Unity之数据持久化——Json
1、Json是什么
JavaScript对象简谱(JavaScript Object Notation)
json是国际通用的一种轻量级的数据交换格式,主要在网络通讯中用于传输数据,或本地数据存储和读取,易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率
游戏中可以把游戏数据按照Json的格式标准存储在Json文档中,再将Json文档存储在硬盘上或者传输给远端,达到数据持久化或者数据传输的目的
Json和Xml的异同:
共同点:都是纯文本,都有层级结构,都具有描述性
不同点:Json配置更简单,Json在某些情况下读写更快速
注意:在以下代码中我存储的文件地址是StreamingAssets文件夹,但通常是使用Application.persistentDataPath,因为StreamingAssets文件夹在某些平台(例如Android)是不可写的
2、编辑Json文件的方式
(1)系统自带——记事本、写字板
(2)通用文本编辑器——Sublime Text等
(3)网页Json编辑器
我用的是vs code,可以直接编辑json文件
3、基础语法
注释和C#中注释方式一致,但是需要设置为”Json with Comments“ 的形式(在vs code右下角设置)
语法规则:
符号含义:
| 大括号{} | 对象 |
| 中括号[] | 数组 |
| 冒号: | 键值对对应关系 |
| 逗号, | 数据分割 |
| 双引号“” | 键名/字符串 |
| 值类型 | 数字(整数或浮点)、字符串、true或false、数组、对象、null |
Json格式是一种键值对结构,表示为:“键名”:值内容
以C#代码为例:
class ClassInfo {
public string name;
public int age;
public bool sex;
public List ids;
public List students;
public Home home;
public Person son;
}
class Person {
public string name;
public int age;
public bool sex;
}
class Home {
public string address;
public string street;
} 将ClassInfo类转换为Json格式为:
// 大括号包裹的代表一个对象
{
// 冒号代表键值对的对应关系
// 逗号就是分割成员变量的间隔符
// Json当中的键一定要用双引号包裹,值是否用双引号由类型决定
"name": "Waylon",
"age": 18,
"sex": true,
"testF": 1.4, // 用于测试支持浮点类型
// 中括号代表数组
"idx": [1,2,3,4],
"students": [
{"name": "Hong", "age": 5, "sex": false},
{"name": "Ming", "age": 6, "sex": true},
{"name": "Qiang", "age": 8, "sex": true}
// 注意:最后一项不要加逗号,否则解析可能会出问题!!!
],
"home": {
"address": "Cheng",
"street": "Chun"
},
"son": null
}
字典的键(数字)会变成双引号字符串形式,转换时要注意!!!
“dic":{“1”:“123”,“key":{"id":1, "num": 3}}同时,Json中不会对private, protected进行解释
4、Excel转Json
暂时可以通过在线转换工具:https://www.bejson.com/json/col2json/
然后【下载Json代码】,转换结果不一定准确
5、JsonUtility序列化
(1)、JsonUtility是什么
JsonUtility是Unity自带的用于解析Json的公共类,它可以:
i、将内存中对象序列化为Json格式的字符串
ii、将Json字符串反序列化为类对象
(2)在文件种存读字符串
i、存储字符串到指定路径文件中
// 参数一:存储路径
// 必须是存在的文件路径,如果没有对应文件夹,会报错
// 参数二:存储的字符串内容
File.WriteAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath+ "/Test.json", "测试存储的json文件");
// 如果Json文件夹不存在则会报错
// File.WriteAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath+ "/Json/Test.json", "测试存储的json文件");ii、在指定路径文件中读取字符串
// 参数一:读取路径
// 参数二:编码格式(可选)
string str = File.ReadAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath+ "/Test.json");(3)使用JsonUtility进行序列化
序列化就是把内存中的数据存储到硬盘上,方法是通过API:JsonUtility.ToJson(对象)
以以下类对象举例:
class Student {
public int age;
public string name;
public Student(int age, string name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
class Person {
public string name;
public int age;
public bool sex;
public float testF;
public double testD;
public int[] ids;
public List ids2;
public Dictionary dic;
public Dictionary dic2;
public Student s1;
public List s2;
private int privateI = 1;
protected int protectedI = 2;
} 然后对该数据类进行序列化
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "Well";
p.age = 19;
p.sex = true;
p.testF = 1.3f;
p.testD = 1.3;
p.ids = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
p.ids2 = new List() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
p.dic = new Dictionary() { { 1, "123" }, { 2, "123" } };
p.dic2 = new Dictionary() { { "1", "123" }, { "2", "123" } };
p.s1 = new Student(1, "Hong");
p.s2 = new List() { new Student(2, "Ming"), new Student(3, "Qiang") };
// JsonUtility.ToJson()可以把类对象序列化为json字符串
string jsonStr = JsonUtility.ToJson(p);
File.WriteAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath+ "/Person.json", jsonStr); 序列化之后的Json文件存储的是:
{"name":"Well","age":19,"sex":true,"testF":1.2999999523162842,"testD":1.3,"ids":[1,2,3,4],"ids2":[1,2,3,4]}可以发现,字典、Student、私有、保护数据没有存储
注意:
- float序列化时会看来有一些误差,但读取的时候不会有影响
- 自定义类需要加上序列化特性[System.Serializable],最外层的类不用添加
[System.Serializable]
class Student {
public int age;
public string name;
public Student(int age, string name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}然后Json中内容是:
{"name":"Well","age":19,"sex":true,"testF":1.2999999523162842,"testD":1.3,"ids":[1,2,3,4],"ids2":[1,2,3,4],"s1":{"age":1,"name":"Hong"},"s2":[{"age":2,"name":"Ming"},{"age":3,"name":"Qiang"}]}- 想要序列化私有变量,需要加上特性[SerializeField]
[SerializeField] private int privateI = 1;
[SerializeField] protected int protectedI = 2;结果为:
{"name":"Well","age":19,"sex":true,"testF":1.2999999523162842,"testD":1.3,"ids":[1,2,3,4],"ids2":[1,2,3,4],"s1":{"age":1,"name":"Hong"},"s2":[{"age":2,"name":"Ming"},{"age":3,"name":"Qiang"}],"privateI":1,"protectedI":2}- JsonUtility不支持字典
- JsonUtility存储null对象不会是null,而是默认的数据
例如:令 s1=null,那么Json文件中存储的是:"s1":{"age":0,"name":""}
(4)JsonUtlity 反序列化
反序列化就是把硬盘上的数据读取到内存中,方法是通过API:JsonUtility.FromJson(字符串)
反序列化时是通过类的成员名与json文件中的键名进行匹配赋值
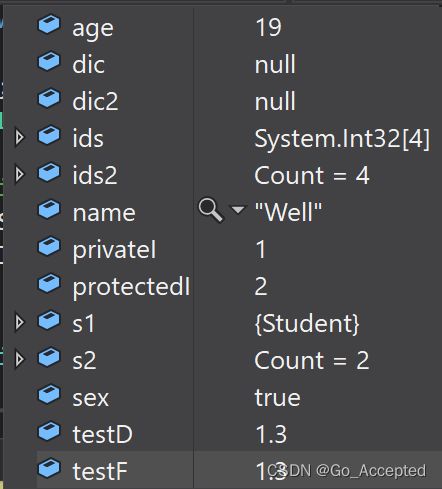
注意:如果Json中数据少了,读取到内存中类对象时不会报错,例如对上面的内容进行反序列化:
jsonStr = File.ReadAllText(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Person.json");
// 方法一:
Person p2 = JsonUtility.FromJson(jsonStr, typeof(Person)) as Person;
// 方法二:
Person p3 = JsonUtility.FromJson(jsonStr); 那么结果显示如下,可以发现字典类的对象是为null的
(5)JsonUtility注意事项
- JsonUtility无法直接读取数据集合
例如一个car.json文件中是这样的:
[
{"id":1, "speed":6},
{"id":2, "speed":10}
]然后对应的对象是:
class Car {
public int id;
public int speed;
}那么是不能够将其直接反序列化到List
{
"listCar":[
{"id":1, "speed":6}
{"id":2, "speed":10}
]
}- 文本编码格式需要是UTF-8,不然无法加载
6、LitJson
(1)LitJson是什么
第三方库,用于Json的序列化与反序列化,LitJson是C#编写,体积小、速度快、易于使用,它可以很容易地嵌入到代码中,只需要将LitJson代码拷贝到工程中即可
(2)获取LitJson
前往LitJson官网
通过官网前往Github获取最新版本代码
将src/LitJson的代码拷贝到Unity工程中,即可开始使用LItJson
(3)使用LitJson进行序列化
方法:JsonMapper.ToJson(对象)
注意:
- 相对JsonUtility不需要加特性
- 不能序列化私有变量
- 支持字典类型
- 需要引用LitJson命名空间
- LitJson可以保存 null 类型
使用和上面同样的例子,但是要把上面的对象、成员的特性移除(因为这些特性是针对JsonUtility的),然后调用:
string jsonStr = JsonMapper.ToJson(p);
File.WriteAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/Person.json", jsonStr);结果为:
{"name":"Well","age":19,"sex":true,"testF":1.3,"testD":1.3,"ids":[1,2,3,4],"ids2":[1,2,3,4],"dic":{"1":"123","2":"123"},"dic2":{"1":"123","2":"123"},"s1":null,"s2":[{"age":2,"name":"Ming"},{"age":3,"name":"Qiang"}]}可以发现,字典能够存储(字典的键都是字符串),同时null能够表示,但是私有、保护变量无法存储,如果存储的有中文,表示方法与JsonUtility也不一样
(4)使用LitJson进行反序列化
方法:JsonMapper.ToObject(字符串)
jsonStr = File.ReadAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/Person.json");方法一:
// JsonData是LItJson提供的类对象,可以用键值对的形式访问其中的内容
JsonData data = JsonMapper.ToObject(jsonStr);
print(data["name"]);
print(data["age"]);方法二:
Person p2 = JsonMapper.ToObject(jsonStr); 但其实现在方法二是会报错的
ArgumentException: The value '1' is not of type 'System.Int32' and cannot be used in this generic collection.因为json文本中字典存储的键都是字符串的形式,与Person类中字典键的int不匹配
然后把Person类中的dic字典注释,继续会有另一个报错:
MissingMethodException: Default constructor not found for type Lesson2+Student这是因为Student类中没有无参构造函数,在其中添加无参构造后就可以正常反序列化
注意:
- 类结构需要无参构造函数,否则反序列化报错
- 字典虽然支持,但是键在使用为数值时会有问题,需要使用字符串类型
(5)注意事项
- LitJson可以直接读取数据集合
还是以car为例:
jsonStr = File.ReadAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/car.json");
Car[] arr = JsonMapper.ToObject(jsonStr);
List arr2 = JsonMapper.ToObject>(jsonStr); 这样是可以直接转化的
如果需要直接转字典,假设一个字典数据dic.json为:
{
"name": 1,
"name2": 2,
"name3": 3,
"name4": 4
}注意!!!如果name4行最后有逗号,后面反序列化会出错
然后直接转为Dictionary:
jsonStr = File.ReadAllText(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/dic.json");
Dictionary dic = JsonMapper.ToObject>(jsonStr); - 文本编码格式需要是UTF-8,不然无法加载
(6)LitJson总结
- LitJson提供的序列化/反序列化方法:JsonMapper.ToJson和ToObject<>
- LitJson不用加特性
- LitJson不支持私有变量
- LitJson支持字典序列化反序列化
- LitJson可以直接将数据反序列化为数据集合
- LitJson反序列化时,自定义类型需要无参构造
- Json文档编码格式必须是UTF-8
7、JsonUtlity和LitJson对比
(1)相同点:
- 都是用于Json的序列化和反序列化
- Json文档编码格式必须时UTF-8
- 都是通过静态类进行方法调用
(2)不同点:
- JsonUtility是Unity自带,LitJson是第三方需要引用命名空间
- JsonUtility使用时自定义类需要添加特性,LitJson不需要
- JsonUtility支持私有变量(加特性),LitJson不支持
- JsonUtility不支持字典,LitJson支持(但是键只能是字符串)
- JsonUtility不能直接将数据反序列化为数据结合(数组字典),LitJson可以
- JsonUtility对自定义类不要求有无参构造,LitJson需要
- JsonUtility存储对象时会存储默认值为不是null,LitJson会存null
8、写一个简单的Json管理器
public enum E_JsonType {
JsonUtility,
LitJson
}
///
/// Json 数据管理,主要用于Json的序列化与反序列化
///
public class JsonMgr {
private static JsonMgr instance = new JsonMgr();
public static JsonMgr Instance => instance;
private JsonMgr() {
}
public void SaveData(object data, string fileName, E_JsonType type = E_JsonType.LitJson) {
string path = Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/" + fileName + ".json";
string jsonStr = "";
switch (type) {
case E_JsonType.JsonUtility:
jsonStr = JsonUtility.ToJson(data);
break;
case E_JsonType.LitJson:
jsonStr = JsonMapper.ToJson(data);
break;
}
File.WriteAllText(path, jsonStr);
}
public T LoadData(string fileName, E_JsonType type = E_JsonType.LitJson) where T : new() {
string path = Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/" + fileName + ".json";
if (!File.Exists(path))
path = Application.persistentDataPath + "/" + fileName + ".json";
if (!File.Exists(path))
return new T();
string jsonStr = File.ReadAllText(path);
T data = default(T);
switch (type) {
case E_JsonType.JsonUtility:
data = JsonUtility.FromJson(jsonStr);
break;
case E_JsonType.LitJson:
data = JsonMapper.ToObject(jsonStr);
break;
}
return data;
}
} 然后为了方便其他项目使用,可以将其打包,但是要注意,由于使用了LitJson第三方库,所以打包时需要将LitJson源代码一起打包
然后右键JsonMgr选择Export Package选择对应的文件夹即可生成对应的Package文件