python网络爬虫与信息提取
python网络爬虫与信息提取
学习视频链接:
https://www.icourse163.org/learn/BIT-1001870001?tid=1464881473#/learn/announce
知识点:
工具:
一、网络爬虫之规则
1.requests库入门
安装requests库
request库的7个主要方法
requests.request()构造一个请求,支撑以下各方法的基础方法requests.get()获取html网页的主要方法requests.post()向网页提交post请求的方法requests.head()获取网页有信息的方法requests.put()向网页提交put请求requests.patch()向网页提交局部修改requests.delete()向网页提交删除请求
后面六个方法调用第一个方法实现的
get方法:
response=requests.get(url,params=None,**kwargs)
url:拟获取页面的url链接
params:url中的额外参数,字典或字节流格式,可选
**kwargs:12个控制访问的参数
Response对象
包含爬虫返回的内容
Response对象的属性:
r.status_coder.text http响应内容的字符串形式,即,url对应的页面内容r.encoding从http的header中猜测的响应内容编码方式r.apparent_encoding从内容中分析出的相应内容编码方式,备选编码方式r.contenthttp响应内容的二进制形式
理解编码:
r.encoding:如果header中不存在charset,则认为编码为ISO-8859-1,但不能解析中文。
r.apparent_encoding:根据网页内容分析编码格式
Request库的异常:
requests.ConnectionError:网络连接异常,如DNS查询失败,拒绝连接
requests.HTTPError:HTTP连接异常
requests.URLRequired:URL缺失异常
requests.TooManyRequests:超过最大重定向次数,产生重定向异常
requests.ConnectTimeout:连接远程服务器超时异常(仅指连接)
requests.Timeout 请求URL超时,产生超时异常,(发出URL请求到获得整个内容)
r.raise_for_status() 能够判断状态码,不是200,产生requests.HTTPError
爬取网页的通用代码框架
import requests
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r=requests.get(url,timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status() # 如果状态不是200,引发HTTPError异常
r.encoding=r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return "产生异常"
if __name__=="__main__":
url="https://www.baidu.com"
print(getHTMLText(url))
http方法:

patch和put的区别:
假设URL位置有一组数据UserInfo,包括UserID、UserName等20个字段。
需求:用于修改了UserName,其他不变。
- 采用patch,仅需向URL提交UserName的局部更新请求
- 采用put,必须将所有20个字段一并提交到URL,未提交字段将被删除
head方法,获取网络资源的概要信息
post方法,向网页提交信息
request方法,最基础的方法
requests.request(method,url,**kwargs)
**kwargs 访问控制参数,均为可选项
-
params:字典或字节序列,作为参数添加到url中
-
data:字典、字节序列、文件对象,作为Request的内容

-
json:JSON格式的数据,作为Request的内容向服务器提交

-
headers:字典,HTTP定制头
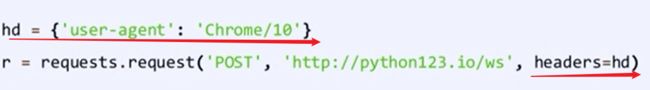
-
cookies:字典或CookieJar,Request中的cookie
-
auth:元组,支持HTTP认证功能
-
files:字典类型,传输提交文件

-
timeout:设定超时时间,秒为单位
-
proxies:字典类型,设定访问代理服务器,可以增加登录验证

-
allow_redirects:True/False,默认为True,重定向开关
-
stream:True/False,默认为True,获取内容立即下载开关
-
verify:True/False,默认为True,认证SSL证书开关
-
cert:本地SSL证书路径
requests.get(url,params=None,**kwargs)
requests.head(url,**kwargs)
requests.post(url,data=None,json=None,**kwargs)
requests.put(url,params=None,**kwargs)
requests.patch(url,params=None,**kwargs)
requests.delete(url,**kwargs)
2.网络爬虫的Robots协议

网络爬虫问题:
服务器性能骚扰、数据法律侵权、隐私泄露

Robots协议:
Robots Exclusion Standard 网络爬虫排除标准
作用:告知,哪些内容可以爬取,哪些内容不可以爬取
形式:在网站根目录下的robots.txs文件

Robots协议规定如果一个网站不提供robots.txt文件,默认允许被爬取。
3.requests库网络爬虫实战(5个实例)
实例1:京东商品页面的爬取
实例2:亚马逊商品的爬取
【注意】定制headers,避免被网站服务器识别为爬虫
一般只需要修改:
headers={'user-agent':'Mazilla/5.0'}
实例3:百度搜索关键词提交(用程序自己提交关键词并搜索)

实例4:网络图片的爬取并保存下来
import requests
import os
url="https://c-ssl.duitang.com/uploads/item/201608/09/20160809112917_ZkVCP.jpeg"
root="F://csnotes//notes//crawler//code//img"
path=root+url.split('/')[-1]
try:
if not os.path.exists(root):
os.mkdir(root)
if not os.path.exists(path):
r=requests.get(url)
with open(path,'wb') as f:
f.write(r.content)
f.close()
print("文件保存成功")
else:
print("文件已存在")
except:
print("爬取失败")
使用图片的原名字,只需要截取/最后的名称
实例5:ip地址的归属地
在网络上找API
网站上面的人机交互方式,“图形文本框点击”在正式向服务器提交的时候都是以链接的形式提交,只要我们知道链接形式,就可以通过Python程序去提交。
网络上任何一个东西都对应一个url,理论上都可以爬取
二、网路爬虫之爬取
1.beautifulsoup4库
安装beautiful soup:
pip install beautifulsoup4
Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的python库
使用beautifulsoup4解析字符串格式的html代码
import bs4
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,'html.parser')
soup2=BeautifulSoup("data",'html.parser') # html字符串形式
soup3=BeautifulSoup(open("D://demo.html"),'html.parser') #html以打开文件形式导入

- beautifulsoup本身解析的是html和xml的文档,与标签树一一对应,通过bs4转换为一个BeautifulSoup类。
- 通过beautifulsoup库使得标签树成为一个变量。即BeautifulSoup类对应一个HTML/XML文档的全部内容
beautifulsoup库解析器
主要使用html.parser解析器

beautifulsoup类的基本元素

元素获取:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r=requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
soup=BeautifulSoup(r.text,"html.parser")
# 获得标签
print(soup.title)
print(soup.a)
# 获得标签的名字
tag=soup.a
print(tag.name)
print(tag.parent.name)
# 获得标签的属性
print(tag.attrs)
print(tag.attrs["class"])
print(tag.attrs["href"])
# 标签的类型
print(type(tag)) #
基于bs4库的对html标签树遍历
html文档标签树
下行遍历:
-
.contents和.children:获得下一层儿子节点列表,可以使用下标
-
.descendants:获取所有子孙节点列表
.contents返回列表类型
.children和.descentdants返回迭代类型,只能用在for循环中
tag=soup.body
# .contents的使用
print(type(tag.contents)) #上行遍历:
- .parent:返回父亲节点
- .parents:返回先辈节点
# .parent的使用
print(type(soup.title.parent)) # 父亲只有一个
print(soup.title.parent)
# .parents的使用
print(type(soup.a.parents)) # 先辈需要遍历
for parent in soup.a.parents:
if(parent is None):
print(parent)
else:
print(parent.name)
平行遍历:
- .next_sibling:返回后一个平行节点标签
- .previous_sibling:返回前一个平行节点标签
- .next_siblings:返回后面所有平行节点标签
- .previous_siblings:返回前面所有平行节点标签
所有的平行遍历发生在同一个父节点下
平行遍历的下一个节点不一定是标签类型,可能是NavigableString类型
<p>
<a href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" class="py1" id="link1">Basic Python</a>
and
<a href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" class="py2" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>
</p>
基于bs4库的html格式输出:prettify()方法
让html友好的输出
- 为html文本的标签和内容增加换行符
- 也可以对每个标签做处理
编码问题:bs4库将每一个读入的html文件或字符串都转换为utf-8编码
2.信息标记与提取方法
信息标记语言
信息标记三种形式
-
**XML(eXtensible Markup Language)**通过标签形式来构建所有信息
XML是基于html发展的一种通用的信息表达形式


XML实例:将每一个信息域定义相关标签,采用嵌套形式组织起来

-
JSON(javaScript Object Notation) 有类型的键值对key:value,采用双引号表示类型



对于javascript等编程语言,可以直接将json格式作为程序的一部分
JSON实例:

-
YAML(YAML Ain’t Markup Language)无类型的键值对key:value

通过缩进表示所属关系

减号表达并列关系

| 表示整块数据 #表示注释

YAML实例:

比较:
-
XML:最早的通用信息标记语言,可拓展性好,但繁琐。
主要应用在:Internet上的信息交互与传递,如html
-
JSON:信息有类型,适合程序处理(js),较XML简洁。
主要应用在:移动应用云端和节点的信息通信,无注释。
用在程序对接口处理的地方,json数据在经过传输之后能够作为程序代码的一部分并被程序直接运行,这样json格式中对数据类型的定义才能最大化发挥作用
缺陷:无法使用注释
-
YAML:信息无类型,文本信息比例最高,可读性好。
主要应用在:各类系统的配置文件,有注释易读
信息提取的一般方法
信息提取指从标记后的信息中,提取出所关注的内容
-
方法一:完整解析信息的标记形式,再提取关键信息
XML、JSON、YAML
需要表及解析器 例如:bs4库的标签树遍历
优点:信息解析准确
缺点:提取过程繁琐,速度慢
-
方法二:无视标记形式,直接搜索关键信息
搜索
对信息的文本,查找函数即可
优点:提取过程简洁,速度较快
缺点:提取结果准确性与信息内容直接相关
-
【使用多】融合方法:结合形式解析与搜索方法,提取关键信息
XML、JSON、YAML +搜索
标记解析器+文本查找函数
实例:提取HTML中所有的URL连接
demo.html
思路:
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
print(link.get('href'))
<>.find_all()方法

# 1.name:字符串检索 标签
# 查找所有a标签
print(soup.find_all('a'))#返回列表类型
# 查找所有a标签或b标签,or
print(soup.find_all(['a','b']))
# 标签名称为true,返回所有标签
print(soup.find_all(True))
import re
# 查找所有以b开头的所有信息
soup.find_all(re.compile('b'))
# 2.attrs:字符串检索 属性
# 带有class='course'属性的p标签
soup.find_all('p','course')
# 属性中id='link1'
soup.find_all(id='link1')
# 正则表达式,id以'link'开头
soup.find_all(id=re.compile('link'))
# 3.recursive是否对子孙全部检索,默认为true。
# 只搜索当前节点的儿子,可置为false
soup.find_all('a',recursive=False)
# 4.string 字符串检索 标签中字符串域
# 精确检索
soup.find_all(string="Basic Python")
# 模糊检索,正则表达式
soup.find_all(string=re.compile("python"))
进行文本检索时:使用find_all函数+正则表达式可以很有效的在html和xml文本中检索到所需要信息或者获得所需要信息的相关区域
find_all()简写形式:

7个扩展方法:

3.实例1:中国大学排名爬取
url:
【软科排名】2021年最新软科中国大学排名|中国最好大学排名 (shanghairanking.cn)
功能描述:
-
输入:大学排名url链接
-
输出:大学排名信息的屏幕输出(排名,大学名称,总分)
-
技术路线:requests-bs4
定向爬虫

程序设计:
- request获取网页内容
getHTMLTest() - bs4提取网页内容到合适数据结构
fillUnivList() - 展示输出结果(存储到数据库)
PrintUnivList()
import requests
import bs4
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def getHTMLTest(url):
try:
r=requests.get(url,timeout=30,headers={'user-agent':'Mazilla/5.0'})
r.raise_for_status()
r.encodingk=r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return ""
def fillUnivList(ulist,html):
soup=BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser")
for tr in soup.find('tbody').children:
if isinstance(tr,bs4.element.Tag):
tds=tr('td') #找到tr标签里面的所有td
ulist.append([tds[0].string,tds[1].string,tds[3].string]) #将每个大学的信息组成一个列表,放到大列表中
def printUnivList(ulist,num):
tplt="{0:^10}\t{1:{3}^10}'t{2:^10}" #中文输出对齐问题
print(tplt.format("排名","学校名称","总分"),chr(12288)) #表头的设置
for i in range(num): #打印学校信息
u=ulist[i]
print(tplt..format(u[0],u[1],u[2]),chr(12288))
def main():
uinfo=[]
url="https://m.dxsbb.com/news/38833.html" # 此处与老师的url不一致
html=getHTMLTest(url) #html=r.text 为字符串
fillUnivList(uinfo,html)
printUnivList(uinfo,20) # 只列出20所学校的相关信息


三、网络爬虫之实战
1.Re库
概念、语法
正则表达式——是用来简洁表示一组字符串的表达式。
- 通用的字符串表达框架
- 简洁,表达一组字符串的特征或者模式,的表达式
- 针对字符串表达“简洁”和“特征”思想的工具
- 判断某个字符串是否属于某个类型
作用
- 表达文本类型的特征(病毒、入侵等)
- 同时查找或替换一组字符串
- 匹配字符串的全部或部分特征
主要应用在字符串匹配中
使用
**编译:**将符合正则表达式语法的字符串 转换成正则表达式特征
编译后的特征与一组字符串对应,编译之前的正则表达式 只是符合正则表达式语法的单一字符串,并不是真正意义上的正则表达式
语法
由字符+操作符构成

常用操作符:





基本使用
Re库是Python的标准库,主要用于字符串匹配
raw string类型(原生字符串类型)
re库采用raw string类型表示正则表达式,表示为:r’text’
如:r’[1-9]\d{5}'和r’\d{3}-\d{8}\\d{4}=\d{7}‘’
raw string是指不包含转义符的字符串
正则表达式的表示类型
当正则表达式中包含“转义字符”时,使用raw string来表示
Re库主要功能函数
re.search()函数
re.match()函数
此时未匹配到,match为空变量
re.findall()函数,返回列表
spolit()函数
将匹配的部分去掉,剩下的部分作为各单个元素放到列表里面
re.finder()函数
re.sub()函数
用一个新的字符串 替换匹配上的字符串
re库的另一种等价用法
re.compile()函数
字符串或者或者原生字符串并不是正则表达式,它只是一种表示。
通过compile编译生成的一个对象regex才是正则表达式,它代表了一组字符串
正则表达式对象 的概念
正则表达式对象 的方法
只需要直接给出相关的字符串就可以了
re库的match对象
match对象就是一次匹配的结果,包含了很多匹配的相关信息
match对象的属性
match对象的方法
match对象包含了一次正则表达式匹配过程中,出现的更多的信息。
只包含一次匹配的结果,如果需要得到每一个返回的对象,需要用finditer()函数实现返回迭代器类型
Re库的贪婪匹配和最小匹配
re库默认采用贪婪匹配,即最长匹配
最小匹配
小结:
正则表达式,是用来简洁表达一组字符串的表达式
re库提供了六个方法
两种调用方式,将资质证表达式编译成正则表达式对象
编程使用中,文本处理和操纵是最常使用的功能,正则表达式很好的支持了文本匹配和文本替换
2.淘宝商品比价定向爬虫
功能描述
- 目标:获取淘宝搜索页面的信息,提取其中的商品名称和价格。
- 理解:淘宝的搜索接口、翻页的处理
- 技术路线:requests+re
url链接接口
程序的结构设计
- 提交商品搜索请求,循环获取页面
- 对于每个页面,提取商品名称和价格信息
- 将信息输出到屏幕上
import requests
import re
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return ""
# 解析网页:不使用beautifulSoup库提取商品信息,只采用正则表达式,提取价格和标题
def parsePage(ilt, html):
try:
plt = re.findall(r'\"view_price\"\:\"[\d\.]*\"',html) #返回的是列表
tlt = re.findall(r'\"raw_title\"\:\".*?\"',html)
for i in range(len(plt)):
price = eval(plt[i].split(':')[1]) #eval能去掉最外层双引号和单引号
title = eval(tlt[i].split(':')[1])
ilt.append([price , title])
except:
print("")
def printGoodsList(ilt):
tplt = "{:4}\t{:8}\t{:16}"
print(tplt.format("序号", "价格", "商品名称"))
count = 0
for g in ilt:
count = count + 1
print(tplt.format(count, g[0], g[1]))
def main():
goods = '书包'
depth = 3 #爬取深度
start_url = 'https://s.taobao.com/search?q=' + goods
infoList = [] # 输出结果
for i in range(depth): # 对每一个页面进行爬取
try:
url = start_url + '&s=' + str(44*i)
html = getHTMLText(url) #获取网页
parsePage(infoList, html) #解析页面
except:
continue #某个页面解析失败跳过继续往后解析
printGoodsList(infoList)
main()
本实例中因为具体数据是script脚本给出的,并非静态html页面,因此采用正则表达式获取
3.股票数据定向爬虫
功能描述
- 目标:获取上交所和深交所所有股票的名称和交易信息
- 输出:保存到文件中
- 技术路线:requests+bs4+re
候选数据网站的选择
- 选取原则:股票信息静态存在于HTML页面中,非js代码生成,没有Robots协议限制。
- 选取方法:查看源代码
- 选取心态:不要纠结于某个网站,多找信息源尝试
程序结构设计
- 从东方财富网获取股票列表
- 根据股票列表逐个到百度股票获取个股信息
- 将结果存储到文件
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
import traceback
def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r=requests.get(url,headers={'user-agent':'Mazilla/5.0'},timeout=30)
print(r.status_code)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding=r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return ""
def getStockList(lst,stockURL): #lst为返回的股票列表 stockURL为获取股票列表的网址
html=getHTMLText(stockURL)
soup=BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser')
a=soup.find_all('a')
for i in a:
try:
href=i.attrs['href']
lst.append(re.findall(r'[s][hz]\d{6}',href)) #【重要】利用正则表达式获取beautifulSoup处理后的文本
except:
continue
def getStockInfo(lst,stockURL,fpath): #lst为股票列表,stockURL为具体股票的链接,fpath为文件地址
for stock in lst:
url=stockURL+stock+".html"
html=getHTMLText(url)
try:
if html=="":
continue
infoDict={} #存储个股的所有信息
soup=BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser')
stockInfo=soup.find('div',attrs={'class':'stock-bets'})
name=stockInfo.find_all(attrs={'class':'bets-name'})[0]
infoDict.update({'股票名称':name.text.split()[0]}) #股票名称后面课程还有其他信息,删减掉
keyList=stockInfo.find_all('dt') #股票信息key
valueList=stockInfo.find_all('dd') #股票信息value
for i in range(len(keyList)):
key=keyList[i].text
val=valueList[i].text
infoDict[key]=val #将信息存储到字典中
#将股票信息保存到文件中
with open(fpath,'a',encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(str(infoDict)+'\n')
except:
traceback.print_exc() #打印错误信息
continue
def main():
stock_list_url="http://quote.eastmoney.com"
stock_info_url="https://gupiao.baidu.com"
output_file='D://BaiduStockInfo.txt'
slist=[] #股票列表
getStockList(slist,stock_list_url) #获取股票列表
getStockInfo(slist,stock_info_url,output_file) #根据股票列表到相关网站获取相应股票信息,并存储到文件中
main()
优化:提升用户体验
- 提高速度
在已知网页编码情况下,可以直接手动赋值编码
增加“不换行 动态进度条”信息展示:采用\r
进度条的\r属性在IDLE中被禁止,可以使用command命令行查看
完整代码
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import traceback
import re
def getHTMLText(url, code="utf-8"):
try:
r = requests.get(url)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = code
return r.text
except:
return ""
def getStockList(lst, stockURL):
html = getHTMLText(stockURL, "GB2312")
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
a = soup.find_all('a')
for i in a:
try:
href = i.attrs['href']
lst.append(re.findall(r"[s][hz]\d{6}", href)[0])
except:
continue
def getStockInfo(lst, stockURL, fpath):
count = 0
for stock in lst:
url = stockURL + stock + ".html"
html = getHTMLText(url)
try:
if html=="":
continue
infoDict = {}
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
stockInfo = soup.find('div',attrs={'class':'stock-bets'})
name = stockInfo.find_all(attrs={'class':'bets-name'})[0]
infoDict.update({'股票名称': name.text.split()[0]})
keyList = stockInfo.find_all('dt')
valueList = stockInfo.find_all('dd')
for i in range(len(keyList)):
key = keyList[i].text
val = valueList[i].text
infoDict[key] = val
with open(fpath, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write( str(infoDict) + '\n' )
count = count + 1
print("\r当前进度: {:.2f}%".format(count*100/len(lst)),end="")
except:
count = count + 1
print("\r当前进度: {:.2f}%".format(count*100/len(lst)),end="")
continue
def main():
stock_list_url = 'https://quote.eastmoney.com/stocklist.html'
stock_info_url = 'https://gupiao.baidu.com/stock/'
output_file = 'D:/BaiduStockInfo.txt'
slist=[]
getStockList(slist, stock_list_url)
getStockInfo(slist, stock_info_url, output_file)
main()
小结
- 区分是js获取的动态网页还是html静态页面
- 合理使用beautifulSoup和re库,特征明显的数据可以直接采用正则表达式获取;一般先采用beautifulSoup库提取数据,再利用正则表达式详细提取
- 优化:实现了爬取进程的动态滚动条
四、网络爬虫之框架——Scrapy框架
1.概述
安装scrapy库(需要关闭)
pip install scrapy
scrapy -h测试安装效果
介绍
爬虫框架结构
5个核心模块+2个中间件
scrapy框架包含三条主要数据流路径:在这5个模块之间,数据包括用户提交的网络爬虫请求以及从网络上获取的相关内容 在这些结构之间进行流动,形成了数据流。
- engine从spiders获取了爬取用户的请求requests,engine转发给scheduler模块,scheduler模块负责对爬取请求进行调度。
- engine从scheduler获得下一个要爬取的网络请求(这个时候的网络请求是真实的,要去网络上去爬取的请求),engine通过中间件发送给downloader模块,downloader模块拿到请求后真实连接互联网并爬取相关网页;将爬取的内容封装形成一个response对象,通过中间件发送给engine,再转发给spiders。
- spiders处理从网络上获取的内容,产生两个数据类型,一个是爬取项items,另一个是网页上感兴趣的新的爬取请求。将数据发送engine,engine将item转发给item pipelines,将requests转发给scheduler
框架入口是spiders,出口是item pipelines
engine,scheduler,downloader都是已有的功能实现
用户需要编写spiders模块和item pipelines模块,基于模板的编写,称为配置
spiders模块用来向整个框架提供要访问的url链接,同时要解析从网络页面上获得的内容
item pipelines模块负责对提取的信息进行后处理
爬虫框架解析
engine:不需要用户修改
- 控制所有模块之间的数据流
- 根据条件触发事件
downloader
- 根据请求下载网页
- 也不需要用户修改
scheduler
- 对所有爬去请求进行调度管理
- 也不需要用户修改
engine和downloader之间的中间件 Downloader Middleware
-
目的:实施engine、scheduler和downloader之间进行用户可配置的控制
-
功能:用户可以自定义修改、丢弃、新增请求或响应
用户可以编写配置代码,一般用户可以不更改这个中间件
spiders:最核心,需要用户编写配置代码
- 解析Downloader返回的响应(Response)
- 产生爬取项(scraped item)
- 产生额外的爬去请求(Request)
Item pipelines
-
以流水线方式处理spider产生的爬取项
-
由一组操作顺序组成,类似流水线,每个操作是一个Item Pipeline类型
-
可能的操作包括:对Item的数据进行清理、检验、查重爬取项中的HTML数据、将数据存储到数据库
-
需要用户配置
从网页中提取出来的item信息,用户希望怎么处理
spider Middleware
-
目的:对请求和爬取项的再处理
-
功能:修改、丢弃、新增请求或爬取项
-
用户可以编写配置代码
requests库和Scrapy库(框架)比较
相同点:
- 都可以对页面进行请求和爬取
- 两者都没有处理js、提交表单、应对验证码等功能(可扩展)
不同点:
非常小的爬取需求:requests
不太小的请求:scrapy框架
自搭框架:requests>scrapy
Scrapy常用命令
scrapy是为持续运行设计的专业爬虫框架,提供操作的Scrapy命令行
命令行格式:
scrapy常用命令
scrapy框架下一个project是一个最大单元,相当于一个scrapy框架;
框架中可以有多个爬虫,每一个爬虫相当于一个spider模块
2.基本使用
scrapy爬虫的第一个实例
产生scrpy框架:
-
建立Scrapy爬虫工程
cmd中cd到特定目录中,
scrapy startproject python123demo -
在工程中产生一个Scrapy爬虫,生成demo.py
-
配置产生的spider爬虫,修改demo.py文件
修改具体链接
更改爬取方法的具体功能
此处实现:将response中的内容写到一个文件中
-
运行爬虫,获取网页
完整版代码
yield关键字的使用
yield是python33个关键字之一
生成器
- 生成器是一个不断产生值的函数
- 包含yield语句的函数是一个生成器
- 生成器每次产生一个值(yield语句),函数被冻结,被唤醒后再产生一个值
生成器的使用一般与循环搭配在一起,可以通过循环调用
普通写法:列举所有可能的值,再返回列表
为什么要有生成器?
-
生成器相比一次列出所有内容的优势:更节省存储空间,响应更迅速,使用更灵活
当n很大时,使用生成器写法
-
生成器写法,urls是一个列表,通过for循环使用yield语句每次提交一个url请求。
start_requests是一个生成器函数,对其调用每次返回一个url链接
基本使用小结
scrapy爬虫的使用步骤
- 创建一个工程和Spider模板
- 编写spider
- 编写item Pipeline
- 优化配置策略
Scrapy爬虫的数据类型
scrapy爬虫提取信息的方法
scrapy爬虫支持多种HTML信息提取方法
- BeautifulSoup
- Ixml
- re
- XPath Selector
- CSS Selector
CSS Selector的基本使用
3.实例:股票数据Scrapy爬虫
步骤1:建立工程和Spider模板
\>scrapy startproject BaiduStocks\>cd BaiduStocks\>scrapy genspider stocks baidu.com- 进一步修改spiders、stocks.py文件
stock.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
import re
class StocksSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "stocks"
start_urls = ['https://quote.eastmoney.com/stocklist.html']
def parse(self, response):
for href in response.css('a::attr(href)').extract():
try:
stock = re.findall(r"[s][hz]\d{6}", href)[0]
url = 'https://gupiao.baidu.com/stock/' + stock + '.html'
yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse_stock)
except:
continue
def parse_stock(self, response):
infoDict = {}
stockInfo = response.css('.stock-bets')
name = stockInfo.css('.bets-name').extract()[0]
keyList = stockInfo.css('dt').extract()
valueList = stockInfo.css('dd').extract()
for i in range(len(keyList)):
key = re.findall(r'>.*', keyList[i])[0][1:-5]
try:
val = re.findall(r'\d+\.?.*', valueList[i])[0][0:-5]
except:
val = '--'
infoDict[key]=val
infoDict.update(
{'股票名称': re.findall('\s.*\(',name)[0].split()[0] + \
re.findall('\>.*\<', name)[0][1:-1]})
yield infoDict
步骤2:编写Spider
- 配置stocks.py文件
- 修改对返回页面的处理
- 修改对新增URL爬取请求的处理
步骤3:编写Pipelines
-
配置pipelines.py文件
-
定义对爬取项Scraped Item的处理类
-
新建了一个类,找到settings.py,配置ITEM_PIPELINE选项,才能找到这个类
pipelines.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here # # Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html class BaidustocksPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): return item class BaidustocksInfoPipeline(object): def open_spider(self, spider): self.f = open('BaiduStockInfo.txt', 'w') def close_spider(self, spider): self.f.close() def process_item(self, item, spider): try: line = str(dict(item)) + '\n' self.f.write(line) except: pass return itemsettings.py
# Configure item pipelines # See https://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'BaiduStocks.pipelines.BaidustocksInfoPipeline': 300, }
生成了一个spider,它能够从东方财富网获得股票的列表,并且针对每一个股票列表生成一个百度股票的链接;并向百度股票的链接进行信息爬取;
对于爬取后的信息,经过spider的处理,提取出其中关键信息,形成字典,并且将这个字典以item类的形式给到了item pipelinses进行后续处理
实例优化




















































