python-数据分析-numpy、pandas、matplotlib的常用方法
一、numpy
import numpy as np
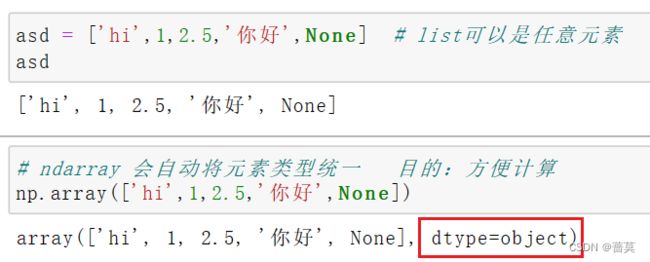
1.numpy 数组 和 list 的区别
2.构造并访问二维数组
使用 索引/切片 访问ndarray元素
切片 左闭右开
np.array(list)
3.快捷构造高维数组
-
np.arange()
-
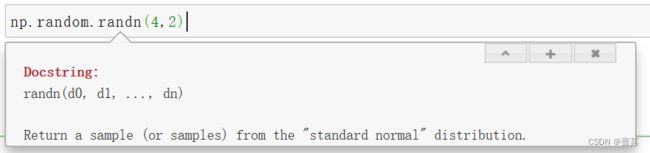
np.random.randn() - - - 服从标准正态分布- - - 数学期望 μ - - - 标准方差 s
使用matplotlib.pyplot模块验证标准正态分布
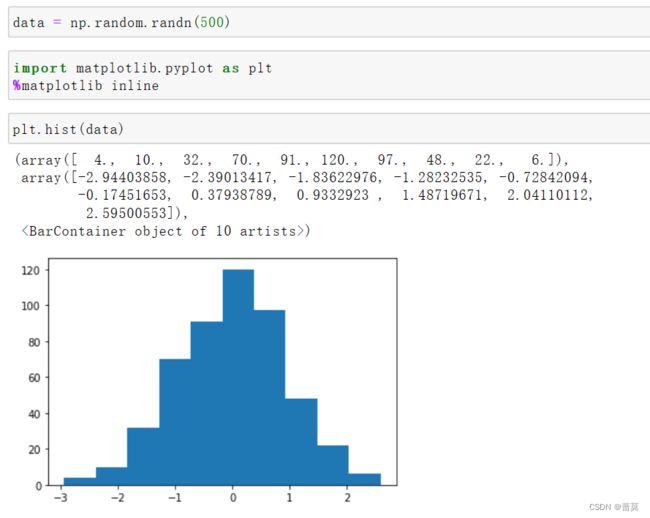
-
np.random.randint(起始数,终止数(行,列))
4.改变数组的形状 几行几列 reshape
二、pandas
数据分析 - - - 数据清洗 - - - 控制过滤 - - - 异常值捕获
map分组 聚合
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pandas善于处理二维数据
1.数据结构 Series 和 DataFrame
Series
series类似于通过numpy产生的一维数据,但series包含索引(可以自己定)

DataFrame
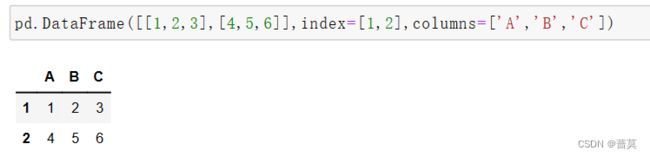
DataFrame是一种二维表格数据结构
创建方法:
-
通过列表创建
行索引是
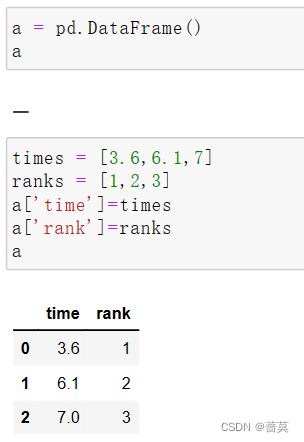
index,列索引是columns先创建一个空的DataFrame,通过列表生成DataFrame
-
通过字典创建
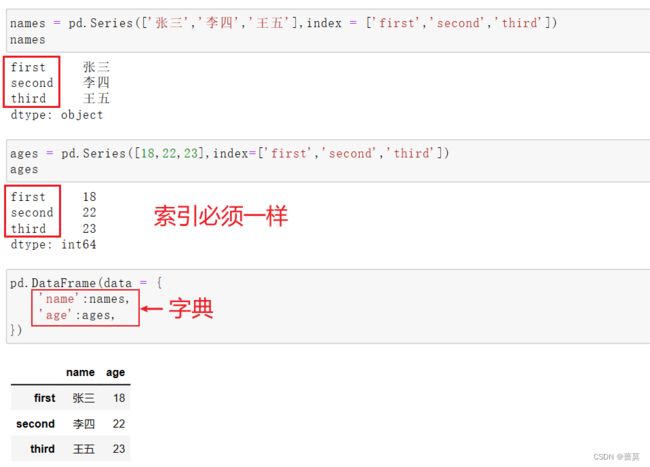
简单创建
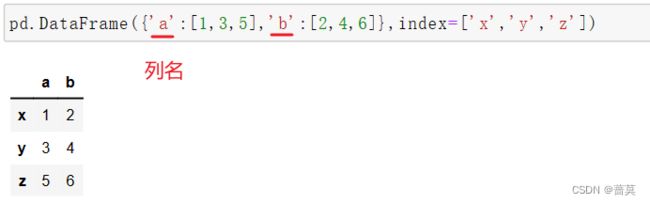
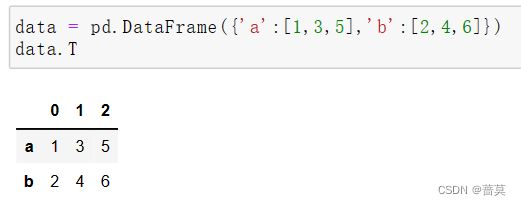
将字典键变成行索引 - - - from_dict - - - orient(朝向)或者使用 T
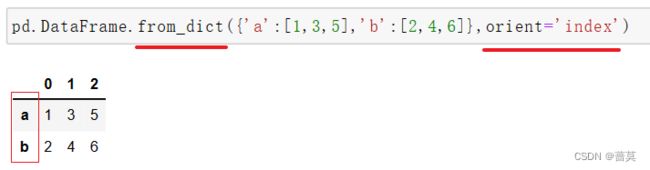
data = {'a':[1,3,5],'b':[2,4,6]} pd.DataFrame(data = data) pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data,orient='index') -
通过二维数组创建
np.arange(12) # array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11])
2.修改索引
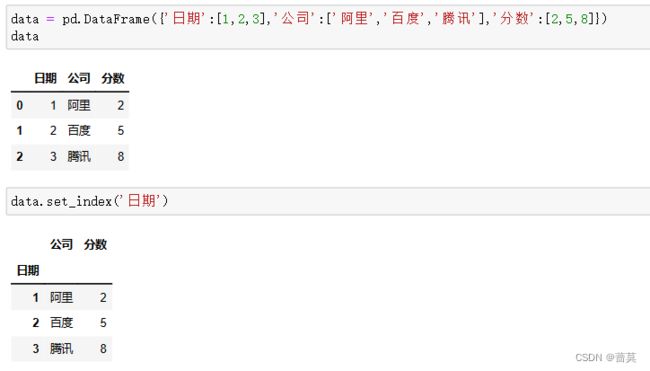
set_index 把常规行变成索引列
不会修改原始数据,若希望修改,使用 inplace=True
data.set_index(‘index’, inplace=True)
修改列名称 rename
修改列名称,使用columns - - - 行 index
使用字典来表达映射关系 - - - {原始数据:新数据}
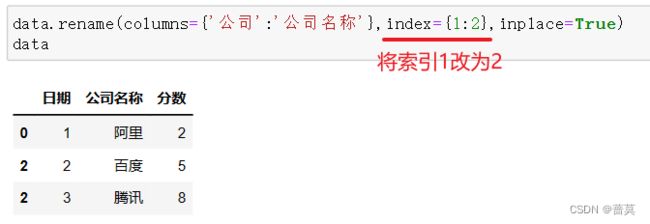
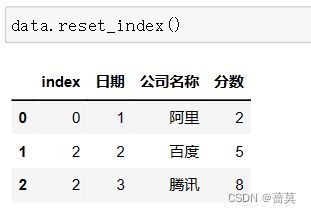
将行索引变成常规列 reset_index()
若想修改原始数据 使用reset_index(replace=True)
3.Excel或csv数据的读取和写入
pd.read_excel(file_name, sheet_name=0, index_col=0)
从左到右,第一个sheet索引是0,该函数返回该页内容 - - - 会将第一行变为列索引 - - - 行索引从0开始
index_col=0 :将第一列变成行索引
header=0:将第一行变成列索引 - - - header=[0,1] 将前两行变成列索引
xxx.to_excel(file_name):将数据写到新的Excel文件
pd.read_csv(file_name, sep=','):读取csv文件,sep默认逗号分隔
index_col - - - header
xxx.to_csv(file_name)
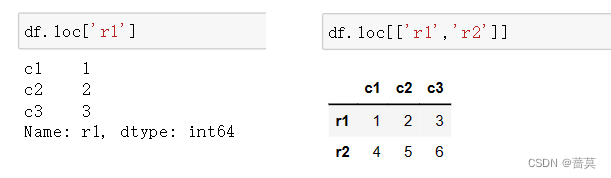
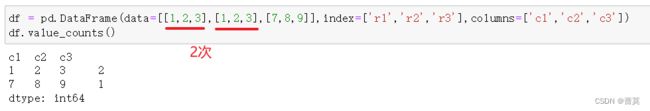
4.pandas数据的读取和筛选
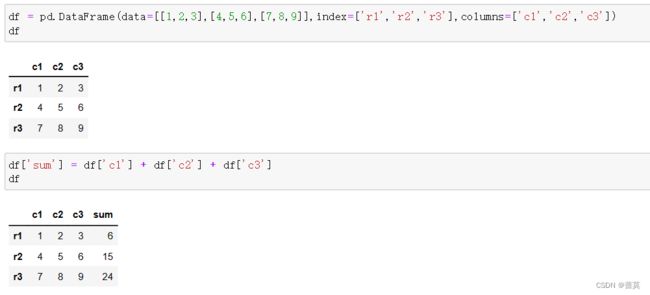
df = pd.DataFrame(data=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]],index=['r1','r2','r3'],columns=['c1','c2','c3'])
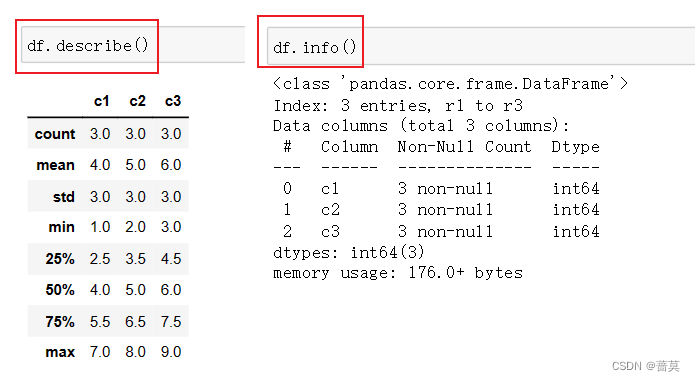
5.数据整体情况查看
- df.shape - - - 查看数据有几行几列
- df.describe() - - - 查看一些统计指标 – 每一列的个数 均值 标准方差 最小值 最大值
- df.info() - - - 查看表格数据的信息 - - - 每一列的个数 是否有空值 每一列的类型
6.数据运算
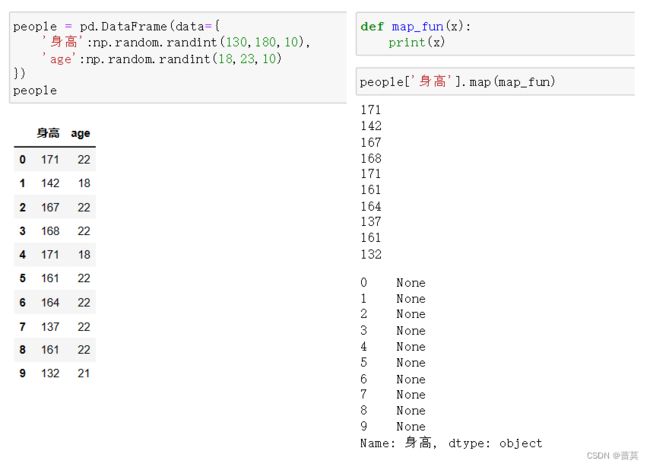
7.数据映射 map()
map()根据列对数据进行映射
map是一个循环遍历的过程
people = pd.DataFrame(data={
'身高':np.random.randint(130,180,10),
'age':np.random.randint(18,23,10)
})
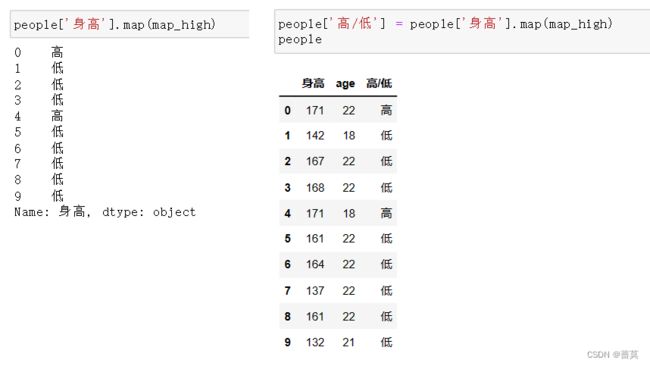
def map_high(x):
if x >= 170:
return '高'
else:
return '低'
people['高/低'] = people['身高'].map(map_high)
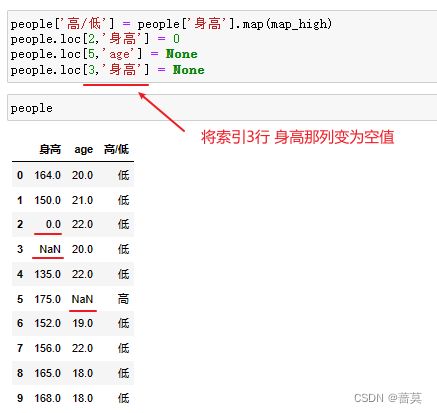
8.空值的填充和查找
NaN空值·
写入空值
填充空值 fillna()
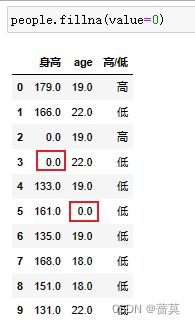
表格数据如果显示NaN,表示此处为空值fillna()函数,可以填充空值
inplace=True表示写入到数据内存
people.fillna(value=0, inplace=True)
将空值NaN使用value替换
查找空值 isnull()
是NaN,返回True - - - True is 1
不是返回False - - - False is 0
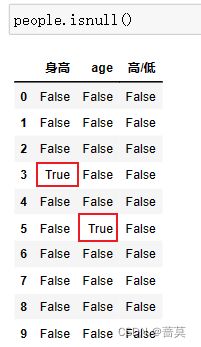
xxx.isnull().sum() 对布尔值进行列方向的求和 - - - - 求出每一列空值的个数
三、matplotlib
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
1.折线图 plt.plot()
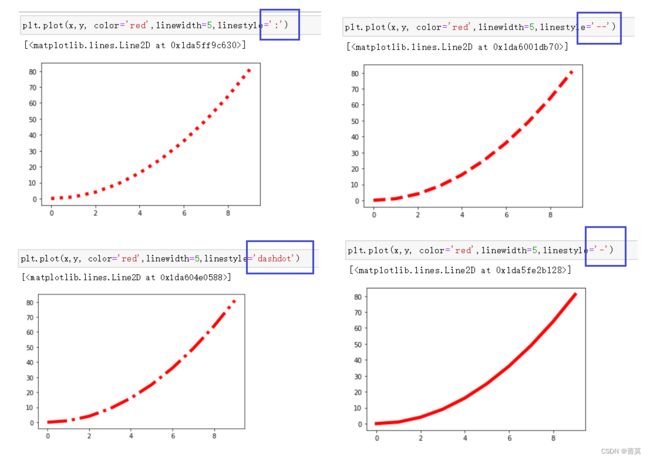
color 线的颜色
linewidth 线的宽度 像素
linestyle 线的风格
![]()
dashed 虚线 dashdot 虚线和点 dotted 点
# 可以省略,但建议写上,强制将前面的绘图代码渲染出来
plt.show()
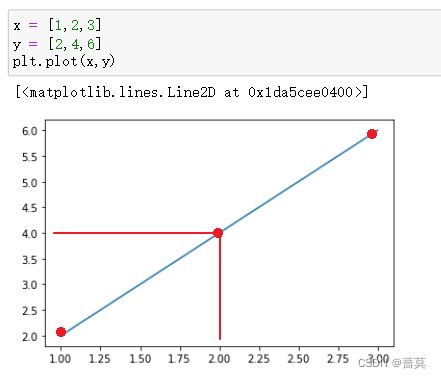
x = [1,2,3]
y = [2,4,6]
plt.plot(x,y)
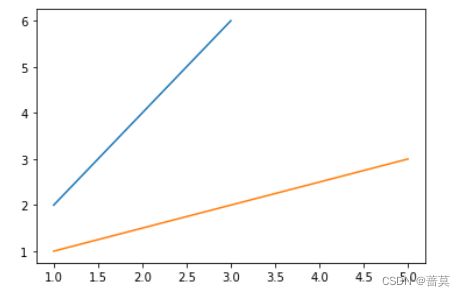
a = [1,3,5]
b = [1,2,3]
plt.plot(a,b)
# 可以省略,但建议写上,强制将前面的绘图代码渲染出来
plt.show()
2.柱状图 plt.bar()
条形图的横轴可以是字符串,起标识作用
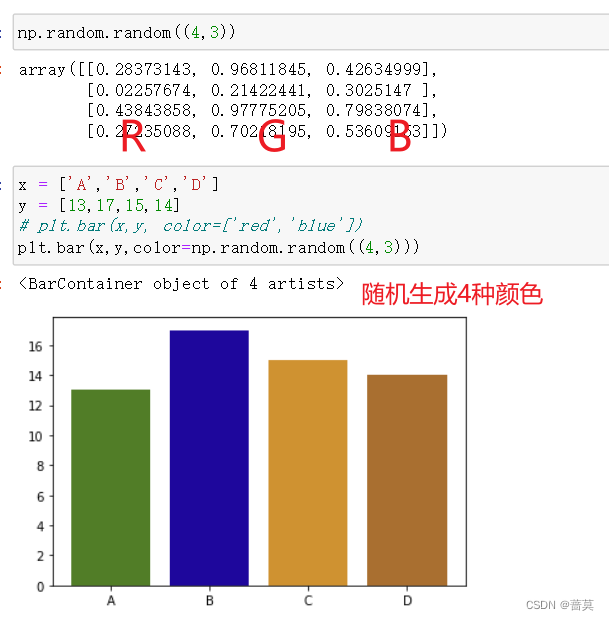
x = ['A','B','C','D']
y = [13,17,15,14]
# plt.bar(x,y, color=['red','blue'])
plt.bar(x,y,color=np.random.random((4,3)))
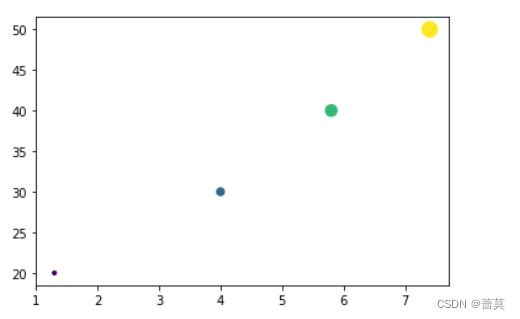
3.散点图 plt.scatter()
回归问题
# 横轴数据
x = [1.3, 4,5.8,7.4]
# 纵轴数据
y = [20,30,40,50]
# 大小 也可以表达第三维数据
size = np.array([1,4,9,16])
plt.scatter(x,y,s=size*10,c=(1,2,3,4))
四、pandas 自带的绘图函数
DataFrame
# 从10到100随机生成一个数据
np.random.randint(10,100) # 74
# 10行3列
np.random.randint(10,100,size=(10,3))
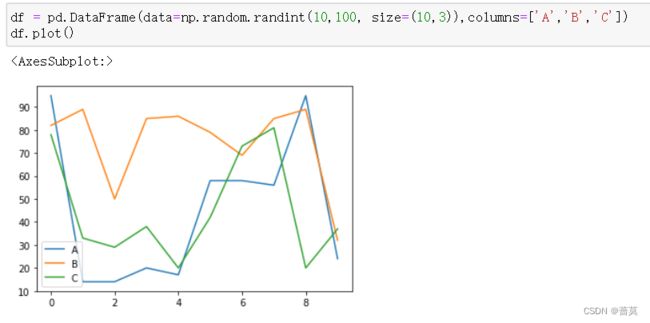
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(10,100, size=(10,3)),columns=['A','B','C'])
df.plot(kind='bar')
kind默认是line
hist 直方图 - - - pie 饼图 - - - box 箱体图 - - - area 面积图
T转置操作
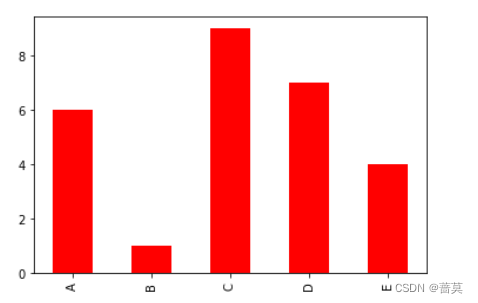
Series
df = pd.Series(data=np.random.randint(1,10,size=5),index=['A','B','C','D','E'])
df.plot(kind='bar',color='red')
1.添加文字说明 标题 坐标轴
np.random.random(3)
# array([0.62461037, 0.88015921, 0.78706271])
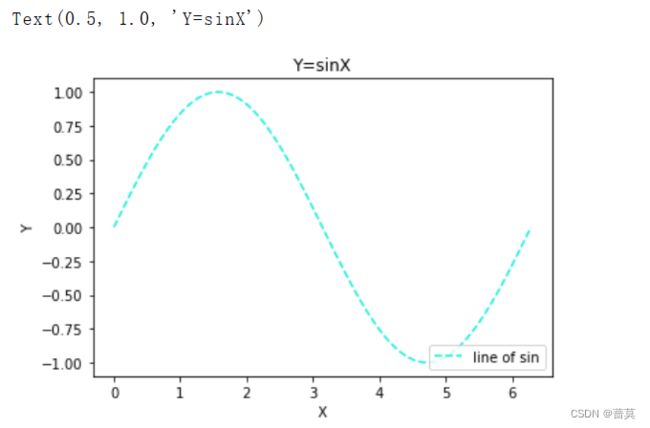
# 从0到2π拆分成100个数,等差数列
x = np.linspace(0,2*np.pi, num=100)
y = np.sin(x)
# label 是图例要展示的内容
plt.plot(x,y,color=np.random.random(3),label='line of sin',linestyle='--')
# 允许展示图例 loc参数可选
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.title('Y=sinX')
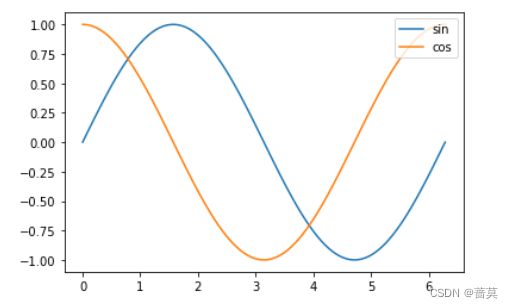
plt.plot(x,np.sin(x),label='sin')
plt.plot(x,np.cos(x),label='cos')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
2.label中文报错解决方法
使用matplotlib画图,默认不支持中文显示
plt.rcParams # 可以查看一些默认属性
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']='SimHei' # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False # 解决符号'-'显示为方框的问题
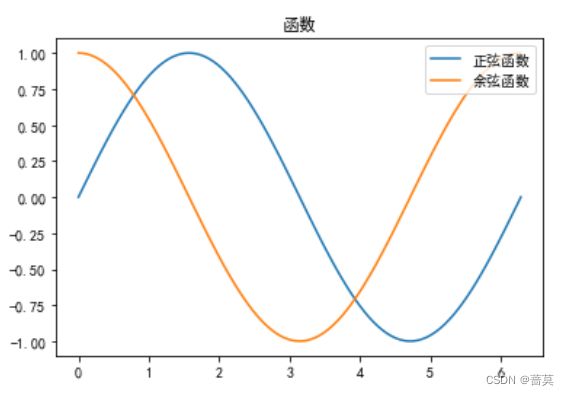
plt.plot(x,np.sin(x),label='正弦函数')
plt.plot(x,np.cos(x),label='余弦函数')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('函数')
五、绘制多个图表 subplot()
三个参数
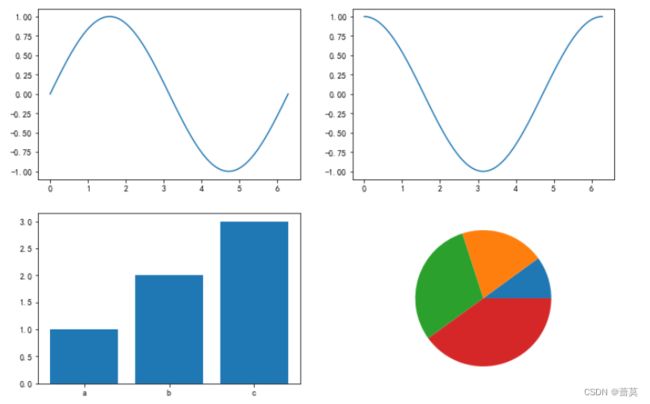
plt.subplot(221) 两行两列第一个
# 调整图表大小
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
ax1 = plt.subplot(221)
ax1.plot(x,np.sin(x))
ax2 = plt.subplot(222)
ax2.plot(x,np.cos(x))
ax3 = plt.subplot(223)
ax3.bar(['a','b','c'],[1,2,3])
ax4 = plt.subplot(224)
# ax4.pie(sizes=[30,40,30],labels=['A','B','C'],colors=['red','blue','yellow'])
ax4.pie(np.array([10, 20, 30, 40]))
plt.show()