Springboot学习3.0
Springboot学习
-
- 1.下载并配置maven
- 2.ideal常用配置
- 3.ideal创建一个maven项目
- 4.右击新建时没有java class选项解决,创建测试文件不在test文件下而在main下解决
- 5.java: 错误: 不支持发行版本 5解决方法
- 6.一些快捷键
- 7.java新语法
- 7.创建一个springboot项目
- 8.启动类核心注解介绍
- 9.打包(jar包)
- 10.application配置文件
- 11.aop
- 12.ide中使用lombok
- 13.lombok工具库
- 14.JdbcTemplate连接数据库
- 15.MyBatis
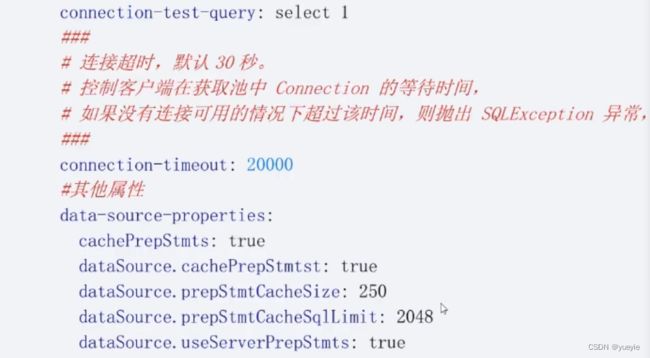
- 16.连接池
- 17.事务处理AOP
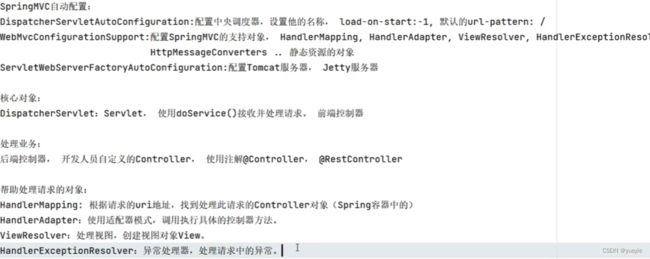
- 18.WebMVC概述
- 19.MVC详解
- 20.MVC自动配置
- 20.SpringMVC中使用servlet
- 21.过滤器Filter
- 22.WebMvcConfig
- 23.文件上传
- 24.全局异常处理
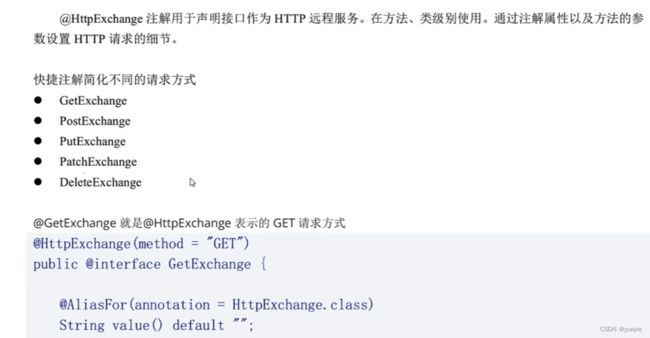
- 25.远程访问@HttpExchange(访问别人的接口)
- 26.视图技术Thymeleaf(类似于jsp,没啥大用)
- 27.redis使用
1.下载并配置maven
(1)Maven环境变量
变量名:M2_HOME
变量值:D:\install\maven\apache-maven-3.8.0
找到Path在环境变量值尾部加入:;%M2_HOME%\bin; //前面注意分号
(2)maven的环境变量是否配置成功
打开dos窗口运行命令mvn -v,出现如下图所示的信息说明安装成功;
(3)修改本地仓库位置(如果不想修改本地仓库位置则这一步骤省略即可)
Maven会将下载的类库(jar包)放置到本地的一个目录下(一般默认情况下maven在本机的仓库位于C:\我的文档中.m2.\repository),如果想重新定义这个目录的位置就需要修改Maven本地仓库的配置:
a.在自己喜欢的位置创建文件夹,此处本人创建的位置是(D:/maven-repository)
b.在安装Maven的目录下找到conf文件夹,在文件夹中找到settings.xml文件,打开并修改localRepository的值,如图:

(4)修改Maven的下载镜像地址为阿里源
安装好Maven时,要及时的修改Maven下载的镜像地址,最好改为国内的下载镜像,例如阿里云中央仓库,华为云中央仓库。
同样打开conf文件夹中的setting.xml文件,找到,注释掉已有的,改为下面的这段代码即可
aliyunmaven
*
阿里云公共仓库
https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public
这个配置可以在阿里云官方配置上看到对应的配置内容
修改完后,再次搭建Maven项目,下载一个大型项目的jar大约10S左右,开发体验度瞬间飙升。
(5)在Idea上配置Maven工具
当我们已经新建了项目,需要退出在管理主界面再配置,这样可以解决配置只针对当前项目的问题
打开IDEA,点击File–> Close Project(关闭所有打开项目,进入到管理首页):
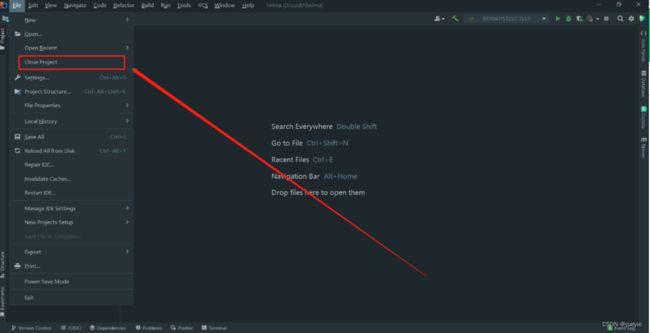
关闭项目后出现如下界面,点击 Customize -->All settings(设置所有):

在弹出的设置界面搜索maven,并点击override,apply,ok

上述修改应该已经解决了,若不行,可使用如下备用方案:,修改其默认文件夹配置,路径为:
C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\JetBrains\IntelliJIdea2022.3\options\project.default.xml文件

(6)配置解决证书等问题
-Dmaven.wagon.http.ssl.insecure=true -Dmaven.wagon.http.ssl.allowall=true
-Dmaven.wagon.http.ssl.insecure=true -Dmaven.wagon.http.ssl.allowall=true -Dmaven.wagon.http.ssl.ignore.validity.dates=true -DarchetypeCatalog=internal
2.ideal常用配置
这些设置最好都在ide管理首页对所有项目进行设置。
(1)修改字体风格和大小

(2)优化导入包

(3)提示不区分大小写

(4)编码设置为utf-8

(5)类复制为json的第三方插件(方便以后开发时候右击复制类为json格式)

使用时如下

{
"id": 0,
"userId": 0,
"title": "",
"summary": "",
"readCount": 0,
"email": ""
}
(6)json数据快速生成类对象插件

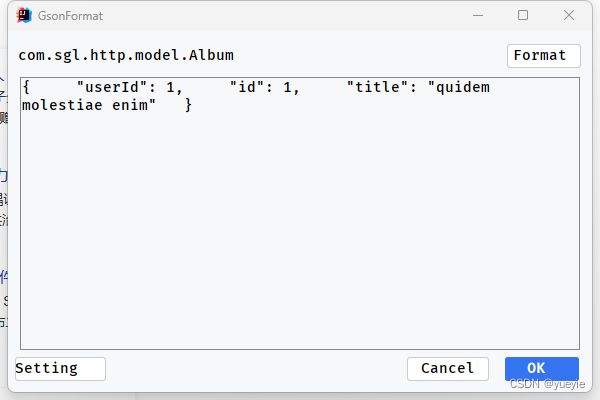
使用时,先复制一个json格式数据,然后鼠标放在java文件中的类名上,按Alt+Insert,并选择Gsonformat

在弹出的框中,粘贴json文件,并点击ok,最终生成该类

3.ideal创建一个maven项目
4.右击新建时没有java class选项解决,创建测试文件不在test文件下而在main下解决
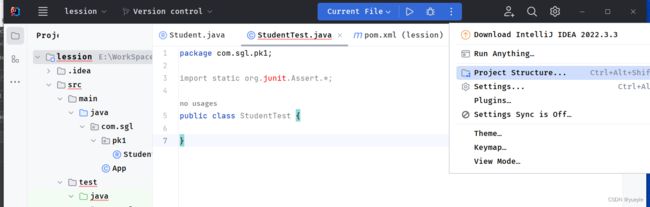
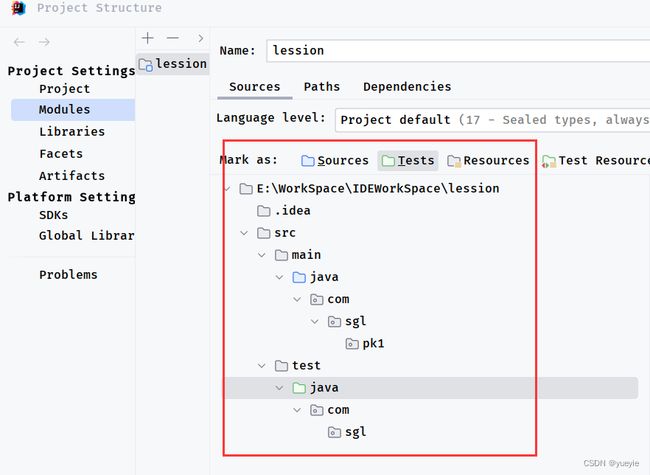
这种情况是ide没有识别到你的sources文件和tests文件,需要自己手动指定。project structure面板,手动指定main文件为sources文件和test文件为tests文件,然后点击apply即可。指定完后工程项目中的main文件和test颜色会变成蓝色和绿色
5.java: 错误: 不支持发行版本 5解决方法
原因是ide默认编译版本为5,需要修改为自己使用的jdk版本,

6.一些快捷键
sout:System.out.println();
变量名.sout:System.out.println(变量名);
7.java新语法
(1)switch中 “case 值->” 和“ case 值:” 不能混用,一个switch块中只能有一种语法格式。
(2)switch作为表达式,赋值给变量需要用yield或case 值->表达式。


(3)文本块
文本块用"""三个双引开始和结束,内容不能与三个双引位于同一行。它属于字符串,可以用+和equals(),substring()等。
String str= """
hello world
[]
df
""";
String str1= """
name:%s
phone:%d
""".formatted("xx",10);
文本块的其实对其方式是以每一行最左边的字符对齐,可用函数str.indent(5);控制前面的空格数。
函数:string stripIndent();删除每行开头和结尾空白
(4)var变量,声明时必须赋初值。
(5)sealed关键字,密闭类型,用于限制继承,可修饰类定义或接口定义,与permits关键字连用。其修饰的类或接口只能被permits后的类继承或实现。子类可用三个关键字修饰final、non-sealed、sealed。
a).final修饰表示到此结束,不能再被继承或实现;
b).non-sealed修饰表示到此后变成可无限继承;
c).sealed修饰表示该子类也是密闭类,需要与permits连用指定继承的子类;
public sealed class Shape permits Circle,Square, Rectangle {
private Integer width;
private Integer height;
public void draw(){
System.out.println("画一个图形shape");
}
}
public final class Circle extends Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("图形circle");
}
}
public non-sealed class Rectangle extends Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("rectangle");
}
}
public sealed class Square extends Shape permits RoundSquare {
}
7.创建一个springboot项目
使用ide嵌入的spring脚手架即可。

web项目模块文件概述:

8.启动类核心注解介绍


启动类作为扫描的起点,扫描同级目录的所有文件并完成对应注解的容器注入
9.打包(jar包)
(1)在pom.xml中build下添加finalName标签,表示打包后的架包名字
<build>
<finalName>mywebfinalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
···
可以显示定义下导出的文件类型名,一般不写会自动默认
<groupId>com.sglgroupId>
<artifactId>Lession02artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<packaging>jarpackaging>
<name>Lession02name>
<description>Lession02description>
然后点击maven,先clean,在package导出
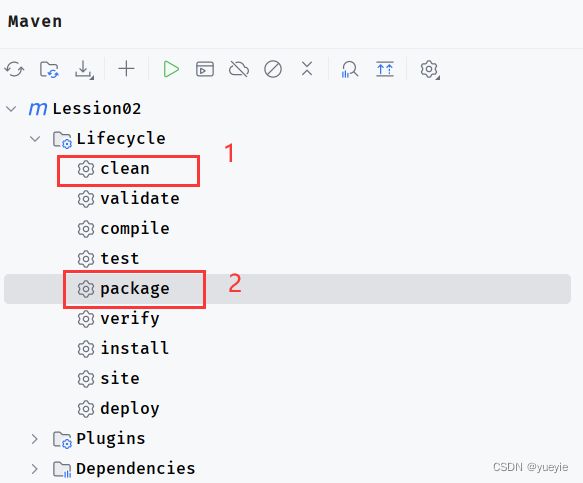
导出的jar包会在target文件夹中出现。普通jar和springboot的jar区别:

10.application配置文件
(1)文件类型介绍
其支持properties和yaml(yml)格式配置文件,properties是java中常用的配置文件格式,key=value。key唯一,文件扩展名为properties。
yaml也是一种配置文件格式,语法为 key:[空格]值。其扩展名为yaml或yml

(2)文件说明
sping boot一般只使用一种格式的配置文件,若两种格式都有,则properties文件优先。
application配置文件的名称和文字都可以修改,约定名称为application,位置在resources目录
![]()
app:
name: lession
owner: sgl
port: 8001
新增的其他配置文件需要放在resources中,可创建一个conf文件夹管理保存
(3)多文件配置
通常若需要把其他配置文件(如数据库配置文件)放在其他配置文件,那么主配置文件需要将其引入
#=========application.yml
#默认项 key: 值
#app.name
app:
name: lession
owner: sgl
port: 8001
#导入其他文件的配置,多个文件用“,”作为分隔符
spring:
config:
import: conf/db.yml,conf/redis.yml
#=======db.yml
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db
user: root
password: root
获取方法和默认配置文件获取一样,或通过Environment类获取
@Value("${app.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String db_url;
(4)总结

(5)快速属性类创建
注意:快速配置时候,需要在启动类Application类中允许配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AppBean.class)
当属性文件属性值比较多,不用一个一个注解,直接统一注解类即可。注意配置文件key值和属性名称要一致,该类需要get、set方法。prefix表示只配置前缀为app的key,其他不管;
注意:类属性为非静态
![]()
若嵌套了,则需要嵌套bean,如下图,security应是一个类,注解配置再主类即可。

(6)数组、列表、结合的属性配置

(7)指定源配置文件配置
需要指定@propertySource注解,如下图:该文件在resources目录下,文件名为group-info.properties

11.aop
要使用aop,需要在pom文件中添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
dependency>
(1)通过切片方式实现日志打印
代码配置实现在调用函数前打印日志信息。
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
//功能增加的方法为:com.sgl.project.service下的所有包,任意类的任意方法和参数
@Before("execution(* com.sgl.project.service..*.*(..))")
public void sysLog(JoinPoint jp){
//用|分隔的以{}开头和结尾
StringJoiner log=new StringJoiner("|","{","}");
DateTimeFormatter formatter=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
log.add(formatter.format(LocalDateTime.now()));
//当前执行的业务方法名称
String methodName=jp.getSignature().getName();
log.add(methodName);
//方法参数
Object[] args=jp.getArgs();
for (Object arg:args) {
log.add(arg==null?"-":arg.toString());
}
System.out.println("日志:"+log);
}
}
12.ide中使用lombok
13.lombok工具库
(1)引入lombok
在pom.xml中添加依赖,或ide创建项目时选择引入了lombok,依赖大致如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.4version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
(2)lombok常用注解
@Data : 注在类上,提供类的get、set、equals、hashCode、canEqual、toString方法
@AllArgsConstructor : 注在类上,提供类的全参构造
@NoArgsConstructor : 注在类上,提供类的无参构造
@Setter : 注在属性上,提供 set 方法
@Getter : 注在属性上,提供 get 方法
@EqualsAndHashCode : 注在类上,提供对应的 equals 和 hashCode 方法
@Log4j/@Slf4j : 注在类上,提供对应的 Logger 对象,变量名为 log
(3)使用示例
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ArticlePO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
虽然方便使用,但不能任意几个参数的构造,且不能对set、get方法添加控制
14.JdbcTemplate连接数据库
(1)引入JdbcTemplate
创建项目是选择依赖SQL->MySQL Driver,或直接在pom中引入依赖

(2)配置ide数据源
数据源不配置应该只是不能在ide中直接看到数据库内容,不影响代码执行。(好像配置了数据源后代码中字段名会有代码提示,但是我没试到)
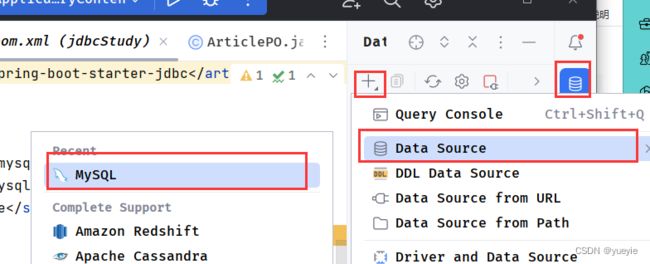
按上图打开数据源配置界面,然后按下图配置自己的数据源,并测试连接

(3)配置代码连接的数据源
在resources/application文件中配置数据源信息(根据文件类型配置,目前是properties格式)
#配置数据源
#这句是可以不写的,会自动识别
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sglblog
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#设置执行数据库脚本 alaways:总是执行(每次运行都执行数据库脚本);never:不执行脚本
spring.sql.init.mode=never
最后一句是用来控制代码创建数据库是否开启的。正常在resources文件下的schema.sql和data.sql会被程序默认用来创建表和数据,数据库需要提前创建好。

配置数据源后即可使用,下面是JdbcTemplate的常用方法

(4)查询语句
使用lombok配置对应bean后,即可使用
在使用JdbcTemplate地方先注册,再使用
下面实例中有map和list的新遍历方式
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void test01() {
String sql="select count(*) as ct from article";
Long count=jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Long.class);
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
//使用一条记录,使用?作为占位符
@Test
void test02() {
String sql="select * from article where id=?";
ArticlePO articlePO= jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(ArticlePO.class),1);
System.out.println("articlePO = " + articlePO);
}
@Test
void testList() {
String sql="select * from article order by id";
List<Map<String,Object>> listMap=jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
listMap.forEach(ls->{
ls.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key+":"+value);
});
});
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
String sql="update article set title=? where id=?";
int rows= jdbcTemplate.update(sql,"二哥头",1);
System.out.println("rows = " + rows);
}
@Test
void testQueryConten() {
String sql= """
select m.*,d.id as detail_id,d.article_id,d.content
from article m join article_detail d on m.id=d.article_id
where m.id=1
""";
List< ArticleMainPO> mainList= jdbcTemplate.query(sql,(rs,num)->{
var id= rs.getInt("id");
var user_id= rs.getInt("user_id");
var title= rs.getString("title");
var summary= rs.getString("summary");
var read_count= rs.getInt("read_count");
var create_time=new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("create_time").getTime()).toLocalDateTime();
var update_time=new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("update_time").getTime()).toLocalDateTime();
//文章内容
var content= rs.getString("content");
var detail_id= rs.getInt("detail_id");
var article_id= rs.getInt("article_id");
ArticleDetailPO detailPO=new ArticleDetailPO(detail_id,article_id,content);
return new ArticleMainPO(id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time,detailPO);
});
mainList.forEach(m->{
System.out.println("m.getId()="+m.getId());
System.out.println("detial="+m.getDetail());
});
}
15.MyBatis
MyBatis需要依赖mysql驱动 、mybatis的starter

首先需要配置属性文件,然后可开始使用,单表增删改查(CRUD)
属性文件配置如下(由于还是用的mysql驱动,所以配置与jdbcTemplate是一样的):
#配置数据源
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sglblog
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#配置mybatis
#支持驼峰命名,下划线
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#日志(控制台输出sql语句等)
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
然后需要在程序入口调用mybatis的标签,让代码自动扫描配置

(1)单表查询
若查询后不需要做更改,直接在接口中就能实现,注意查询结果与类属性的对应即可,可让表的列名与类的属性名一样或互为驼峰对应。
注意:mybatis3.4以后,不需要在使用@param注解占位了,直接变量名和语句中名字一样就行。

public interface ArticleMapper {
//按主键查询(当数据库表列名和类的属性名一致时,会自动完成赋值)
//当在配置文件配置了运行驼峰命名那么下划线和驼峰都会默认相同,如user_id与userId一致
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id=#{articleId}
""")
//让查询结果与类直接对应有几种方式
//1.查询结果集字段名与类的属性名直接对应,可在查询中用as或其他方式(配置了驼峰命名,则更宽泛一些)
//2.自己定义结果集与类的对应关系(在同一个类里面结果集可通过@ResultMap进行复用,从而减少代码)
// 本类中若其他函数结果集和这个一样(如返回List),可不声明@Result,而是使用如下标签
// @ResultMap("BaseArticleMap")
@Results(id="BaseArticleMap",value = {
//是否是主键(默认false),结果列名,类属性名
@Result(id=true,column = "id",property = "id"),
@Result(column ="user_id",property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "title",property = "title"),
@Result(column = "summary",property = "summary"),
@Result(column = "read_count",property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time",property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time",property = "updateTime"),
})
ArticlePO selectById(@Param("articleId")Integer id);
//mybatis3.4以后可改写为:
ArticlePO selectById(Integer articleId);
}
//调用是先注册,在调用即可
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
void testQueryObj() {
ArticlePO articlePO=articleMapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println("articlePO = " + articlePO);
}
@Autowired需要注册多个属性时,可用直接在类上用@RequiredArgsConstructor注解,就自动注册了该类的所有属性。
(2)增删改
//insert
//由于有个主键id为自动增加,所以新增时into article后不太好省略表的列名,不然得吧把id也要传值
@Insert("""
insert into article(user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time)
values(#{userId},#{title},#{summary},#{readCount},#{createTime},#{updateTime})
""")
int insertArticle(ArticlePO po);
//update
@Update("""
update article set read_count=#{readCount} where id=#{id}
""")
int updateReadCount(Integer id,Integer readCount);
//delete
@Delete("""
delete from article where id=#{id}
""")
int deleteById(Integer id);
(3)小结


ResultMap的xml使用方式如下:
新建一个Map
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.sgl.mybatis.mapper.ArticleMapper">
<resultMap id="sglArticleMapper" type="com.sgl.mybatis.po.ArticlePO">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId"/>
<result column="title" property="title"/>
<result column="summary" property="summary"/>
<result column="read_count" property="readCount"/>
<result column="create_time" property="createTime"/>
<result column="update_time" property="updateTime"/>
resultMap>
mapper>
然后在配置文件中定义mapper文件位置
注意:SpringBoot项目的classpath包含三个:
a)src/main/java路径
b)src/main/resouces路径
c)第三方jar包的根路径
#指定自定义mapper文件的位置(mapper文件夹下的任意文件夹中的任意xml文件)
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mappers/**/*.xml
使用时候直接使用resultMap的id指定即可
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id=#{articleId}
""")
@ResultMap("sglArticleMapper")
ArticlePO selectById(@Param("articleId")Integer id);
(4)SQL提供者(增删改查四个提供者)
使用提供者,可以把对数据库的操作语句都放在一个提供者类中,然后使用@SelectProvider注解
注:可使用多个提供者类来使用,如把四类语句写在4个类等。
//创建提供者类,注意方法要用静态
public class SqlProvider {
//定义静态方法
public static String selectArticle(){
return "select * from article where id=#{id}";
}
public static String updateSql(){
return "update article set update_time=#{newTime} where id=#{id}";
}
}
//使用提供者
@SelectProvider(type= SqlProvider.class,method = "selectArticle")
@ResultMap("sglArticleMapper")//使用xml形式的map
ArticlePO selectByProvider(Integer id);
@UpdateProvider(type = SqlProvider.class,method = "updateSql")
int updateProvider(Integer id, LocalDateTime newTime);
//insert语句和之前的一直,mybatis会通过名字自动解析类属性对应到字段
@InsertProvider(type = SqlProvider.class,method = "insertSql")
int insertProvider(ArticlePO po);
(5)@One一对一查询
//类定义
//注意:ArticleMainPO 对应的表其实没有最后一个detail项。
public class ArticleMainPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
private ArticleDetailPO detail;//一对一
}
public class ArticleDetailPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
//使用
@Select("""
select * from article_detail where article_id=#{articleId}
""")
ArticleDetailPO selectDetail(Integer articleId);
@Select("""
select * from article where id=#{id}
""")
//定义结果集时,可以不用全部都写出对应,只有特殊的才需要单独声明
//一对一中参数数目:数据库哪个列,对应类的那个属性,获取方式one,然后通过什么方法获取,获取类型:懒加载
//这样可以由查询主表,直接根据关联条件,查询到关联表
@Results({
@Result(column = "id",property = "detail",
one=@One(select = "com.sgl.mybatis.mapper.ArticleMapper.selectDetail",fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
ArticleMainPO selectAllArticle(Integer id);
(6)@Many一对多查询
public class ArticleEntity {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//多个评论
List<CommentPO> comments;
}
//使用:与one类似
@Select("""
select * from comment where article_id=#{articleId}
""")
List<CommentPO> selectComments(Integer articleId);
@Select("""
select * from article where id=#{id}
""")
@Results({
@Result(column = "id",property = "comments",
many=@Many(select = "com.sgl.mybatis.mapper.ArticleMapper.selectComments",fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
ArticleEntity selectAllComment(Integer id);
(7)mybatis其他配置方式
mybatis可在application中配置,也可以把其配置单独放在xml文件,然后在application中引入xml文件即可:
//application中配置mybatis文件路径为:同级目录中的mybatis-config.xml文件
mybatis.config-location=classpath:mybatis-config.xml
然后可参照官网属性进行配置
DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
configuration>
16.连接池
默认连接池为HikariCP,具体配置可参看HikariCP官网上的说明
#默认连接池,可修改为其他的,比如Tomcat,DBCP等
spring.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
17.事务处理AOP
事务回滚需要在内入口出添加开启事务管理注解(默认已开)
//开始事务管理(默认就开启了,不加该注解也行)
@EnableTransactionManagement
//扫描mapper接口的位置
@MapperScan(basePackages ="com.sgl.mybatis.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyBatisStudyApplication {...}
/**
* @Transactional:事务控制注解
* 位置:1.方法上;2.类上
* 放在方法上更好些,类上表示类的所有方法都是事务
* 事务回滚:
* 1.默认对运行时异常,执行回滚rollback
* 2.rollbackFor:需要回滚的异常列表:
* @Transactional(rollbackFor = {IOException.class})
*/
@Transactional
@Override
public boolean postNewArticle(ArticlePO article, String content) {
//新增文章
int rows=articleMapper.insert_sw_Article(article);
//抛出异常
if(article.getReadCount()<1){
//throw的异常为抛出异常,会进行事务回滚
throw new RuntimeException("文章数量需不能小于1");
}
//添加文章内容
ArticleDetailPO detailPO=new ArticleDetailPO();
detailPO.setArticleId(article.getId());
detailPO.setContent(content );
int dRows=articleMapper.insert_sw_detail(detailPO);
return (rows+dRows)==2?true:false;
}
事务不能执行的情况:
(1)非事务方法调用事务方法,则事务处理将失去作用,即不会回滚;但事务方法A调用事务方法B,B中的事务处理正常执行;
(2)事务方法中若创建线程操作则处于线程中的事务处理无效;
18.WebMVC概述

spring web依赖,自带了json库,Tomcat、mvc等,方便web开发
(1)返回html模型视图,给特定jsp(html)使用
thymeleaf视图文件默认放在resources/templates中,controller中返回的模型,只要名字与视图名一致,会自动解析,下图展示一个返回html视图和对应数据model
顺便说:resources/static用于存放静态资源,如图片,文件等。静态资源只要放在resources文件进行,推荐放在static目录

DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<div style="margin-left: 200px">
<h3>视图测试h3>
<div th:text="${title}">div>
<div th:text="${time}">div>
div>
body>
html>
(2)返回json视图(即json数据)
@RequestMapping("exam/json")
public void responseJson(HttpServletResponse res) throws IOException {
String json="{\"name\":\"展示\",\"age\":20}";
//应答,通过HttpServletResponse输出
res.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out=res.getWriter();
out.println(json);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
@RequestMapping("/exam/json1")
//这个注解会使用jackson架包,自动把类数据转换为json字符串数据,并返回,相当于完成了上面的out功能
@ResponseBody
public User getUserInfo(){
User user=new User();
user.setUsername("就辅导费");
user.setAge(12);
return user;
}
注意:类注解为@RestController,方法注解无需 @ResponseBody即可返回string、对象等;
但若类注解为@Controller,方法上不加@ResponseBody,则返回的的string只能是对应的视图,没有则报错,若想正常返回,需要如上所示,使用PrintWriter对象输出。
所以最好直接使用注解、
(3)请求方式

19.MVC详解
(1)Controller

@RestController推荐使用,而@Controller已经不推荐使用了。
springboot中路径匹配默认为PahtPatternParser模型,若要修改,需要在application配置文件中配置;

(2)接收参数
A)、用参数和对象接收参数
get请求时“?”后的参数可通过方法上的参数名对应接收,也可通过类变量接收(类的属性名和参数变量名相同则接收成功,不相同则为null),类的参数需要有set、get方法和无参数构造方法。

![]()
B)、用HttpServletRequest接收参数
@GetMapping("/param/p3")
@ResponseBody
public String param3(HttpServletRequest request){
String name=request.getParameter("name");
String age=request.getParameter("age");
return name+","+age;
}
C)、用@RequestParam接收参数

D)、获取请求头里的参数

E)、使用@RequestBody接收数据(post、json)

注意,在ide自带的请求测试中:
###回车:表示一个新的请求;
请求url回车相连的行用于设置header;
空一行后,用于输入请求体RequestBody

F)、使用Reader、InputStream读取post请求体的数据
//使用Reader、InputStream读取post请求体的数据
@PostMapping("/param/json2")
@ResponseBody
public String p6(Reader reader){
StringBuffer content=new StringBuffer("");
try (BufferedReader bin=new BufferedReader(reader)){
var line="";
while ((line=bin.readLine())!=null){
content.append(line);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "p7="+content.toString();
}
G)、数组类型接收
get请求接收,post感觉不太行,应该直接用json
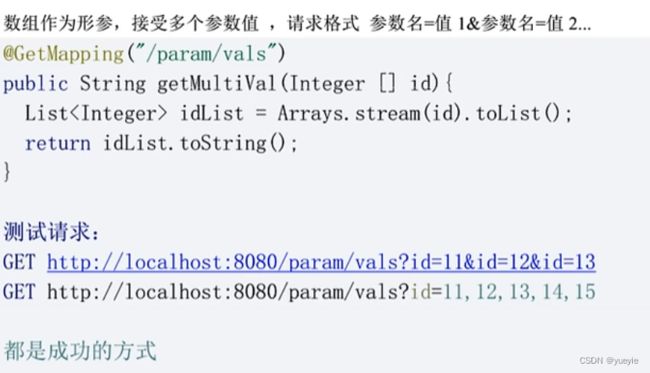
(2)参数验证
可自己加判断验证,也可用定义好的属性注解,给bean的属性做验证。

首先需要添加校验依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validationartifactId>
dependency>
@Data
public class Article {
private Integer id;
@NotNull(message = "必须有作者")
private Integer userId;
@NotBlank(message = "必需有标题")
//@Size认为null是有效值
@Size(min=3,max=30,message = ">3,<20")
private String title;
@NotBlank(message = "必需有副标题")
@Size(min=3,max=30,message = ">5,<60")
private String summary;
@DecimalMin(value = "0",message = "不能小于0")
private Integer readCount;
//邮箱格式验证,没有加非空验证,这个验证时email要么为"",要么格式正确
@Email(message = "不合格邮箱格式")
private String email;
}
//=======使用==========
//发布新文章
//@Validated 验证bean
//BindingResult 错误结果绑定(包含bean的验证结果)
@PostMapping("/article/add")
public Map<String, Object> addArticle(@Validated @RequestBody Article article, BindingResult br){
//service 方法处理文字业务
//返回结果
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
if(br.hasErrors()){
List<FieldError> fieldErrors=br.getFieldErrors();
fieldErrors.forEach(field->{
map.put(field.getField(),field.getDefaultMessage());
});
}
return map;
}
参数分类验证
当一些情况时需要验证,一些则不需要验证(如添加不需要验证id,修改则需要id非空)
首先在bean中声明分类接口,并给属性附上:
//组就是接口名
public static interface AddArticleGroup{};
public static interface EditArticleGroup{};
@NotNull(message = "id不为空",groups = {EditArticleGroup.class})
@Min(value = 1,message = "id>0",groups = {EditArticleGroup.class})
private Integer id;
@NotNull(message = "必须有作者",
groups = {AddArticleGroup.class,EditArticleGroup.class})
private Integer userId;
然后使用时也指定目前是使用哪种情况接口即可:
public Map<String, Object> addArticle(@Validated(Article.AddArticleGroup.class) @RequestBody Article article, BindingResult br){
//service 方法处理文字业务
//...
}
(3)页面视图View
需要有对应的视图html文件,视图使用的方式:
a)、使用Model作为参数,放回视图名
//使用sping框架的Model
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
@RequestMapping("/exam/quick")
public String quick(Model model){
//调用service,处理请求,获取数据
model.addAttribute("title","算法");
model.addAttribute("time", LocalDateTime.now());
//request.setAttribute("title","算法");
//指定一个视图,显示数据
return "quick";//它是视图文件的名称
}
b)、使用ModelAndView作为返回值
@GetMapping("/hello")
public ModelAndView hello(){
//ModelAndView 表示数据和视图
ModelAndView mv=new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("name","信息");
mv.addObject("age",10);
mv.setViewName("hello");
return mv;
}
c)、返回json并指定response状态
@RequestMapping("/exam/json5")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<User> returnEntity(){
User user=new User();
user.setUsername("就辅导费");
user.setAge(12);
ResponseEntity<User> response=new ResponseEntity<>(user, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
return response;
}
20.MVC自动配置
在application.properties中可进行如下配置
#路径匹配策略(2.6以上版本默认就是path_pattern_parser策略)
spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy=path_pattern_parser
#配置服务器
server.port=8001
#项目路径名
server.servlet.context-path=/api
#request,response字符编码
server.servlet.encoding.charset=utf-8
#强制request,response设置charset字符编码
server.servlet.encoding.force=true
#日志路径(tomcat)
server.tomcat.accesslog.directory=D:/exam
#启用访问日志
server.tomcat.accesslog.enabled=true
#日志文件名前缀
server.tomcat.accesslog.prefix=mylog
#日志文件日期时间
server.tomcat.accesslog.file-date-format=.yyyy-MM-dd
#日志文件名称后缀
server.tomcat.accesslog.suffix=.log
#post请求内容最大值,默认2M
server.tomcat.max-http-form-post-size=2000000
#服务器最大连接数
server.tomcat.max-connections=8000
#配置DispatherServlet
#中央控制器路径访问路径变为/api/course/你的路径
spring.mvc.servlet.path=/course
#servlet的加载顺序,越小创建时间越早
spring.mvc.servlet.load-on-startup=0
#时间格式,可以在接受请求参数使用
spring.mvc.format.date-time=yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
20.SpringMVC中使用servlet
(1)、用注解方式使用servlet
servlet类要添加注解@WebServlet,用于配置web.xml中servlet名称、路径等信息;
/**
* @WebServlet:等同于web.xml中油罐servlet的声明
*
* HelloServlet
* xxxx
*
*
* /helloServlet
*
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/helloServlet",name="HelloServlet")
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out=resp.getWriter();
out.println("spring中的servlet");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
然后在启动类中添加@ServletComponentScan注解,用于扫描@WebServlet。

(2)、用编码方式使用servlet
这种方式不需要在启动类添加注解,也不需要给servlet添加注解,但是要创捷ServletRegistrationBean对象注册一个的servlet和其路径等,多个就用多个ServletRegistrationBean。
首先创捷servlet:
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out=resp.getWriter();
out.println("登录servlet");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
然后创建注册文件
@Configuration
public class WebAppConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean(){
//创建ServletRegistrationBean 注册登记一个或多个servlet
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean=new ServletRegistrationBean<>();
registrationBean.setServlet(new LoginServlet());
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/user/login");
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
return registrationBean;
}
}
21.过滤器Filter
(1)、用注解方式
与servlet类似,需要添加@WebFilter注解,并在启动类扫描该注解
//所有的controller都要经过过滤器
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*")
public class LogFilter implements jakarta.servlet.Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
String uri=((HttpServletRequest)servletRequest).getRequestURI().toString();
System.out.println("过滤器执行了,uri:"+uri);
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
}
//在启动类添加注解
@ServletComponentScan(basePackages = "com.sgl.servletstudy")
(2)、用编码方式
与servlet一样,创建FilterRegistrationBean 并注册对应的的filter,然后可以去掉filter类上的注解和启动类上的注解
//就在上一个的WebAppConfig 配置类中添加filter注册方法就行
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean(){
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean=new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new LogFilter());
filterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
filterRegistrationBean.setOrder(2);//设置顺序
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
(3)过滤类顺序
在注解方式中,默认内名称的字母顺序执行;在编码方式中,在注册时可使用函数setOrder进行控制顺序:
(4)使用spring框架中内置的filter类
使用方式就是编码式

这个默认过滤器好像运行在debug模式,所以要在配置文件application中设置,具体哪个默认过滤器使用情况需要去类定义里面看下。
loggin.level.web=debug
注意:监听器Listerer的使用与Filter一样,不再详述
22.WebMvcConfig
(1)、页面跳转控制器


(2)、数据转换控制器
声明一个实现Formatter的自定义格式转化器
/**
* 将请求参数字符串转换为对象DeviceInfo
*/
public class DeviceFormatter implements Formatter<DeviceInfo> {
@Override
public DeviceInfo parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException {
DeviceInfo info=null;
if (StringUtils.hasText(text)){
String[] items=text.split(";");
info=new DeviceInfo();
info.setItem1(items[0]);
info.setItem2(items[1]);
info.setItem3(items[2]);
info.setItem4(items[3]);
info.setItem5(items[4]);
}
return info;
}
@Override
public String print(DeviceInfo object, Locale locale) {
StringJoiner joiner=new StringJoiner("#");
joiner.add(object.getItem1()).add(object.getItem2())
.add(object.getItem3()).add(object.getItem4())
.add(object.getItem5());
return joiner.toString();
}
}
然后再实现WebMvcConfigurer中覆盖addFormatters方法

(3)、拦截器
拦截器在调用控制器之前实现拦截,用于权限控制等,如实现zhangshan操作员只能看文章,不能修改、删除。使用方式与其他两个一样。
首先创捷文章controller
@RestController
public class ArticleController {
@PostMapping("/article/add")
public String addArticle(){
return "添加";
}
@PostMapping("/article/editor")
public String editorArticle(){
return "修改";
}
@DeleteMapping("/article/delete")
public String deleteArticle(){
return "删除";
}
@PostMapping("/article/query")
public String queryArticle(){
return "查询";
}
}
然后创捷有权限的拦截器
public class AuthInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
//假设张三只能查
private static final String COMMON_USER="zhangsan";
//判断登录用户是否有权执行相应动作
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("=====AuthInterceptor权限拦截器====");
//登录用户
String loginUser=request.getParameter("loginUser");
//获取请求的uri地址
String requestUri=request.getRequestURI();
//判断用户是否有权操作
if(COMMON_USER.equals(loginUser)&&(
requestUri.startsWith("/article/add")||
requestUri.startsWith("/article/editor")||
requestUri.startsWith("/article/delete")
)){
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
最后登记注册拦截器

多个拦截器,声明多个实现HandlerInterceptor 的类,在登记时用order设置拦截顺序

23.文件上传
#上传文件的保存路径
spring.servlet.multipart.location=D://exam
设置分别是:单个文件最大值,一次请求最大值
//传统上传
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(HttpServletRequest request){
try {
for(Part part:request.getParts()){
String filename=extractFileName(part);
//蒋文件写入服务器目录(目录在配置文件中设置)
part.write(filename);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
private String extractFileName(Part part){
String contentDisp=part.getHeader("content-disposition");
String[] items=contentDisp.split(";");
for (String s:items) {
if(s.strip().startsWith("filename")){
return s.substring(s.indexOf("=")+2,s.length()-1);
}
}
return "";
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<div style="margin-left: 200px">
<h3>上传文件h3>
<form action="upload" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post">
选择文件:<input type="file" name="upfile"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="上传">
form>
div>
body>
html>
spring中的上传
@Controller
public class UploadFileController {
//上传文件
@PostMapping("/uploadFile")
public String uploadFile(@RequestParam("upfile")MultipartFile multipartFile){
System.out.println("开始处理上传文件");
Map<String, Object> info=new HashMap<>();
try {
if(!multipartFile.isEmpty()){
info.put("上传文件的参数名字",multipartFile.getName());//upfile
info.put("内容类型",multipartFile.getContentType());
var ext="unknow";//文件扩展名
var filename=multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();//原始文件名,如a.jpg
if(filename.indexOf(".")>0){
ext=filename.substring(filename.indexOf(".")+1);
}
//生成服务器使用文件名称
var newFileName= UUID.randomUUID().toString()+"."+ext;
var path="D://exam//"+newFileName;//存储服务器文件
//把文件保存到path目录
multipartFile.transferTo(new File(path));
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("info = " + info);
//重定向到index页面
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
多文件上传,前端多几个type=file,且name一样的input标签;
后端把MultipartFile改为MultipartFile[]
@PostMapping("/files")
public String uploadFile(@RequestParam("upfile")MultipartFile[] multipartFiles){
System.out.println("开始处理上传文件");
Map<String, Object> info=new HashMap<>();
try {
for (MultipartFile multipartFile:multipartFiles) {
if(!multipartFile.isEmpty()){
info.put("上传文件的参数名字",multipartFile.getName());//upfile
info.put("内容类型",multipartFile.getContentType());
var ext="unknow";//文件扩展名
var filename=multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();//原始文件名,如a.jpg
if(filename.indexOf(".")>0){
ext=filename.substring(filename.indexOf(".")+1);
}
//生成服务器使用文件名称
var newFileName= UUID.randomUUID().toString()+"."+ext;
var path="D://exam//"+newFileName;//存储服务器文件
//把文件保存到path目录
multipartFile.transferTo(new File(path));
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("info = " + info);
//重定向到index页面
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
24.全局异常处理
(1)、可以声明一个类来自定义处理所有类型的异常,一种类型只能处理一次。
/**
* 1.在类的上面加上@ControllerAdvice,@RestControllerAdvice
* 灵活组合@ControllerAdvice和@ResponseBody
* 2.在类中自定义方法,处理各种异常
* 方法定义同controller类中的方法定义
*/
//控制器功能增加,给controller增加异常处理功能,类似AOP的思想
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptioinHandler {
//定义方法处理数字异常
/**
* @exceptionHandler:指定处理异常的方法
* 位置:在方法上面
* 属性:是异常类的class数组,如果你的系统抛出的异常类型于@ExceptionHandler什么的相同,有当前方法处理异常
*/
// @ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class})
// public String handlerArthmeticException(ArithmeticException e, Model model){
// String error=e.getMessage();
// model.addAttribute("error",error);
// return "exp";//就是试图
// }
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class})
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,String> handlerArthmetic2Exception(ArithmeticException e){
String error=e.getMessage();
Map<String,String> error1=new HashMap<>();
error1.put("msg",e.getMessage());
error1.put("tips","被除数不能为0");
return error1;//返回数据
}
}
处理数据校验异常,JRS303
@ExceptionHandler({BindException.class})
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> handlerJSR303Exception(BindException e){
//MethodArgumentNotValidException
System.out.println("===========JSR303===========");
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
BindingResult result=e.getBindingResult();
if(result.hasErrors()){
List<FieldError> errors=result.getFieldErrors();
errors.forEach(filed->{
map.put(filed.getField(),filed.getDefaultMessage());
});
}
return map;
}
(2)、使用标准ProblemDetail类
以上两个异常处理函数都是自定义的map作为返回对象,很不规范,不能让所有异常统一,spring提供了异常返回类用于解决这个问题。

运用异常返回类ProblemDetail函数可为
//BookNotFoundException为继承了RuntimeException的类
@ExceptionHandler({BookNotFoundException.class})
@ResponseBody
public ProblemDetail handlerBookNotFoundException(BookNotFoundException e){
ProblemDetail problemDetail=ProblemDetail.forStatusAndDetail(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND,e.getMessage());
//type:异常类型,是一个uri,uri找到解决问题的途径
problemDetail.setType(URI.create("/api/probs/not-found"));
problemDetail.setTitle("图书异常");
return problemDetail;
}
返回的标准错误示例:

(3)、扩展ProblemDetail
若默认字段不能满足要求,可扩展该类,自定义字段以Map
@ExceptionHandler({BookNotFoundException.class})
public ErrorResponse handlerException(BookNotFoundException e){
ErrorResponse errorResponse=new ErrorResponseException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND,e);
return errorResponse;
}
后记:
要使用最后两种方式处理异常,需要开启支持
#开启支持RFC7807
spring:
mvc:
problemdetails:
enabled: true
感觉用得不多,不再详述。
25.远程访问@HttpExchange(访问别人的接口)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webfluxartifactId>
dependency>
(1)在该你对象中统一指定访问前缀地址
public interface TodoService {
//一个方法就是一个远程服务(远程接口调用)
@GetExchange("/todos/{id}")
Todo getTodoById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id);
@PostExchange(value = "/todos/",accept = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
Todo createTodo(@RequestBody Todo newTodo);
//修改资源
@PutExchange("/todos/1")
ResponseEntity<Todo> modifyTodo(@PathVariable Integer id,@RequestBody Todo todo);
//删除
@DeleteExchange("todos/{id}")
void removeTodo(@PathVariable("id") Integer id);
}
//代理对象
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class HttpConfig {
//创建服务接口的带你对象,基于WebClient
@Bean
public TodoService requestService(){
WebClient webClient=WebClient.builder().baseUrl("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com").build();
//创建带你工厂
HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory=HttpServiceProxyFactory.builder(WebClientAdapter.forClient(webClient)).build();
//创建某个接口的带你服务
return httpServiceProxyFactory.createClient(TodoService.class);
}
}
(2)使用HttpExchange注解给类设置访问基地址
@HttpExchange(url="https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/")
public interface AlbumsService {
//查询专辑
@HttpExchange(method = "GET",url = "/albums/{id}")
Album getById(@PathVariable Integer id);
}
//同样需要在HttpConfig 中创建代理,只是不在需要写基地址
//创建代理
@Bean
public AlbumsService albumsService(){
WebClient webClient=WebClient.create();
//创建带你工厂
HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory=HttpServiceProxyFactory.builder(WebClientAdapter.forClient(webClient)).build();
//创建某个接口的带你服务
return httpServiceProxyFactory.createClient(AlbumsService.class);
}
上面是远程接口返回数据到class,同样声明对象为Record也能正常接收远程接口返回的数据。

(3)定义一个通用的代理
可自定义连接超时时长,错误捕获等
//定制http服务代理
@Bean
public AlbumsService albumsService(){
//超时设置reactor.netty.http.client.HttpClient;
HttpClient httpClient= HttpClient.create()
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS,30000)//连接时间ms
.doOnConnected(conn->{
conn.addHandlerLast(new ReadTimeoutHandler(10));//读超时10s
conn.addHandlerLast(new WriteTimeoutHandler(10));//写超时
});
WebClient webClient=WebClient.builder()
.clientConnector(new ReactorClientHttpConnector(httpClient))
.defaultStatusHandler(HttpStatusCode::isError,clientResponse -> {
System.out.println("*************WebClient请求异常*************");
return Mono.error(new RuntimeException("请求异常"+clientResponse.statusCode().value()));
}).build();
//创建带你工厂
HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory=HttpServiceProxyFactory.builder(WebClientAdapter.forClient(webClient)).build();
//创建某个接口的带你服务
return httpServiceProxyFactory.createClient(AlbumsService.class);
}
26.视图技术Thymeleaf(类似于jsp,没啥大用)

类似于JSP的升级
(1)表达式

(2)if-for

(3)thymeleaf配置
基本都是默认配置好,包括文件路径,编码等,也可以自己再配置

注意:thymeleaf使用时,在HTML文件中应该有这行
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
注意:通常model文件分为po文件和vo文件,po对应数据库,vo对相应显示的文件类,即po>=vo,可用第三方工具库hutool来实现转换,该插件需要引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutoolgroupId>
<artifactId>hutool-allartifactId>
<version>5.8.16version>
dependency>
使用时大致如下:
List<ArticleVO> articleVOS = BeanUtil.copyToList(listPO, ArticleVO.class);
27.redis使用
redis是最常用的缓存数据库,常用于存储用户登录token、临时数据、定时相关数据等。
redis是单线程的,所以redis的操作是原子性的,这样可以保证不会出现并发问题。
redis基于内存,速度非常快,据测试,redis读的速度是110000次/s,写的速度是81000次/s
(1)、redis下载安装配置
redis官网下载并解压,无需安装,直接使用,

运行直接双击redis-server.exe即可
![]()
然后再装一个可视化工具
(2)、springboot中配置
引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
并配置:yml
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.169.133
port: 6379
password: 123456
database: 0
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 8 # 最大连接数
max-wait: 1ms # 最大阻塞时间
max-idle: 4
min-idle: 0
接着写个config类解决下中文存储显示乱码问题
/**
* redis配置(解决存储乱码)
* 主要是配置Redis的序列化规则,替换默认的jdkSerializer
* key的序列化规则用StringRedisSerializer
* value的序列化规则用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 设置常规key value 的序列化策略
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 这里使用一般的json处理,就不容易存在兼容性问题。否则可能需要对应的json才能解析序列化的数据
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 设置hash类型的序列化策略
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 注入连接工厂
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}
}
(3)、redis使用