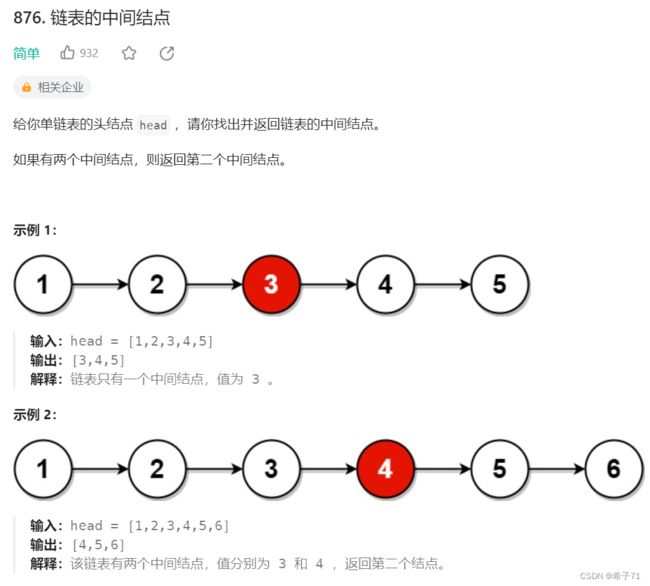
思路:快慢指针
最开始快指针fast和慢指针slow都指向头节点,fast每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步。

链表长度为奇数:fast指向尾节点时,slow就是中间节点。
链表长度为偶数:fast指向NULL时,slow指向中间两个节点的靠后的节点。
实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode*fast=head,*slow=head;
while(fast&&fast->next){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
注:while中的条件是且,只要fast或fast->next中一个是空就跳出循环
5.合并两个有序链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/

思路一:尾插到新链表
两串链表分别由两个指针遍历,二者取小的尾插到新链表中
实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
struct ListNode*newlist=NULL,*cur=NULL,*tail=NULL;
if(list1==NULL)
return list2;
else if(list2==NULL)
return list1;
while(list1&&list2){
if(list1->val<list2->val){
if(tail==NULL){
tail=newlist=list1;
}
else{
tail->next=list1;
tail=tail->next;
}
list1=list1->next;
}
else{
if(tail==NULL){
tail=newlist=list2;
}
else{
tail->next=list2;
tail=tail->next;
}
list2=list2->next;
}
}
if(list1){
tail->next=list1;
}
else if(list2){
tail->next=list2;
}
return newlist;
}
一开始要进行判断链表是否为空的原因:有可能连个链表有一个是空链表,也可能两个链表都为空。
注意:if、else if、else要符合逻辑,以下是一个错误案例:
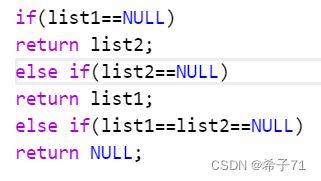
三条判断语句是分支关系,进入一条语句就默认进入不了其他语句,但很明显第三条判断语句成立时,前两条也会成立,这三条语句不是相互独立的分支关系。当不删除第三条判断时,程序会错误。
思路二:哨兵位法
不带哨兵位时,对于头节点的确定需要单独处理,带上哨兵位后,所有节点都可以用相同程序处理,最终返回哨兵位之后的那一个节点就行。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
struct ListNode* head=NULL,*tail=NULL;
if(list1==NULL)
return list2;
if(list2==NULL)
return list1;
head=tail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
while(list1&&list2){
if(list1->val<list2->val){
tail->next=list1;
list1=list1->next;
}
else{
tail->next=list2;
list2=list2->next;
}
tail=tail->next;
}
if(list1)
tail->next=list1;
else
tail->next=list2;
struct ListNode*del=head;
head=head->next;
free(del);
return head;
}
可不可以直接返回哨兵位的下一个节点?不可以,因为哨兵位是动态开辟的空间,必须要先释放掉哨兵位后才能返回。
6.输出链表倒数第k个节点
链接: https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/529d3ae5a407492994ad2a246518148a?tpId=13&tqId=11167&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking
思路:快慢指针,快指针先走k步
走法一:fast走k步后再与slow同时走,当fast走到NULL时,slow就是倒数第k个位置。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
/**
*
* @param pListHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode* fast,*slow;
fast=slow=pListHead;
while(k--){
if(fast==NULL)
return NULL;
fast=fast->next;
}
while(fast){
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
走法二:fast走k-1步后再与slow同时走,当fast走到尾节点时(fast->next=NULL),slow就是倒数第k个位置。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
/**
*
* @param pListHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode*fast,*slow;
fast=slow=pListHead;
while(--k){
if(!fast) return NULL;
fast=fast->next;
}
if(!fast) return NULL;
while(fast->next){
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
为何有两次“if(!fast) return NULL;”?
第一次在while中进行判断,排除掉k大于节点长度2或以上。
第二次在while后进行判断,排除掉k比节点长度大1的情况,例如当节点长度为5而k为6时,指针最终指向尾节点后的空指针出时,–k变成0,不会再进入循环,因此出循环后要立马返回空指针。如图:

7.链表分割
链接: https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking

思路:先分成两个链表,后合并
写法一:分开的两条链表都不带哨兵位
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
// write code here
ListNode* Lhead,*Ltail;
Lhead=Ltail=NULL;
ListNode* Ghead,*Gtail;
Ghead=Gtail=NULL;
ListNode* cur=pHead;
while(cur){
if(cur->val<x){
if(Ltail==NULL){
Lhead=Ltail=cur;
}
else{
Ltail->next=cur;
Ltail=Ltail->next;
}
}
else{
if(Gtail==NULL){
Ghead=Gtail=cur;
}
else{
Gtail->next=cur;
Gtail=Gtail->next
}
}
cur=cur->next;
}
if(!Ltail)
return Ghead;
Ltail->next=Ghead;
if(Gtail)
Gtail->next=NULL;
return Lhead;
}
};
写法二:将节点分别尾插到哨兵位后
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
// write code here
struct ListNode* Lhead,*Ltail,*Ghead,*Gtail;
Lhead=Ltail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
Ghead=Gtail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* cur=pHead;
while(cur){
if(cur->val<x){
Ltail->next=cur;
Ltail=Ltail->next;
}
else{
Gtail->next=cur;
Gtail=Gtail->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
Ltail->next=Ghead->next;
Gtail->next=NULL;
struct ListNode* head=Lhead->next;
free(Lhead);
free(Ghead);
return head;
};
};
注意:最终返回的是Lhead的下一个节点,并且要free掉Lhead和Ghead。
8.判断链表是否是回文结构
链接: https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking

思路:找中间点,逆置后半段,对分叉进行比较
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
struct ListNode* FindMiddleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* fast,*slow;
fast=slow=head;
while(fast&&fast->next){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct ListNode* ReverseList(struct ListNode* node){
struct ListNode* newhead,*cur,*intersection;
newhead=cur=intersection=node;
cur=cur->next;
while(cur){
struct ListNode* next=cur->next;
cur->next=newhead;
newhead=cur;
cur=next;
}
intersection->next=NULL;
return newhead;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
//先找到链表的中间节点
struct ListNode* middle=FindMiddleNode(head);
//逆置后半段链表
struct ListNode* head2=ReverseList(middle);
while(head&&head2){
if(head->val!=head2->val)
return false;
head=head->next;
head2=head2->next;
}
return true;
}
};
9.找出两相交链表的第一个公共结点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
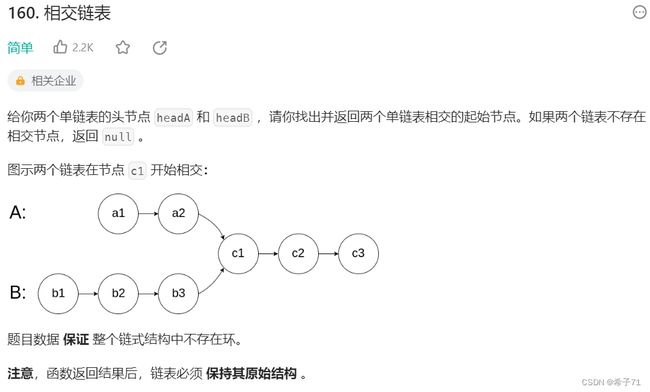
分析:
1.两链表相交不可能呈X形,在相交节点后两链表一定是重合的,因为一个节点不可能有两个next。
2.判断是否相交的方法:看尾节点是否相等。
3.找相交节点:先遍历两个链表,算出链表长度差,差几个节点则长链表先走几步。然后两链表同时走,边走边比较值,如果值开始相等,则该节点为首个相交节点。
注:暴力求解思路:将一个链表中的节点的地址值与另一链表中所有节点的地址值比较,直到发现地址相等,则该地址下的节点为首个相交节点。时间复杂度O(n^2)。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
//计算两链表长度
struct ListNode* cur1=headA,*cur2=headB;
if(!cur1) return NULL;
if(!cur2) return NULL;
int count1=1;
int count2=1;
while(cur1->next){
cur1=cur1->next;
count1++;
}
while(cur2->next){
cur2=cur2->next;
count2++;
}
if(cur1!=cur2) return NULL;
int sub=count1-count2;
//注意将cur1和cur2要重新指向原链表的头
cur1 = headA;cur2 = headB;
//让长链表先走差距步
if(sub>0){
while(sub){
cur1=cur1->next;
sub--;
}
}
else{
sub=-sub;
while(sub){
cur2=cur2->next;
sub--;
}
}
//两指针同时走,直到指向节点的地址相同
while(cur1!=cur2){
cur1=cur1->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
return cur1;
}
在最开始计算两链表长度时,while中的条件为什么是curA->next而不是curA?
答:如果是curA的话,跳出循环时指针指向的是尾节点后的空节点,此时无法进行尾节点的比较。如果是cur->next的话,跳出循环两个指针都指向尾节点,可以进行节点地址的比较,从而判断两链表是否相交。
小tip:手动构建一个链表方便调试oj
将以下代码复制到记事本中,并将文件命名为listOJ.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include